Ch 10: Sliding Filament Mechanism+ Sarcomere Structure
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
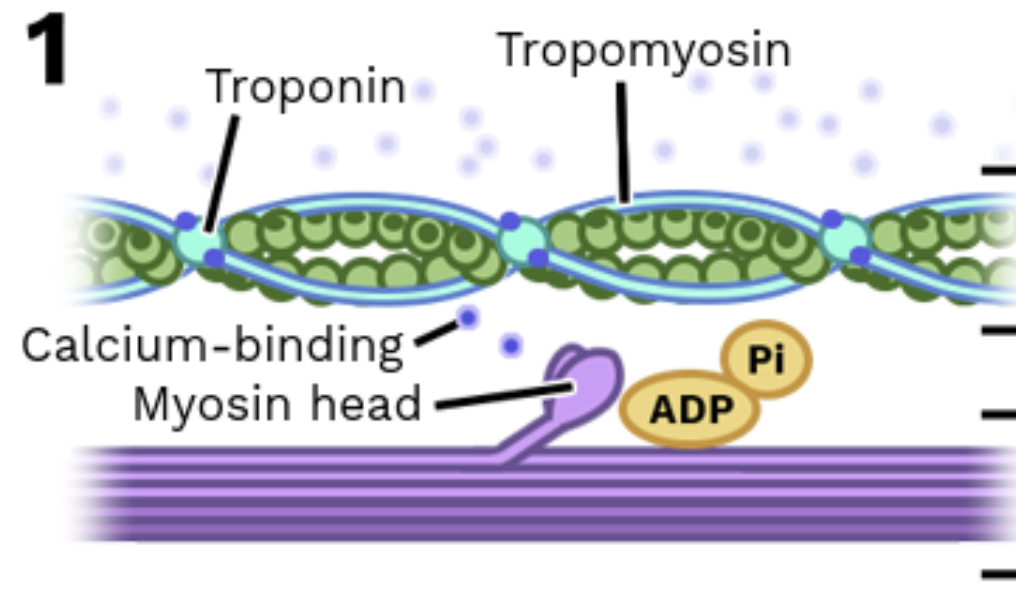
Stage 1: Myosin gets ready (cocked position)
ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP + phosphate, giving energy to the myosin head.
This puts it into the cocked (ready) position to reach for actin.
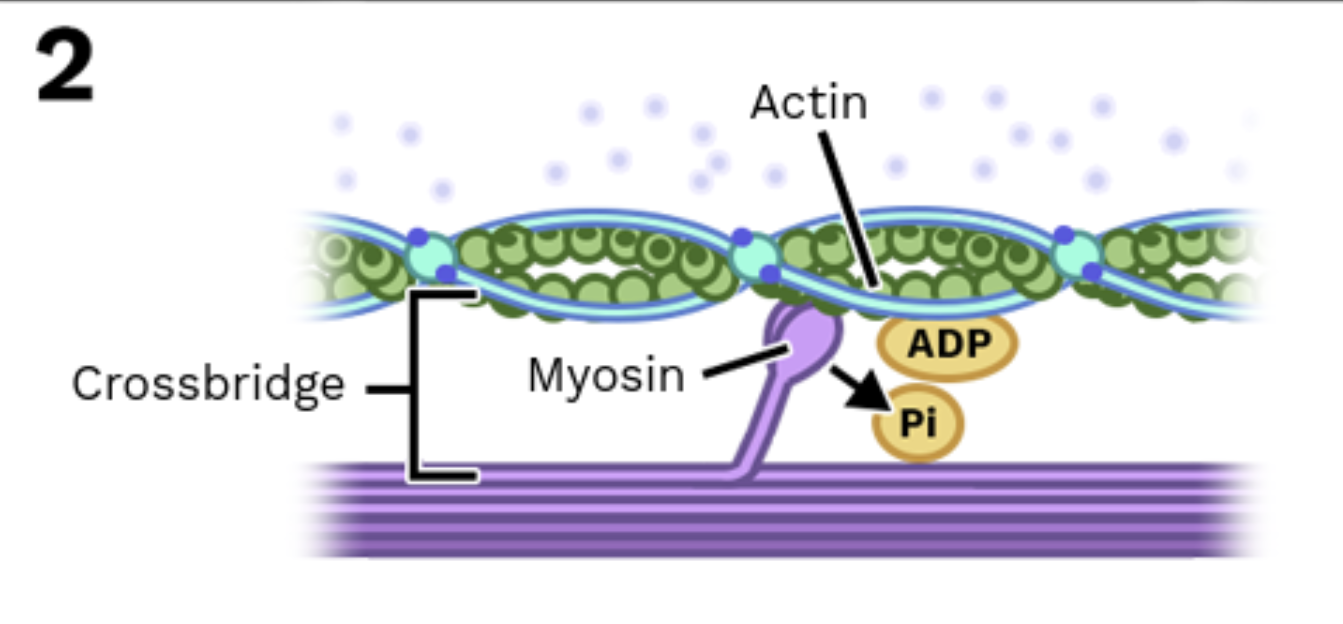
Stage 2: Myosin grabs actin
Calcium binds to troponin, which moves tropomyosin out of the way.
Now myosin can attach to the binding site on actin.
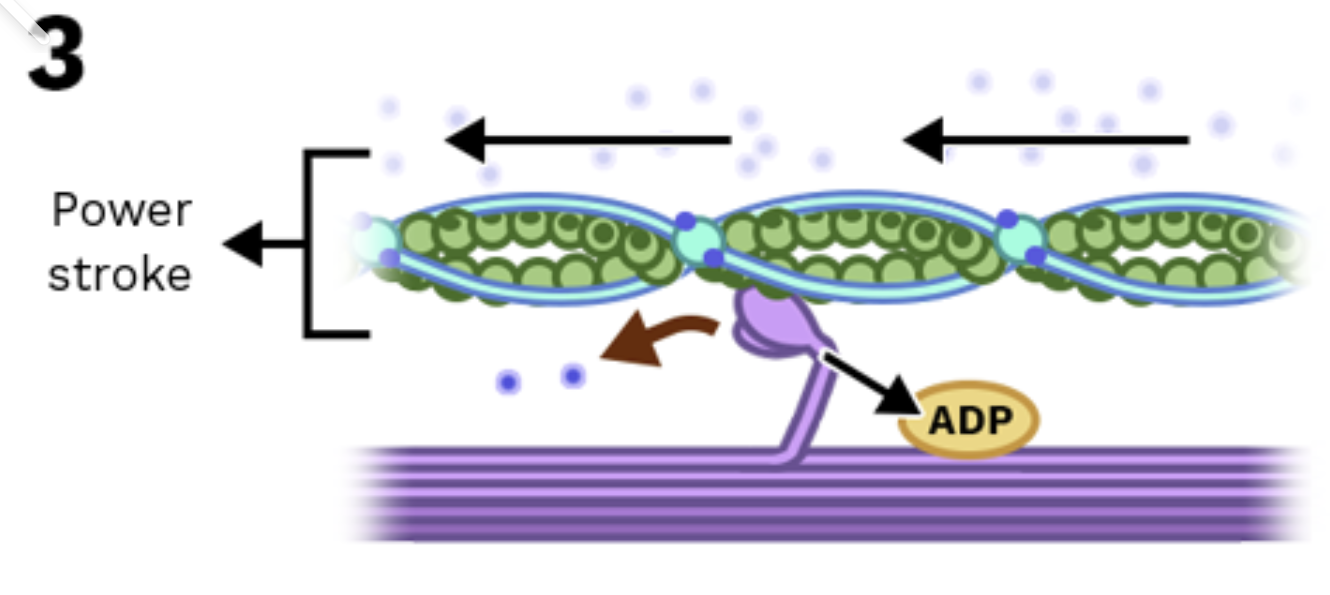
Stage 3: Myosin pulls actin (power stroke)
The myosin head bends and pulls actin forward.
ADP + phosphate are released.
🔁 After the pull, a new ATP is needed to repeat the cycle.
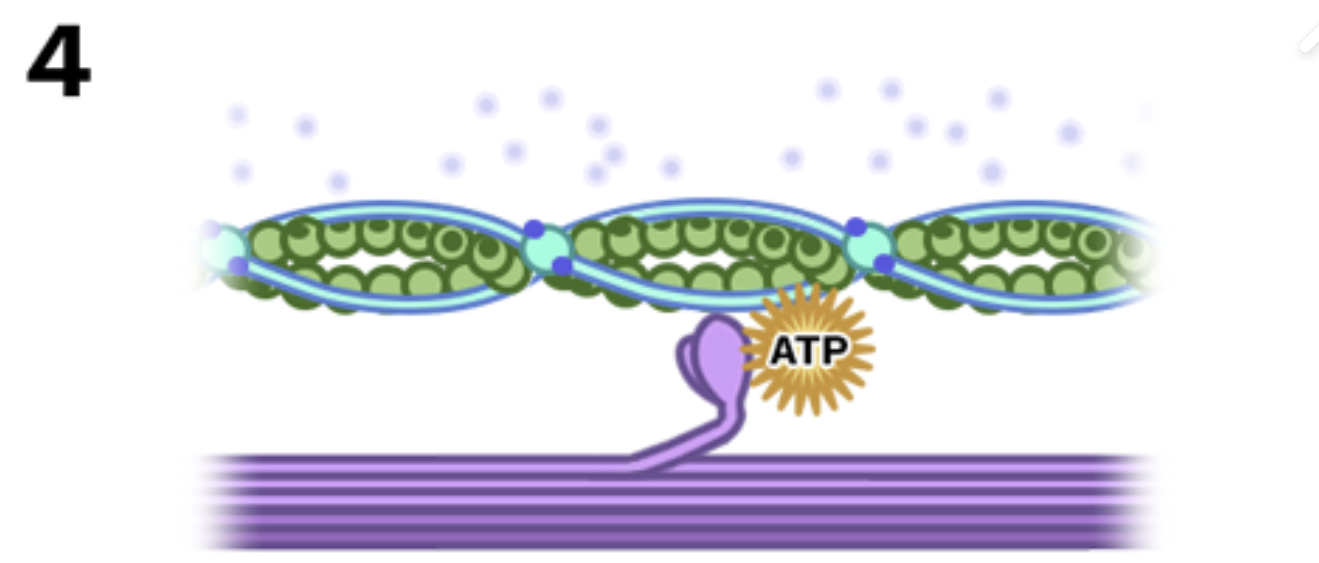
Stage 4: Myosin lets go
A new ATP binds to myosin, causing it to release from actin — and the cycle starts over.
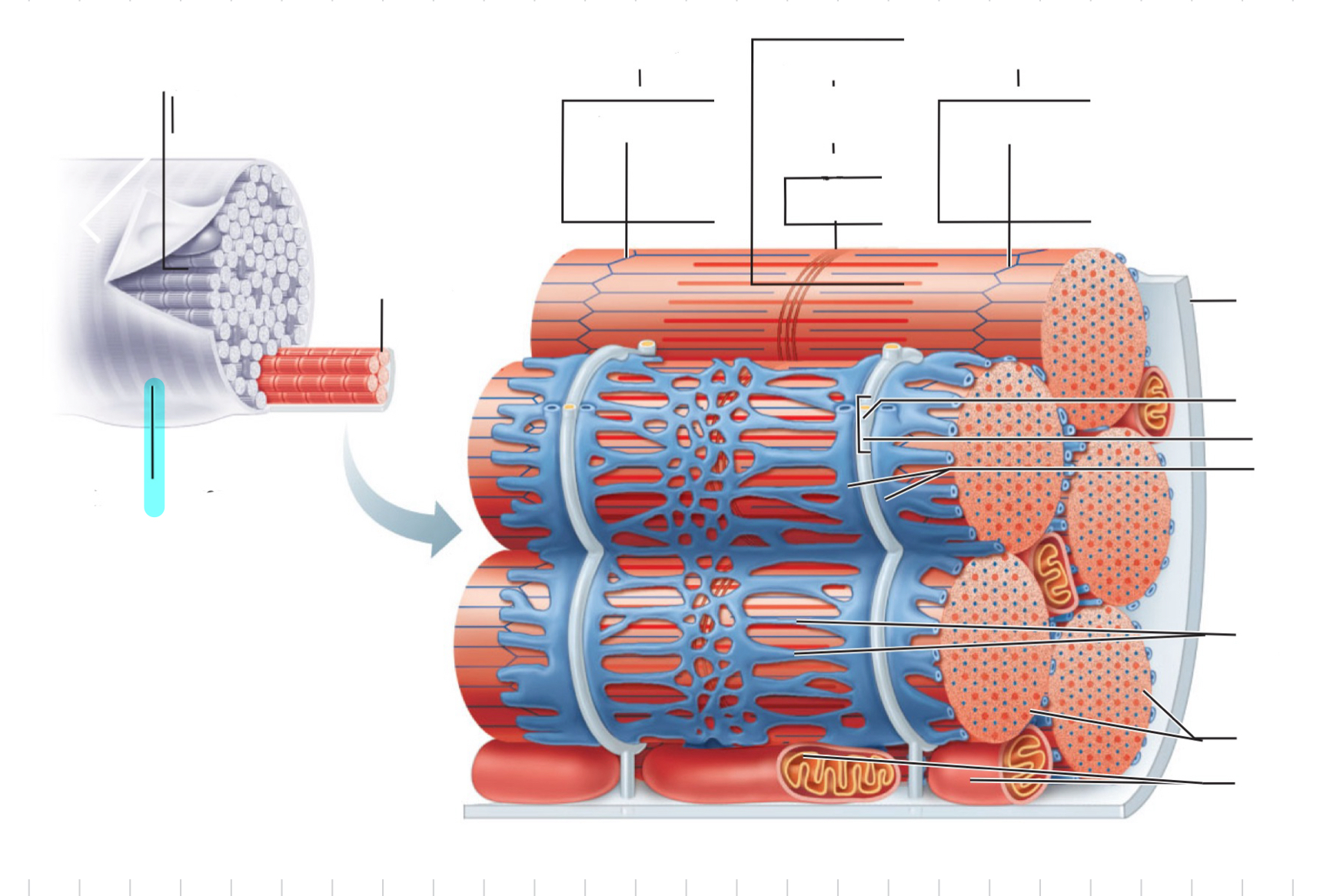
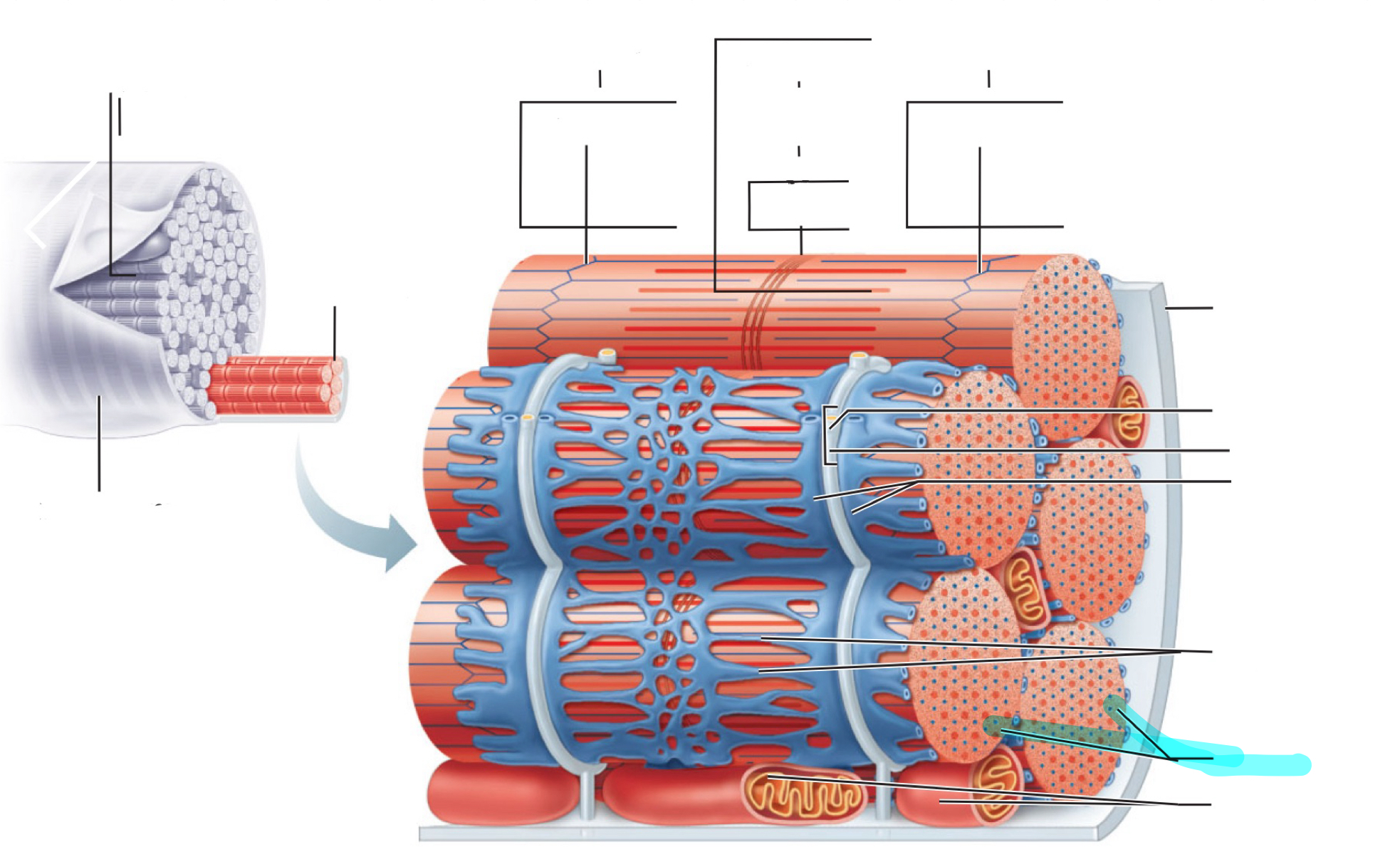
Sarcolemma
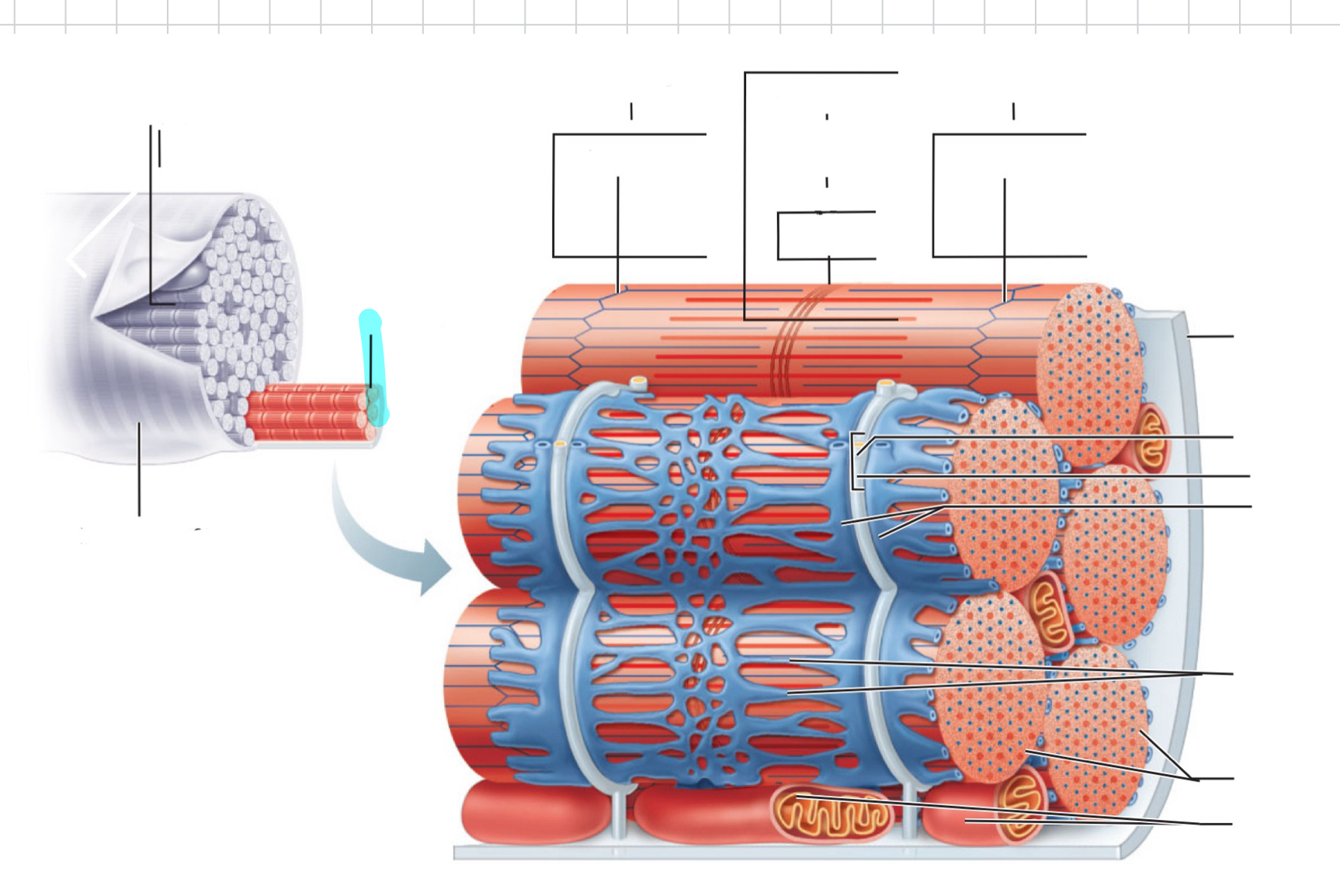
Myofibril
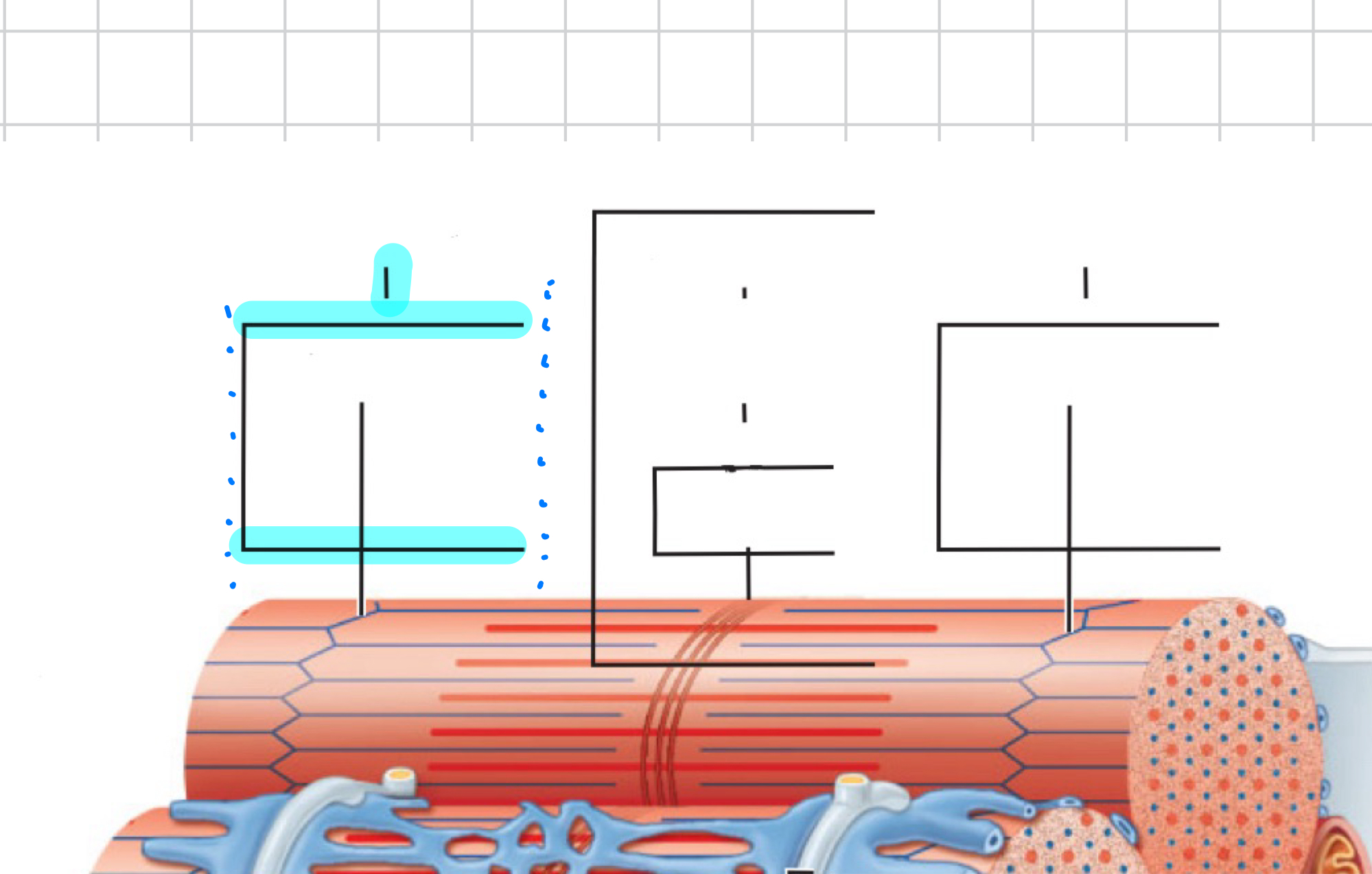
I band
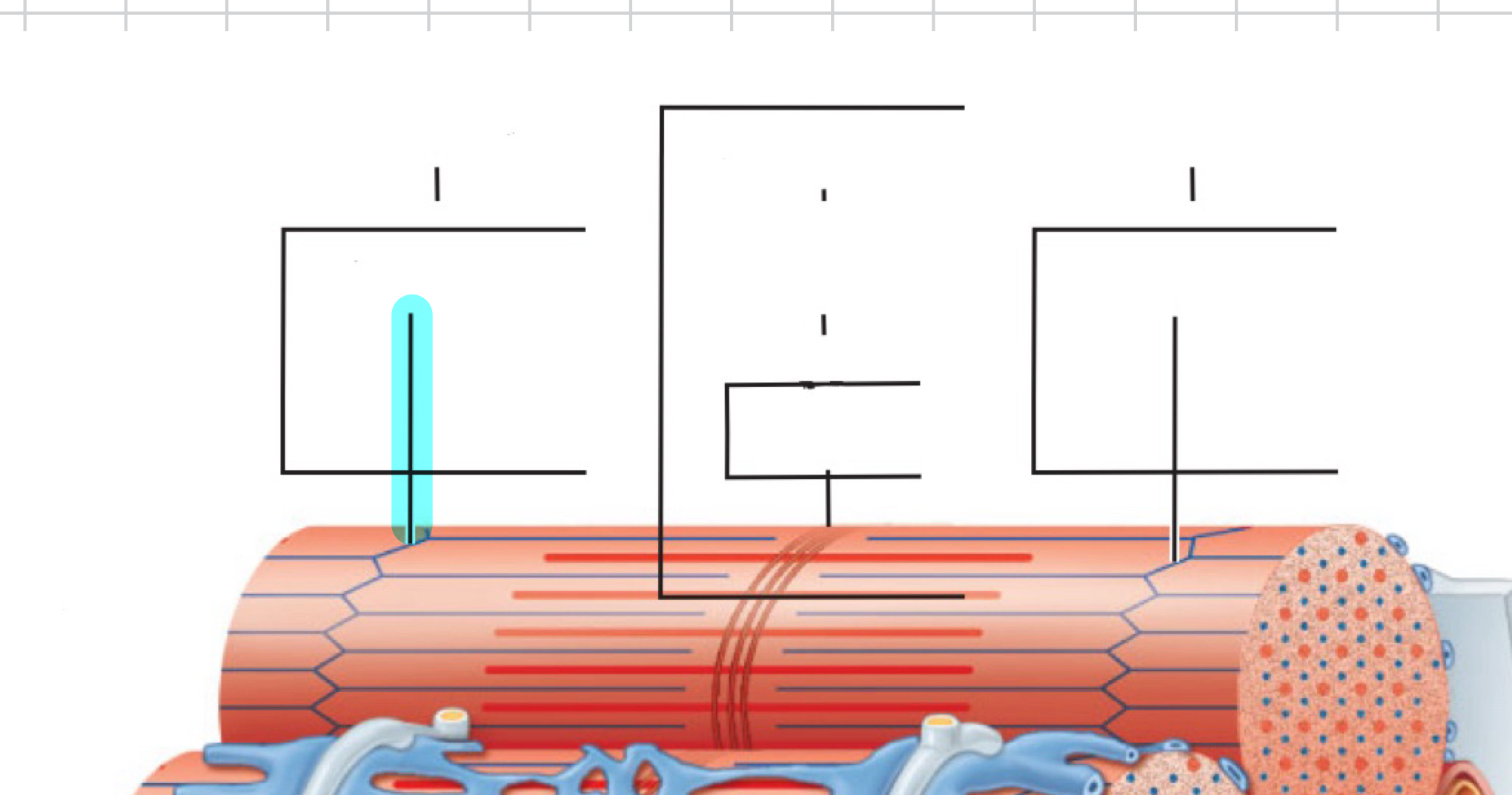
Z disc
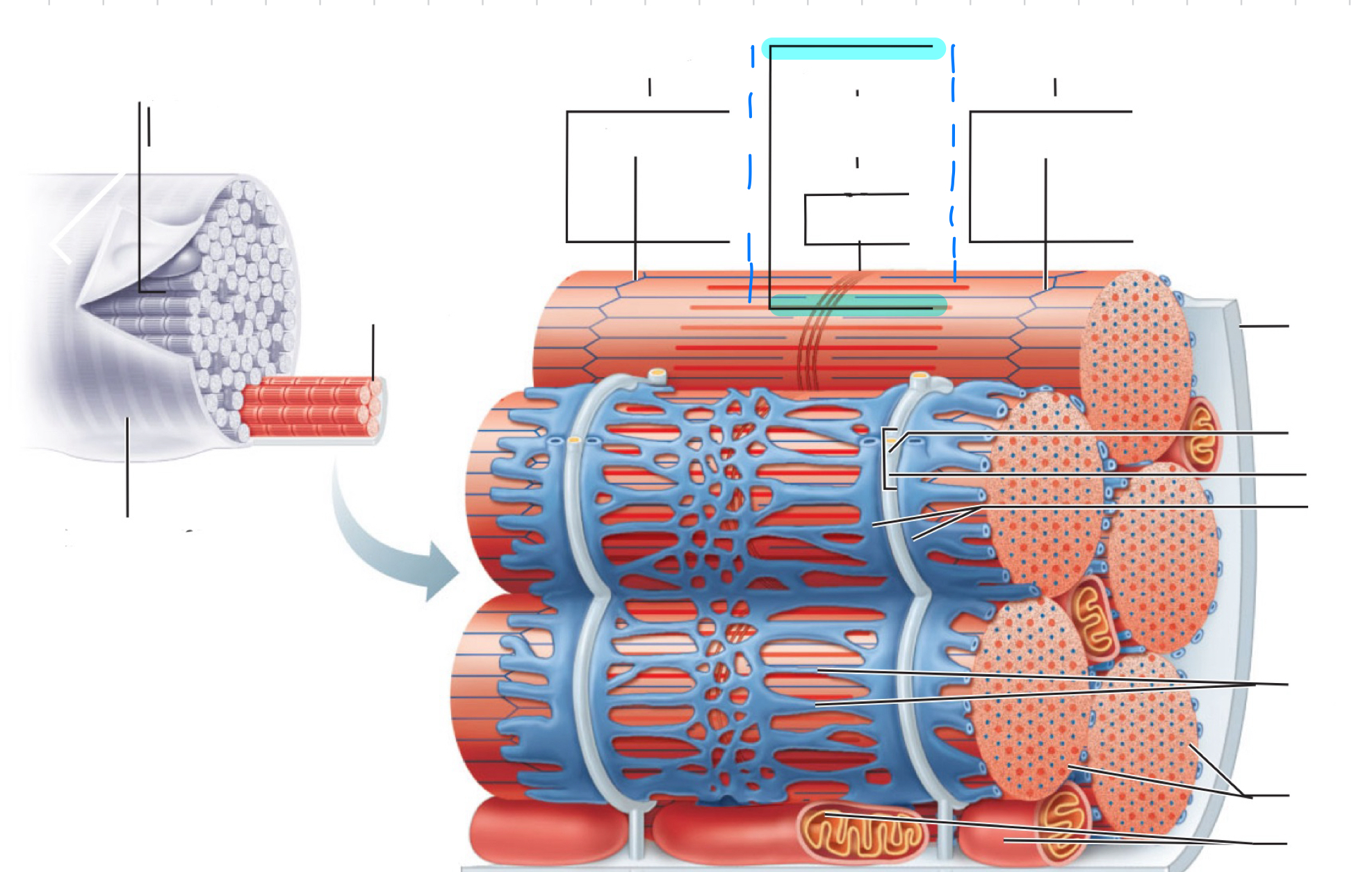
A band
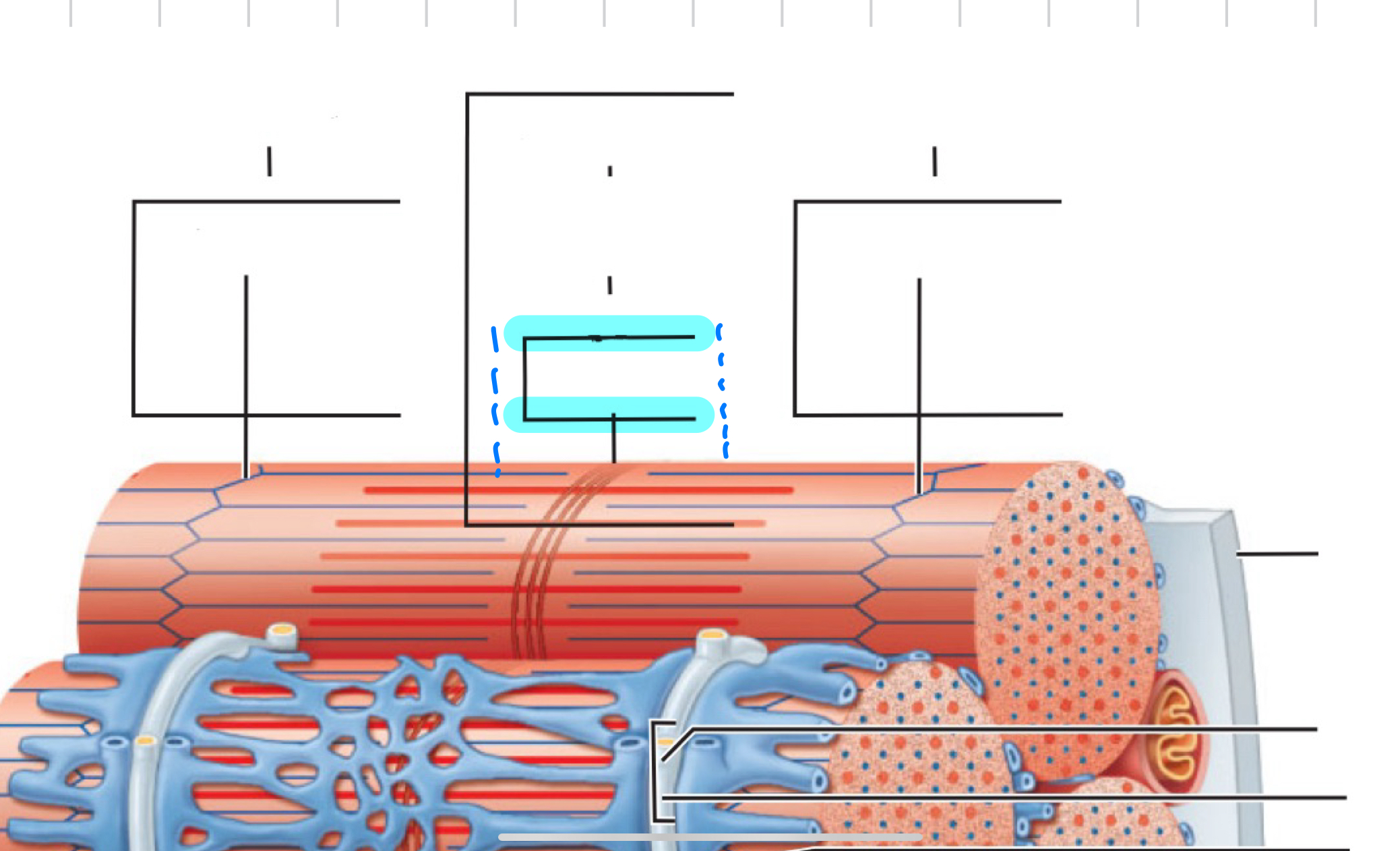
H zone
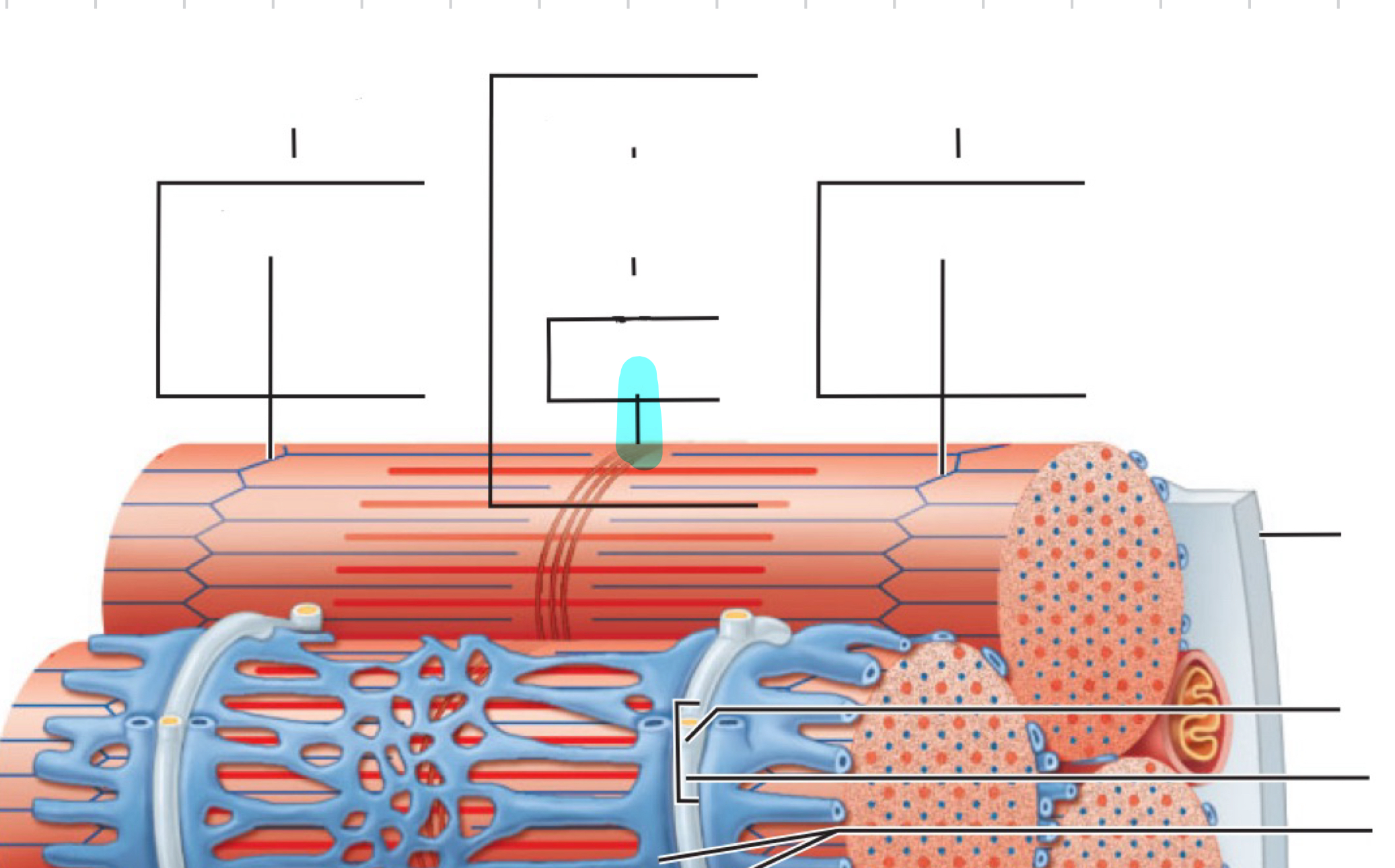
M line
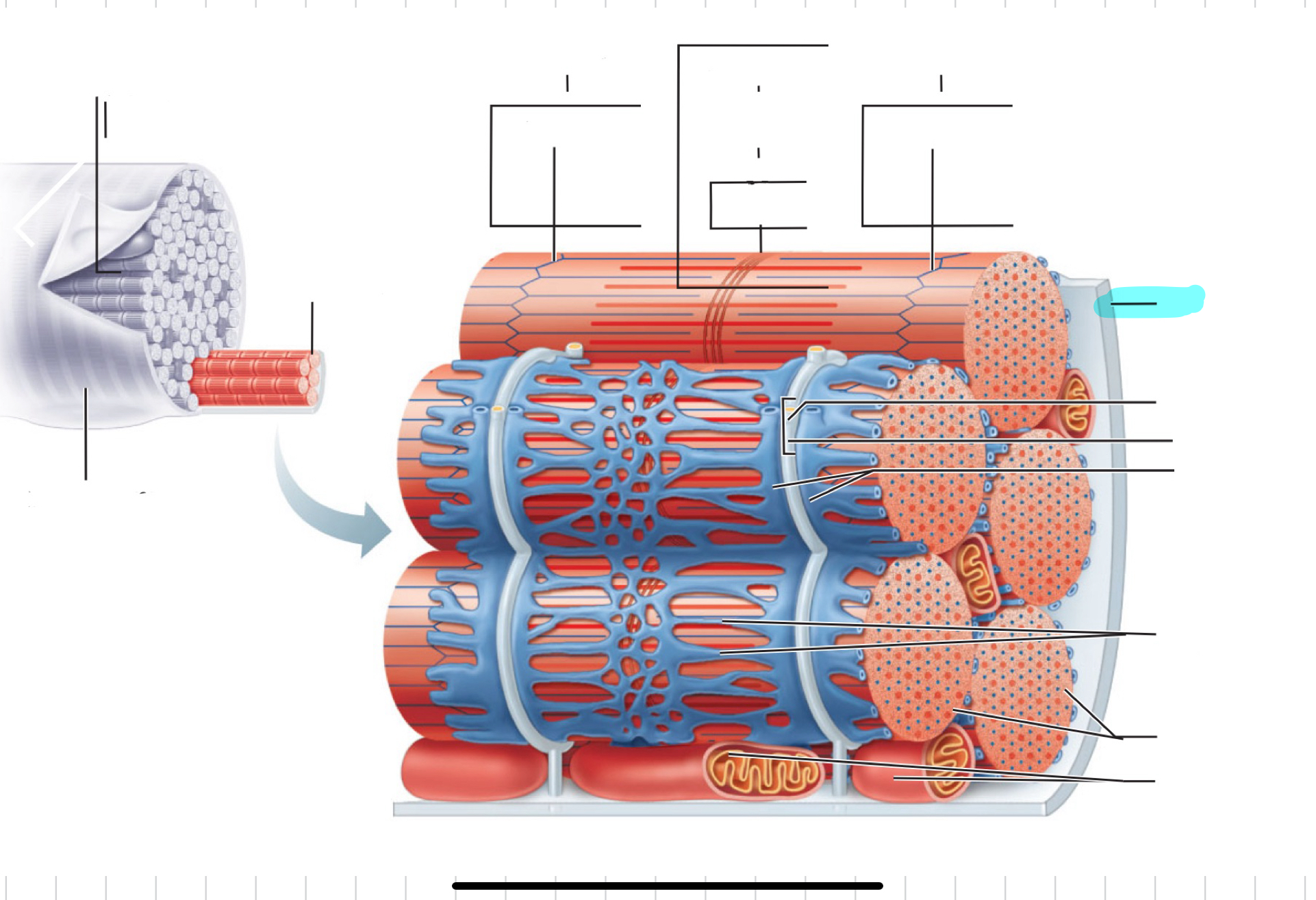
Sarcolemma
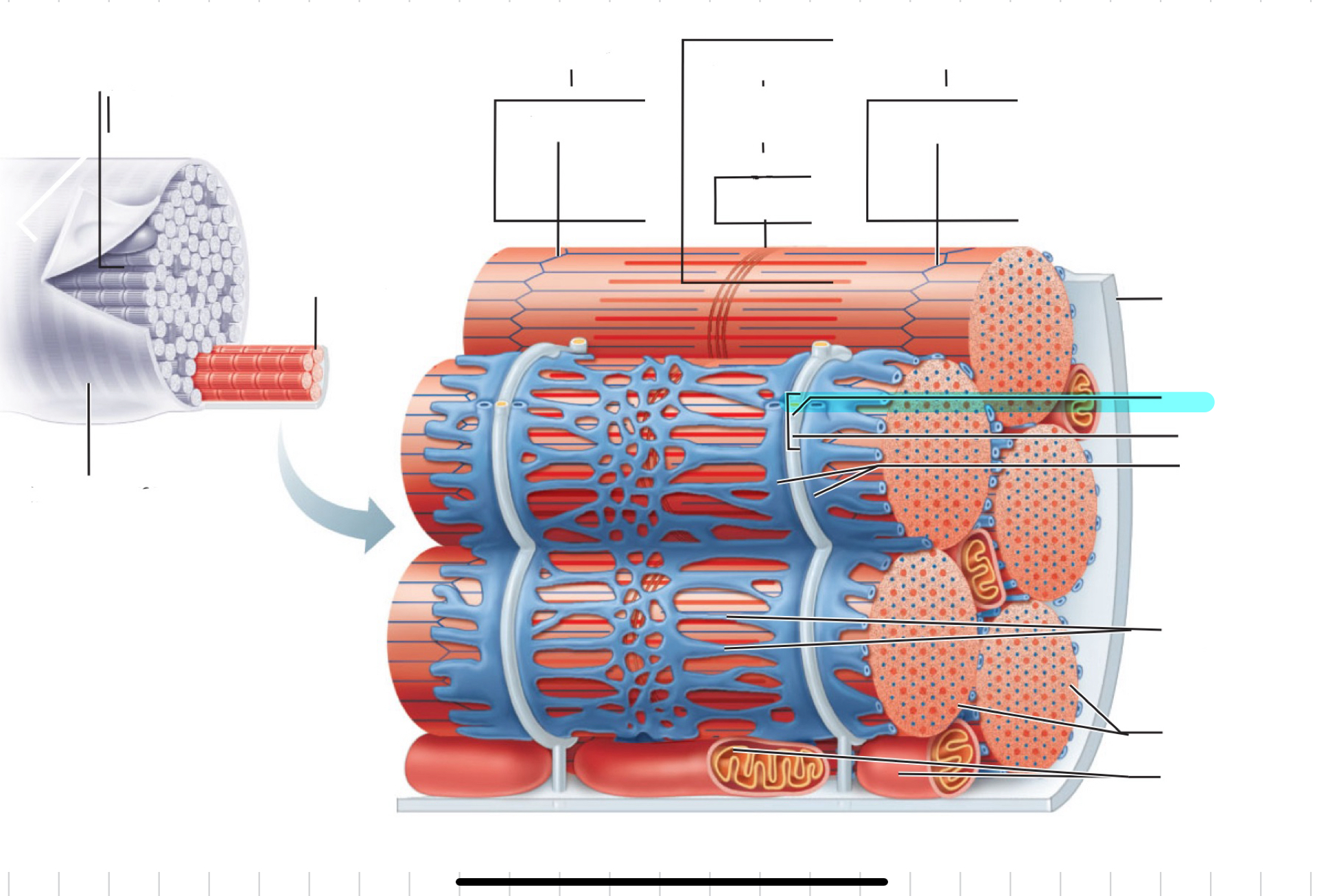
Traid
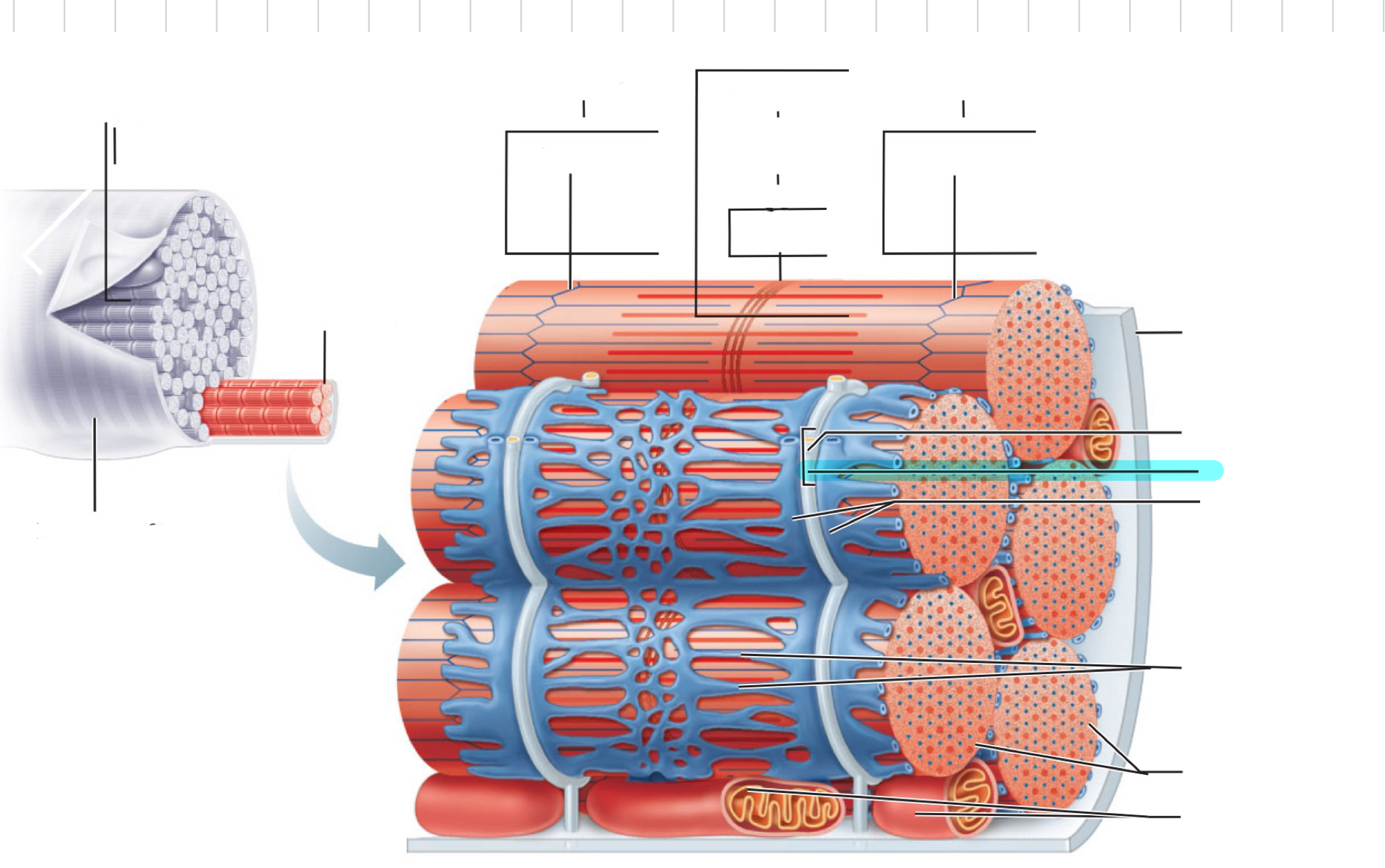
T tubule
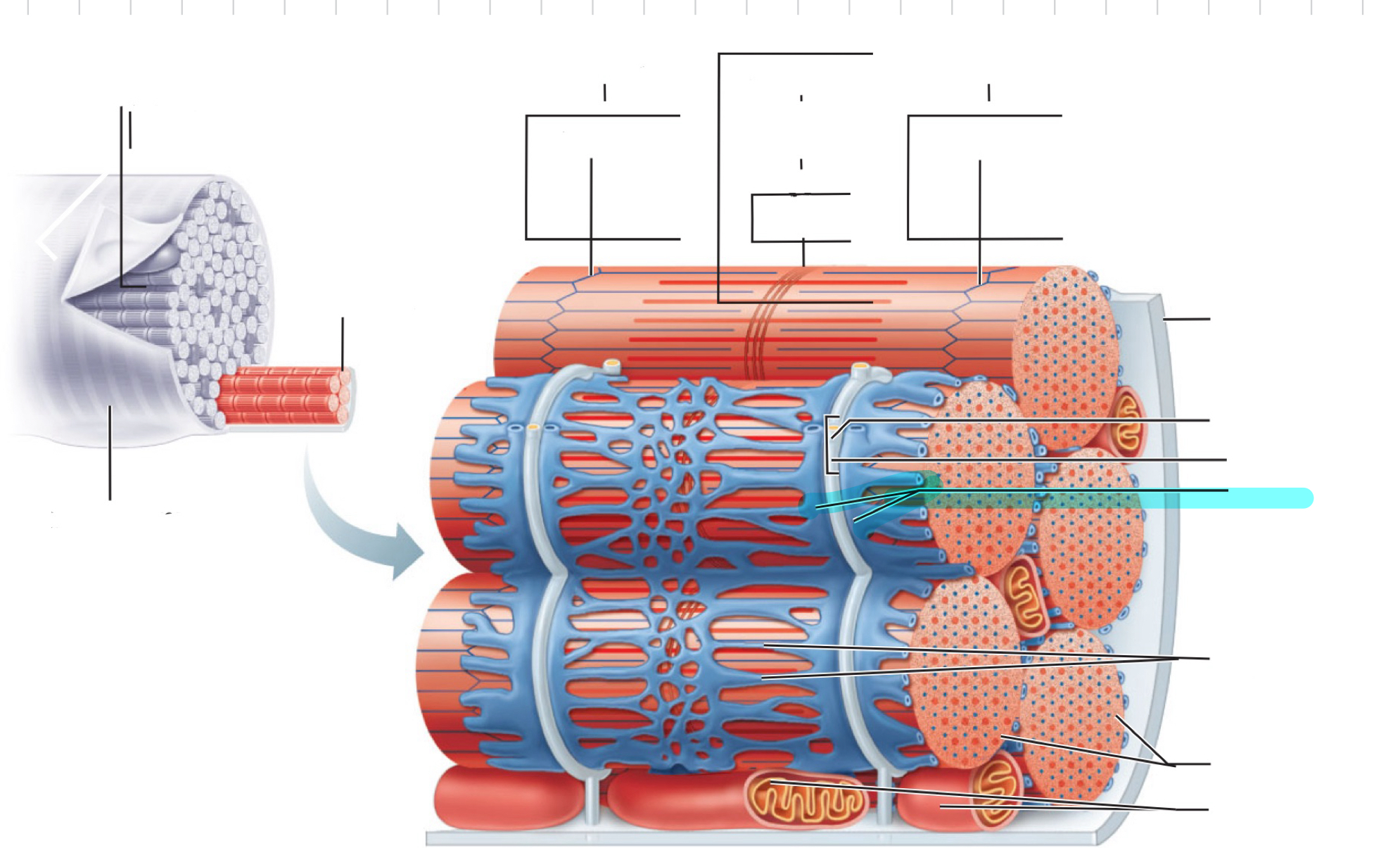
Terminal cistern of the sarcoplasm reticulum
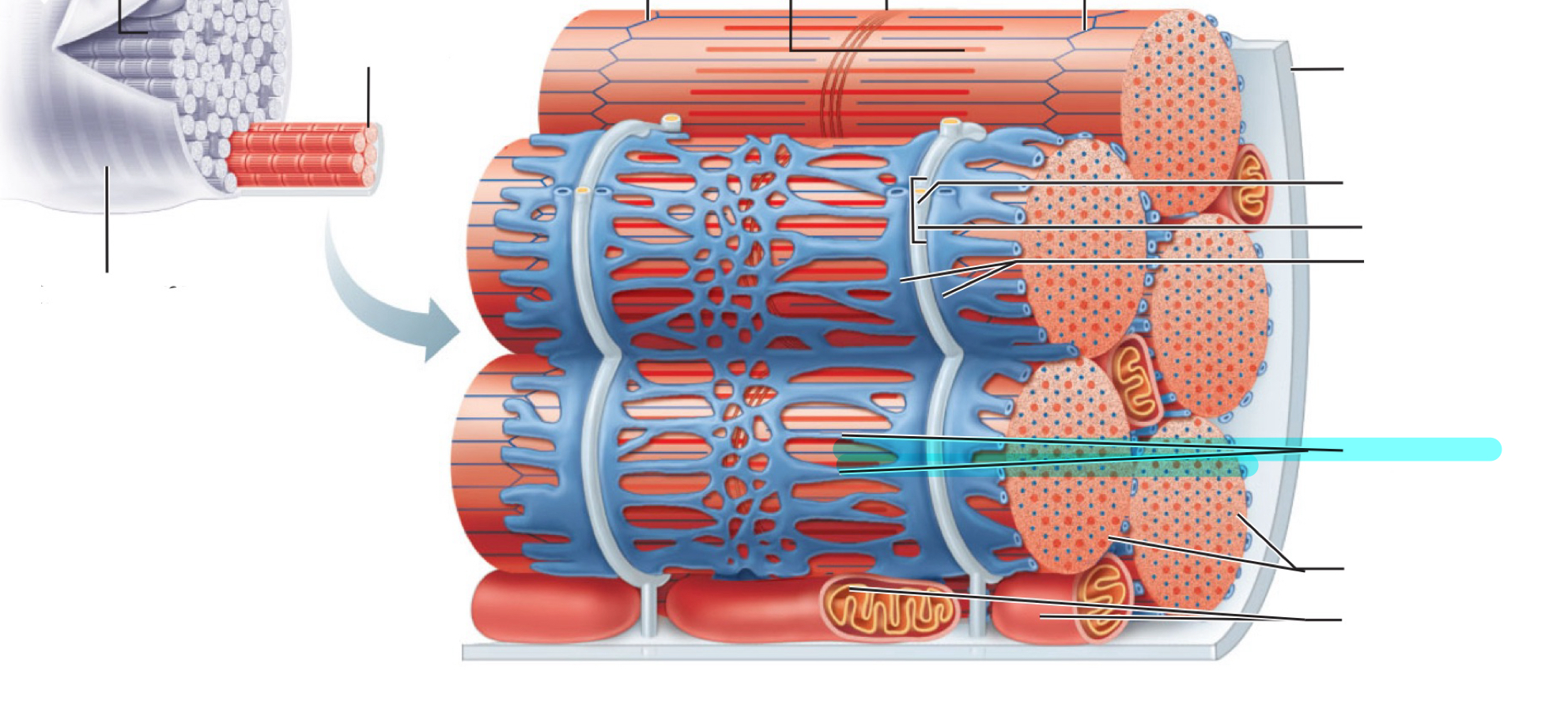
Tubules of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Myofibrils
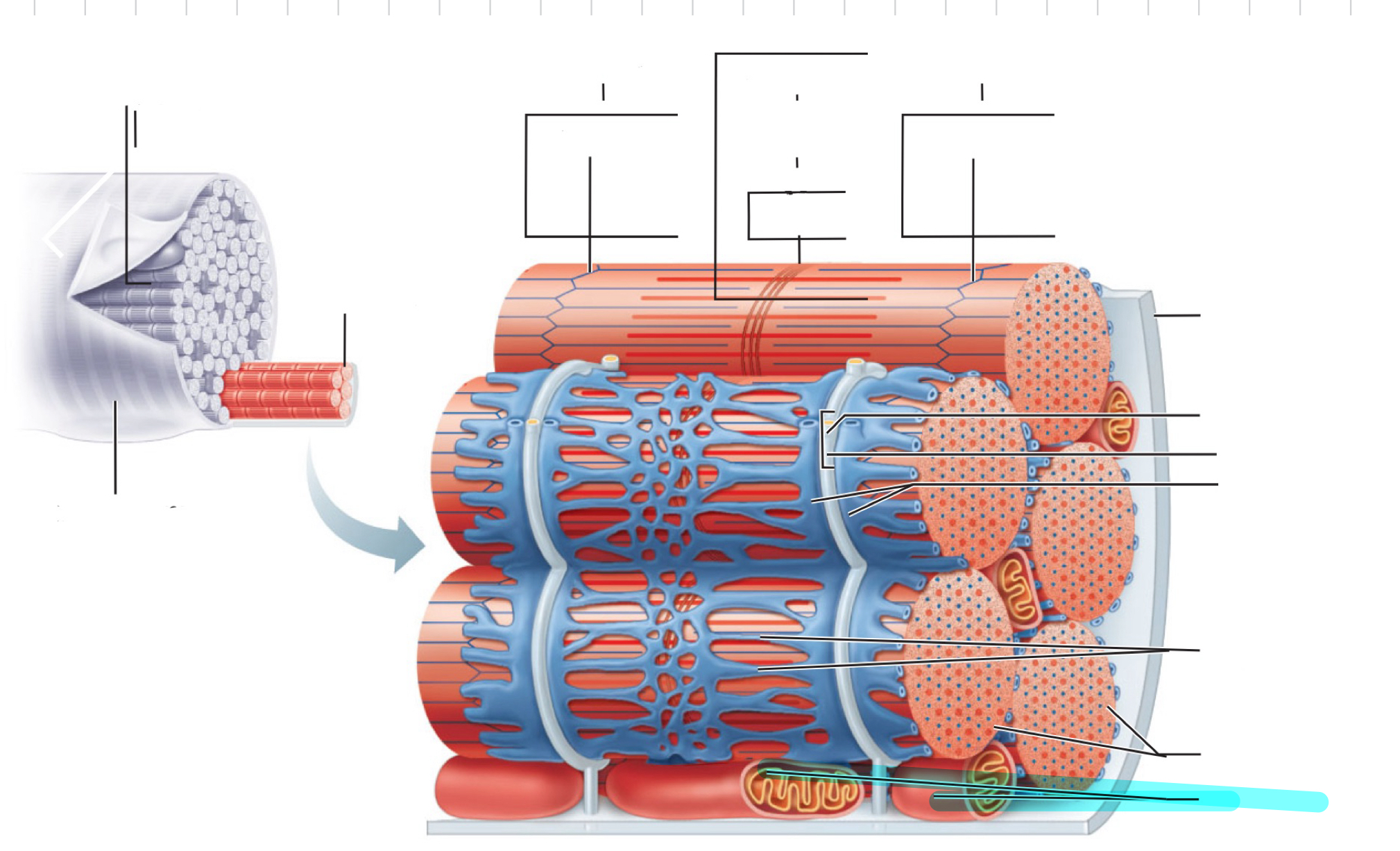
Mitochondria
I band
Sarcomere
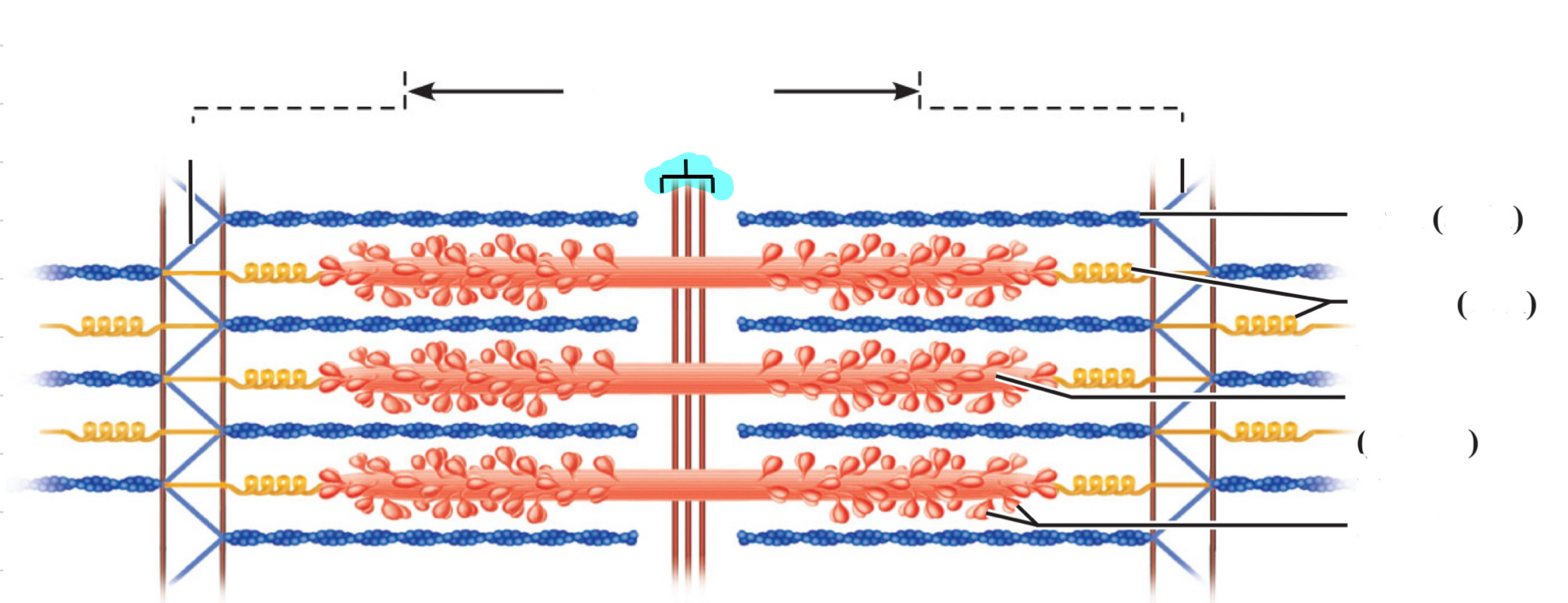
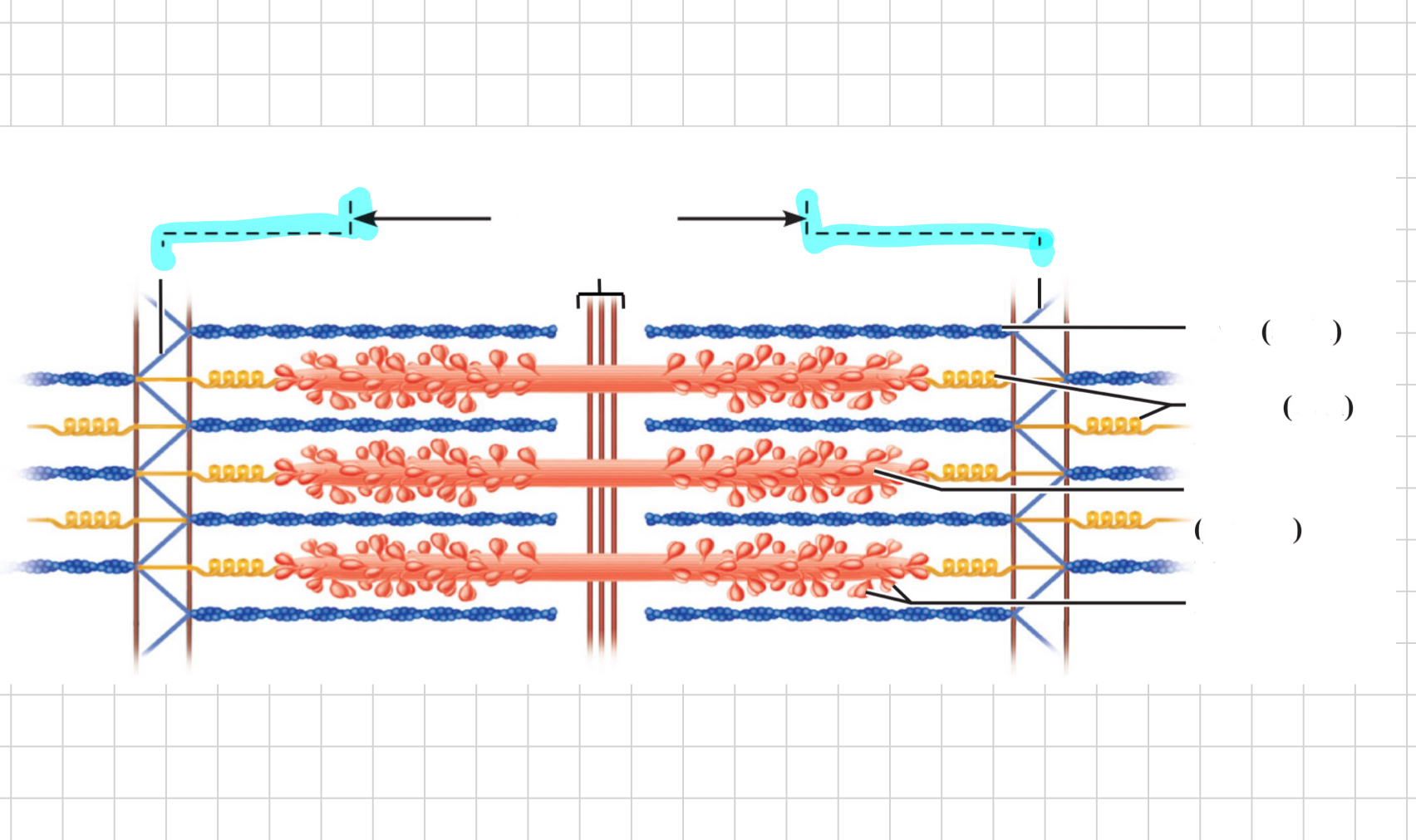
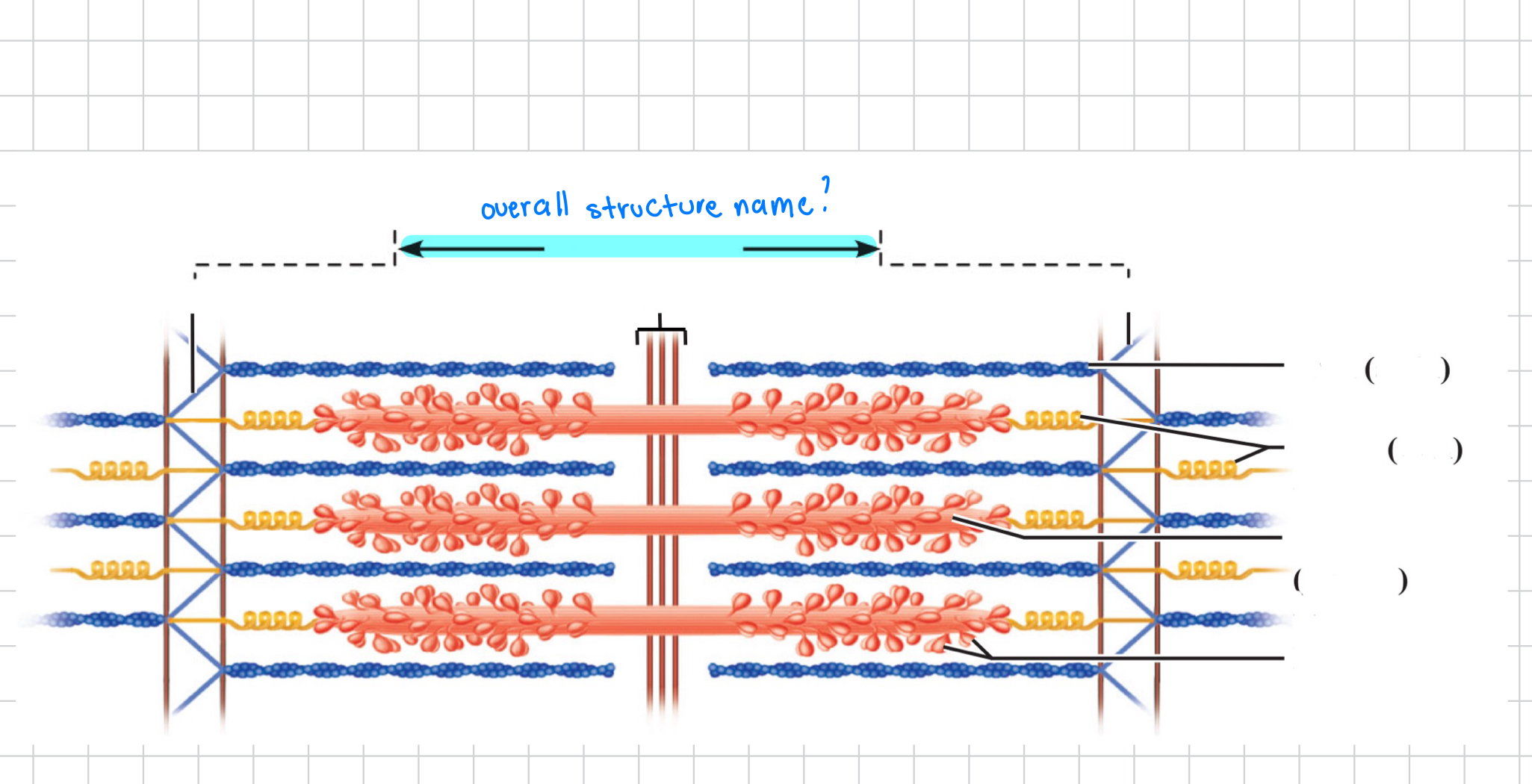
M line
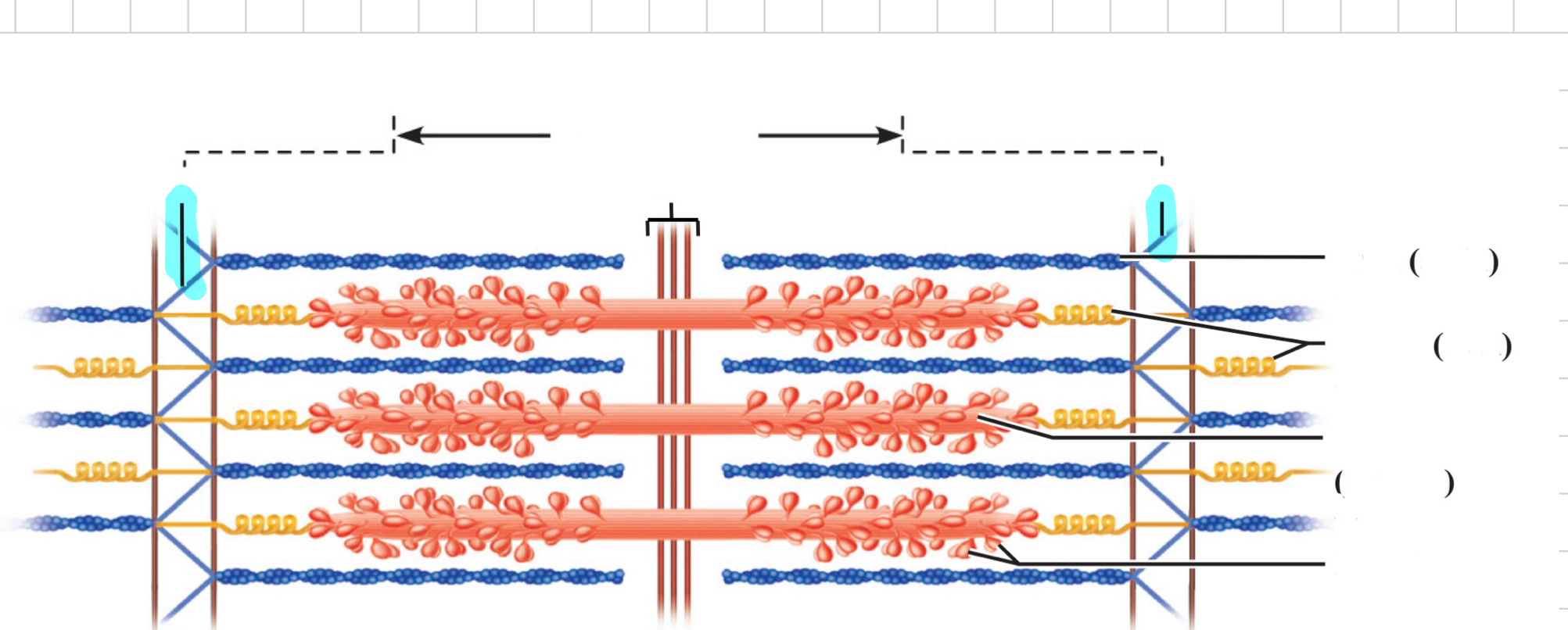
Z disc
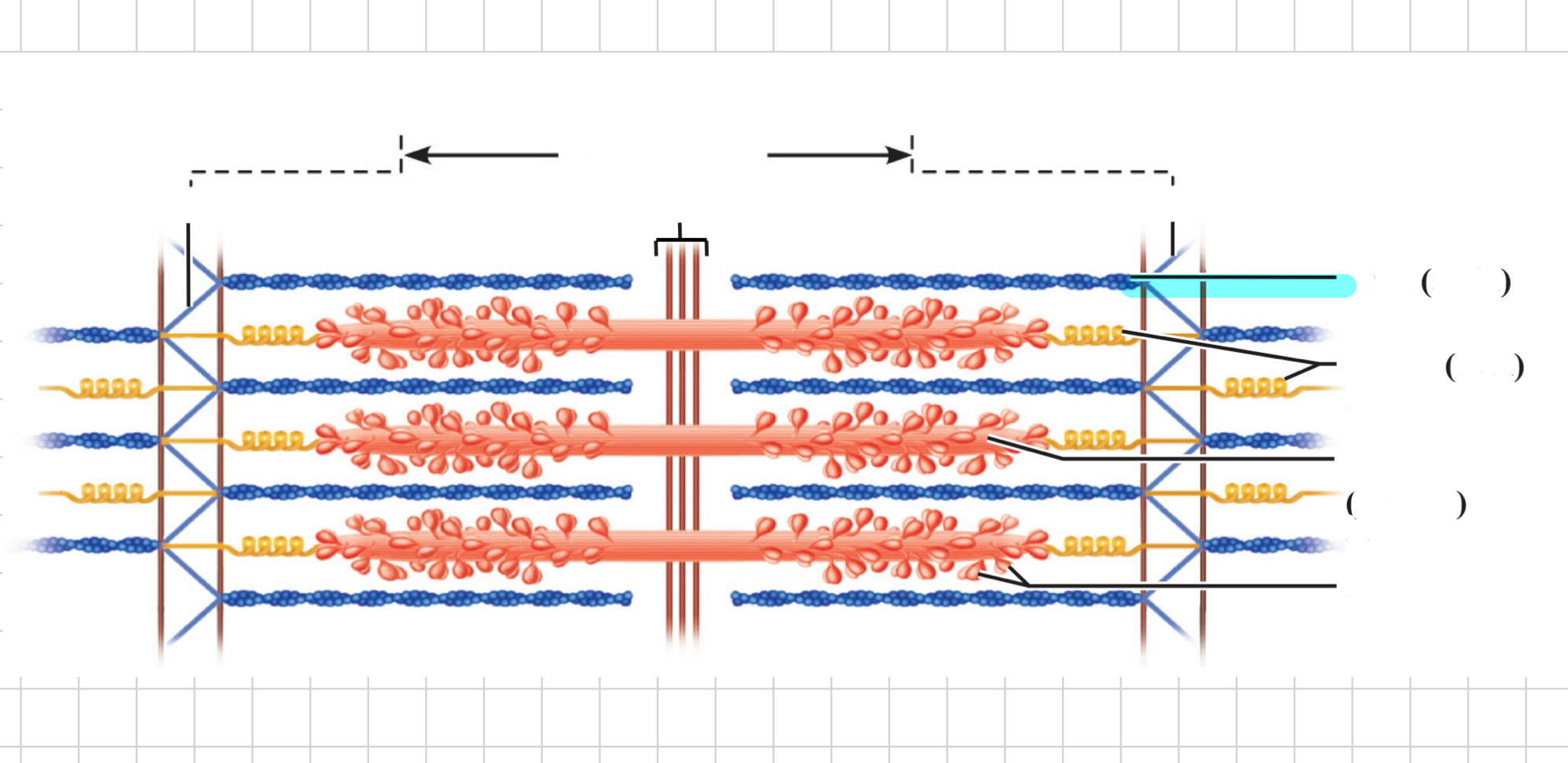
Thin (actin) filament
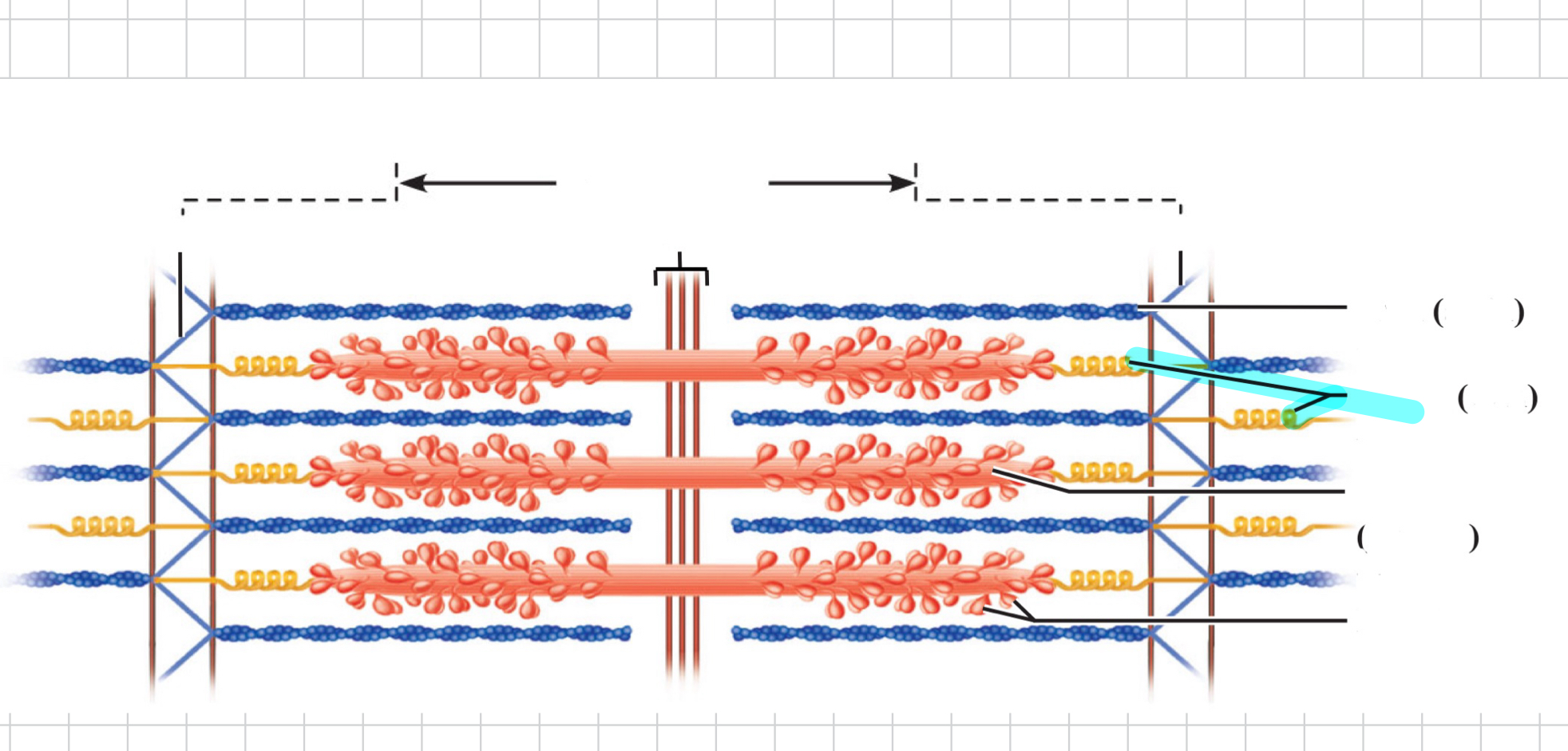
Elastic (titin) filaments
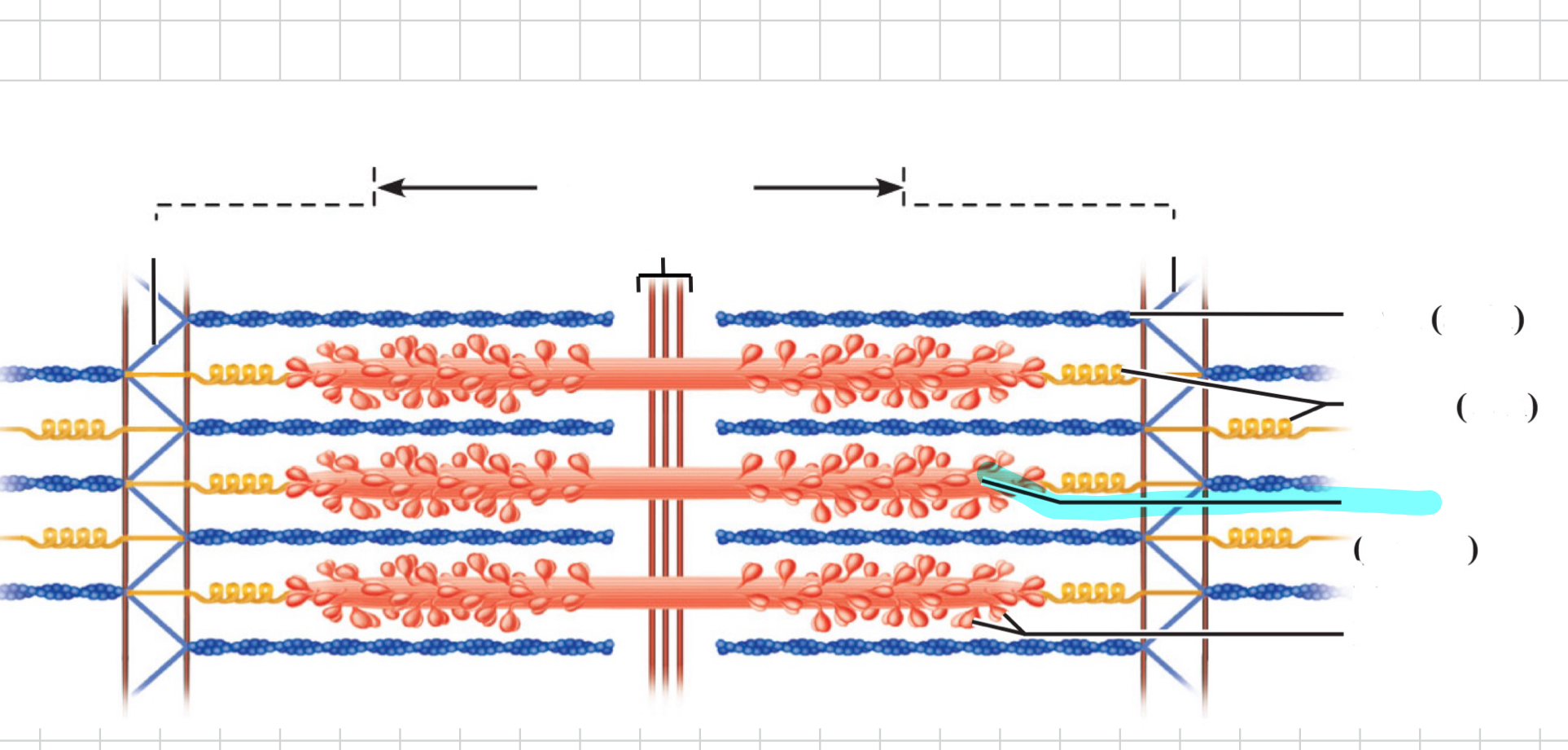
Thick (myosin) filament
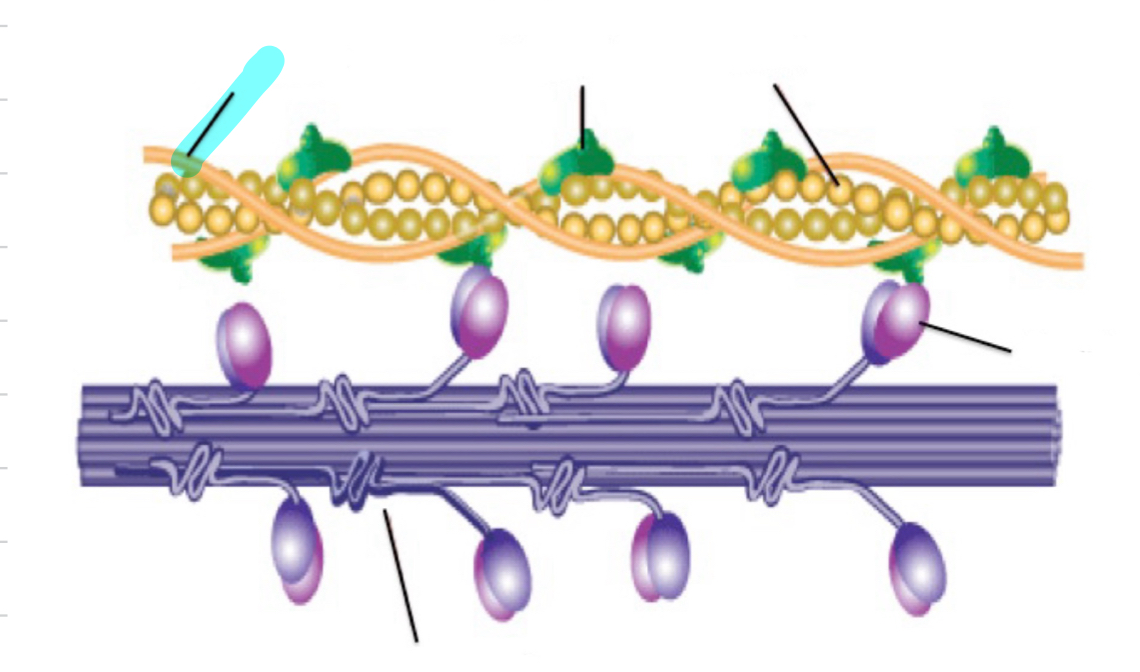
tropomyosin
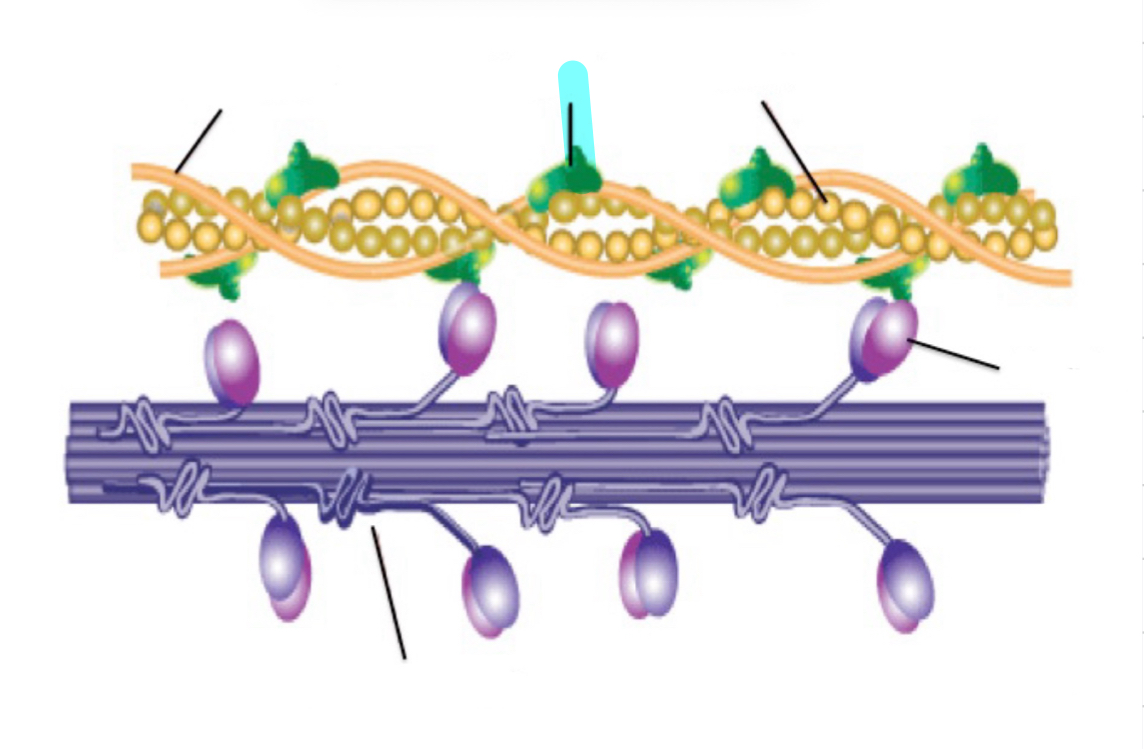
troponin
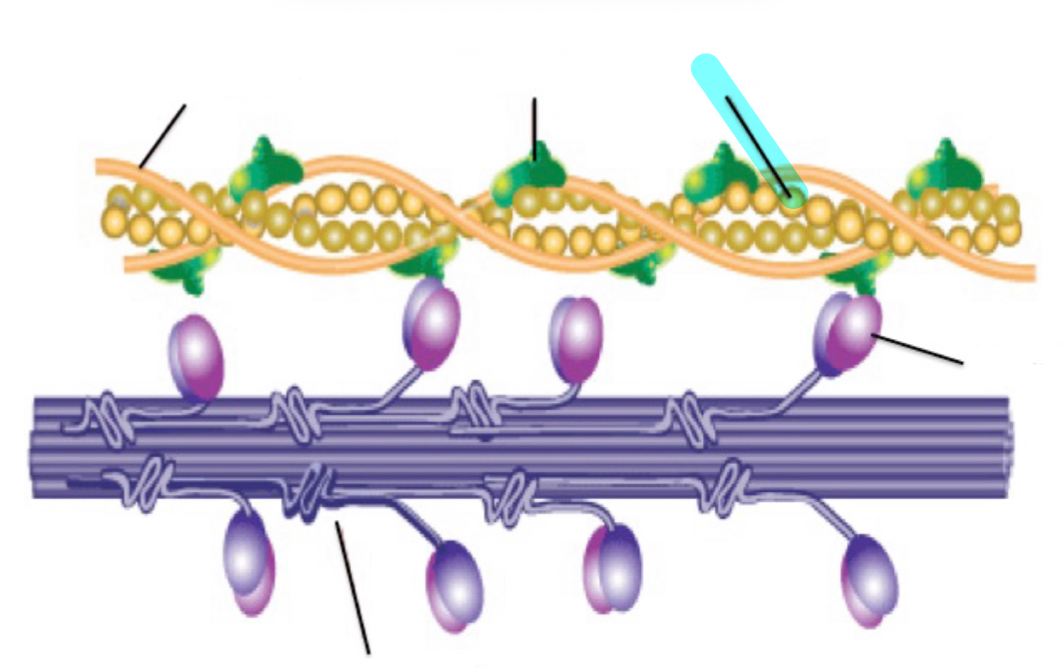
Actin
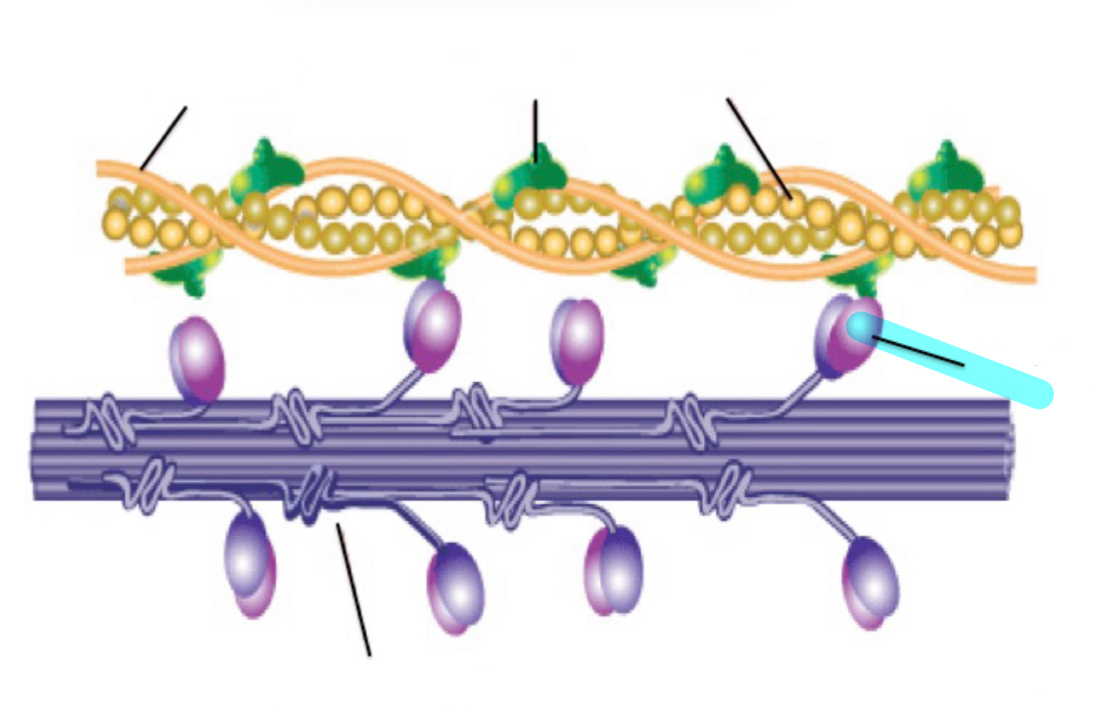
Myosin
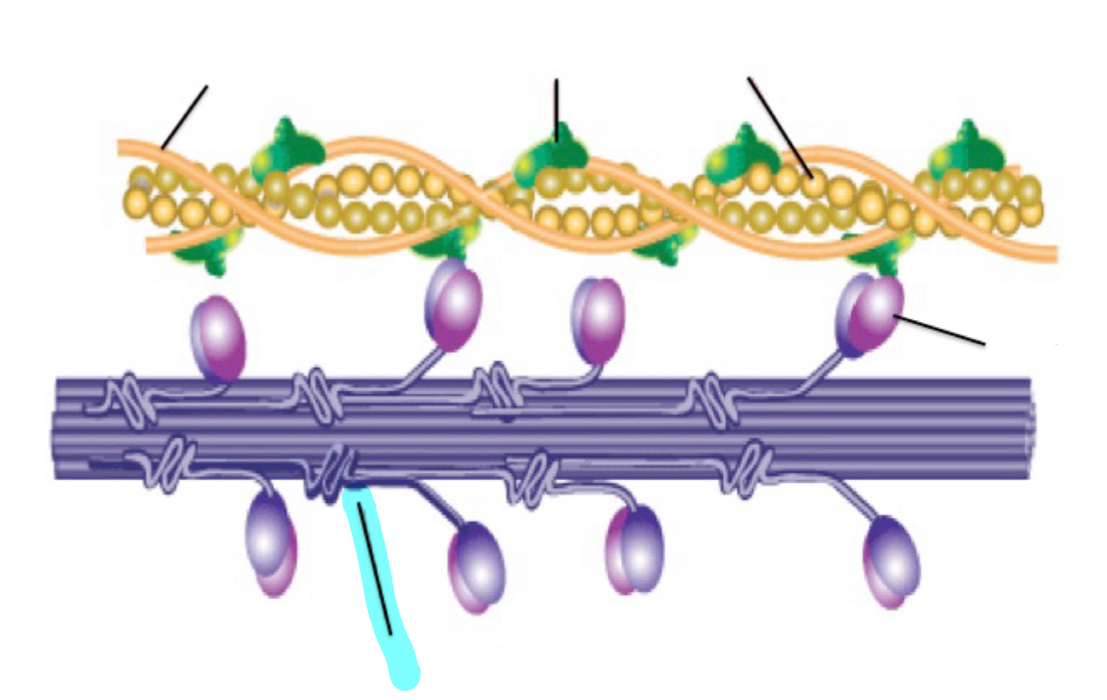
Myosin filament