Reproductive Hormones in Males
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
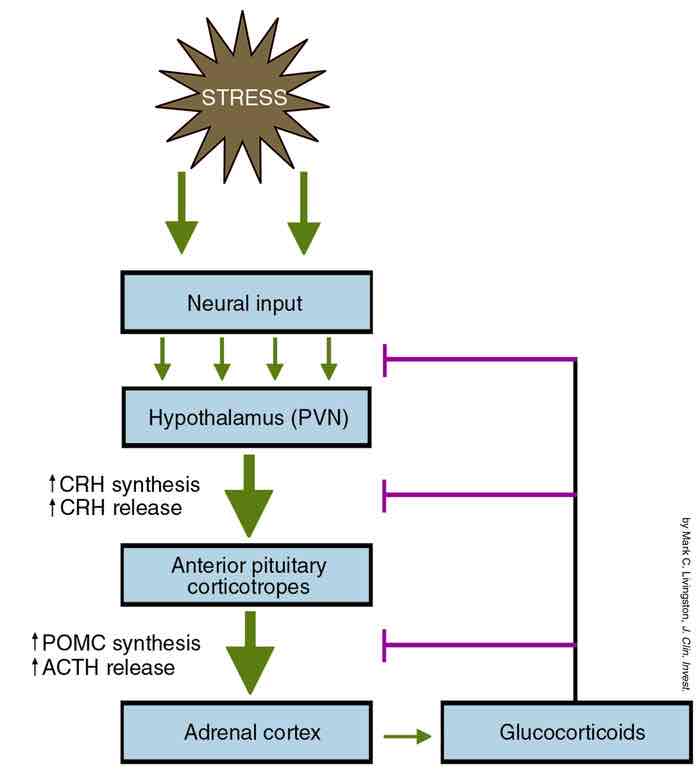
What are corticotrophs?
These are cells in the anterior pituitary gland that produce hormones that regulate stress. They respond to signals from the hypothalamus by releasing adrenocorticrotropin (ACTH) into the bloodstream. This stimulates the release of glucocorticoids
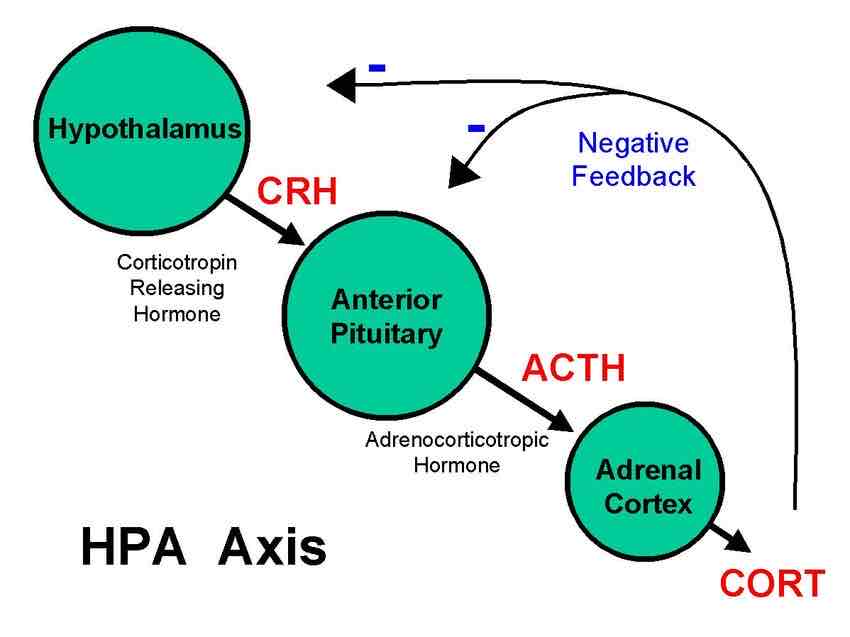
What are thyrotrophs?
These are endocrine cells within the pituitary gland that produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
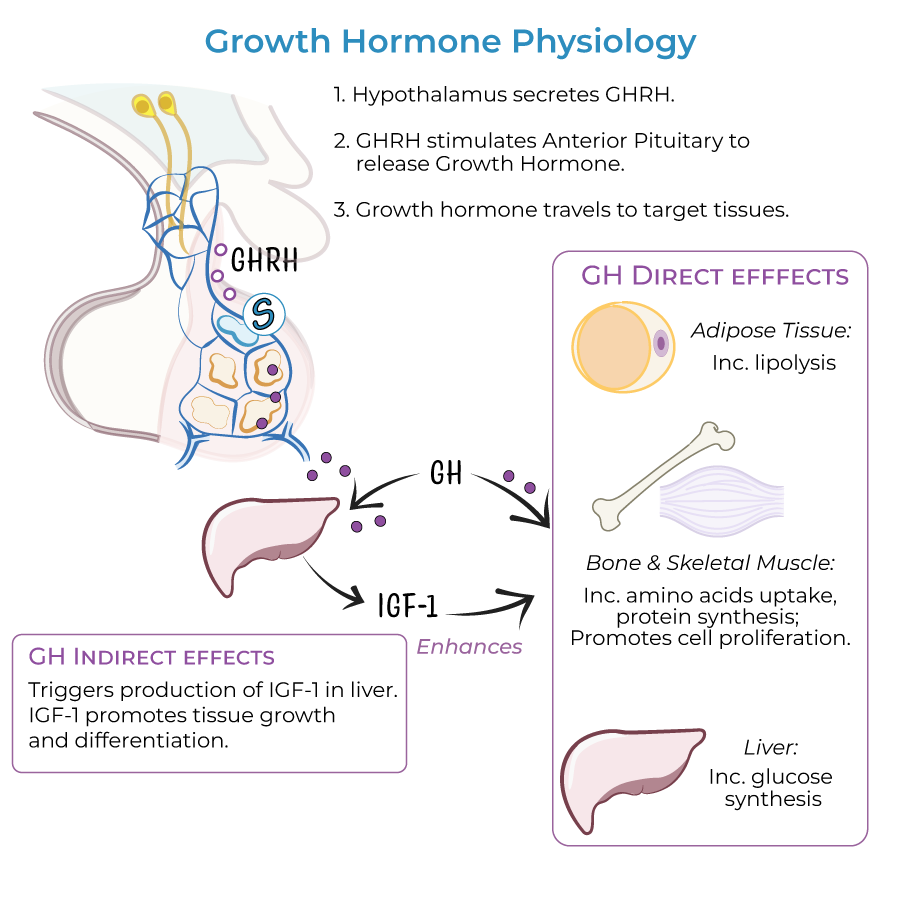
What are somatotropic cells?
These are cells within the anterior pituitary that produce growth hormones. GH significantly impacts the liver and adipose tissue.
What are lactotrophs?
These are cells within the pituitary gland that produce prolactin (PRL), supporting lactation, reproduction, and metabolism
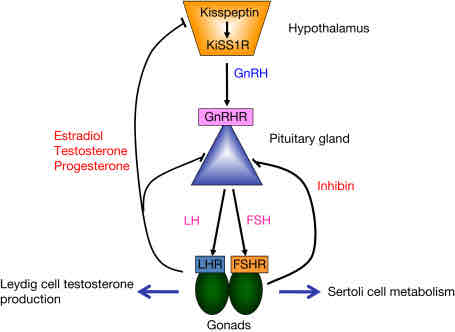
What are gonadotrophs?
These are hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary gland that regulate the reproductive system and sexual development. The different types are GnRH, LH, and FSH. These hormones impact the sex’s gonads
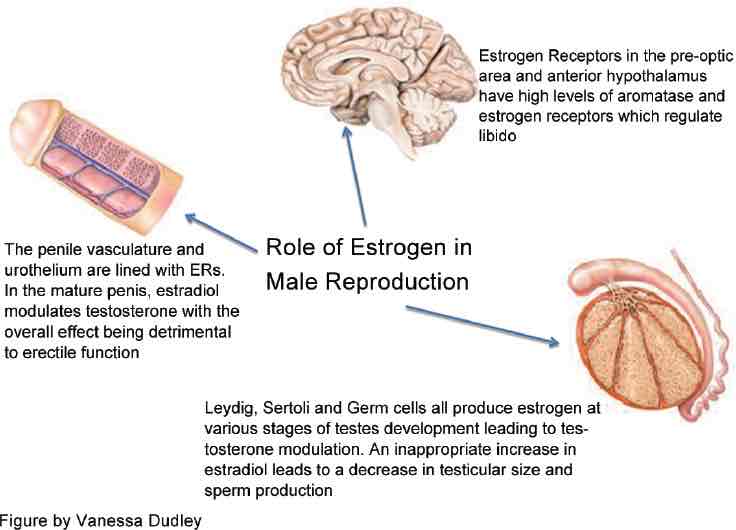
What enzyme converts testosterone into estradiol?
Aromatase
Why is estradiol important for sexual male function?
In the testes, spermatogenesis is modulated at every level by estrogen, starting with the hypothamamus-pituitary-gonadal axis, followed by Leydig, sertoli, and germ cells, finishing with the epithelium, epididymis, and mature sperm
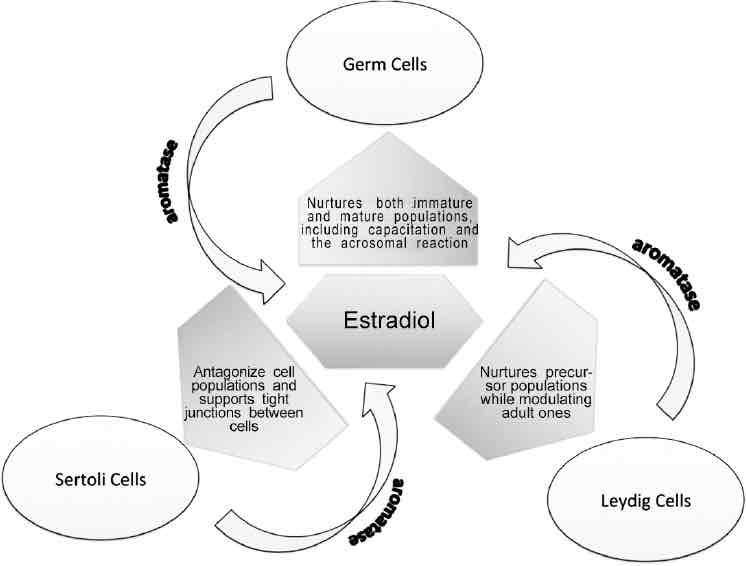
What is the role of estradiol in spermatogenesis? (Within the image)
How many carbons do cholesterol have?
27 Carbons
How many carbons does progesterone have?
21 Carbons
How many carbons does testosterone have?
19 Carbons
How many carbons does estradiol have?
18 Carbons
Why is progesterone important in males?
This hormone influences spermiogenesis, sperm capacitation/acrosome, and testosterone biosynthesis in Leydig cells
What happens to male hormones when castrated?
The hypothalamus will release GnRH, stimulating the anterior pituitary gland to release LH and FSH due to the lack of testosterone. The production of GnRH will reduce once it signals the lack of testosterone feedback from the testes. Testosterone normally acts to suppress GnRH, but without any testosterone signaling (even negative feedback), the hypothammus receives no signal to inhibit GnRH production, leading to a decrease in release
What is Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone?
This is a hormone that is released from the hypothalamus to signal/stimulate the anterior pituitary gland to release gonadotropins such as FSH and LH