AP Macroeconomics Unit 2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Circular Flow Diagram
A visual representation of the flow of goods, services, and money in an economy, illustrating the interactions between households, firms, and the government.
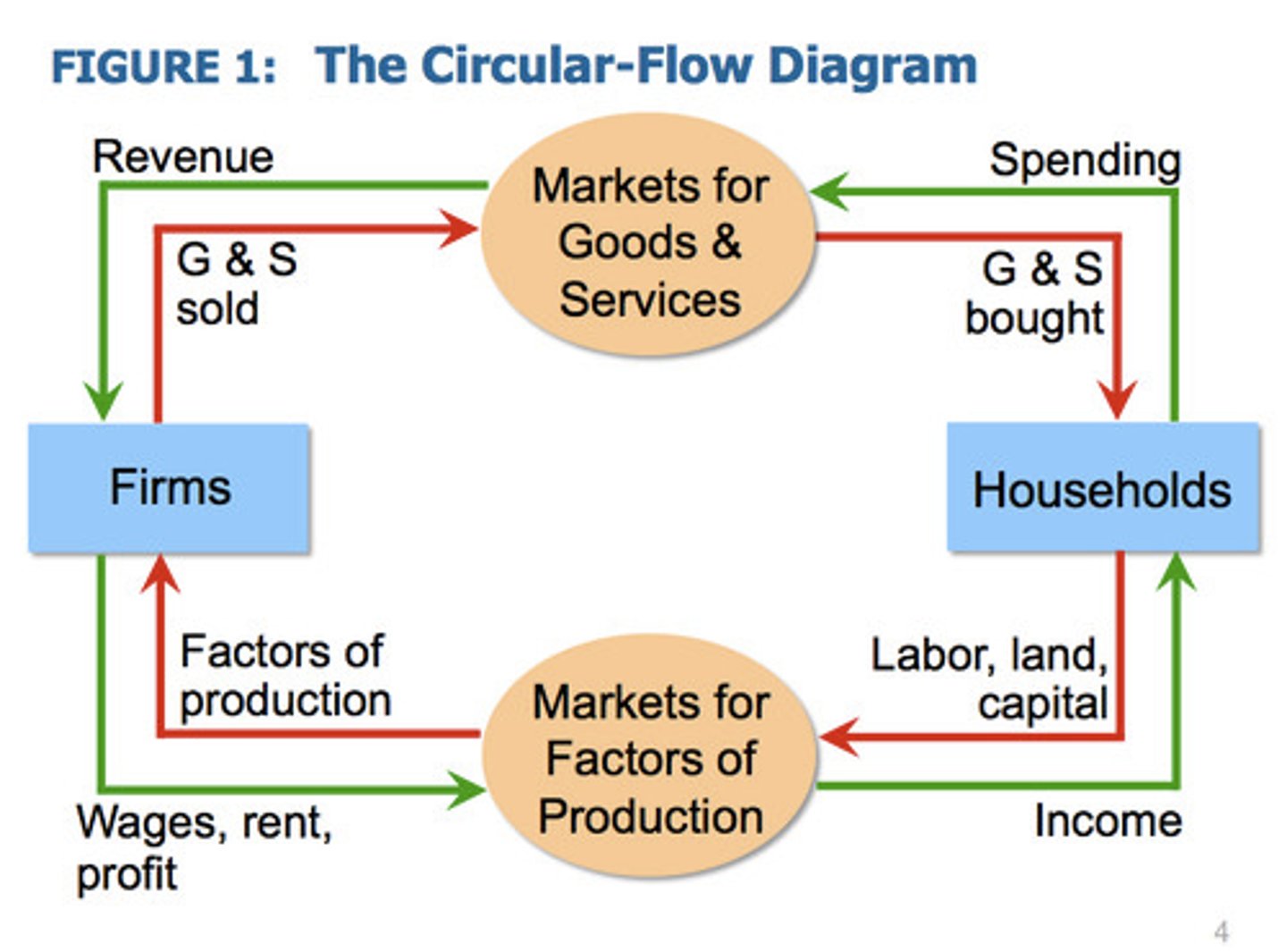
household
A group of individuals living together and making joint economic decisions, such as consumption and savings.
firm
An organization that produces goods and services for the market.
government spending
spending by all levels of government on final goods and services; the total expenditures made by the government on goods, services, and transfer payments.
transfer payments
Payments made by the government to individuals without expecting a good or service in return (i.e. welfare, unemployment benefits)
imports
goods produced abroad and sold domestically
exports
goods produced domestically and sold abroad
net exports
spending on domestically produced goods by foreigners (exports) minus spending on foreign goods by domestic residents (imports)
product market
the market in which households purchase the goods and services that firms produce; the place where final goods and services are bought and sold to households or consumers
factor/resource market
The market where factors of production (land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship) are bought and sold. Especially, capital and labor
Intermediate goods
goods used as inputs in the production of final goods.
finals goods
goods that are consumed by end-users.
employed
paid employees, self-employed, and unpaid workers in a family business; either part time or full time
unemployed
people not working who have looked for work during previous 4 weeks and still remain jobless
labor force
sum of employed and unemployed
unemployment rate
the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed.
labor force participation rate
The percentage of the working-age population that is in the labor force.
discouraged worker
A person who has given up looking for employment due to the belief that no jobs are available.
underemployed
Individuals who are working part-time but desire full-time employment or are working jobs that don't fully utilize their skills.
frictional unemployment
A type of unemployment caused by workers voluntarily changing jobs and by temporary layoffs; unemployed workers between jobs.
structural unemployment
unemployment resulting from a mismatch between the skills of the labor force and the requirements of available jobs.
cyclical unemployment
unemployment that rises during economic downturns and falls when the economy improves
natural rate of unemployment
The level of unemployment that exists in the economy when it is producing at its potential output.
efficiency wages
Wages set above the equilibrium to attract and retain higher-quality workers.
inflation
A general increase in the price level of goods and services over time.
deflation
A general decrease in the price level of goods and services over time
disinflation
a reduction in the rate of inflation
price index
a number that compares prices in one year with some earlier base year; a measurement that shows how the average price of a standard group of goods changes over time
market basket
representative group of goods and services used to compile the consumer price index (i.e. Food and Beverages (milk, chicken, full service meals...); a selected mix of goods and services that tracks the performance of a specific market or segment.
consumer price index
A measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services; measures the overall change in consumer prices based on a representative basket of goods and services over time.
real values
values that have been adjusted for inflation, thus stripping the price effect and enable side to side comparison of actual output
nominal values
values unadjusted for the effects of inflation
menu costs
the costs to firms of changing prices
shoe leather costs
the costs associated with increased transactions due to inflation.
unit-of-account costs
arise from the way inflation makes money a less reliable unit of measurement
nominal GDP
The total value of goods and services produced in a country, measured in current prices.
real GDP
The total value of goods and services produced in a country, adjusted for inflation.
base year
The year used as a reference point for constructing a price index.
GDP deflator
is an economic metric used to measure inflation; helps determine the rise in prices of goods and services. This metric includes all final goods, including exports. a measure of the price level calculated as the ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP times 100; a measure of the overall price level of goods and services produced in an economy, relative to the base year.
Business Cycle
a period of macroeconomic expansion followed by a period of contraction; the recurring fluctuations in economic activity, including expansion, contraction, peak, and trough.
expansion/recovery
the phase of the business cycle characterized by economic growth and increasing employment.
contraction
the phase of the business cycle characterized by a decline in economic activity.
recession
a significant decline in economic activity, lasting for an extended period.
peak
the point at which the economy reaches its highest level of output before entering a contraction.
trough
the point at which the economy reaches its lowest level of output before entering an expansion.
potential output
The real output (GDP) an economy can produce when it fully employs its available resources; the maximum sustainable level of output an economy can produce without causing inflation.
output gap
the gap between real GDP and potential GDP, the difference between actual output and potential output.
positive output gap
When actual GDP is above the productive potential of the economy and it is in boom; when actual output exceeds potential output.
negative output gap
When actual GDP is below the productive potential of the economy; when actual output is below potential output.