Topic 3.7 - Optical Isomerism
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What property must a
carbon atom have for the
molecule to display optical
isomerism about that carbon
atom?
4 different substituents attached to one carbon
atom
What are the similarities and
differences between two
optical isomers?
Same atoms and bonds, but they are non-superimposable
mirror images of one another. NOT IDENTICAL in chemical
properties necessarily.
Differ in the way they rotate plane polarised light - rotate
plane of polarisation by the same angle but in different
directions.
What word is used to
describe optically active
molecules?
chiral
What are the pair of isomers
called?
Enantiomers
What is the chiral centre?
The carbon that has four different substituents
attached to it
How is the chiral centre
denoted?
C* (star on C)
Give two examples of chiral
molecules. Draw one of
them (both enantiomers).
All alpha amino acids, except glycine.
Lactic acid / 2-hydroxypropanoic acid
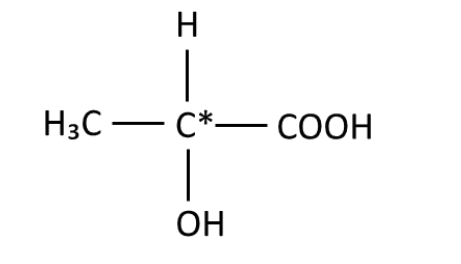
How is light polarised?
By passing it through a polaroid filter, so
oscillations are only in one plane.
What effect does the
racemic mixture have on
plane polarised light?
None, as the rotation by each enantiomer
cancels out to nothing
What effect does the +
isomer have on plane
polarised light?
Rotates plane of polarisation by x 0 clockwise
What effect does the -
isomer have on plane
polarised light?
Rotates plane of polarisation by x o anti clockwise
(same angle, opposite direction)
What is the structure of a
polarimeter?
Light source (unpolarised light) → polarising filter (polarised
light) → polarised light passes through compartment
containing sample → detector determines the angle of
rotation of the plane polarised light
What are polarimeters used
for?
To identify which enantiomer is present, the
purity of the sample, the concentration of the
sample etc.
What is the first stage of the
synthesis of lactic acid
(2-hydroxypropanoic acid)
from ethanal? (Equation).
(Reagents are KCN and HCl but it is acceptable
to write HCN in the balanced equation as this is
the H + from the HCl and -
CN from KCN)
CH 3
CHO + HCN → CH 3
CH(OH)CN
Why is the CH 3 CH(OH)CN
molecule formed chiral?
H, CH 3
, OH and CN groups attached to the
central chiral carbon atom - 4 substituents
What is the second stage of
the synthesis of lactic acid
(2-hydroxypropanoic acid)
from ethanal?
Hydrolysis: CH 3
CH(OH)CN + HCl +2H 2
O →
CH 3
CH(OH)COOH + NH 4
Cl
How does this second stage
affect the chirality?
Does not affect it - still racemic as chirality not
affected by this stage.
Are racemic mixtures
formed in nature? Why?
Not often, as enzyme mechanisms are 3D so
only form one enantiomer
Why is optical isomerism a
problem for the drug
industry?
Sometimes, only one enantiomer is effective due
to enzyme’s active site/cell receptors being 3D.
What are the options to
resolve the issue of only
one enantiomer being
effective?
1. Separate enantiomers - difficult and expensive as have
very similar properties
2. Sell racemate - wasteful as half is inactive
3. Design alternative synthesis to only produce one
enantiomer.
Examples of optically active
drugs?
Ibuprofen, Thalidomide
Why is ibuprofen able to be sold as
a racemate, even though the +
isomer is needed to treat
inflammation?
Sold as 50% racemate.
But body converts 60% of R- isomer to S+ isomer → end up
with 80% S+ isomer