Section 2 10 Group 7, the halogens
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Properties of Halogens
Diatomic
Going down the group the atomic radius increases
The electronegativity decreases going down the group
The MP and BP increases going down the group, due to van der waals forces.
G,G,L,S => F, Cl, Br, I
Why is the bond enthalpy of F-F weak?
The small size of fluorine atom, leads to repulsion between the non-bonding electrons because they are close.
The trends of oxidising ability going down group 7:
The oxidising ability of the halogens increases going up the group. They tend to get more reduced.
This is where a more reactive halogen F> Cl > Br > I gets displaced from a less reactive halogen.
The trends of reducing power of the halides:
Going down the group the reducing power increases.
Sodium chloride and concentrated sulfuric acid
No redox reaction takes place, only acid-base reaction
Because Chlorine is a weak reducing agent

Sodium Bromide and concentrated sulfuric acid
Acid base and redox reaction
Bromine reduces Sulfur from +6 to +4
Observations: A red-brown fumes
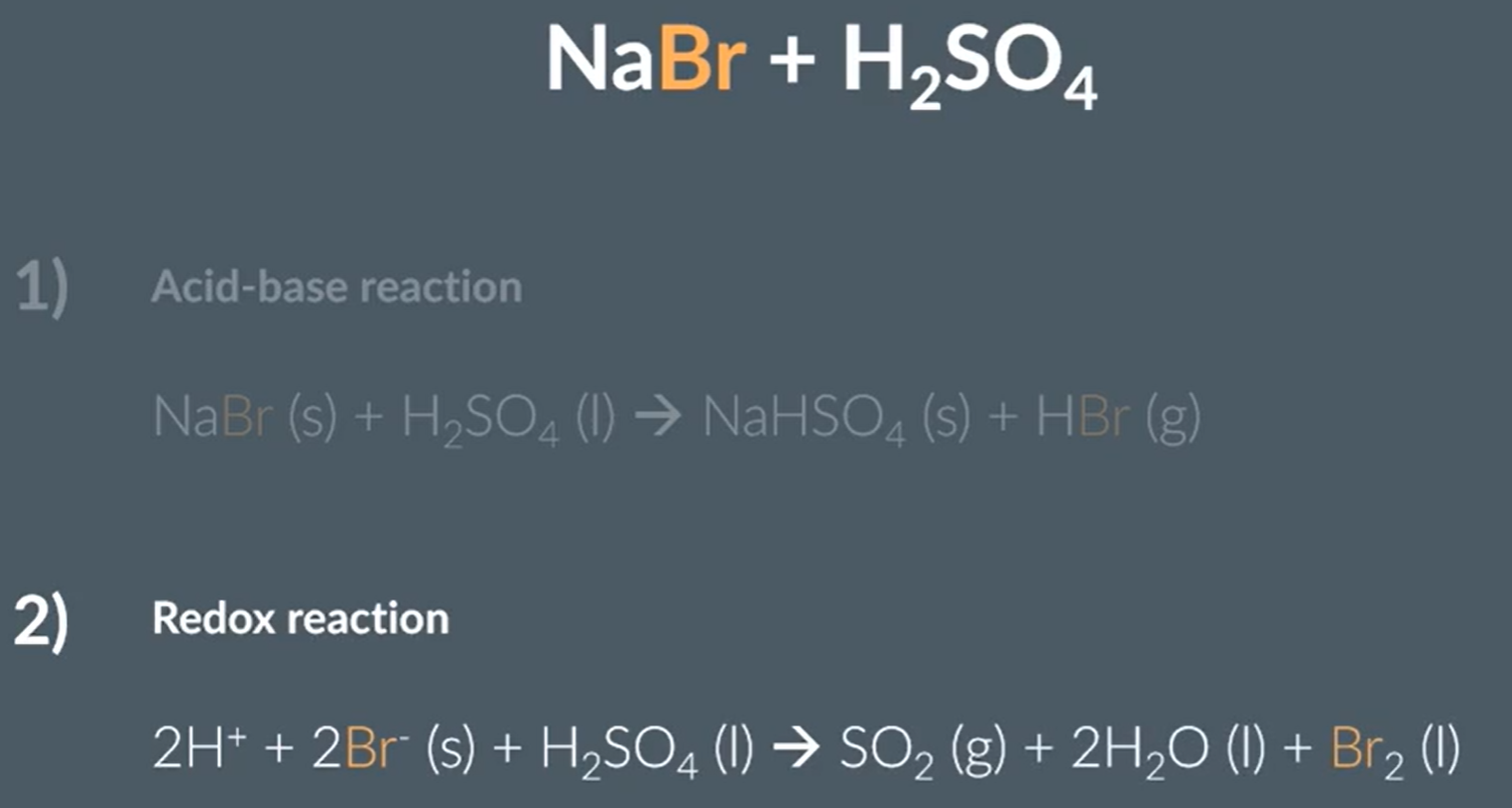
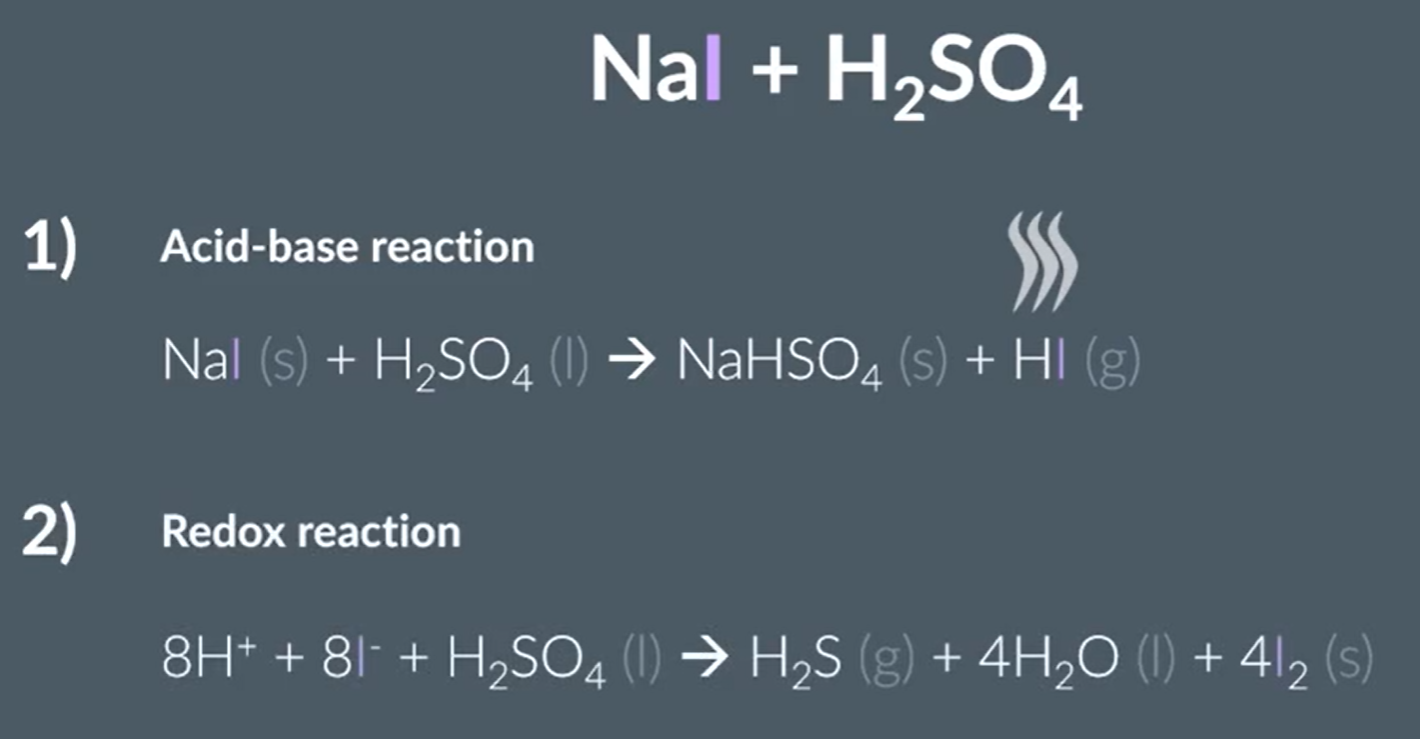
Sodium Iodide and concentrated sulfuric acid
Acid base and redox reaction
Iodine reduces Sulfur from +6 to -2
Hydrogen sulfide rotten eggs smell
Iodine black or grey solid
Purple stemy fumes
Chlorine reaction with water with no sun
This reaction is a disproportionation reaction, as Chlorine gets reduced and oxidised.

Chlorine reaction with water with sunlight

Chlorine reaction with alkali (Sodium hydroxide)
NaClO where the ClO ions is used to kill microorganism
