Human Nutrition: Body Systems and Digestion Overview
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
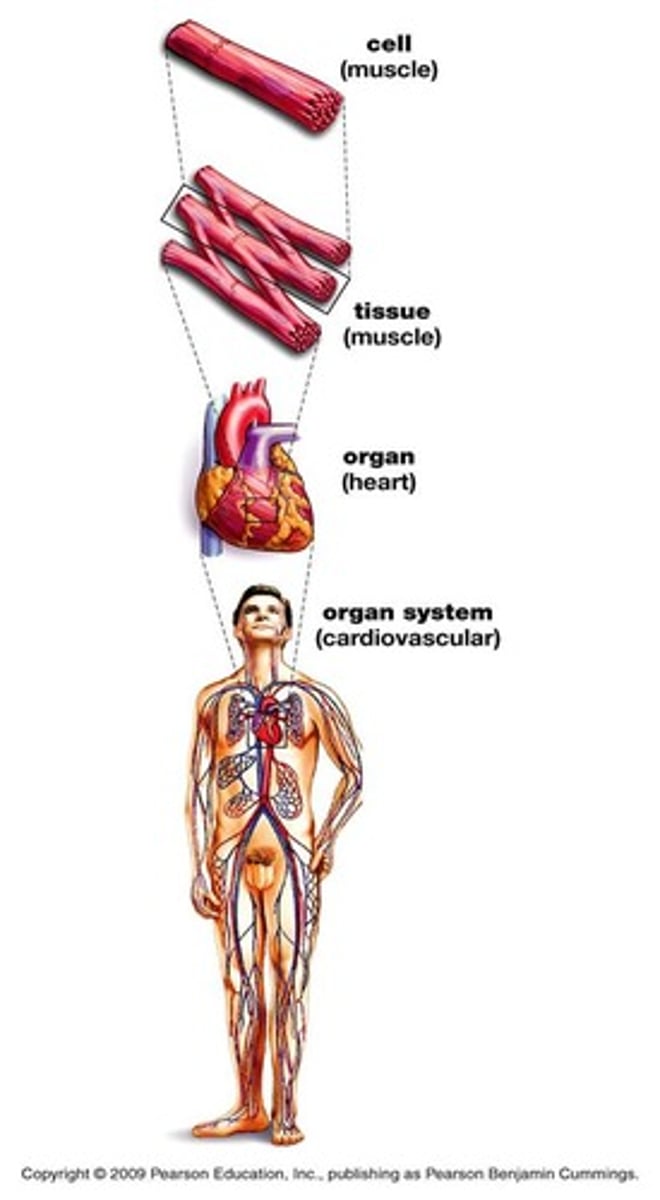
Tissue
Collection of cells performing a specific task.
Organ
Group of tissues performing a common function.
Organ System
Groups of organs with similar functions.
Plasma Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer separating cytoplasm from outside.
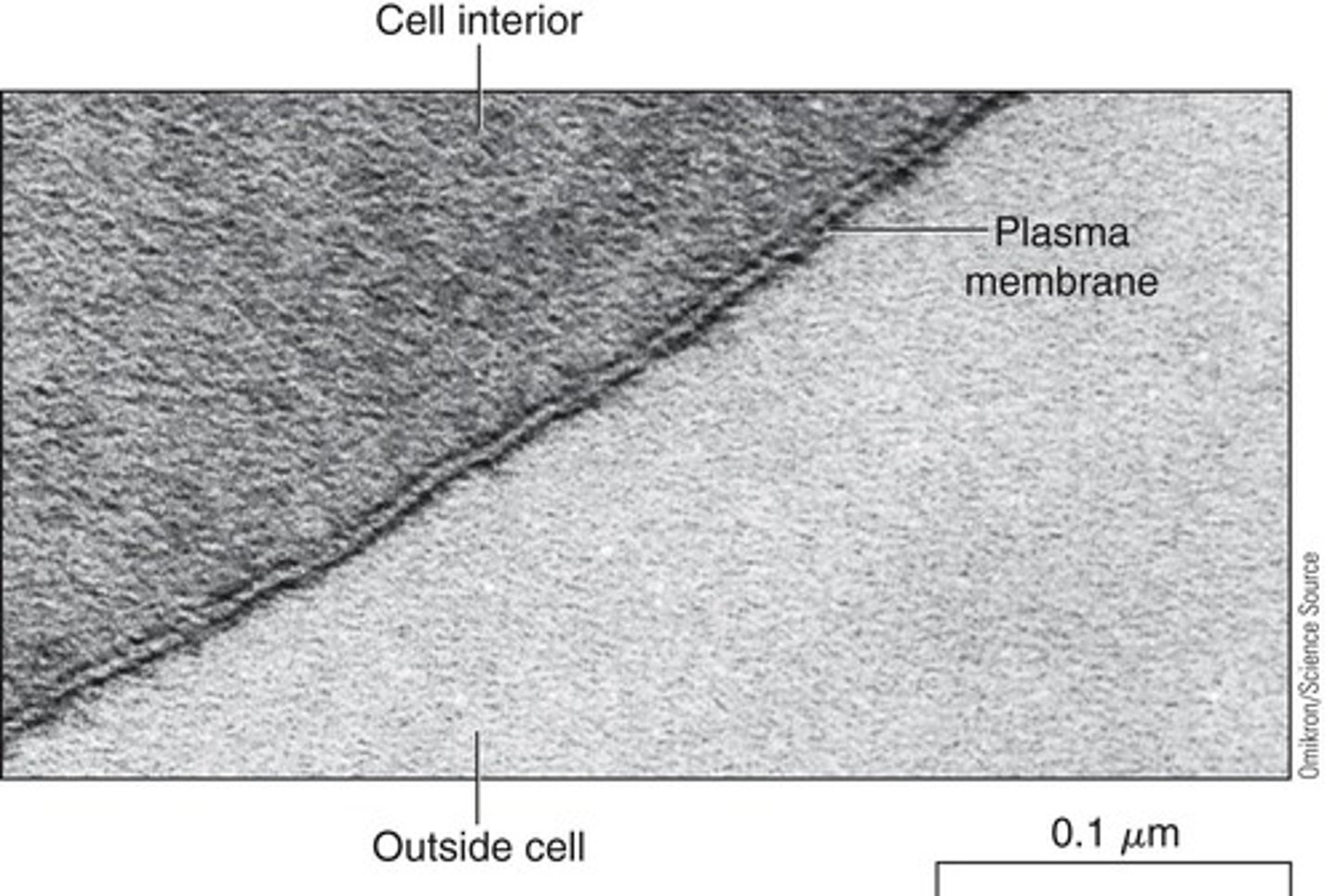
Cytoplasm
Fluid and organelles within the cell, excluding nucleus.
Anaerobic Respiration
Metabolism occurring without oxygen in the cytoplasm.
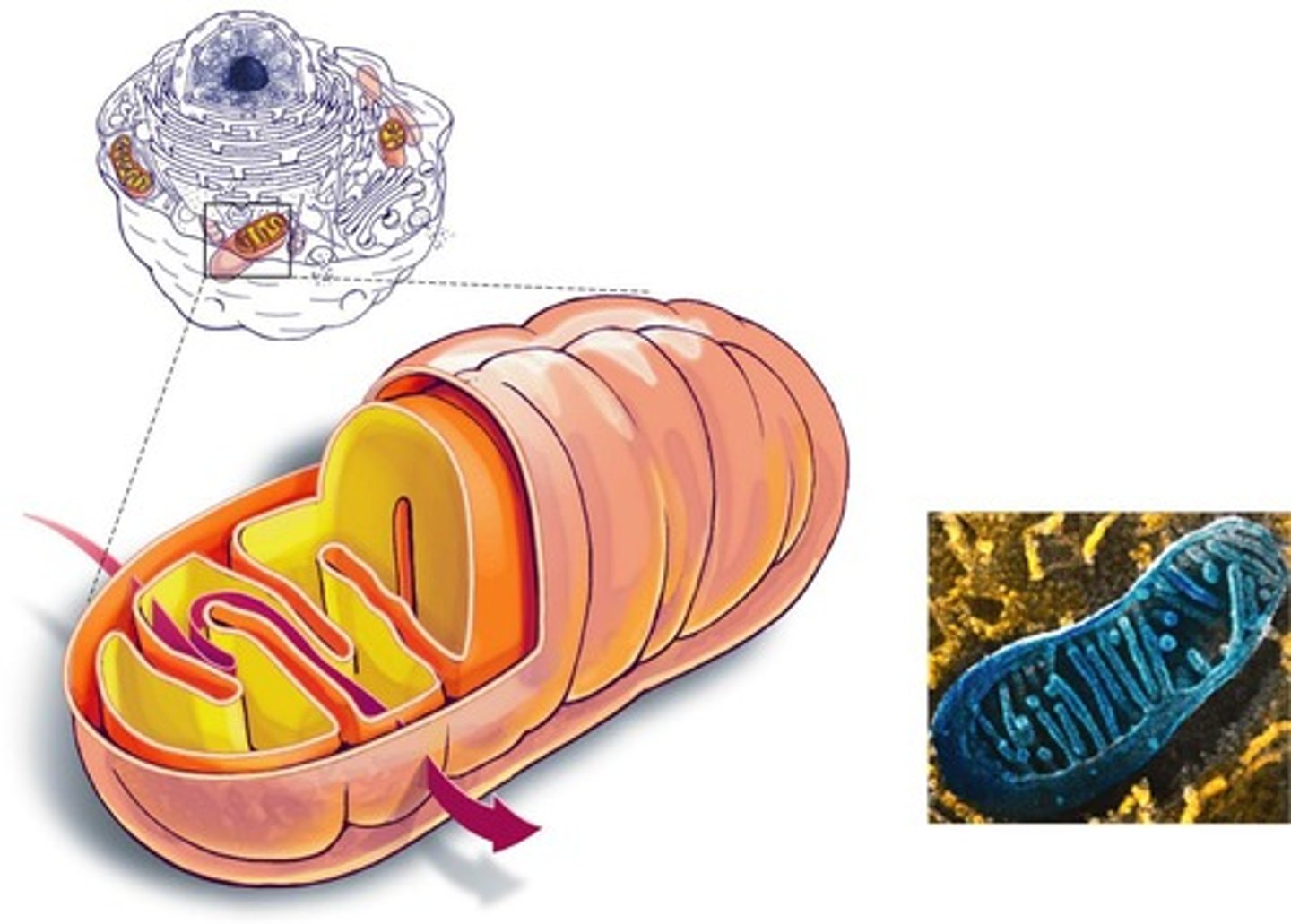
Mitochondria
Site for ATP synthesis; requires oxygen.
Nucleus
Contains genetic material; controls cell actions.
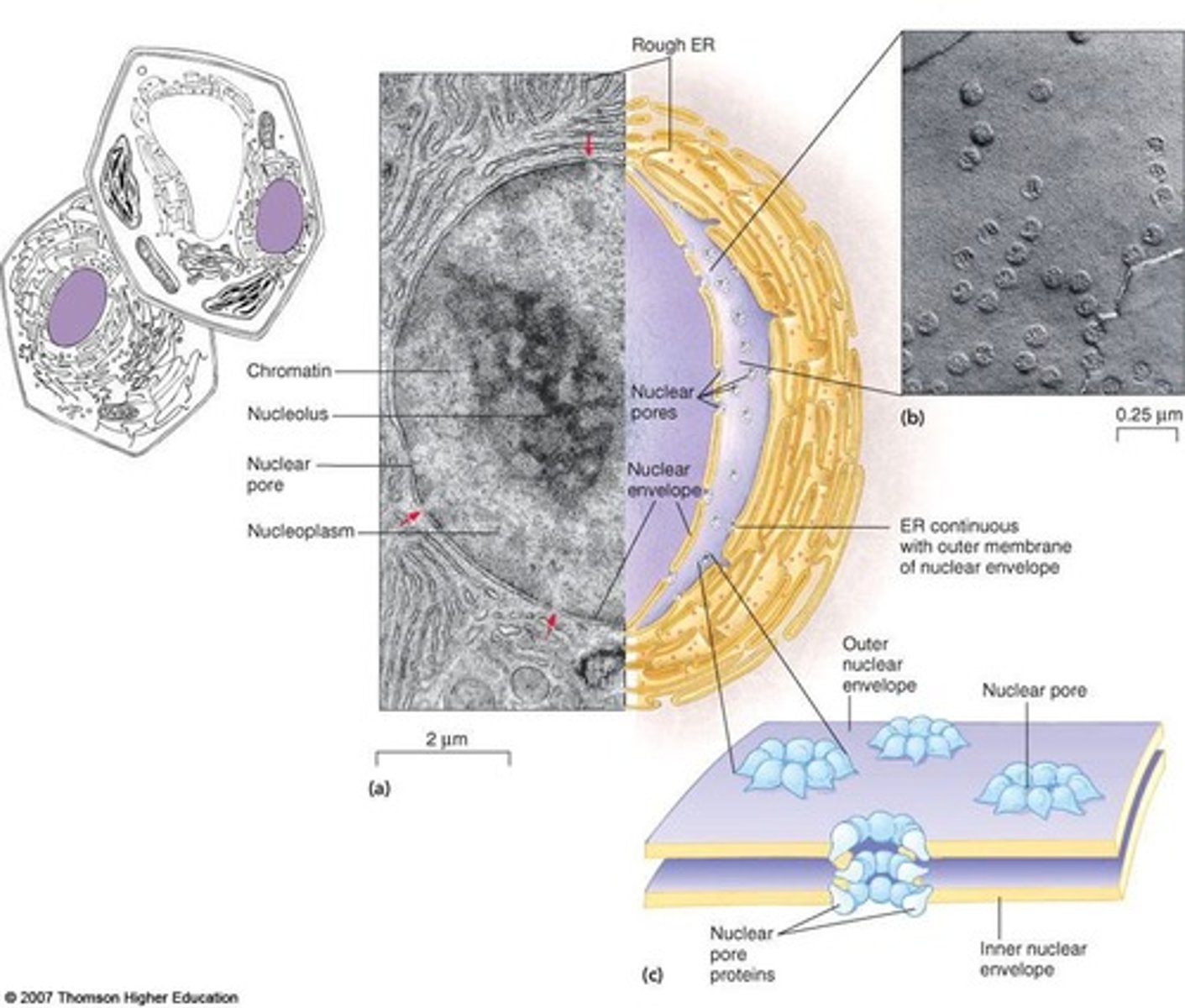
Chromosomes
46 structures containing genetic information in DNA.
RNA Transcription
Process of transcribing DNA into messenger RNA.
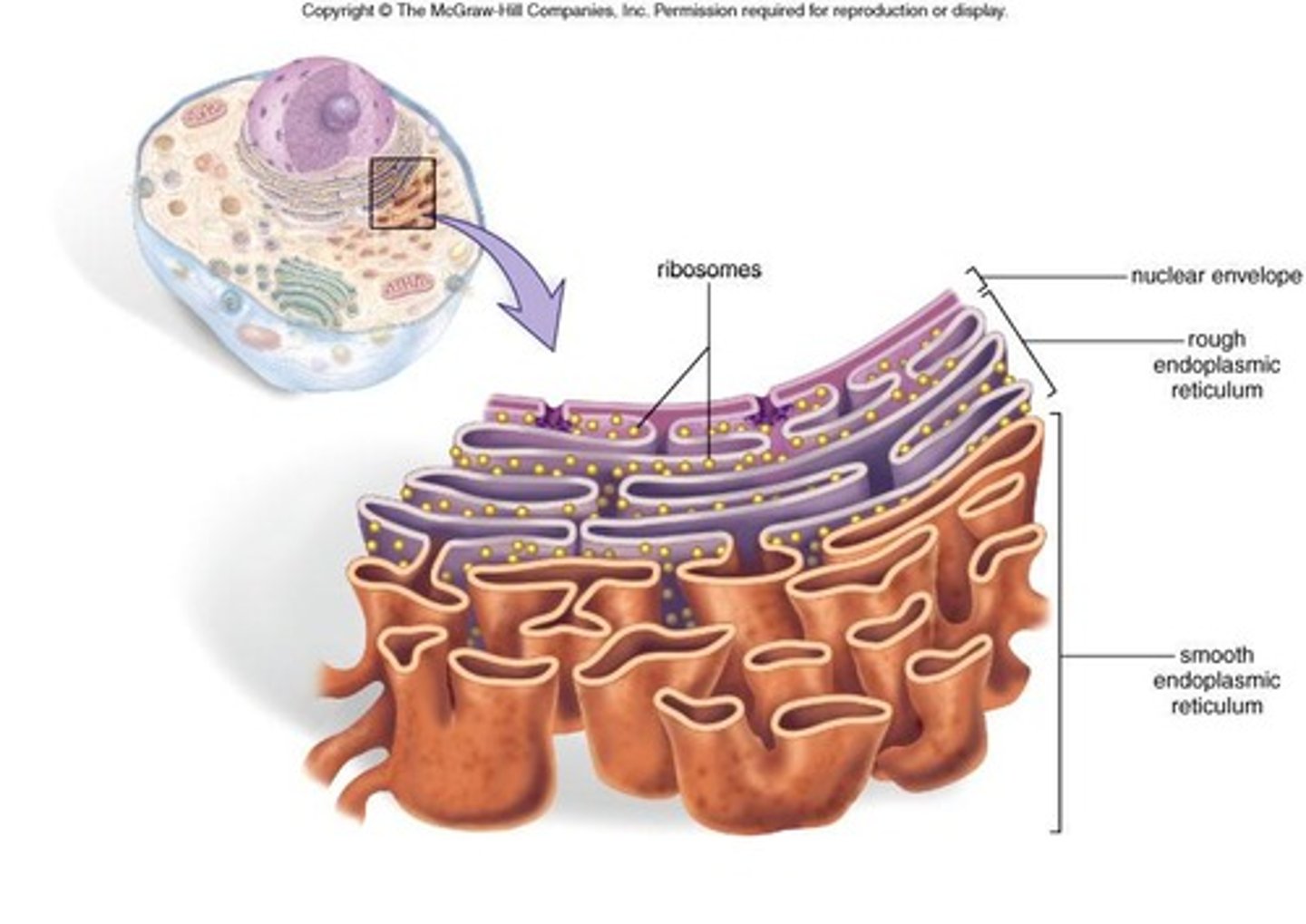
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Network of membranes for protein and lipid synthesis.
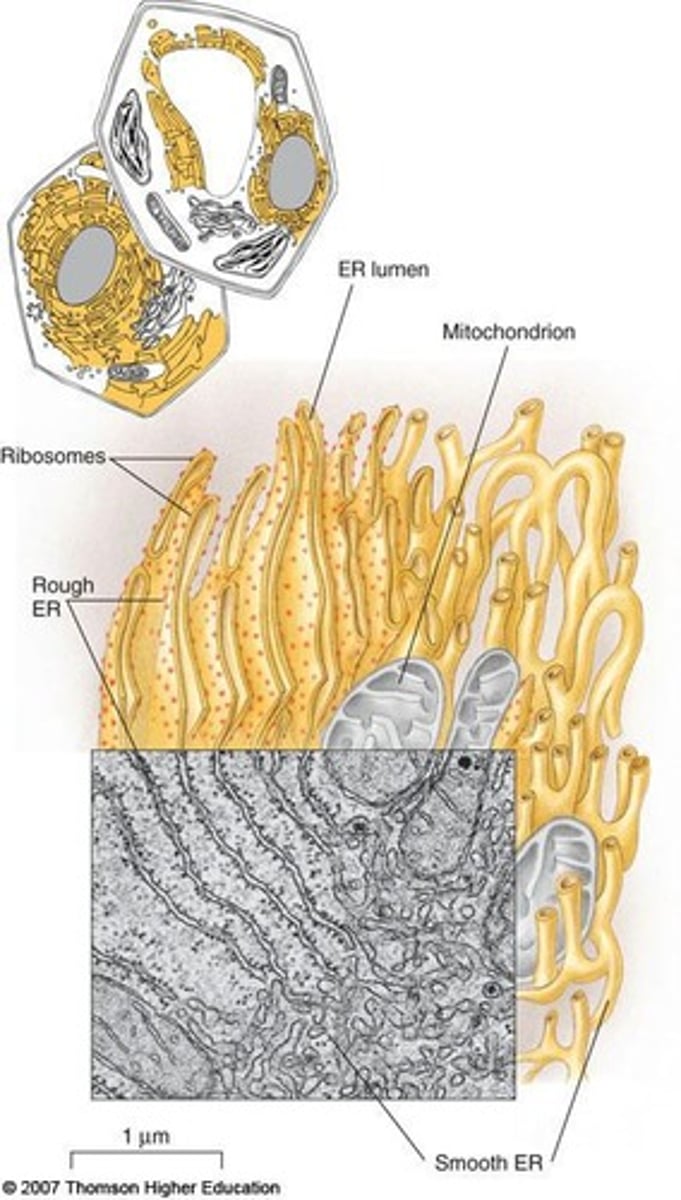
Smooth ER
Lipid synthesis and detoxification; no ribosomes.
Rough ER
Protein synthesis site with ribosomes on surface.
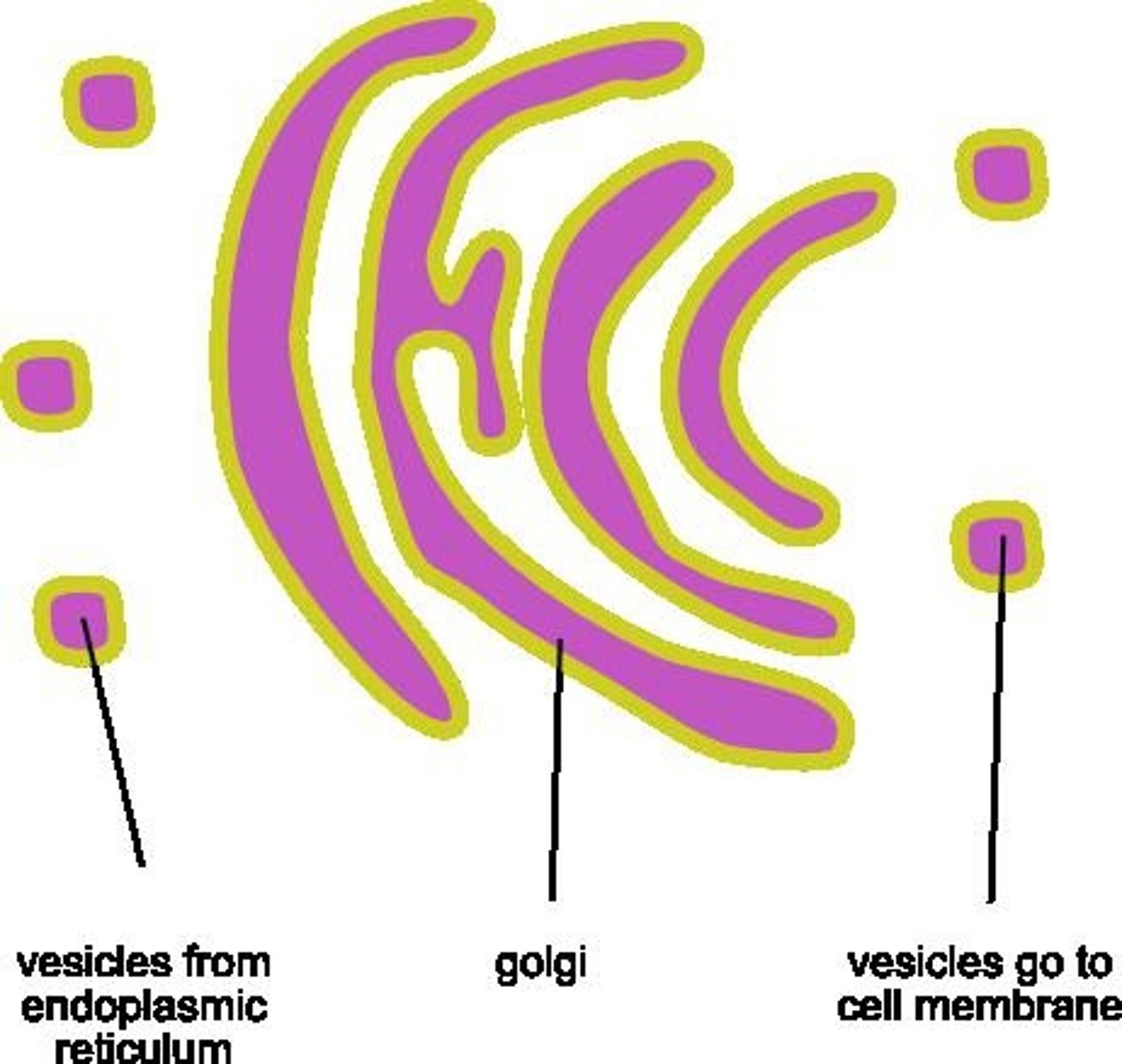
Golgi Complex
Packages and exports proteins to other cell parts.
Peroxisome
Detoxifies harmful chemicals; contains catalase enzyme.
Lysosome
Contains digestive enzymes to break down organelles.
Cell Metabolism
Chemical processes maintaining life in cells.
Anabolic Metabolism
Requires energy to build molecules.
Catabolic Metabolism
Releases energy by breaking down molecules.
Vitamins and Minerals
Regulate enzyme activity in metabolic reactions.
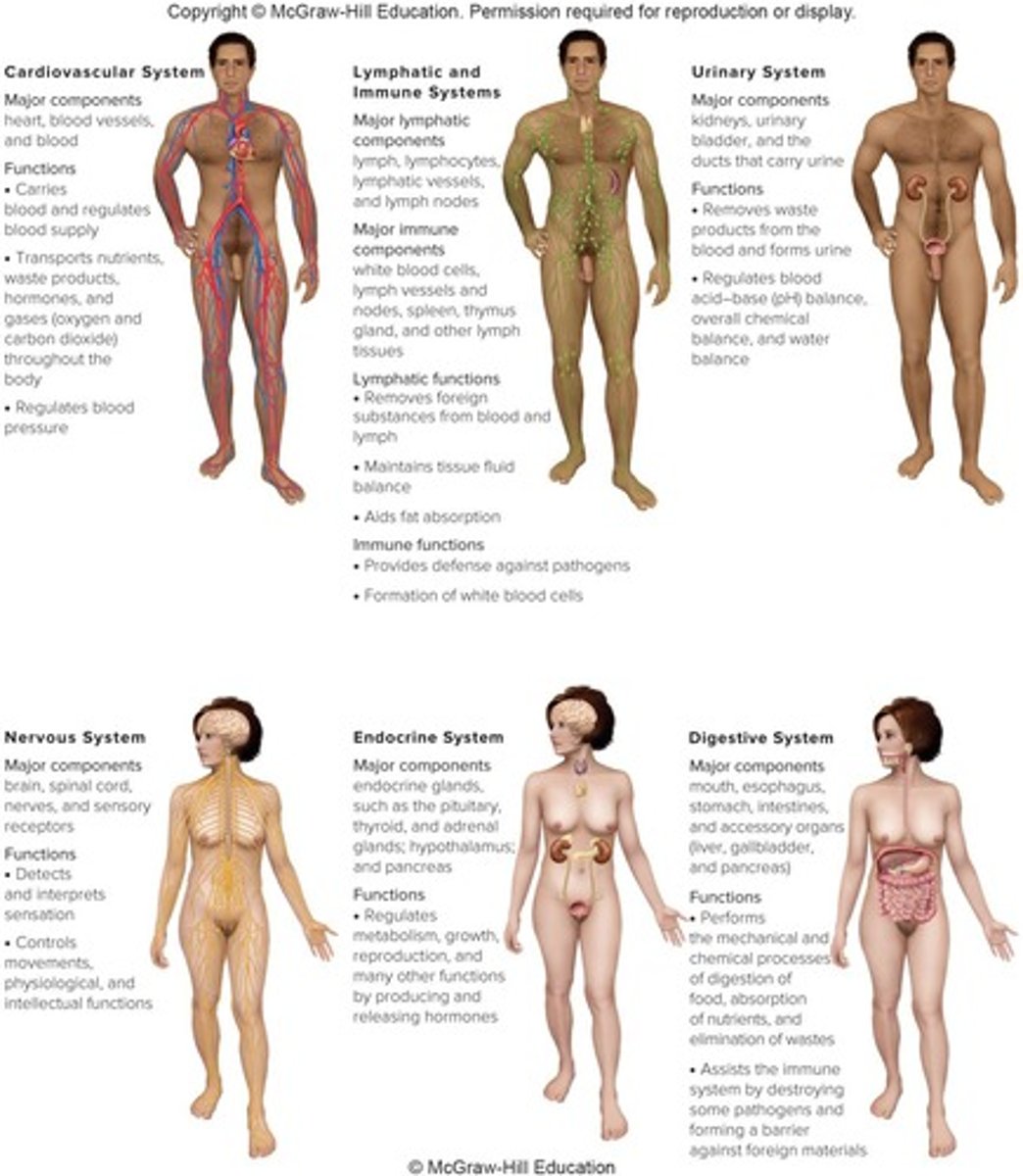
Cardiovascular System
Transports nutrients, waste, gases, and hormones.
Hepatic Portal Circulation
Flow of nutrient-rich blood from intestines to liver.
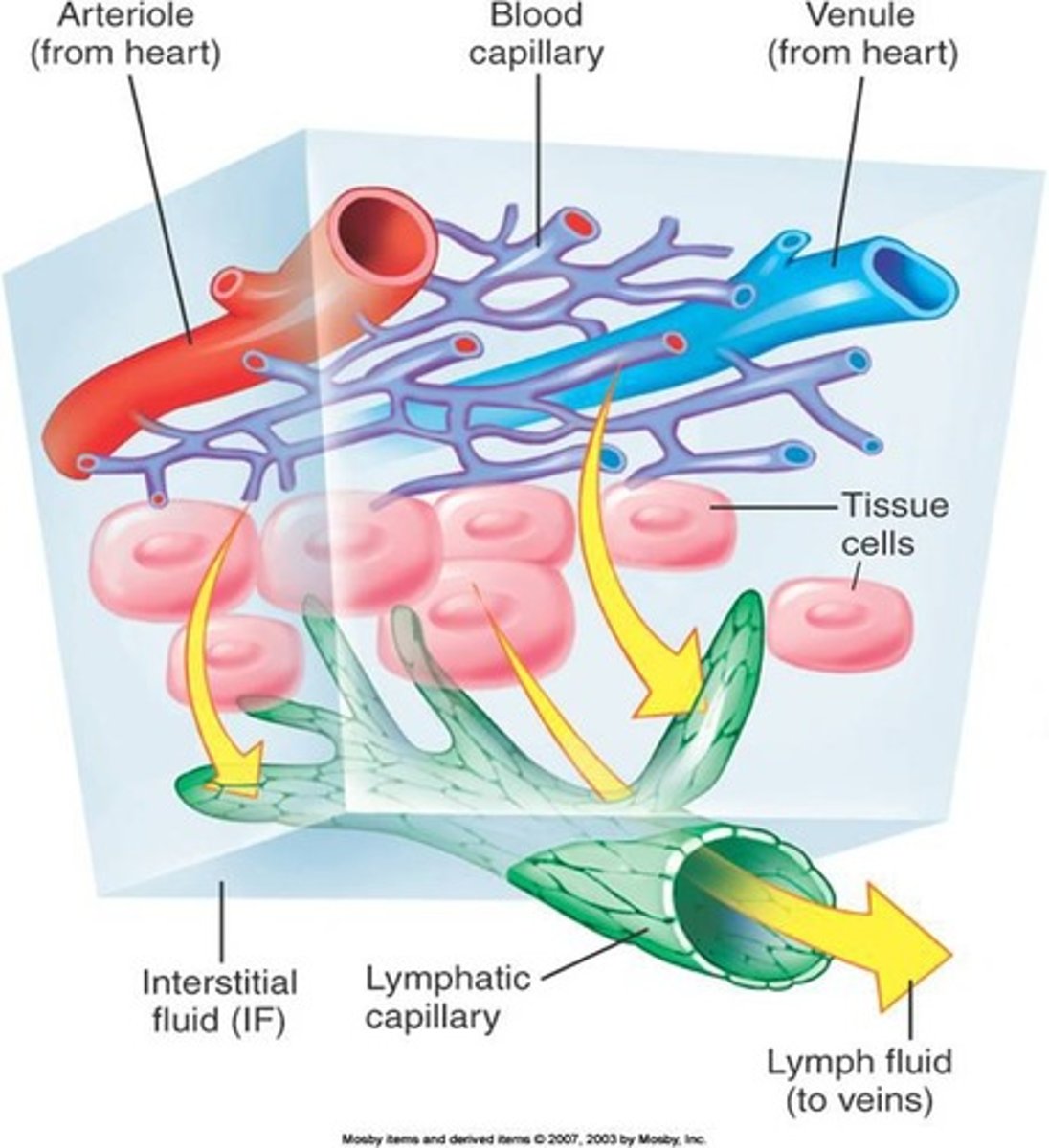
Lymphatic System
Drains fluid surrounding cells; contains lymph.
Lymphatic vessels
Transport lymph fluid into bloodstream.
Elephantiasis
Swelling caused by lymphatic obstruction.
Lacteals
Lymphatic vessels that absorb dietary fats.
Urinary system
Filters blood waste and regulates body balance.
Erythropoietin
Hormone stimulating red blood cell production.
Cranberry consumption
May protect kidney health.
Central nervous system
Integrates internal and external body information.
Neurons
Cells generating electrical currents for communication.
Sodium and potassium
Nutrients used by neurons for electrical currents.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals for brain function from nutrients.
Glucose
Preferred fuel source for the brain.
Endocrine system
Regulates metabolism and produces hormones.
Permissive hormones
Hormones that activate other hormones.
Antagonistic hormones
Hormones that inhibit other hormones.
Synergistic hormones
Hormones that work together for effect.
Insulin
Lowers blood glucose by promoting glycogen synthesis.
Glucagon
Raises blood glucose by converting glycogen.
Immune system
Defends against pathogens with innate and adaptive immunity.
Innate immunity
Nonspecific defenses against pathogens.
Adaptive immunity
Specific response by white blood cells.
Antibodies
Blood proteins binding foreign proteins.
Antigens
Substances inducing immune sensitivity or resistance.
Digestion
Breakdown of large molecules into nutrients.
Absorption
Uptake of nutrients into bloodstream or lymph.
Gastrointestinal tract
Organs for digestion and nutrient absorption.
Motility
Movement of food through the GI tract.
Mastication
Chewing process to break down food.
Bolus
Food mass mixed with saliva, swallowed.
Chyme
Mixture of gastric juices and partially digested food.
Peristalsis
Muscular contractions moving food through GI tract.
Cecum
First part of the large intestine.
Ascending Colon
Section of colon moving upward from cecum.
Transverse Colon
Horizontal section of the large intestine.
Descending Colon
Colon section moving downward toward sigmoid.
Sigmoid Colon
S-shaped section before the rectum.
Rectum
Final section of the large intestine.
Anal Canal
Last part of the digestive tract.
Oral Cavity
Mouth area where food is chewed.
Taste Buds
Receptors on tongue sensing food flavors.
Umami
Savory flavor associated with brothy foods.
Oleogustus
Flavor associated with fat.
Saliva
Watery fluid aiding food digestion.
Amylase
Enzyme breaking down starch in saliva.
Lipase
Enzyme breaking down fat in digestive tract.
Esophagus
Tube connecting pharynx to stomach.
Pharynx
Organ connecting oral and nasal cavities.
Epiglottis
Flap preventing food from entering trachea.
Cardiac Sphincter
Muscle controlling entry from esophagus to stomach.
Intrinsic Factor
Substance enhancing Vitamin B12 absorption.
Microvilli
Folds increasing surface area for nutrient absorption.
Colon
Final segment of the large intestine, absorbs water.
Gut Flora
Bacteria in the colon producing vitamins.
Flatulence
Gas produced from undigested sugars fermentation.
Feces
Waste material containing water, fiber, and bacteria.
Anal Sphincters
Muscles controlling feces elimination from the rectum.
Hygiene Hypothesis
Over-sanitization may increase allergies and autoimmune diseases.
Peptic Ulcers
Stomach ulcers caused by H. pylori bacteria.
H. pylori
Bacteria causing increased stomach acid and ulcers.
Acid Reflux
Gastric acid backing up into the esophagus.
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, severe acid reflux.
Gallstones
Cholesterol crystals causing abdominal pain and discomfort.
Gallbladder Removal
Common treatment for symptomatic gallstones.
Constipation
Difficult or infrequent bowel movements.
Diarrhea
Increased frequency or fluidity of bowel movements.
Celiac Disease
Immune reaction to gluten in genetically predisposed individuals.
Gluten
Protein in wheat, rye, and barley.
Nonceliac Gluten Sensitivity
Gastrointestinal distress without intestinal damage from gluten.
Villi
Intestinal projections that absorb nutrients.