Fragile environments
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
what is a fragile environment
is a place vulnerable to change and may struggle to recover from any changes
give some examples of fragile environments
tropical rainforests, cold environments/polar regions, coral reefs, deserts
what are the natural causes of desertification
soil erosion which leads to the loss of nutrients, rainfall patterns become less predictable leading to drought/lack of vegetation, reduced vegetation meaning no nutrients are added to soil through the decomposition of dead organic matter
what are the human causes of desertification
overgrazing means vegetation has all gone due to animals, over-cultivation leads to nutrients in soil being used, deforestation removes shade from soils stopping roots binding together in the soil, population growth puts increased pressure on the lands
what is deforestation
is the feeling and clearance of trees
what’s some natural causes of deforestation
wildfires are a natural cause of deforestation
what are human causes of deforestation
hydropower for building dams and reservoirs to provide electricity, agriculture so huge areas are cleared for plantation, logging - trees are filled for timber, settlements as populations grow more space is cleared for housing, mining for clearance of land to obtain precious minerals
what is some evidence for climate change
ice cores which trap ash, air bubble and microbes, preserved pollen, historical sources , tree rings
what is the Milankovitch cycle
refers to long-term changes of the Earths orbit and position which changes affect how much solar radiation the earths receives
how does volcanic eruptions cause climate change
lead to vast quantities of ash being ejected into the atmosphere that blocks solar radiation leading to a decrease in temperatures
how does atmospheric dust cause climate change
asteroids and meteors entering the earths atmosphere may increase the amount of dust, which decreases temperatures
what is the essential part of the greenhouse effect
greenhouses gases in the atmosphere allow short wave radiation from the sun through to the earths surface which is absorbed and re-radiated as long wave radiation which causes heat to help maintain the earths average temperature
what are the 4 main greenhouse gases
water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide
what is the natural source of water vapour
evaporation from the oceans/seas and plants
what is the natural source of carbon dioxide
volcanic eruptions, wildfires and respiration
what is the natural source of methane
emitted from oceans and soils as part of decomposition
what is the natural source of nitrous oxide
soils and oceans
what has increased amount of greenhouse gases led to?
led to the greenhouse effect
what is the green house effect (bad)
less long wave radiation (heat) can escape the atmosphere meaning that the global temperature increases
what are the human sources of carbon dioxide
burning of fossil fuels, wood and deforestation
what are the human sources of methane
decay of organic matter
what are the human sources of nitrous oxide
artificial fertilisers and burning fossil fuels
what are the social impact of desertification
malnutrition as people don’t get enough nutrients, food shortages cause famine, migration and conflict between migrants and the local population
what are the environmental impacts of desertification
reduced plant growth as soil nutrients are depleted, loss of biodiversity, sedimentation in rivers as soil is washed into water system, increased deforestation, increased water stress
what are the economic impacts of desertification
decreasing income for farmers as they cant grow enough crops or raise enough livestock to sell, increased rural poverty, dependence on aid , decreased investment in communities due to lack of money
what are the environmental impacts of deforestation
-reduces biodiversity, decreases interception + filtration which reduces evaporation causing precipitation, increases overland flow leading to soil erosion and sedimentation of rivers, enhanced greenhouse effect and local climate change
what’s the social impacts of deforestation
indigenous communities have less land to live on and less food available and have to give up their way of life leading to loss of culture and tradition , improved quality of life for some due to increase income and jobs, increased risk of landslides and flooding of settlements
what are the economic impacts of deforestation
more jobs available in mining, forestry and agriculture causing increased income for the country through exports of goods from the forest
what are the social impact of climate change
health, employment and homes
why is health a social impact of climate change
increased temperatures and lack of precipitation may lead to spread of disease e.g. water-borne diseases, respiratory diseases due to the stagnant air during heat waves increases air pollution, diets may be restricted leading to malnutrition and famine
how are homes impacted by climate change
increased flooding due to sea level rising and increased frequency and severity of storms will lead to displacement of large numbers of people
how is employment effected socially by climate change
loss of job opportunities due to changes in tourism and agriculture which can lead to a negative multiplier effect
what are the economic impacts of climate change
agriculture, employment and settlements
how it agriculture impacted by climate change
Farmers may need to change the crop they grow if climate conditions become unsuitable
Coastal flooding may lead to salt intrusion
Reduced availability of water will mean that irrigation is limited or impossible
Food shortages will lead to malnutrition and famine
how is employment effected economically by climate change
Job opportunities may change or decrease because:
Tourism may decline in some areas for example ski resorts may close due to the lack of reliable snow
Coastal resorts may be at risk of flooding leading to the closure
Farmers may have to change the crop they grow or livestock they raise or leave farming
In some areas, agriculture may decline due to rising temperatures or changing rainfall patterns
how are settlements impacted by climate change
Settlements in low-lying areas may have to be abandoned or need additional defences against sea level rise:
Moving settlements or improving flood defences will be costly
what are the environmental impacts of climate change
sea level rise, natural hazards, ecosystems change
how are sea levels rising impacted by climate change
Warmer temperatures cause the water in seas and oceans to expand, increasing the sea level
Melting ice is adding to the increasing volume of water
Low-lying coastal areas and islands are at higher risk of flooding
Beach erosion will increase leading to greater coastal erosion
Coastal ecosystems including coral reefs and mangrove swamps will be affected
how are natural hazards impacted by climate change
Changes in climate patterns are likely to increase the frequency and severity of storms
The frequency and length of droughts are increasing
Dry conditions lead to the increased risk of wildfires
Rising sea levels together with increased storms lead to increased flooding risk
how are ecosystems changing impacted by climate change
The location of biomes may shift to the north (Northern Hemisphere) and south (Southern Hemisphere) as they rely on specific climate conditions:
Polar and tundra biomes are at risk of becoming extinct as they cannot shift any further north/south
Increasing sea temperatures and ocean acidification have resulted in coral bleaching
Migration and behaviour patterns of animals affected by changing temperatures:
Fish species are moving north and south of their usual habitats to seek cooler water
Reduced hibernation due to warmer winters
Mangrove swamps and coral reefs are threatened by rising sea levels
what are some responses to desertification
water shortage solutions, education, agriculture, agroforestry, afforestation, genetically modified crops with high yield and fertilisers, contour stones and terraces
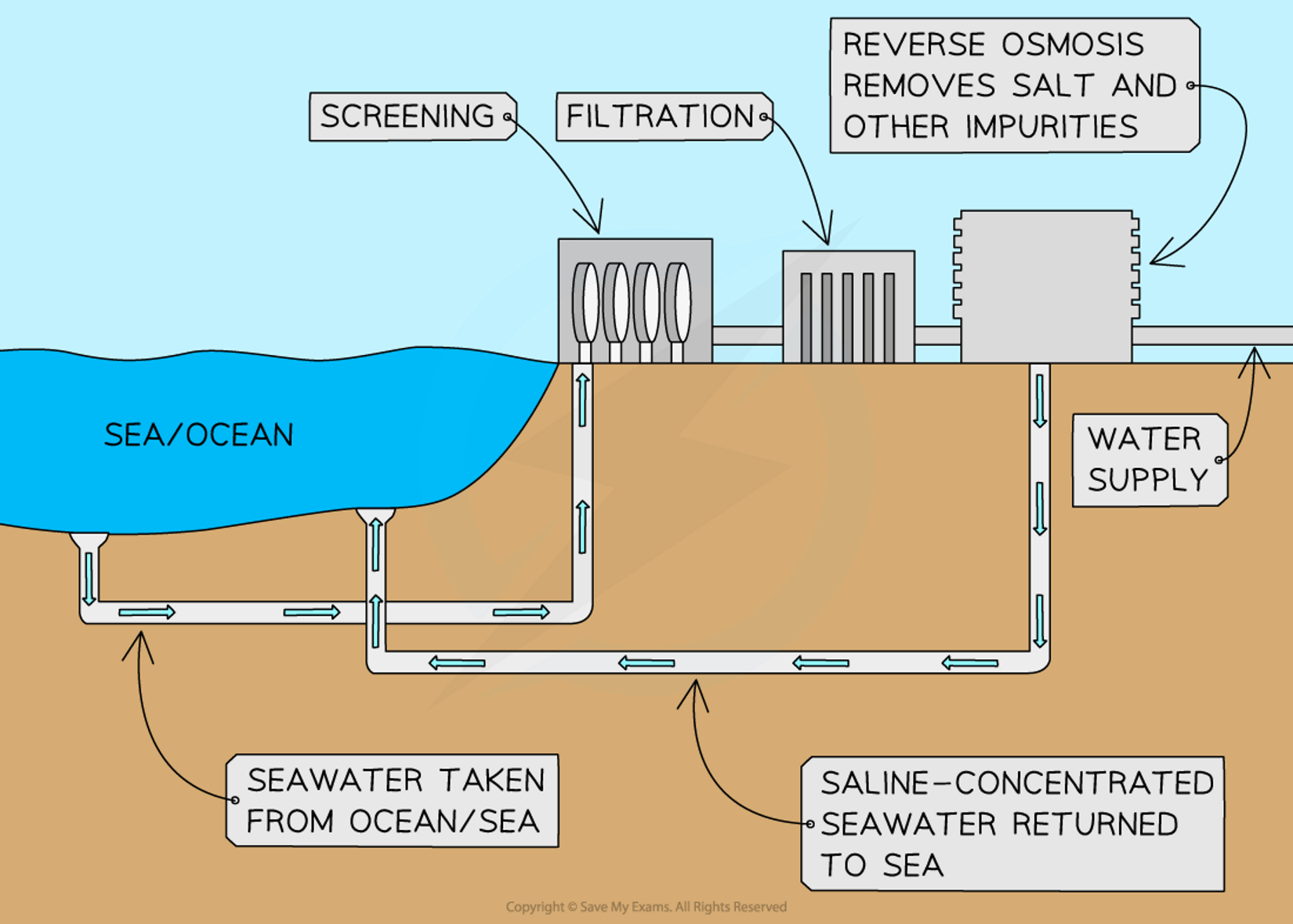
what is the water shortage solutions for desertification
Water shortages are a key issue in areas at risk from desertification
Desalination can be used to increase water supply but the process is expensive
This means that only some countries can afford it
Groundwater can be abstracted using water pumps but care must be taken not to over-abstract
what is done with education as a response to desertification
Education including:
Sustainable farming methods including agroforestry and crop rotation, which help to keep the soil healthy
Family planning to reduce population growth
what is done with agriculture as a response to desertification
Focus on livestock breeds which are better adapted to drier conditions
Reduced herd size
Use high yield varieties (HYV)
Crop rotation
what is done to afforestation in response to desertification
This combines agriculture with forestry, which means some trees remain, which:
decreases deforestation
provides shade as well as increasing infiltration and interception, which reduces soil erosion
provides organic matter from the trees and adds nutrients to the soil
what is done to fertilisers and crops in response to desertification
Fertilisers, HYV and GM crops can:
Increase the yield
Reduce the amount of land cultivated
HYV and GM crops may also be:
Drought resistant
Pest resistant
what is done to contour stones and terraces in response to desertification
These help to reduce soil erosion by:
Preventing the soil from being blown or washed away
Increasing infiltration of water and reducing overland flow
Ensuring that dead organic matter stays in one place and can decompose adding nutrients to the soil
Give an example of a place where deforestation has happened and the sustainable management of the rainforest
The Amazon rainforest located in the north of South American, strategies can be on an international, national and local level
what are the international strategies used for management of the Amazon rainforest
UN Forum on Forests was established in 2000 and is committed to the management, conservation and sustainable development of all types of forests
The UN Sustainable Development Goals include the sustainable management of forests
International treaties protect certain areas such as the Central Amazon Conservation Complex (CACC) which is a World Heritage Site. This means hunting, logging, fishing and access are limited
Trade restrictions on endangered species and timber have been imposed
The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) aims to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten the survival of the species
what are the national strategies used for management of the Amazon rainforest
Brazil's forest code requires landowners to maintain a proportion of their land as forest. However, the amount they need to maintain was reduced from 80% to 50% in 2012
In 2004 the DETER satellite was launched. It:
There are 68 National Parks in Brazil. These are protected areas where the aim is to conserve the ecosystem
A reforestation project which is part of the Amazonia Sustainable Landscapes Project. It aims to:
restore 30,000 hectares of land to the forest by 2023 which will involve planting 73 million trees.
It is a partnership project between:
Conservation International
Brazilian Ministry of Environment
The Global Environment Facility (GEF)
The World Bank
The Brazilian Biodiversity Fund (Funbio)
what are the local strategies used for management of the Amazon rainforest
Agroforestry combines agriculture with forestry, which means some trees remain, which:
Decreases deforestation
Provides shade as well as increasing infiltration and interception, which reduces soil erosion
Provides organic matter from the trees and adds nutrients to the soil
Increases biodiversity due to the variety of plants grown
Education of people involved in the exploitation and management of the rainforest
Small-scale projects such as the Marajo Project which preserves almost 90,000 hectares of Amazon forest. It includes:
A tree nursery to grow saplings to be planted in areas which have been cleared
The new trees help to bind the soil reducing soil erosion and increasing infiltration
Agroforestry is encouraged reducing the need to over-cultivate and clear areas
School-based agricultural education and scholarships
international responses to global warming + climate change involve response that can what?
either adapt or migrate
give some examples of international responses
Paris agreement in 2015 where the globe agreed to limit global warming to 2oC and agreed to reduce CO2 emission by at least 60%
what is the Kyoto protocol in 1997
delegates from 15 countries agreed to reduce greenhouse emission in which developing country’s like China and India were exempt from this agreement. USA did not sign up for treaty and in 2011 Canada withdrew stating with USA and China the treaty would never work
what countries share Borneo
Indonesia, Malaysia and Brunei
what island size ranking is Borneo
3rd biggest island in the world
name some of Borneo’s key animal species
Orangutang, Asian elephant, Borneo leopard, Rhinoceros
list some threats to the Bornean Rainforest
deforestation
illegal wildlife trade
rubber plantations
mining
where is the Borneo on the map
South east Asia, by the pacific and Indian ocean but mainly boarders the southern China sea
what are some sustainable management strategies in Borneo’s Indonesian Rainforest
selective logging and replanting
ecotourism
education and awareness
REDD + initiatives
sustainable palm oil certification ISPO
heart of Borneo initiative
how does selective logging help manage Borneo’s deforestation
controlled logging of mature trees, leaving younger trees to grow, allows the forest to recover. This is coupled with replanting efforts to ensure the forests overall health and biodiversity.
how does ecotourism help manage Borneo’s deforestation
tourism that focuses on environmentally sensitive activities can create jobs for local communities while generating revenue for forest conservation. Provides income while preserving the forest.
how does education and awareness help protect Borneo’s rainforest from deforestation
promoting the value of biodiversity and the importance of rainforests through educational programs/schools can help build support for sustainable practises
how does REDD+ initiatives help protect Borneo’s rainforest
REDD+(Reducing Emission from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) programs incentivize the conservation of forests and promotes sustainable forestry practises, contributing to climate change mitigation
how does the heart of Borneo Initiative help protect Borneo’s rainforest
is an agreement between Indonesia, Malaysia and Brunei to protect 22 million hectares of rainforest through sustainable land use planning
how does sustainable palm oil certification (ISPO) help protect Borneo’s rainforest
The Indonesian Sustainable Palm Oil (ISPO) certification standard aims to ensure palm oil production is environmentally and socially responsible, reducing deforestation associated with palm oil cultivation
What developed country case study are we doing for responses to climate change and global warming
Norway
what are 3 different groups we are looking at for their response
individuals, organisations and governments
what where the governments response and how does it work- NORWAY
Policy implementation- various policies aimed at reducing gas emissions, including carbon taxes, regulations for industry’s. Which they introduced a climate action plan to focus on reducing emissions in Land use, land use-change and Forestry.
adaption measure- prepare for impacts of climate change such as strengthening coastal defences and developing climate -resilient infrastructure.
carbon pricing- one of the highest carbon taxes in the world, encourages industries to cut emissions and investing in renewable energy
what where the organisational responses and how does it work- NORWAY
NGOs- environmental non governmental organisations (NGOs) actively campaign for stronger climate policies and support research and development of renewable energy technologies
renewable energy- companies can adopt sustainable practises to reduce their carbon emissions and invest in renewable energy sources
educational institution- universities and research institutions play vital role in advancing climate science and educating then next generation of environmental experts
what are the individual responses and how do they work - NORWAY
electric vehicles- Norway has the highest percentage of EVs per capita with government subsidies making them more accessible
sustainable living practises- adopting eco-friendly habits, such as reducing waste, using public transport and supporting green business and reducing consumption to lower their carbon footprint
What developing country are we choosing for response to climate change and global warming
India
why is India vulnerable to climate change
due to its geography, population and dependence on agriculture
what extreme weather events does India face
heatwaves, floods and cyclones
what are some of the responses from the government to try help reduce global warming and climate change - INDIA
Net-Zero pledge by 2070- India has committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2070 to help reduce global warming
afforestation and renewable energy- the government is investing in large-scale tree planting and solar energy projects aiming to reduce reliance on fossil fuels
investment in infrastructure- investing in infrastructure projects, including flood defences and drought-resistant farming techniques to mitigate climate change and protect vulnerable communities from floods, droughts and rising sea levels
what are some of the responses from the organisations to try help reduce global warming and climate change -INDIA
Green technologies and renewable energy- Organisations including NGO’s are investing in green technologies and renewable resources to reduce dependence on fossil fuels
Community based solutions- some organizations are implementing community based solutions like water harvesting and rainwater management to enhance resilience to climate change impact. Revive traditional crops, build climate proof infrastructure and promote sustainable farming
what are some of the responses from individuals to try help reduce global warming and climate change -INDIA
reducing carbon footprint- by living eco-friendly life’s and adapting solar energy, reducing plastic use, using public transport and reducing meat consumption
climate activism and awareness- citizens are increasingly involved in protests, petitions and awareness campaigns to demand stronger climate change policies
innovative farming techniques- farmers are using drought resistant crops and water conservation methods to adapt to changing climate conditions.