week 2 ppt Clinical Decision-Making in Periodontal Care
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Clinical Decision-Making
Team process for diagnosing periodontal conditions.
Purpose of the Fundamental Diagnostic Questions
Key inquiries to assess periodontal health status.
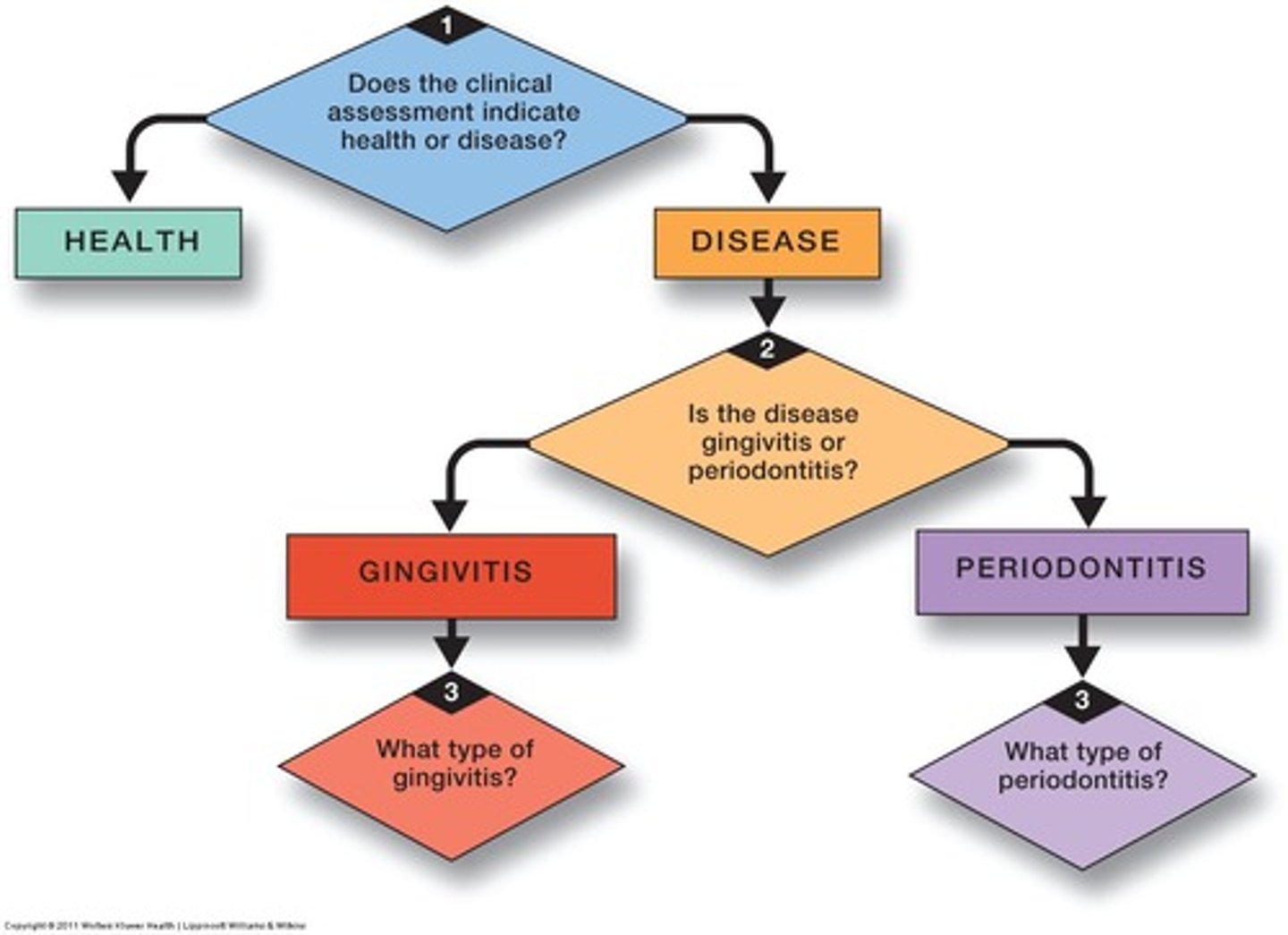
What are the 3 fundamental questions?
1.Does the clinical assessment indicate periodontal health or inflammatory disease in the periodontium?
2.If the clinical assessment indicates inflammatory disease, is the disease gingivitis or is it periodontitis?
3.If the patient has gingivitis, what type of gingivitis? (or periodontitis)
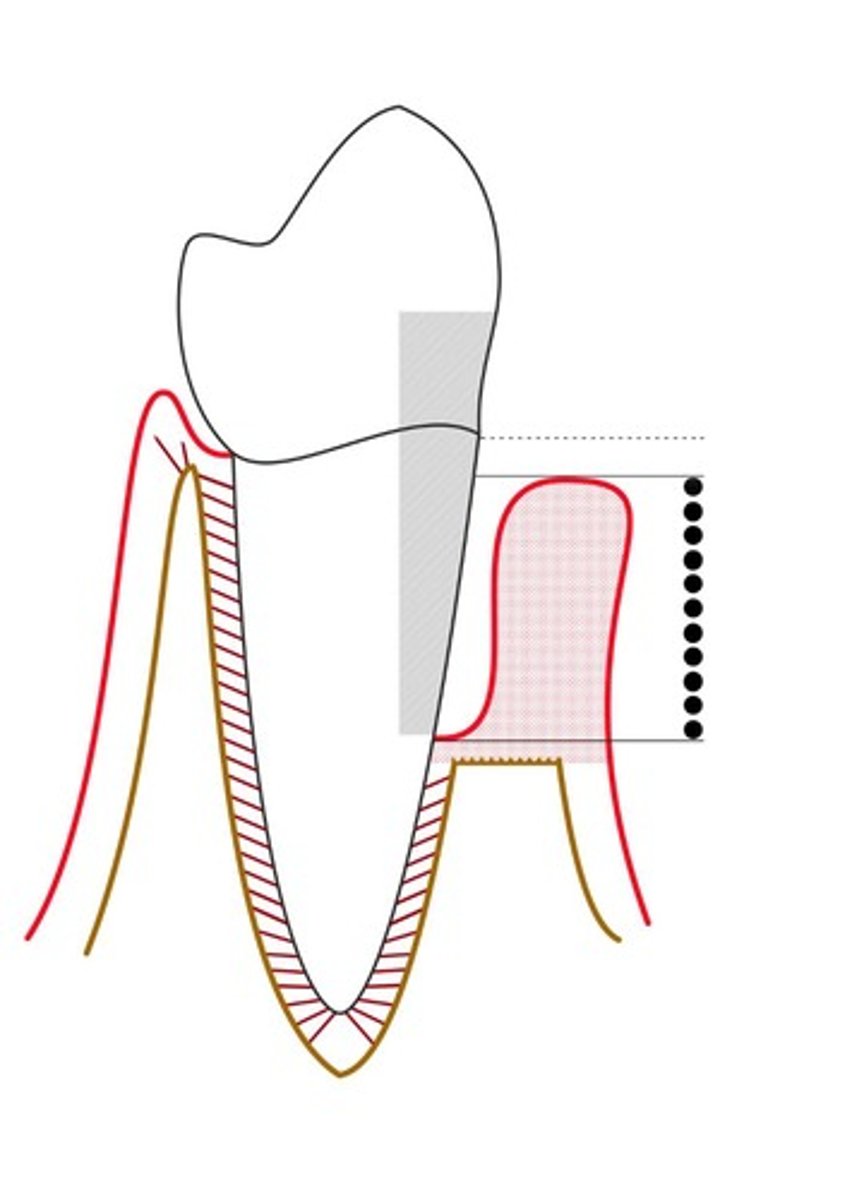
Signs of Inflammation
Clinical indicators of periodontal disease presence.
Symptoms of Disease
Patient-reported issues indicating possible periodontal problems.
Silent Disease
Periodontal disease without noticeable symptoms for patients.
If patient notices disease, this means what?
Disease has progressed
Symptoms of Stage IV periodontitis:
Loose teeth, difficulty chewing, profuse gingival bleeding, or bad taste in mouth
Periodontal Health
Absence of overt or hidden inflammation signs.
Gingivitis
Inflammation without loss of periodontal attachment.
Periodontitis
Inflammation with loss of periodontal attachment.
Documenting Periodontal Disease
Standardized recording of periodontal conditions and severity.
Peri-implant mucositis
damage to soft tissue only
Peri-implantitis
damage to soft tissue and surrounding bone
What is "Flexibility" in Diagnosis
Adjusting diagnosis based on multiple periodontal conditions.
Important to realize that "gingivitis" or "periodontitis" may not.....
represent the total periodontal condition
Examples of flexibility
-recession
-aberrant frenum/muscle positioning
Case Type System
Classification system for classifying perio conditions/reporting to insurance companies.
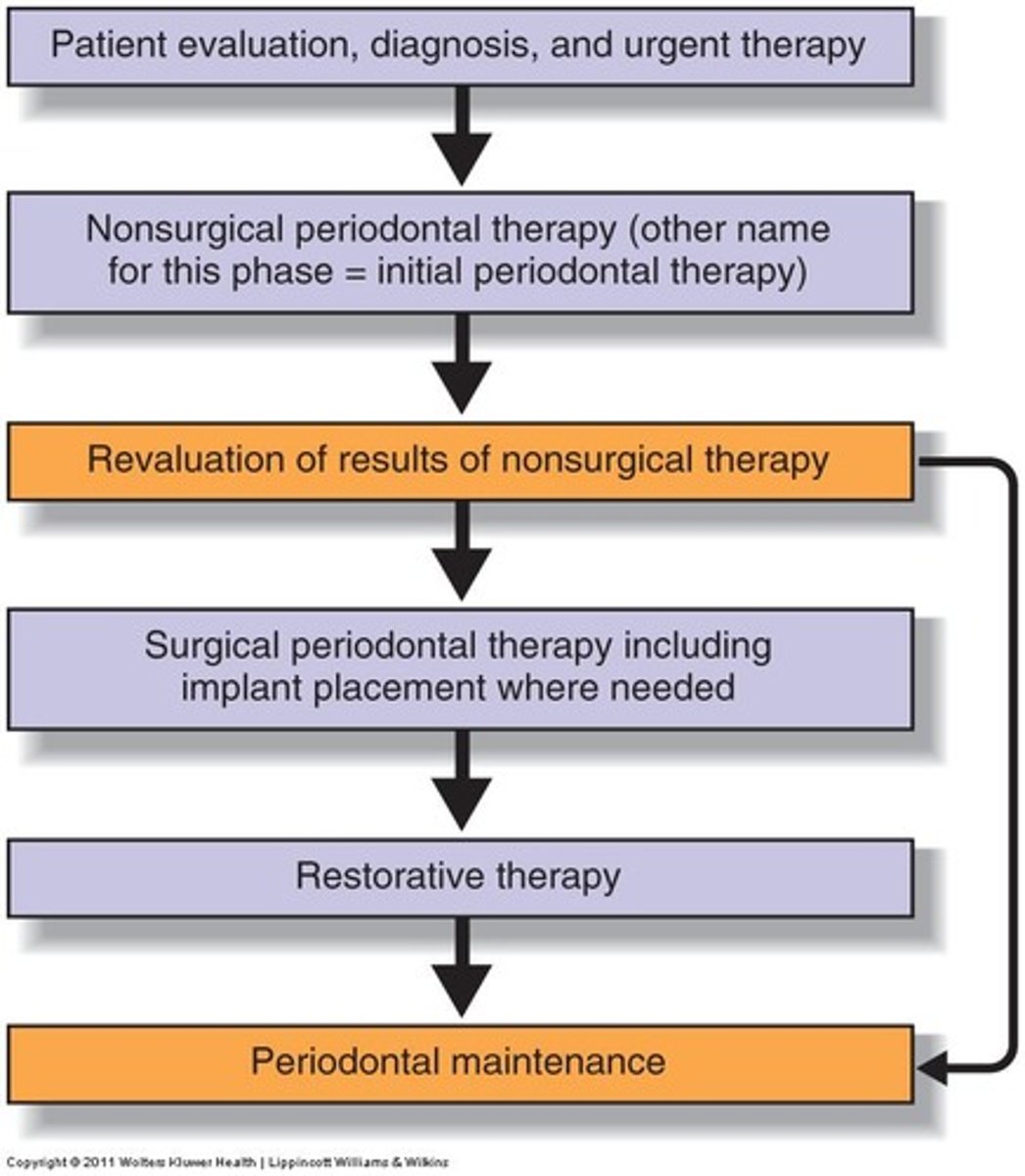
Purpose of Periodontal Master Treatment Plan
Sequential outline for DDS/DH to eliminate disease and restore a healthy periodontal environment.
Assessment Phase
Initial data collection and immediate treatment needs. (emerg, exo)
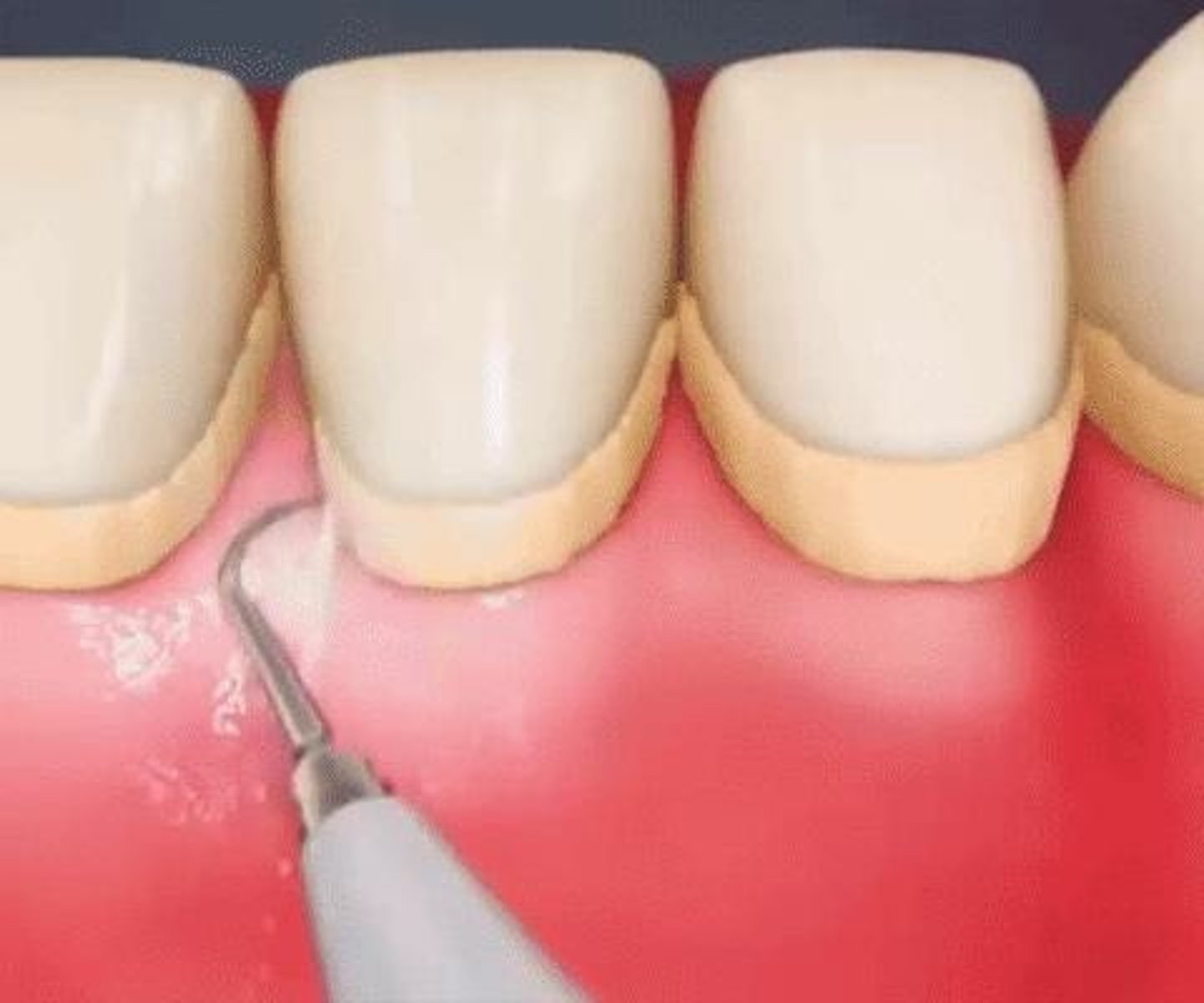
Nonsurgical Periodontal/
Bacterial Control
Therapy
Using measures like educational/DH care to control gingivitis and periodontitis.
Surgical Therapy
Invasive procedures such as surg, imp, and RCT for periodontal disease management.
Restorative Therapy
Restoration and replacement of damaged or missing teeth. (Re-eval after 6 weeks)
Periodontal Maintenance
Ongoing care throughout life to prevent disease recurrence.
Refractory Periodontitis
Worsening condition despite compliance with treatment.
Periodontal care requires adjustment overtime because:
-it's dynamic & changes overtime.
-tissue can remodel
-perio destruction can happen throughout life
Documentation Requirements
Includes assessment data and treatment services performed.
Chart/Progress Notes
Records of assessment data, patient tx done and educational instructions.