IB Biology Unit 1
1/66
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Cell Theory:
All living things are made up of cells
cells are the smallest units of life
cells come from preexisting cells
Exceptions to cell theory and why
Aseptate Fungal Hyphae: continuous cytoplasm, does not have septa
Muscle Fibres: multinucleated and have 1 continuous plasma membrane
giant algae: large unicellular organism
How do you calculate magnification
M = I/A
Define emergent Properties
Arise from the interaction of individual components in a complex system
Define cell differentiation
Newly formed cells have the ability to differentiate and become specialized. They all have an identical genome and the expression of certain genes makes them differenciate.
Gene Packing of active genes:
packaged in euchromatin for transcription
Gene packaging of inactive genes
packaged in heterochromatin
What are stem cells?
Unspecialized cells
key qualities of stem cells
Self renewal —> they can continuously divide/replicate
Potency —> differentiate into any specialized cell
what are totipotent stem cells?
Found in the embryo and can specialize into anything (T = furthest in the alphabet so the cells can specialize further into anything)
what are pluripotent stem cells?
Found in the embryo, can specialize into nearly anything and are research useful (pluri = multiple)
Applications for pluripotent stem cells:
Parkinson’s disease: nerve cells
what are multipotent stem cells?
derived from adult stem cells limited range of differentiation (Multi —> more —> more years old)
Applications for multipotent stem cells
Can be used to treat leukaemia: Bone marrow can specialize into any type of blood cell
What are unipotent stem cells?
adult stem cells, can only divide into the same type of cell (uni = 1)
Applications for unipotent stem cells:
Used to treat burn victims: skin cells can make more skin cells
Stargard’s Disease
Genetic, progressive blindness: embryonic stem cells are applied to retinal cells
Artificial stem cell techniques: somatic cell nuclear transfer
creation of embryonic clones by fusing a diploid nucleus w/ an enucleated egg
Artificial stem cell techniques: Nuclear reprogramming
Induce a change in gene expression of a cell so it can differentiate into a desired cell
Light microscopes
they can view living things
they have a lower magnification
Electric Microscopes
High magnification
they can only view dead specimens
Draw and label a prokaryotic cell
Pili
70 S ribosomes
Nucleoid
Plasmid
Slime capsule
Cell wall
Cell membrane
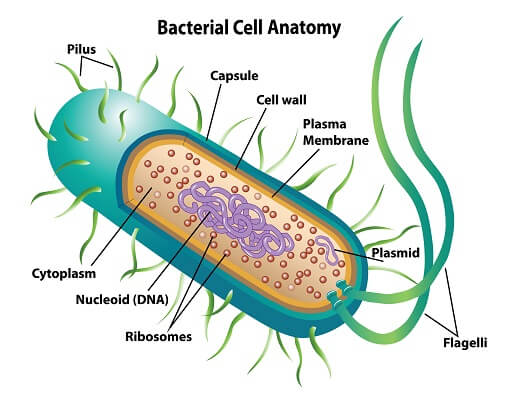
Functions of components of a prokaryotic cell:
Pili
70 S ribosomes
Nucleoid
Plasmid
Slime capsule
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Pili: helps with adhesion
70 S ribosomes: sites for protein synthesis
Nucleoid: contains a singular strand of DNA
Plasmid: small independent DNA
Slime capsule: Made of polysaccharides
cell wall: maintains shape
cell membrane: controls what enters and leaves the cell
flagellum: works as a motor
how do prokaryotic cells divide?
Binary fission:
A circular strand of DNA is copied in the cell
2 DNA loops attach to membrane
membrane elongates and pinches off through cytokinesis
What is the difference between a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells:
compartmentalized
mitochondria
chloroplasts
double membrane
nucleus
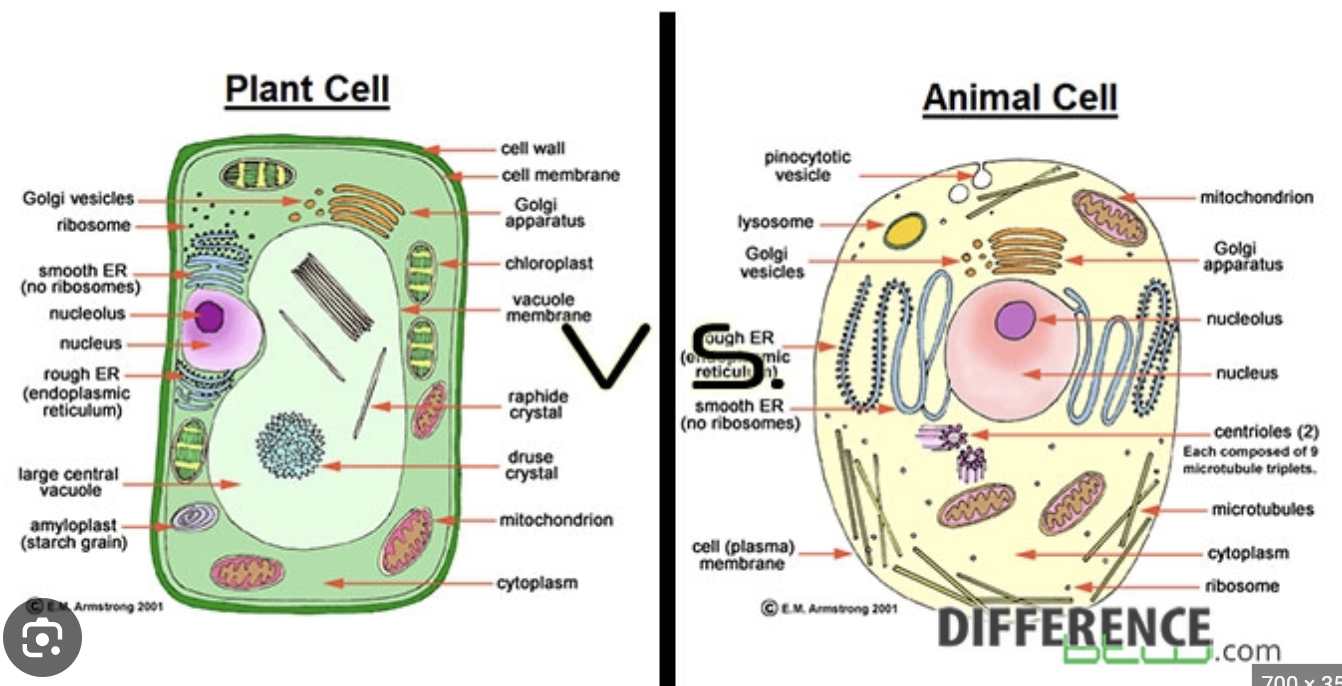
Parts of a eukaryotic animal cell and their functions
cell wall: maintains shape
cytoplasm: medium for chemical reactions
80 S ribosomes: protein synthesis
ER: membrane network
RER: protein synthesis
SER: creation/storage of lipids
Golgi body: storage/processing proteins
mitochondria: energy
nucleus: DNA storage
Lysosome: sac w/ enyzmes
Parts of a eukaryotic animal cell and their functions
cell wall: maintains shape
80 S ribosomes: protein synthesis
ER: membrane network
RER: protein synthesis
SER: creation/storage of lipids
Golgi body: storage/processing proteins
mitochondria: energy
nucleus: DNA storage
vacuole: hydrostatic pressure
chloroplasts: site of photosynthesis
cell wall: external covering
cytoskeleton: boning/structure
draw and label a eukaryotic animal and plant cell
Fluid Mosaic Model:
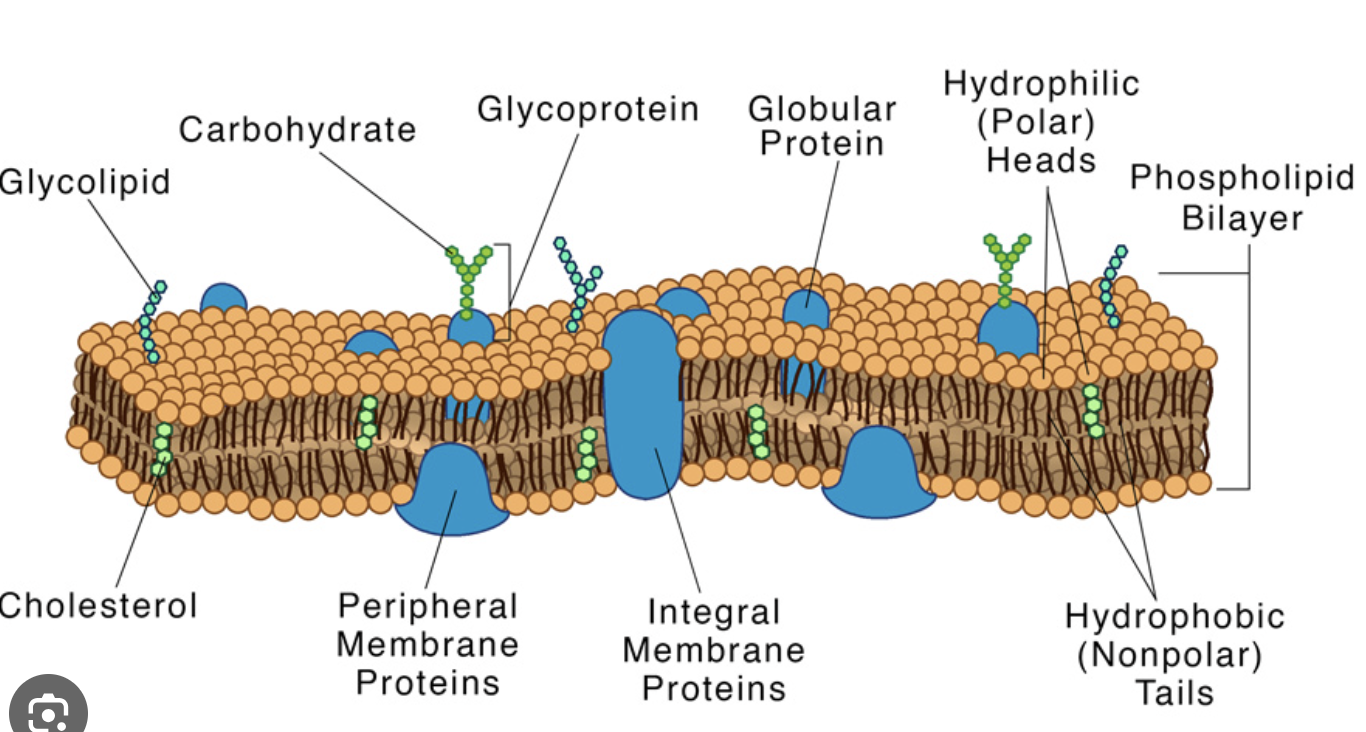
Functions of phospholipids:
Amphipathic
polar head: hydrophilic
non-polar tail: hydrophobic
Function of Channel Proteins
transmembrane protein:
passive transport of ions at a fast rate
Function of glycoproteins
transmembrane protein:
alter their shape to translocate solute, active transport
(G for glyco: G for gemini —> change)
Functions of integral proteins
Transmembrane protein:
keep toxins out
Functions of peripheral proteins
temporarily attached:
lies on the surface of the membrane
cellular communication and binding site for carbohydrate
carbohydrate:
Binding point and identifies the cell
cholesterol:
stabilizes the membrane, amphipathic, reduces the fluidity of the membrane and prevents crystallization.
Davson Danielli
phospholipids sandwiched between a layer of proteins on each side
Membrane transport: Passive transport
goes along the concentration gradient and is divided into: facilitated diffusion, osmosis and simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion:
Through channel proteins, large/polar molecules move
simple diffusion:
movement of small particles from high concentration to low
osmosis:
net diffusion of H2O —> from low solute concentration to high
active transport is divided into:
direct and indirect
what is indirect:
indirectly uses energy: coupling molecules —> a molecules using another molecules ATP (Piggy backing)
what is direct:
a molecule using its on ATP
what factors affect diffusion?
temperature, molecule size, gradient steepness
what is vesicular transport
Substances are transported within a cell in membrane-bound vesicles.
Hypertonic
too much solute outside so water escapes the cell and makes it shrivel
hypotonic
there is too much solute in the cell so water enters and makes it bulge
isotonic
balanced osmolarity
sodium potassium pump:
active transport: 3 sodiums leave the cell while 2 potassiums enter through the SP pump
Endosymbiotic theory
1 prokaryotic cell engulfed another and engulfed mitochondria and chloroplasts
evidence for endosymbiosis
MAD DR
Membrane: double membrane
Antibiotic resistance: bacterial origin
Division: similar to binary fission
DNA: naked and circular
Ribosomes: 70 S ribosomes in chloroplasts and mitochondria
eukaryotic cell division
Cell cycle:
interphase
making DNA
Cellular functions
G1: cel is growing and producing more cytoplasm
S: Synthesis, DNA is replicated
G2: cell prepares for division
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
Steps of mitosis
PMAT
Prophase: chromosomes supercoil, microtubules grow on opposite sides
Metaphase: Spindle fibres grow, attach to the centromere, and chromosomes align in the middle
Anaphase: spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart
Telophase: spindle fibers are dissolved and nuclear membranes form around each cell
cytokenisis: microtubule breaks the cell in 2
What are the cell checkpoints:
G0: resting state after cell divides
G1: checks nutrients, growth factors and DNA for damage
G2: check size and error in DNA replication
Mitotic index calculation
cells in mitosis/ number of cells
Necrosis
Murder: an injured cell, lacks nutrients, has toxins
cell swells —> increases in osmotic pressure
cell bursts —> can cause damage in surrounding cell
Apoptosis
Cell suicide: necessary death because of mutations
cell contents are repackaged
cell shrinks + breaks down into apoptotic bundles
apoptotic bodies are engulfed
Cancer: what are metasis
cells from primary to secondary structure
tumour can invade other tissue
can travel into blood supply
invade healthy cells and start dividing
How does smoking increase chances of cancer?
strong positive correlation between both:
4000 chemicals —> 600 are carcinogenic
normal cell vs cancer cell
normal cell:
small cytoplasm
regulated division
clear structure
Cancer cell:
large cytoplasm
irregular/rapid division
unclear structure
mutagens: what are they?
Mutated genes: changes in the genetic sequence
What causes mutagens:
exposure to ultraviolet waves
x rays
viruses like hepatitis
what are oncogenes?
genes with potential to cause cancer
Pro-oncogenes, what are they?
stimulate growth/cell cycle, can make it very rapid and irregular
tumor repressor genes:
repress the cell cycle, apoptosis
what happens if tumor repressor genes stop working?
higher risk for cancer