Functional Groups and Water/H-bonding
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is an acid?
electron acceptors
proton donors
What is a base?
electron donor
proton acceptor
pka of sulfonic acid
1
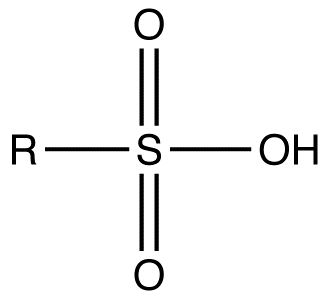
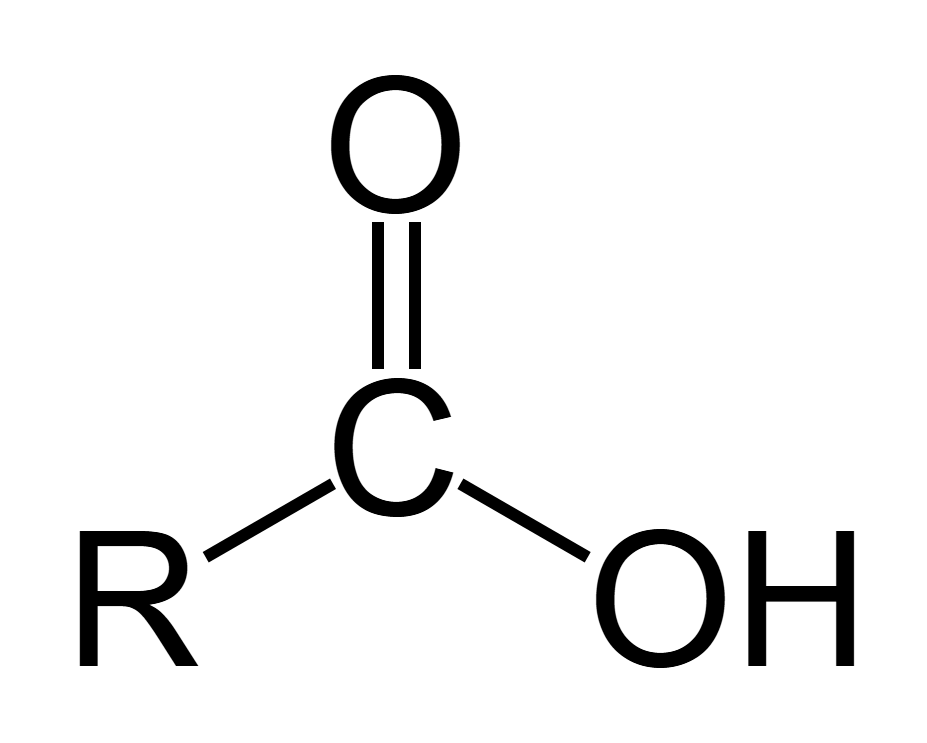
pka of carboxylic acid
5
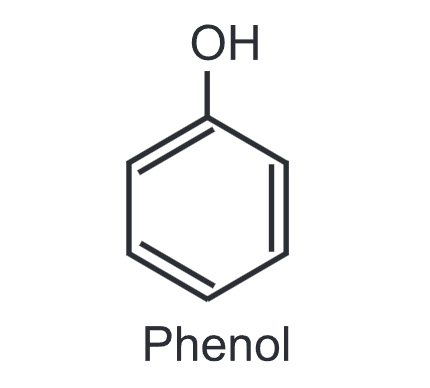
pka of phenol
10
pka of aliphatic amine (technically its CA)
10
pka of aromatic amine (technically its CA)
5
What does the Henderson-Hasselbach equation measure?
the relationship between pH and pKa
- pH = variable depending on environment
- pKa = constant value
pH of mouth, stomach, intestine, and blood?
mouth = 6
stomach = 1-3
small intestine = 6-8 blood = 7.4 (7.35-7.45)
Hepatic Portal System
blood flow between liver an GI tract
Rule of 9s
difference of pH and pka = # of 9s for ionized/unionized ratio
- if difference = 0 = 50:50
- difference = 1 = 90:10
- difference = 99:1
etc
Dipole
partial positive and partial negative charges (weak charges)
partial charges and full charges favor …..
water solubility
polar substances (do/do not) dissolve in water
nonpolar substances (do/do not) dissolve in water
polar = do
nonpolar = do not
solvation shell
shell of H2O surrounding charged atom
-maximizes solute-solvent H-bonding
- if hydrogen bonding is not possible —> water squeezes substances (ex. oil) out
What is the Henderson-Hasselbach Equation?
pH = pKa + log10[unprotonated/Protonated] ?
is phenol acidic or basic?
acidic
-OH = ability to donate an H+
is an aliphatic amine acidic or basic?
basic
what is a hydrogen bond?
electrostatic attraction between the oxygen atom of one water molecule and the hydrogen of another
hydrogen bonding is relatively (weak/strong)
weak
Hydrogen Bonds Account for the ….
Relatively High Melting Point of Water
Hydrogen acceptor and Hydrogen donator
acceptor = electronegative atom
ex. C=O, N, O, C=O,
donor = hydrogen atom covalently bonded to another electronegative atom
ex. O-H , N-H
amphipathic
has regions that are polar/charged and regions that are nonpolar
- ex. AA
are straight or bent hydrogen bonds stronger?
straight
hydrophilic definition
compounds that dissolve easily in H2O
- generally charged or polar compounds hy
hydrophobic definition
nonpolar molecules such as lipids and waxes
Which gases are nonpolar?
CO2, O2, N2
which amino acids are not soluble in aqueous solutions?
hydrophobic + nonpolar amino acids (carbon chains w/ no dipoles)
7 aliphatic AA
GAVLIP (M)
GLY/G, ALA/A, VAL/V, LEU/L, ILE/I, PRO/P, MET/M
3 aromatic
PTT
PHE/F, TYR/Y, TRP/W
Which amino acids are capable of H-bonding?
neutral (uncharged) polar amino acids (can perform dipole-dipole interactions)
amides
GLN/Q, ASN/N
sulfonic
CYS/C
Alcoholic
SER/S
THR/T
which amino acids are soluble in aqueous solutions?
polar AA
neutral
STAGC (Serine, Threonine, Asparagine, Glutamine Cysteine)
charged
positive
HAL (Histidine, Arginine, Lysine)
negative
ED (Glutamate/Glutamic acid, Aspartate/Aspartic acid)
hydrophobic effect
nonpolar regions cluster together
polar regions arrange to maximize interactions w/ each other + solvent
Hydrogen bonds are between _______
neutral, polar groups
peptide bonds
Where is H-bonding found in protein structures?
secondary structures
alpha helix (n + (n+4) )
beta sheets (n + (n+3) )
ionic interactions
attraction + repulsion
- bonds in peptides (primary structure, ionized COO- & NH3+)
Van der Waals interaction / London Dispersion forces
distance-dependent weak attractions + repulsions between transient dipoles
any 2 atoms in close proximity
Hydrogen bonds are covalent/noncovalent
noncovalent