EAC 4: Electricity and Magnetism Fundamentals Problems
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Matter can be found in the following forms:
A. Solid
B. Liquid
C. Gas
D. Each of the above
D. Each of the above
A substance that cannot be reduced into a simpler substance is called a/an:
A. Element
B. Mixture
C. Compound
D. Solution
A. Element
A molecule is the smallest possible particle that retains the characteristics of a:
A. Element
B. Mixture
C. Compound
D. Solution
C. Compound
The atomic number is determined by:
A. Number of electrons
B. Number of protons
C. Number of neutrons
D. Both A and B
B. Number of protons
If an oxygen atom has 8 protons and 8 neutrons, and 2 more neutrons are added, the atomic weight becomes:
A. 12
B. 10
C. 16
D. 18
D. 18
The maximum number of electrons in a shell is given by:
A. Ne = 2n^2
B. Ne = n^2
C. Ne = 2^n
D. Ne = 2n
A. Ne = 2n²
Electrons at the conduction band are called:
A. Free electrons
B. Valence electrons
C. Deep state electrons
D. Shallow electrons
A. Free electrons
The energy gap of an insulator inthe order of
A. Zero electron volt
B. One electron volt
C. Five electron volts
D. One tenth electron volt
C. Five electron volts
Inmaterials,what do you call the region that separates the valence and conduction bands
A. Energy gap
B. Forbidden band
C. Insulation band
D. Energy gap or forbidden band
D. Energy gap or forbidden band
Wha tdo you call the positively charged ion?
A. Anion
B. Cation
C. Domain
D. Proton
B. Cation
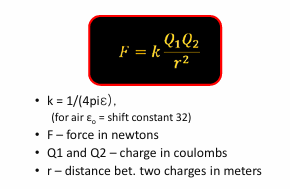
Determine the force in Newton between two 4uC charges by 0.1 meter in air.
a.1.44 N
b.14.4 N
c.144 N
d.1440 N
b.14.4 N
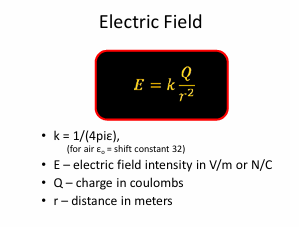
Find the electric field intensity 10 cm form a charge Q = 5nC
a.450 N/C
b.4.5k N/C
c.900 N/C
d.900k N/C
b. 4.5k N/C
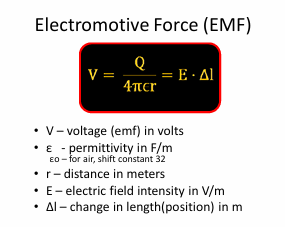
A 2 nC point charge will produce what potential at 2m away?
a.4 volts
b.6 volts
c.7.5volts
d.9 volts
d. 9 volts
Which of the following actions describes the easiest way to accumulate a static electric charge?
A. Friction between two conductors
B. Friction between two insulators
C. Pressure between two conductors
D. Pressure between two insulators
B. Friction between two insulators
Electrostatic lines of force are drawn in which of the following manners?
A. Entering negative charge, entering positive charge
B. Entering negative charge, leaving positive charge
C. Leaving negative charge, leaving positive charge
D. Leaving negative charge, entering positive charge
B. Entering negative charge, leaving positive charge
The measure of electric field strength per unit length is known as electric field intensity or simply electric intensity. What is its unit?
A. Volt/meter (V/m)
B. Joules/Coulomb-meter (J/Cm)
C. Newton/Coulomb (N/C)
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
A charged body at rest is said to exhibit an electric field, which interacts with other bodies. The study of this phenomenon is known as:
A. Electricity
B. Electrostatics
C. Electromagnetism
D. Field interactions
B. Electrostatics
How does permittivity affect electric field intensity?
A. It causes the field intensity to increase.
B. It causes the field intensity to decrease.
C. It causes the field intensity to fluctuate up and down.
D. It has no effect on field intensity
B. It causes the field intensity to decrease
What is the electric force between 2 u quarks separated by 1.0E-16meters? This is a typical separation inside a proton
a. 10.1 kN
b. 10.3 kN
c. 10.7 kN
d. 10.9 kN
B. 10.3 kN
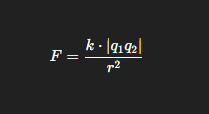
Charges of -6 nC and +4 nC are 3 m apart. Determine the electric field at a point midway between them.
a. 40 N/C toward the positive charge
b. 40 N/C toward the negative charge
c. 8 N/C toward the positive charge
d. 8 N/C toward the negative charge
b. 40 N/C toward the negative charge
The strength of the electric field in the region between two parallel deflecting plates of a cathode-ray oscilloscope is 25 kN/C. Determine the force exerted on an electron passing between these plates.
a. 4×10⁻¹⁵ N
b. 5×10⁻¹⁵ N
c. 6×10⁻¹⁵ N
d. 8×10⁻¹⁵ N
a. 4×10⁻¹⁵ N

What current density corresponds to a drift velocity of 6.0×10⁻⁴ m/s in a silver conductor? (σ = 61.7 MS/m, μ = 0.0056)
a. 6.61 MA/m²
b. 5.56 MA/m²
c. 8.67 MA/m²
d. 1.01 MA/m²
a. 6.61 MA/m²
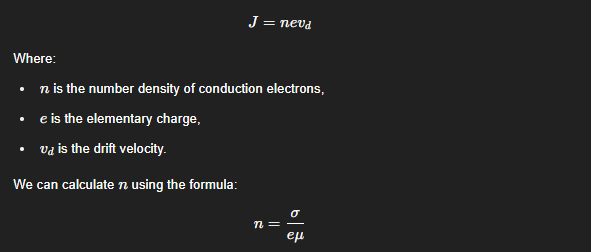
AWG 12 copper conductor has 80.8 mil diameter. A 50-foot length cable carries a current of 20 A. Find the voltage drop across the cable. (σ = 58 MS/m, μ = 0.0032)
a. 3.59 V
b. 1.59 V
c. 3.78 V
d. 4.67 V
b. 1.59 V

What is the density of free electrons in a metal for a mobility of 0.0046 m²/V-s and a conductivity of 29.1 MS/m?
a. 5.98×10²⁸ electrons/m³
b. 0.89×10²⁸ electrons/m³
c. 3.1×10²⁸ electrons/m³
d. 3.96×10²⁸ electrons/m³
d. 3.96×10²⁸ electrons/m³
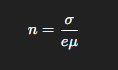
The temperature at which ferromagnetic materials lose their magnetic properties is called:
A. Neel temperature
B. Curie temperature
C. Absolute zero
D. Inferred absolute zero
B. Curie temperature
It is used to maintain the strength of magnetic field:
A. Storer
B. Gausser
C. Energizer
D. Keeper
D. Keeper
A piece(s) of magnetically soft iron that is placed on or between the pole faces of a permanent magnet to decrease the reluctance of the air gap and thereby reduce the flux leakage of the magnet:
A. Jacket
B. Horseshoe magnet
C. Keeper
D. Mandrel
C. Keeper
A natural magnet is called a:
A. Magnesia
B. Permanent magnet
C. Lodestone
D. Temporary magnet
C. Lodestone
It is the capacity of a substance to become magnetized and is expressed as a ratio between the magnetization produced in a substance to the magnetizing force producing it:
A. Magnetic conductivity
B. Magnetic resistivity
C. Magnetic susceptibility
D. Magnetic reluctivity
C. Magnetic susceptibility
When you demagnetize properly by applying an AC field and then gradually reduce it to zero, this process is called:
a) Damping
b) Degaussing
c) Decaying
d) Gaussing
b) Degaussing