ESF Principles of Genetics Exam 4
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
What is recombinant DNA?
joining of DNA molecules from different biological sources
What three people were awarded the 1978 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their contributions to gene splicing?
Daniel Nathans, Hamilton Smith, and Werner Arber.
What are clones?
recovered copies of recombinant DNA molecule.
What are clones used to study?
structure and orientation of DNA
What are restriction enzymes?
They cut the DNA into specific parts
What are vectors?
carrier DNA molecules that can replicate cloned DNA fragments
What is transformation?
the assimilation of external DNA by a cell.
What is a recognition sequence?
aka restriction site, palindromic sequence where restriction enzymes cut
Enzymes with what four base recognition sequence will cut often and produce very many small fragments.
AGCT
How many types of restriction enzymes are there?
200 kinds
What is DNA ligase?
seals gaps, covalently bond the two stands
What is annealing?
allows recombinant DNA molecules to form via complementary base pairing.
After annealing, are the two strands covalently bonded?
no
T/F plasmids are vectors
true
DNA vectors must have what three things?
1. Several restriction enzyme sites
2. able to replicate independently.
3. carry a selectable gene marker
What is the replication origin?
allows the plasmid to replicate using host cells replication enzymes.
What is a selectable gene marker?
something that can distinguish host cells from those that have taken them up from those that have not.
What are examples of a selectable gene marker?
Ampicillin resistance
LacZ
What are two approaches used for transformation?
calcium ions with brief heat shock
electroporation with pulse of electricity
What are phage vectors?
phages that carry pieces of bacterial DNA during transduction
Why are phage vectors still used today?
can carry 2x as long DNA inserts than a plasmid vector (45kb).
What are bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) and yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs).
Large fragments of DNA 100-300k bp, don't copy as often.
What is a DNA library?
collection of cloned DNA.
What are the two types of DNA libraries?
Genomic & complementary
What is a genomic library?
a collection of all of the cloned DNA fragments from a target genome
What is a complementary DNA library?
made from mRNAs, represents genes that were transcriptionally active during collection.
What are complementary DNA libraries made by? (using what enzyme)
Reverse Transcriptase
What are the three major benefits of PCR?
1. no need to clone host cells
2. copies specific dna sequence through in vitro reactions
3. can amplify target DNA sequences in very small amounts.
What are the three steps of PCR?
1. Denaturation
2. Primer annealing
3. Extension/Elongation
What machine is used for PCR?
thermocycler
How many primers does PCR use?
two
Where do primers anneal to in PCR?
denatured DNA
What is taq polymerase?
heat stable DNA polymerase
What is RT-PCR?
reverse transcriptase PCR
copies single stranded DNA into double stranded DNA
What are the three limitations of PCR?
need to know some information of the sequence for primers.
minor contamination = major problem
can't amplify long segments
What are the advantages of PCR?
diagnoses genetic disorders
good for studying single cells, fossils, or crime scene
What is DNA sequencing?
identifies the base sequence in a fragment of DNA
What is sanger sequencing?
cheapest option, manual/automated.
What does each sangar sequencing reaction contain?
template, primer, DNA polymerase, four normal dNTPs, and small amount of a single type of ddNTP.
How do you separate the DNA fragments during manual sanger sequencing?
electrophoresis separates nucleic acids/proteins by size
electrophoresis of fragments reveals base sequence of DNA fragments.
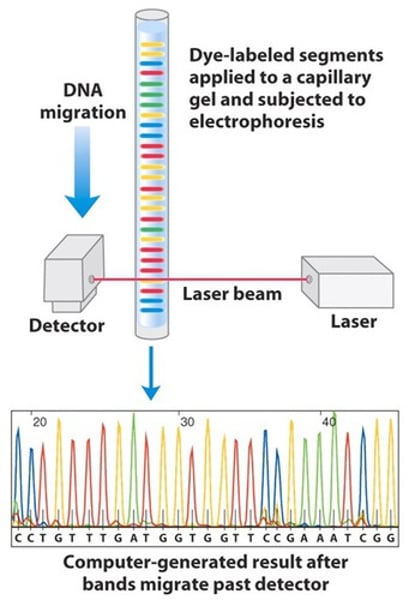
When reading a manual sanger sequence do you read from the top or the bottom.
bottom
How does manual sanger sequencing show you the bases?
peaks represent bands on the gel with each band labeled with a different terminating color.
What is Moore's Law?
The number of transistors in an integrated circuit doubles every 2 years
What is the Carlson Curve
the biotechnology equivalent of Moore's Law, sequencing costs will be at least as fast as Moore's Law
What is the two-part classical genetics approach?
1. Using spontaneous mutations/mutants
2. Generate linkage maps using mutant strains
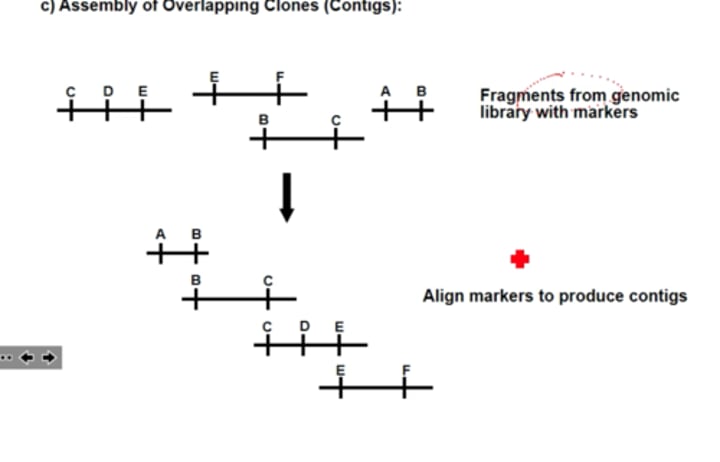
What is whole-genome sequencing?
AKA shotgun-cloning
genomic dna cut into contigs.
chromosome assembled by computers
fragments aligned based on identical DNA sequences

What are contigs? (or continuous fragments)
overlapping DNA frags that together make a continuous DNA molecule within chromosome.
Bioinformatics studies what.
gene structure, gene sequence/expression, protein structure/expression
What is GenBank?
NCBI database of DNA sequences
What does each sequence receive in GenBank? What is it used for?
An accession number. Its used to access and retrieve a sequence.
Whats annotation?
the process of identifying genes, their regulatory sequences, and their functions.
BLAST. What is it. Define it. NOW! DO IT!!
Basic Local Alignment Search. Identifies portions that align with or are the same as an existing sequence.

Whats the "E Value"?
expect value. Based on the number of matching sequences in database expected by chance.
What are homologous genes?
genes that are evolutionarily related
What are orthologs?
genes from different species thought to have descended from a common ancestor.
What are paralogs?
homologous genes in the same species.
What do paralogs result from?
duplications.
Yoooo whats up h-omi(e)c ?!
Whats an omic, give examples.
Specific area of study. Ex:
Proteomics - proteins
Transcriptomics - RNAs
Metabolomics - metabolites
Glycomics - sugars
Toxicogenomics
What is transcriptome analysisi?
studies expression of genes by genome qualitatively and quantitatively.
What is qualitative transcriptome analysis?
identifies which genes are expressed and which are not
What is quantitative transcriptome analysis?
measures varying levels of expression of different genes
What does proteomics allow us to do?
allows us to compare proteins in normal and diseased tissue
What is two-dimensional gel electrophoresis? (2DGE)
technique that separates hundreds/thousands of proteins
What does 2DGE use to separate proteins?
isoelectric focusing.
What is isoelectric focusing?
proteins migrate based on net charge and pH
What is SDS PAGE?
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
What is innate immunity?
defenses tailored to a specific pathogen.
What are bacterial innate immunities?
restriction enzymes
blocking phage adsorption & DNA insertion
induce apoptosis in infected cells
How do bacteriums protect their own DNA from restriction enzymes?
methylating the DNA
What does CRISPR-Cas mean?
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats
What percent of bacteria species have CRISPR loci? What percent of Archaea?
40% of bacteria
90% of archaea
What do we mean by "molecular memory".
viral sequences within CRISPR loci that serve as memory of previous viral attacks
What does it mean to be polygenic trait?
multiple genes control for the trait
How do you find out the number of polygenes?
High probability of being on exam.
1/(4^n)= ratio of F2 individuals expressing either extreme phenotype
Genetics Review Question: Calculate the number of polygenes:
P: Red X White
F1: Pink
F2: 1/64 white , 1/64 red, 31/32 pink
1/64 = 1/(4^n)
What is broad-sense heritability (H^2)?
Measures the contribution of the genotype variance to the total phenotypic variance.
What is the formula for broad-sense heritability?
H^2 = Vg / Vp
lowercase are subscript
What does broad sense heritability formula allow you to examine?
the relative importance of genetic versus environmental factors.
How do you find total phenotypic variation?
Vp = Vg + Ve + Vg+e
Vg+e will either be given or not mentioned.
Vg in parental cross is negligible.
Vp of parent and F1 = average of both's Vp's
lowercase are subscript
T/F prokaryotes have an adaptive immune system.
true
What is adaptive immunity of prokaryotes dependent on?
CRISPR-associated cas genes.
What do CRISPR - associated cas genes do?
encode for Cas proteins that function as DNases and RNases.
What do DNases and RNases do?
cut DNA and RNA respectively.
How are spacers in CRISPR aquired?
phage DNA cut into frags which is inserted into CRISPR loci. Repeat sequences duplicated to each side of the new spacer.
What is a protospacer?
small fragments of invading phage DNA that will become a spacer.
How do you find environmental variation (Ve)?
Phenotypic variation of parent + Phenotypic variation of F1 divided by 2 (average)
How do you find genotypic variation (Vg)?
Vp - Ve = Vg
How do you find H^2?
Vg / Vp of F2
Whats narrow-sense heritability?
the proportion of phenotypic variance due to additive genotypic variance alone.
What are additive genes?
Genes that add something to some aspect of the phenotype
What are crRNAs?
short CRISPR-derived RNAs
What is crRNA biogenesis?
production of crRNAs
What is the target interference in the CRISPR-Cas mechanism?
crRNAs associate with Cas nucleases to find then cleave viral DNA.
T/F Additive alleles are easy to select for.
True
What is a single guide RNA (sgRNA)?
20 nucleotide targeting sequence joined to as little tracrRNA possible for Cas9 function.
What is tracrRNA?
Binds to crRNA and forms an active complex with Cas9
T/F any sequence with a PAM can not be targeted for cleavage in vitro.
False, it can be!
It just needs a sgRNA with crRNA and tracrRNA; and Cas9.
What is reverse genetics?
learning about the function of a gene by deleting it and seeing what happens
An example of transgenic crop resistances are...
Roundup Ready line with glyphosate resistance.
The benefit of Golden Rice is...
enhanced levels of B carotene, the precursor to vitamin A.