Genetics
5.0(1)Studied by 5 people
0%Unit 2 Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/25
Last updated 1:35 AM on 3/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
46
How many chromosomes do humans have?
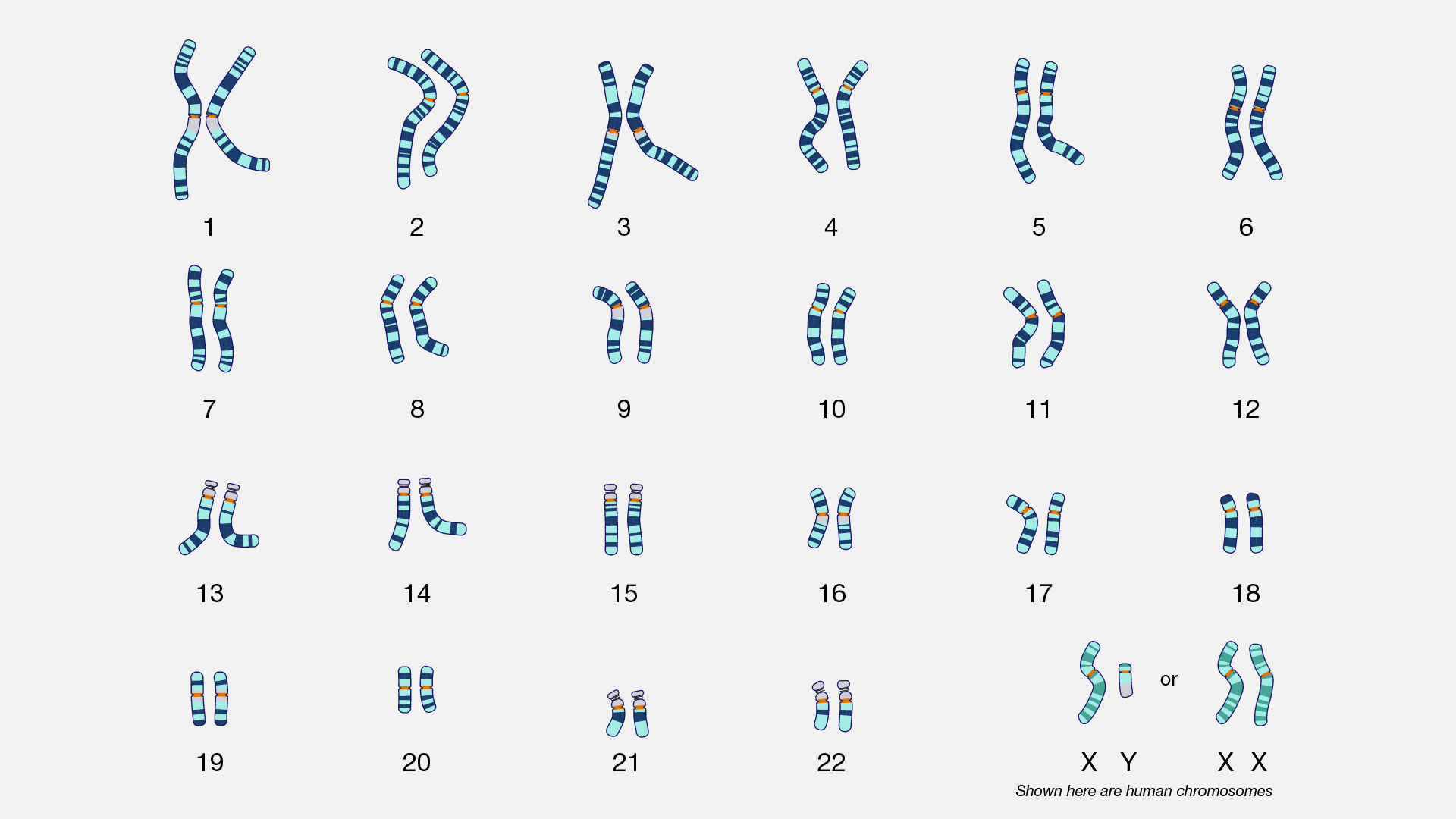
2
New cards
23
How many chromosomes does one get from each parent?
3
New cards
Autosomal genes
Chromosomes 1-22
4
New cards
Sex-linked Genes
chromosome 23
\
either XY or XX
\
either XY or XX
5
New cards
Sex-Linked Traits
= traits on only either X or Y chromosome
* most are carried on the X
* if a defect is carried on the X, then the males are more likely to get a defect (since no other X chromosome is there to dominate/cover the recessive gene)
* most are carried on the X
* if a defect is carried on the X, then the males are more likely to get a defect (since no other X chromosome is there to dominate/cover the recessive gene)
6
New cards
Sex-limited Traits
= traits limited by hormone level
\
* gene is on both X and Y chromosomes, BUT whether it is expressed or not depends on reproductive hormone levels
\
ex. baldness depends on level of testosterone
\
* gene is on both X and Y chromosomes, BUT whether it is expressed or not depends on reproductive hormone levels
\
ex. baldness depends on level of testosterone
7
New cards
Klinefelter Syndrome
= 1+ extra X chromosome(s)
\
**XXY or XXXY**
\
* only in males
* slow motor/speech development
* puberty delayed or absent
* low testosterone levels
* breast development
* taller than average
* usually infertile
* gay/bisexual
\
**XXY or XXXY**
\
* only in males
* slow motor/speech development
* puberty delayed or absent
* low testosterone levels
* breast development
* taller than average
* usually infertile
* gay/bisexual
8
New cards
Turner Syndrome
= 1 X and no Y
\
**XO**
\
* results in child being a girl
* short
* broad chest/neck
* no puberty → infertile
\
**XO**
\
* results in child being a girl
* short
* broad chest/neck
* no puberty → infertile
9
New cards
XYY Syndrome
= an extra Y chromosome
(no special name for this syndrome)
* male
* genital anomalies
* cerebral cortex atypical development
* low intelligence/autism-related symptoms
* does NOT cause extreme masculinity
* low fertility
(no special name for this syndrome)
* male
* genital anomalies
* cerebral cortex atypical development
* low intelligence/autism-related symptoms
* does NOT cause extreme masculinity
* low fertility
10
New cards
Triple-X Syndrome
= 3 Xs
\
**XXX**
\
* girl
* mild cognitive defects
* usually go undiagnosed
* low fertility
\
**XXX**
\
* girl
* mild cognitive defects
* usually go undiagnosed
* low fertility
11
New cards
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS)
= in XY people, androgen receptors (for male sex hormones like testosterone) are defected/absent
* so embryos develop as females
* infertile
* so embryos develop as females
* infertile
12
New cards
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
* recessive metabolic disorder (AKA missing a gene that codes for an enzyme that digests parts of what you eat (in this case, ketons))
* if they don’t get broken down, they gather in brain and damage brain cells
* → significant intellectual disabilities
* if they don’t get broken down, they gather in brain and damage brain cells
* → significant intellectual disabilities
13
New cards
Sickle Cell Disease
= recessive disease with malformed red blood cells
lot of sickle cell = body deprived of oxygen = pain
\
Heterozygote Advantage: protects against malaria
lot of sickle cell = body deprived of oxygen = pain
\
Heterozygote Advantage: protects against malaria
14
New cards
Cystic Fibrosis
= recessive disease
* extra thick mucous in lungs/digestive system
\
Heterozygote Advantage: carriers have an extra mucous which protects them better from diarrhea
* extra thick mucous in lungs/digestive system
\
Heterozygote Advantage: carriers have an extra mucous which protects them better from diarrhea
15
New cards
Tay Sachs
= neurodegenerative recessive disease
\
* almost all die before 5 yrs
* more prominent in Eastern European Jews
\
Heterozygote Advantage: protects carriers from tuberculosis
\
* almost all die before 5 yrs
* more prominent in Eastern European Jews
\
Heterozygote Advantage: protects carriers from tuberculosis
16
New cards
Huntington’s Disease
= dominant neurodegenerative disease
\
* 100% fatal, no cure
* BUT not fatal until 50-60s (after having kids, that’s why it persists in population)
\
\
* 100% fatal, no cure
* BUT not fatal until 50-60s (after having kids, that’s why it persists in population)
\
17
New cards
Down’s Syndrome
= 3 copies of chromosome 21 (AKA trisomy-21)
* wide range of symptoms (autism spectrum: mild to severe)
* random mutation/non-heritable
* wide range of symptoms (autism spectrum: mild to severe)
* random mutation/non-heritable
18
New cards
Monozygotic
1 egg → 2 babies
\
= identical twins
* share same genes
\
= identical twins
* share same genes
19
New cards
Dizygotic
2 eggs → 2 babies
\
= fraternal twins
* don’t share same genes
* but nurture is going to be more similar
\
= fraternal twins
* don’t share same genes
* but nurture is going to be more similar
20
New cards
Same nature, different nurture
a type of twin study
= identical twins separated at birth
\
* useful in determining the effect of **nurture** (since nature is controlled for)
* more useful in showing differences in physical stuff like blood pressure
= identical twins separated at birth
\
* useful in determining the effect of **nurture** (since nature is controlled for)
* more useful in showing differences in physical stuff like blood pressure
21
New cards
Different nature, same nurture
a type of twin study
= fraternal twins raised together
\
* same-sex fraternal twisn compared to each other AND a different aged sibling (also of the same sex)
* → then, compare who is more similar, twins to each other, or each twin compared to other sibling?
\
* these studies more useful in showing more sensitive stuff (personality, interests)
= fraternal twins raised together
\
* same-sex fraternal twisn compared to each other AND a different aged sibling (also of the same sex)
* → then, compare who is more similar, twins to each other, or each twin compared to other sibling?
\
* these studies more useful in showing more sensitive stuff (personality, interests)
22
New cards
Concordance Rate
= probability that 2 people have the same disorder based on their relationship to each other
\
ex.
person A has Senioritis
\
person B’s relationship to person A: | Concordance Rate for person B:
\---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Identical Twin = 46% concordance rate (46 chance that person B has it)
\
Sibling = 15% concordance rate
\
Unrelated person = 6% concordance rate (since this person is unrelated, this rate is applicable to the entire population, AKA 6% would be the **prevalence rate**)
\
ex.
person A has Senioritis
\
person B’s relationship to person A: | Concordance Rate for person B:
\---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Identical Twin = 46% concordance rate (46 chance that person B has it)
\
Sibling = 15% concordance rate
\
Unrelated person = 6% concordance rate (since this person is unrelated, this rate is applicable to the entire population, AKA 6% would be the **prevalence rate**)
23
New cards
Heritability
= the % of “nature” in the nature-nurture debate
(AKA how much contribution genetics has to a trait/disorder)
\
ex. alcoholism has a 60% heritability rate
* 60% is **explained** by __genetics__, so 40% is due to the __environment__
* does **NOT** mean that there’s a 60% chance for a child of an alcoholic to become one
\
(AKA how much contribution genetics has to a trait/disorder)
\
ex. alcoholism has a 60% heritability rate
* 60% is **explained** by __genetics__, so 40% is due to the __environment__
* does **NOT** mean that there’s a 60% chance for a child of an alcoholic to become one
\
24
New cards
Genetic Predisposition
= the probability of developing a disease
\
* __not to be confused__ with heritability
\
* __not to be confused__ with heritability
25
New cards
Heterozygous vs Homozygous Genes
Individuals carrying two identical alleles (RR or rr)
vs.
different alleles (Rr)
vs.
different alleles (Rr)
26
New cards
Phenotype vs Genotype
unique sequence of DNA. (the two alleles a person has inherited for a particular gene)
vs.
the detectable expression of this genotype – a patient's presentation/appearance
\n
vs.
the detectable expression of this genotype – a patient's presentation/appearance
\n