Lecture 1: 6/25
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Define Operative Dentistry
Operative Dentistry is a branch of oral health service concerned with restoration of form, function, and esthetics for each tooth that has been ravaged by caries, trauma, erosion, abrasion, and attrition.
Prevention and non-surgical management of hard tissue conditions (caries, erosion and tooth wear) are among modern operative dentistry approaches.
Operative dentistry may also deal with restorations of teeth affected by genetic abnormalities such as enamel hypocalcification and dysplasia (minor) or dentinogenesis imperfecta (major).
Operative dentistry also deals with minor to moderate esthetic concerns such as diastema closures, thanks to adhesive dentistry, and bleaching.
What are the components of success in dental procedures?
Material
Operator Team
Patient
What are Material & Instrument factors:
Interfacial seal
Technique sensitivity
Biocompatibility
Bioactivity, ion-release
Solubility
Biochemical/ wear durability
Appearance/ Esthetics
What are patient factors:
Caries risk
Oral hygiene
Diet
Occlusion habits
Cooperation during procedure
Regular visits
What are Operator factors:
Case & material selection
Assessment and planning
Preparation
Isolation and placement technique
Basic skills
Documentation, follow up and maintenance
Assistant support
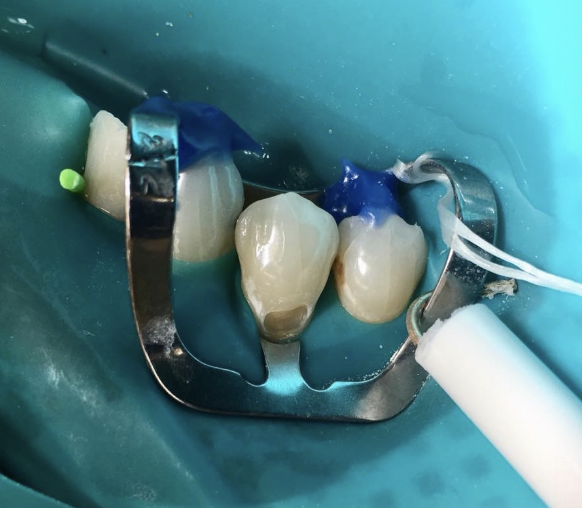
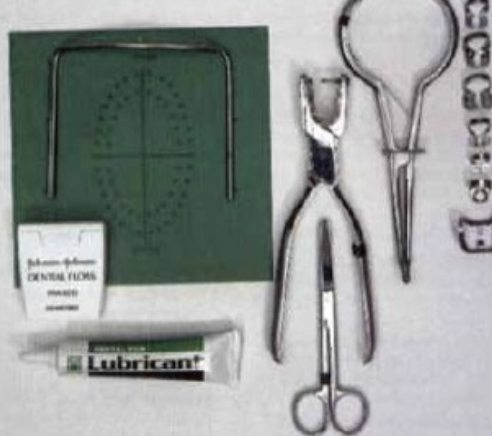
What is field isolation
Isolating an area of mouth or a tooth to perform treatment without interference from soft tissues, the tongue, saliva and other fluids
What is considered the most complete and effective method of isolation?
Rubber damn
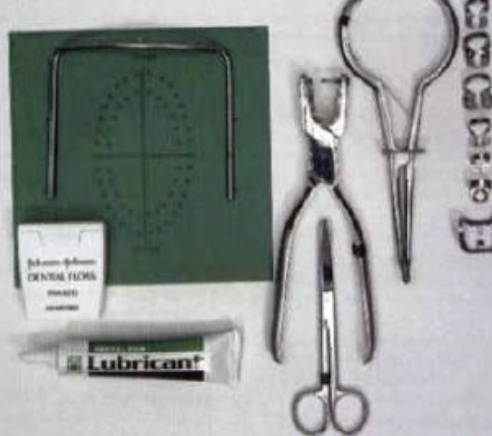
For some procedures like RCT, lack of rubber dam isolation is considered
Inadequate practice
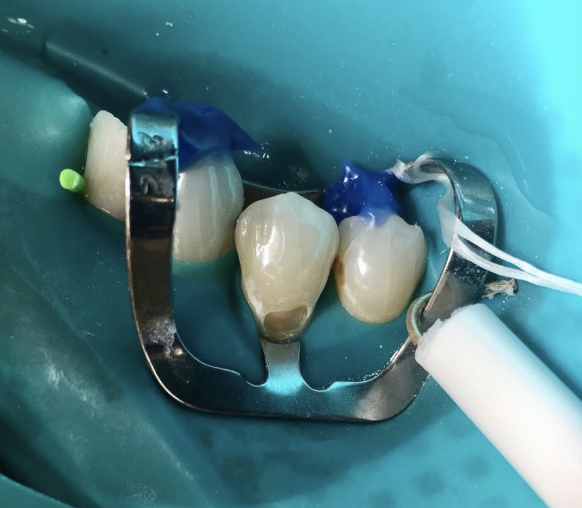
What does airway protection do?
Prevents aspiration or swallowing of objects. Patient feeling of safety and security
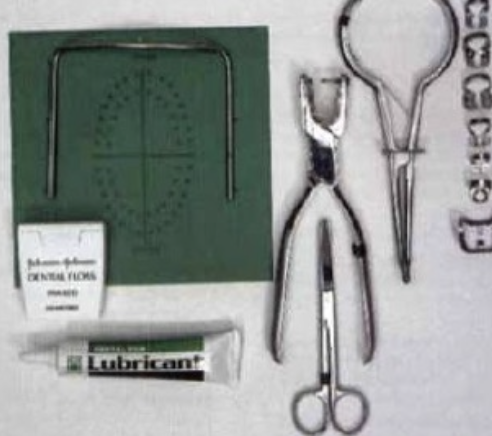
What does patient management do?
Reduces talking, reduces the need to swallow, expectorate
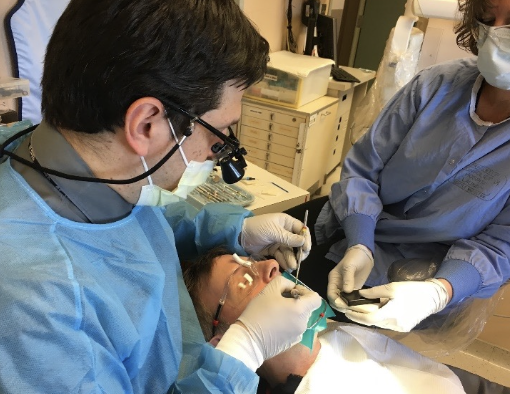
What is reduced microbial transmission? From who to whom?
From patient to operator; from operator to patient; from patient’s saliva to patient’s tooth pulp
Name some operator factors
Increased accessibility to operative site
Improves visibility of the working field
Prevents fogging of the dental mirror (by breathing)
Better rinsing and suction performance
Better patient management
Facilitates work in quadrants
If you have salivary contamination, what is highly compromised?
Enamel and dentin bonding
This is a requirement for bonded restorations
Good isolation
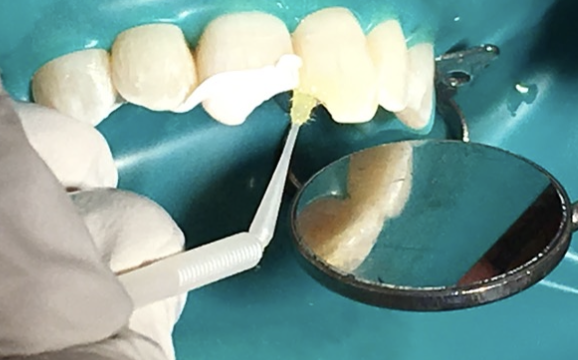
Using good isolation is also advantageous in
Glass ionomer and amalgam. It is especially important if pulp space is violated, and limiting bacterial contamination
What is a rubber dam made of?
Classic material was latex; be aware of allergies (incidence increasing, including asthma, anaphylaxis)
**we use non-latex, silicone based
What is the benefit of using a non-latex, silicone based rubber dam?
Better shelf life and autoclavable, but tear strengths are somewhat lower
What are some colors of rubber dams that are available?
For contrast with tooth/tissues: blue, purple, pink, green, grey- it is a matter of personal preference. For non-latex, the most common color is green (both sides are the same, online latex which had a shiny and dull side
What form does rubber dam come in?
Sheets (6'“x6”) are classic, pre-cut. 5×5 are sometimes used for pediatric patients
What is the shelf-life of a rubber dam?
Non-latex shelf life is very good. Does not require refrigeration (unline latex types)
How thick is the rubber dam?
Non-latex is available only in medium thickness (latex was available in 5 thicknesses)
What are the types of rubber dam punches?
Ainsworth-type and Ivory-type
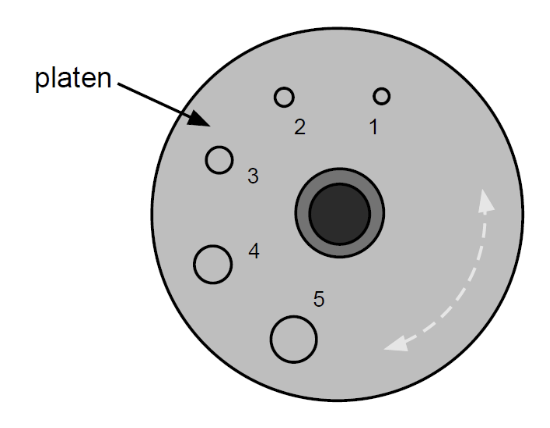
What is this?
A diagram depicting hole sizes
**Be sure hole is centered under the punch, or you will damage the platen. Get good clean, complete holes!
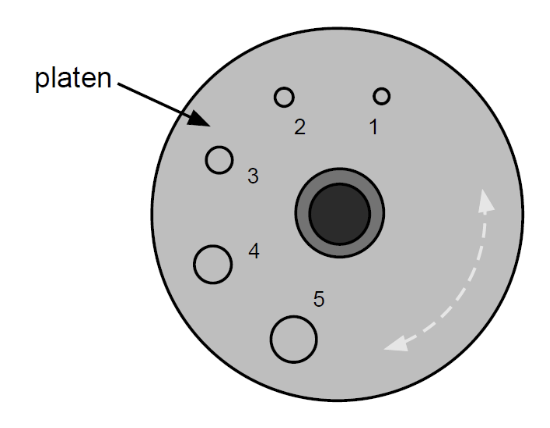
Hole #1 is used for
Maxillary: Lateral incisors
Mandibular: Central incisors
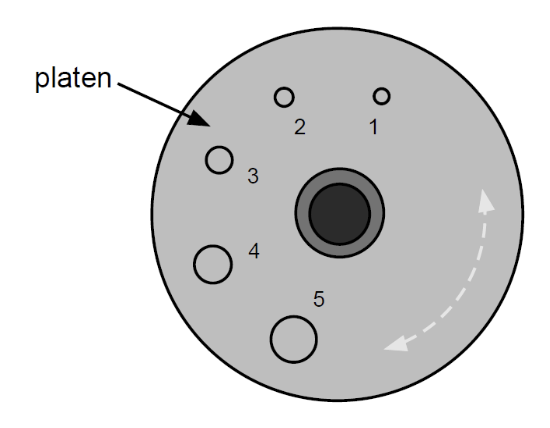
Hole #2 is used for
Maxillary: Central and Lateral incisors
Mandibular: none
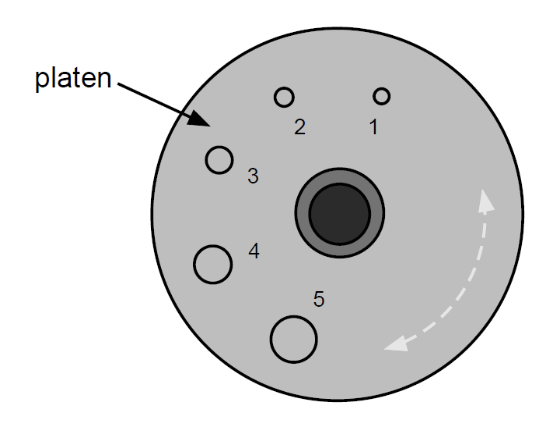
Hole #3 is used for
Maxillary: Canines and Premolars
Mandibular: Canines and Premolars
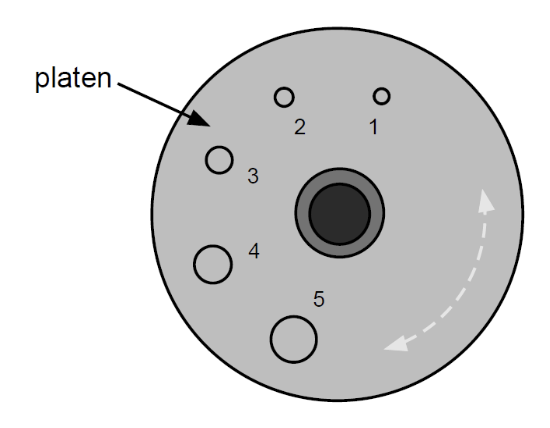
Hole #4 is used for
Maxillary: Molars
Mandibular: Molars
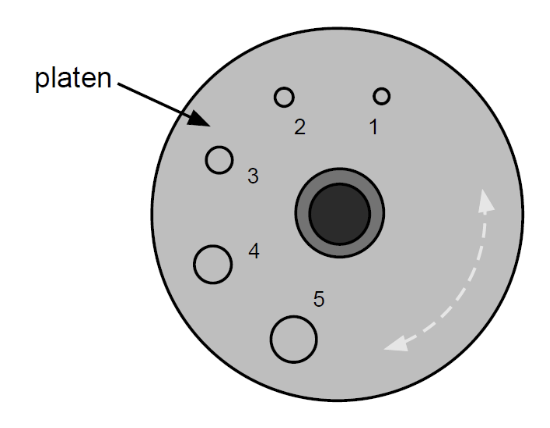
Hole #5 is used
As a retainer
Guide for hole-punching
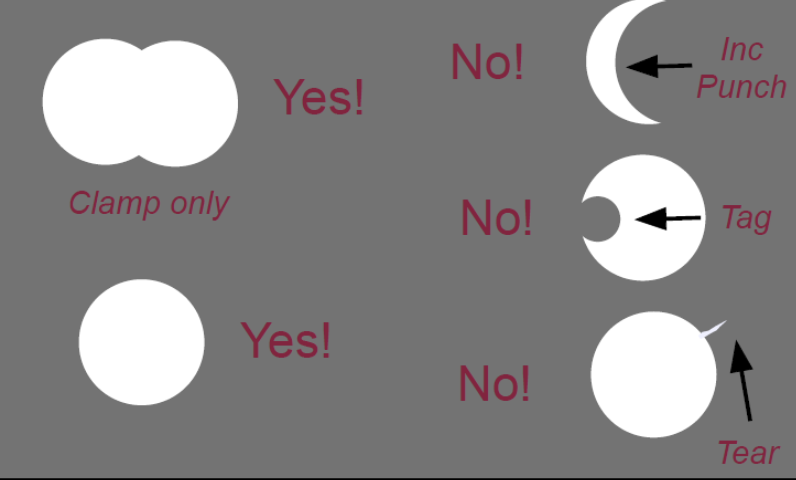
Some items to keep in mind when hole punching
A beginner’s tendency is to use too big of a hole (this gives a poor seal, and is harder to invert)
Overlapping holes may be useful (for winged clamp only)
Incomplete or poor punches will lead to tears/problems
Retainers are also known as
Clamps
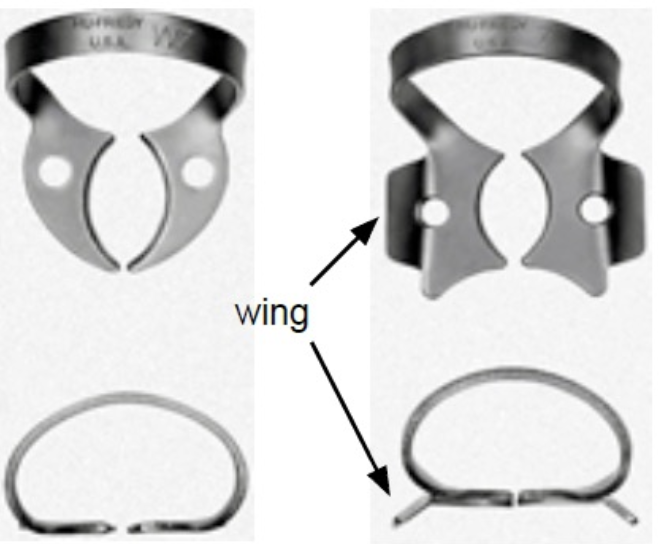
What are the components of a retainer (clamp)?
Jaws, Points, Holes, Bow, Wings, Notches
What are clamps made of?
Stainless steel material (high modulus = stiff)
What are some styles of clamps?
Winged, wingless (W): provide dam retention and tissue retraction
What are winged clamps useful for?
To place dam and clamp together

What clamp is this? What tooth is it used for?
W2; used for premolars

What clamp is this? What tooth is it used for?
W3; Premolars/Molars

What clamp is this? What tooth is it used for?
W4; Molars
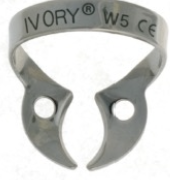
What clamp is this? What tooth is it used for?
W5; Upper molars

What clamp is this? What tooth is it used for?
5; Upper molars (has wings)

What clamp is this? What tooth is it used for?
8AD; Second molar (partially erupted); extended bow

What clamp is this? What tooth is it used for?
Molars (partially erupted); has jaws with points that vertically engage the tooth

What clamp is this? What tooth is it used for?
Premolar, canine, incisor, Cl V gingival retraction
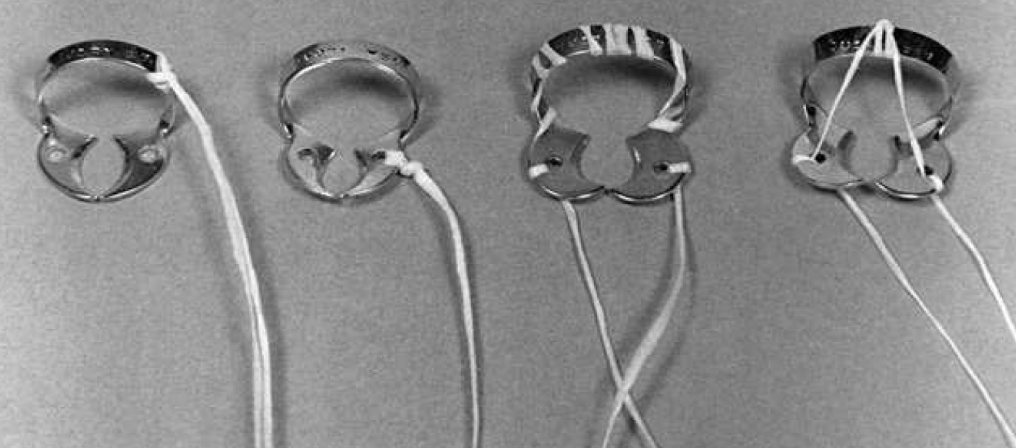
Different methods of tying ligature
What are some types of forceps?
Ivory type vs Stokes types (they both have a lock feature)

What kind of forcep is this
Ivory
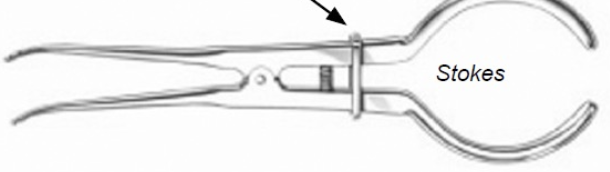
What kind of forcep is this?
Stokes

What are the types of frames?
Young’s or plastic

What are napkins used for?
Patient comfort and moisture control
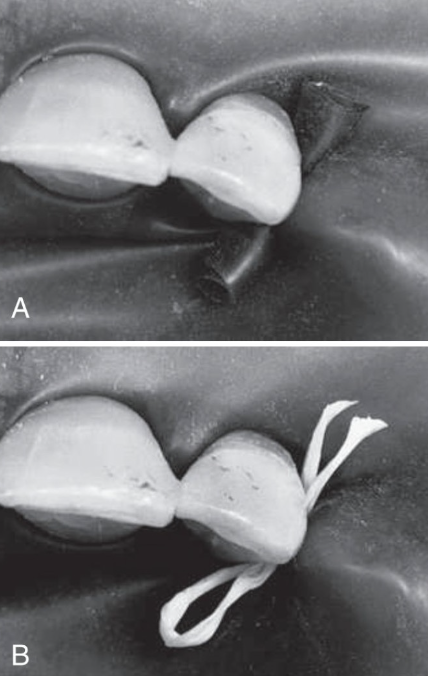
What do you use to anchor the last tooth?
Dental dam stabilizing cord
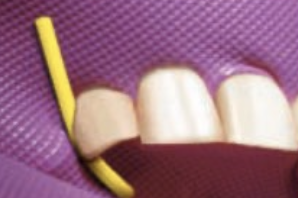
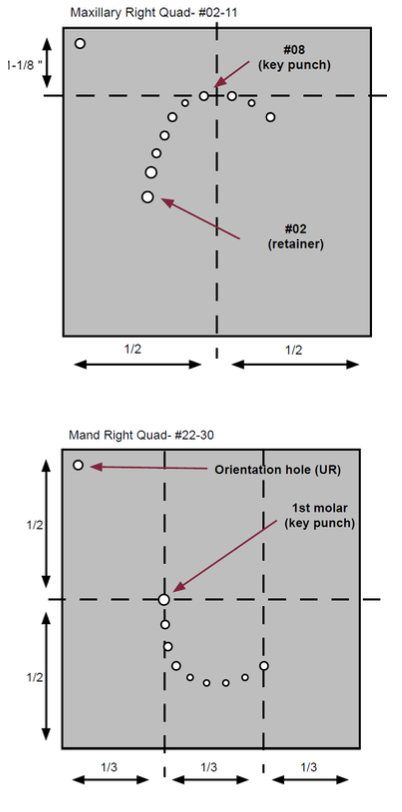
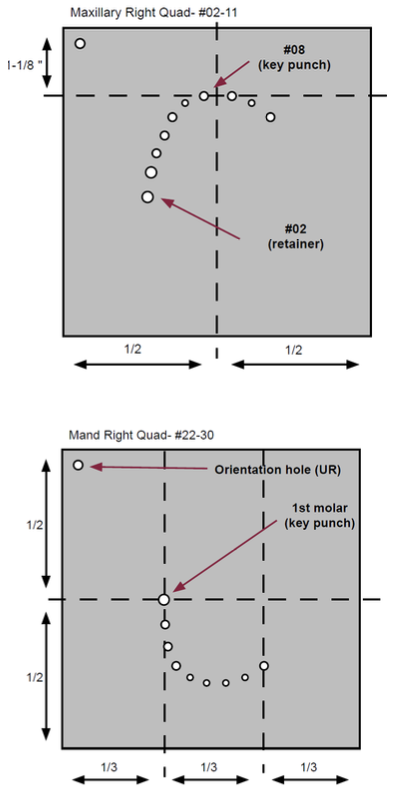
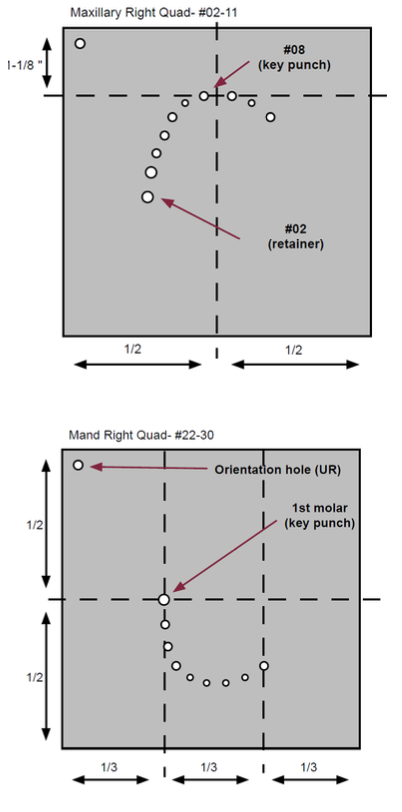
What is the purpose of an orientation hole?
Punching a small hole in the upper right of the dam will help the operator sort out the orientation when applying the frame
What is a key punch?
An initial punch in the rubber dam
For maxilla: It will generally be the central incisor
For mandible: It will generally be the clamped tooth
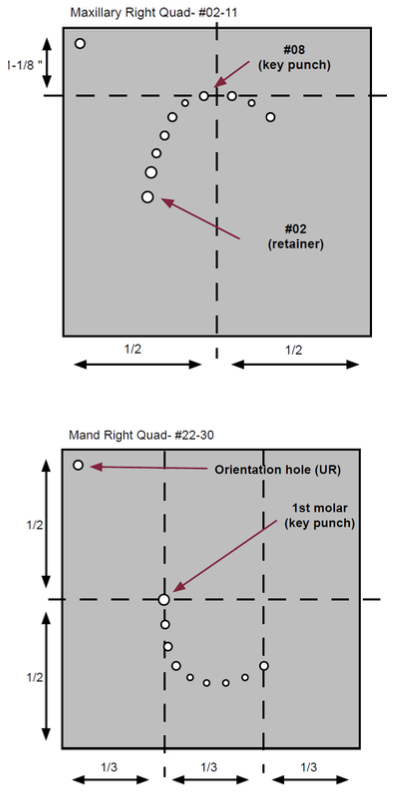
What is the ideal length for ligature?
18”
Where should you place lubricant like vaseline?
On the tissue side of the dam with a gloved finger or swab —> making it easier to sit on the teeth and is placed on the backside
What is an important indicator that your clamp is stable?
Trying to rock the bow with the finger to test its stability; the clamp should have a 4-point contact, not impinge on tissue, not be on rubber dam and be stable
What affect would managing the floss ligature have on the clamp?
Figure out an appropriate orientation so it does not interfere with the seal
Which tooth should you secure first?
The tooth furthest from the clamp through the dam first. Then secure it with a ligature or other retainer
What will using waxed floss do?
The wax will “grab” the rubber dam and help carry it through the contacts
How should you floss the rubber dam in?
A bit at a time, with a slight B/L “sawing” motion
How should you manage the B/L surfaces?
Using a prob, cord packing instrument, discoid-cleoid to invert the edges and tuck them in
What else should do you in regards to inverted edges?
Apical tension on the dam in combination with managing the B/L surfaces
On which teeth or people should you avoid putting a clamp on, or use a rubber dam?
DO NOT clamp ceramic prosthetics
DO NOT use a rubber dam on patients with orthodontic wires and brackets
What are some special circumstances in clinic to consider?
Extensive cervical caries
Crown preparation
Extensively broken down teeth
Use of blockout resin to seal holes
Block out resin usage
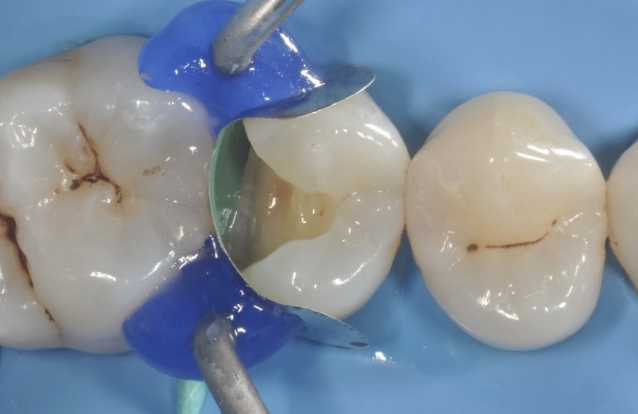
Block out resin usage primary and secondary isolation
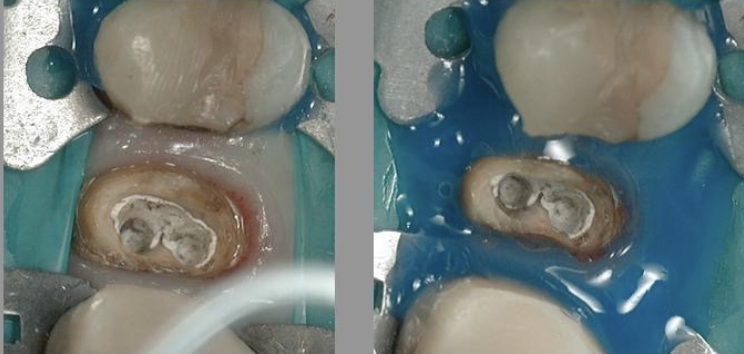
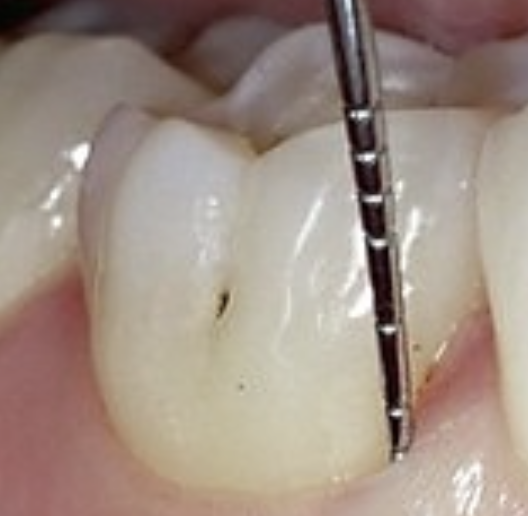
What are buccal pit caries?
Small, pinpoint depressions that are most commonly found at the ends or cross-sections of grooves
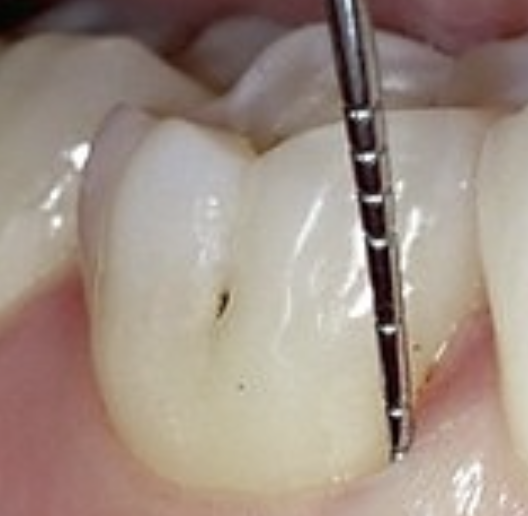
Where are buccal pits found?
On the facial surfaces of molars. For all types of pits and fissures, the deep infolding of enamel makes oral hygiene along the surfaces difficult, allowing dental caries to develop more commonly in these areas
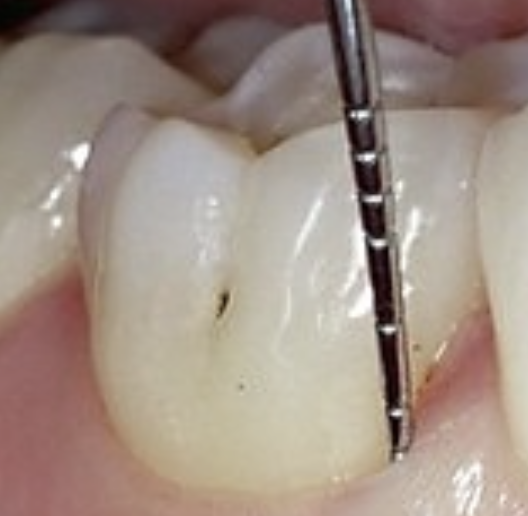
What is the shape of buccal pit caries?
They follow an ovoid shape at the gingival end of the groove
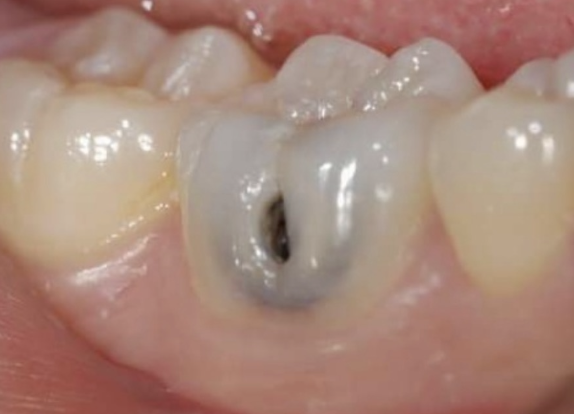
What happens if you have an untreated active moderate lesion?
It can grow into an advanced lesion, which will involve more extensive preparation and/or pulpal complications
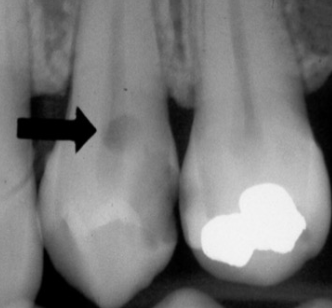
Radiographic example of buccal pits
Name the 10 instruments that should be in an operative cassette