lecture 1c: joints
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
classifications
structural or functional
structural classification of joints
how they’re linked
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial
functional classification of joints
how the move
synarthrotic
amphiarthrotic
diarthrotic
syarthrotic
immovable
amphiarthrotic
slightly moveable
diarthrotic
freely movable
joint
point of attachment between two bones
fibrous joints
held together with dense CT containing many collagen fibers
found in bones close in contact
3 types
syndesmosis
suture
gomphosis
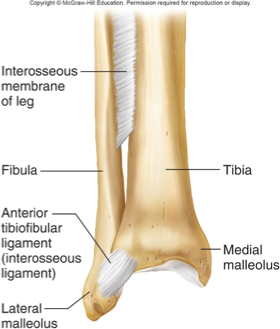
syndesmosis
bones bound by a sheet of dense CT (interosseous membrane) or a bundle of dense (regular) connective tissue (interosseous ligament)
amphiarthrotic (flexible, may twist)
ex.: b/w tibia and fibula
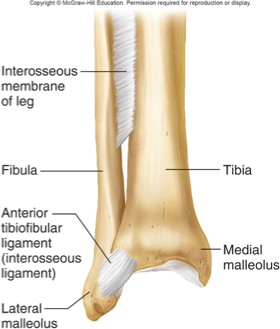
suture
fibrous
between flat bones of skull
thin layer of connective tissue sutural ligament) connects bones
synarthrotic (immovable)
chiropractors can put pressure on but can’t move
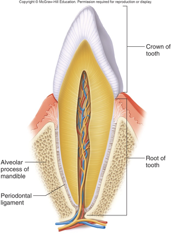
gomphosis
fibrous
cone-shaped bony process in a socket in jawbone
tooth in jawbone, anchored by periodontal ligament
synarthrotic (immovable)
cartilagenous joints
2 types
connected by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage
synchondrosis
symphysis
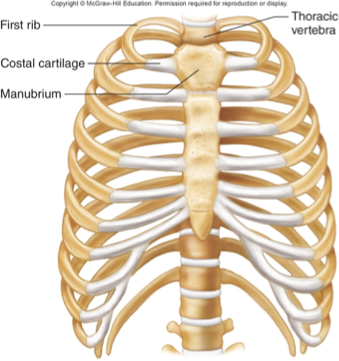
synchondrosis
cartilaginous
bands if HYALINE cartilage unite bones
some are temporary, such as epiphyseal plate (ossification converts this to a synostosis)
between manubrium and first rib (costal cartilages, permanent, synarthrotic)
if it was all bone, CPR wouldn’t work
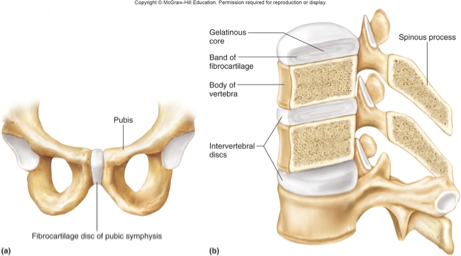
symphysis
cartilagenous
pad of FIBROUS cartilage between bones
toughest cartilage - absorbs shock when walking/running
amphiarthrotic
pubic symphysis & intervertebral discs
synovial joints
most joints
diarthrotic
movable
structure of synovial joint
articular cartilage covers articular end of bones
made of HYALINE cartilage (all bones start as hyaline, moves to end as ossified)
joint capsule, consists of 2 laters
outer fibrous layer, composed of ligaments
inner layer, synovial membrane, which secretes synovial fluid
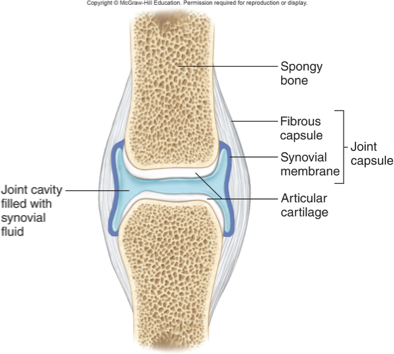
bursa
reduce friction between structures
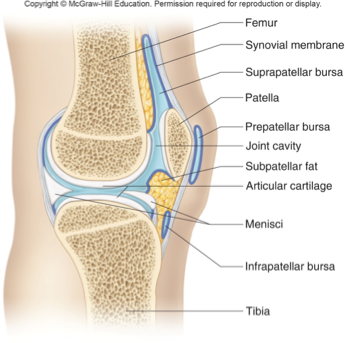
synovial membrane
makes/secretes synovial fluid
types of synovial joints
6:
ball-and-socket
condylar
plane
hinge
pivot
saddle
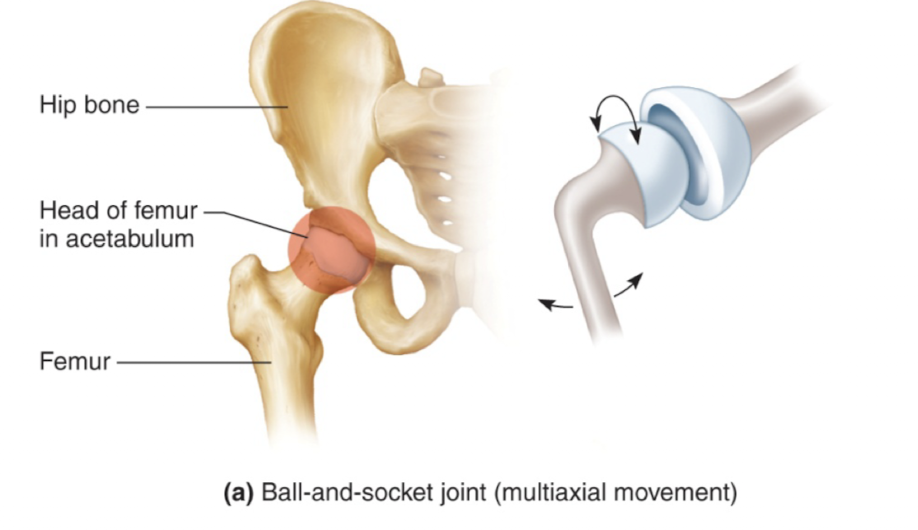
ball and socket
round head in cup-shaped cavity
widest range of motion
multiaxial, plus rotation
hip, shoulder
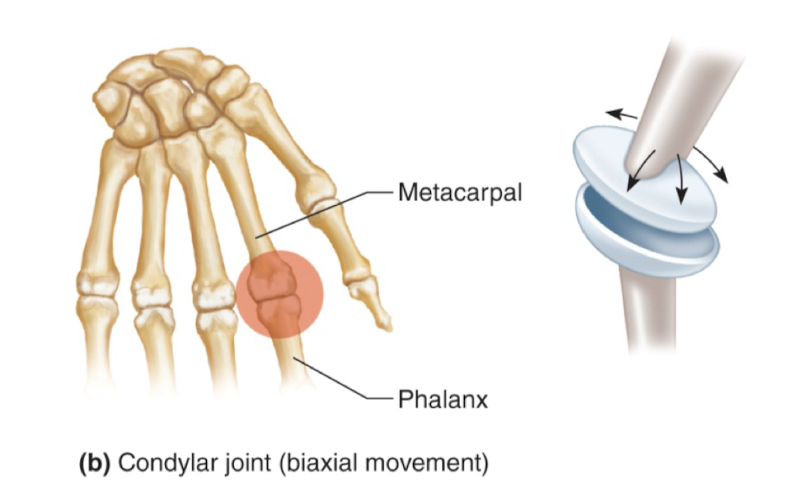
condylar joint (aka ellipsoidal)
oval condyle fits into elliptical cavity
back-and-forth, side to side (biaxial, no rotation)
between metacarpals and phalanges
plane (gliding) joint
almost flat, or slightly curved
back-and-forth and twisting
nonaxial movement
wrist and ankle joints
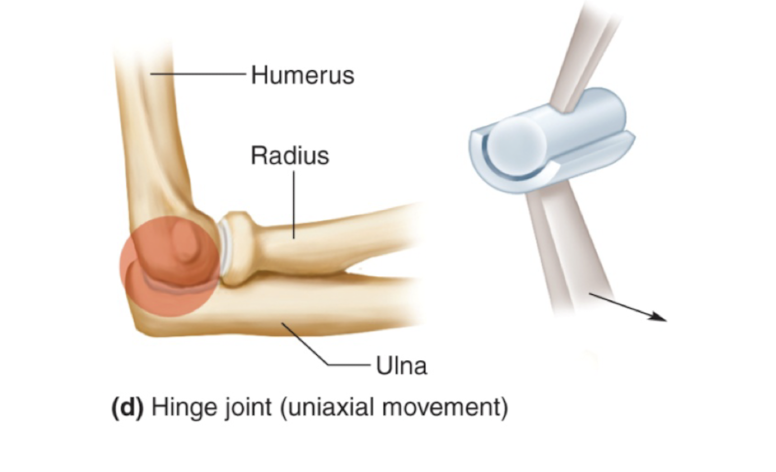
hinge joint
convex surface fits into concave surface of other bone
uniaxial
elbow, between phalanges, mandible
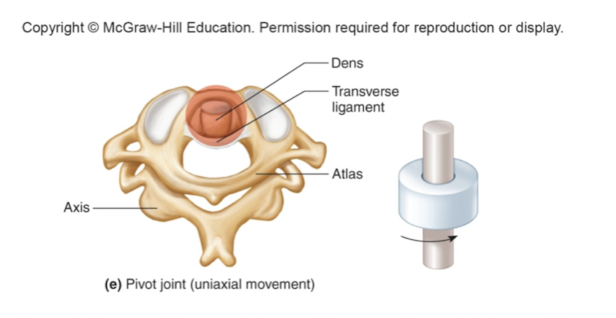
pivot joint (trochoid)
cylindrical surface rotates within ring of other bone
uniaxial (rotation only)
atlas (C1) and dens of axis (C2)
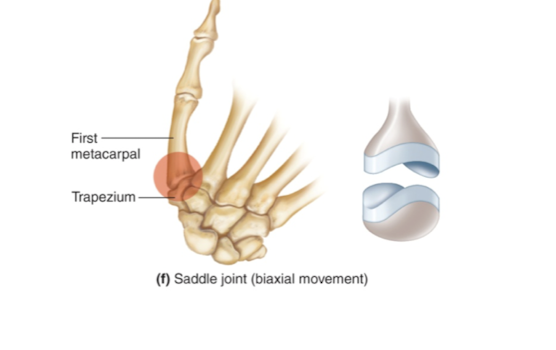
saddle joint (sellar)
both bones have concave and convex surfaces
biaxial movement
carpal and metacarpal of thumb
origin
relatively fixed end of the muscle (aka proximal)
doesn’t move
insertion
more moveable end of skeletarl muscle (aka proximal)
movement at a joint occurs when a muscle__ and its fibers pull the __ towards the __
contract, insertion, origin
dorsiflexion vs plantar flexion
dorsiflexion: toes up toward you
plantarflexion: planting something in ground
circumduction vs rotation
circumduction is flexion + extension and ab+adduction combination, making a circle
rotation is spinning a bone around its long axis
supine vs prone
supine = face up
prone = face down
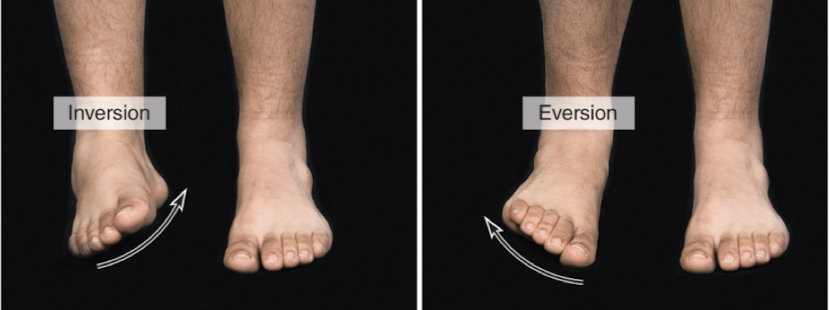
inversion vs eversion
inversion: turn sole of foot in medially
eversion: turn sole foot laterally