Section 10: Earthlike Planets - Venus and Mars
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Earths ROtation: Extra info
Terrestrial planets move as one solid body (no differential rotation)
Equator rotates faster than the poles → takes the same amount of time for different distances
Venus Observations
It appears very bright in the sky.
Even small telescopes reveal that Venus goes through phases like the Moon.
Galileo discovered the full range of Venusian phases.
Used this observation to argue that Venus orbits the Sun, not the Earth.
Venus’ surface is hidden by dense clouds.
Density nearly identical to Earth’s
Also similar radius
Venus Atmosphere
Clouds reflect ~70% of sunlight
Observations become difficult.
Surface pressure ~100 times Earth’s.
Very different in composition from Earth’s atmosphere.
Mainly composed of CO2 → 96.5%
Phosphene found on venus despite no life
Has sulphuric acid rain
Taller troposphere than earth - first part of the sky
Surface temperature: ~730 K (over 850 °F),
Phosphene
composed of one phosphorus atom and 3 hydrogen atoms → made industrially or through life
Found on venus despite not having life
Runaway greenhouse effect
a climate process where a planet's atmosphere traps heat, causing temperatures to rise uncontrollably
Evaporate water
Venus Geological Activity
relatively high, almost as active as Earth.
similar to how Earth might appear without erosion or sediment deposition.
No water or ice and low surface wind speeds mean:
Very little erosion or weathering → due to high temperatures there can be no water or ice to cause erosion
Surface features remain preserved for hundreds of millions of years
Molten Core: but rotation is too slow to have ionic movement that creates a magnetic field
Magnetic field from the solar winds interacting with the ionosphere
Lowland lava Plains
make up 75% of venus’s surface created by lava eruptions
No plate tectonics however → has mantle convections causing crustal stress
Mantle Convections and Tectonic Forces in Venus
Convection currents of molten rock in Venus’ mantle push, pull, and stretch the planet’s crust
Tectonic features
Geological structures created by these forces
Rift Valleys
Places where the crust has ripped apart
Mountain ranges
caused by tectonic compressions
Venus two main continental-sized highland regions
Rise above the plains → created by crust compression and maintained by mantle convection
Aphrodite terra
Largest continent covering one third of the planets circumference
Ishtar terra
Contains Maxwell Mountains, the highest region on Venus.
Peaks rise ~11 kilometers above surrounding lowlands.
Named after James Clerk Maxwell, the only male-named feature on Venus.
Age of Venus’s Surface
YOUNG SURFACE JUST MEANS RECENT GEOLOGICAL ACTIVITY
Impact crater density is used to estimate relative surface ages:
Dense atmosphere protects from smaller projectiles
Average age of the venusian plains: 300–600 million years
Significant and recent geological activity → younger than earths continental crust
Large craters still seem fresh → little erosion
SMall impactors burn up and don’t reach the surface
Global Volcanic Resurfacing Event: Thought to have erased most of the older craters
Subsurface Volcanism and Crustal Bulges
rising magma can accumulate beneath the crust, causing uplift and bulges
Creating Coronae: Large circular or oval features
Venus’s Rotation
The surface is obscured by clouds, so rotation cannot be observed visually.
Rotation measured via radar signals bounced off Venus.
Radar detected topographical features of venus
Rotation period: 243 Earth days on the axis → sidereal day
Slow retrograde rotation may be due to powerful collisions during solar system formation
Orbital period around Sun: 225 Earth days
Solar day (Sun returning to same sky position): 117 Earth days
Retrograde Rotation
when an object spins in the opposite direction of its orbital motion or the rotation of its primary body
Radar Maps
Images are constructed from radar wavelengths
Bright regions indicate rough terrain.
Darker regions indicate smooth terrain.
Mars Observations
Distinctly red in color, caused by iron oxides in its soil.
This red color may explain Mars’ historical association with war and blood.
Telescope resolution limits: ~100 km from Earth, similar to seeing the Moon with the unaided eye.
At this resolution, no topographic details (mountains, valleys, craters) are visible.
Visible features mars features
Bright polar ice caps
Dusky surface markings that change with seasons
Distinct red colour
Caused by the clay and iron oxides in the srufcae
Half the size of earth
Lower density than earth
Mars Polar Caps
Southern Cap: Never goes smaller than 350km
Below 150Kelvin: Includes water ice and dry ice (CO2 frozen)
Northern Cap: Never goes smaller than 1000km
Above 150kelvin in the summer: Only water ice
Mars Atmosphere
Thin atmosphere
<1% of earth atmospheric pressure
Main Composition: 95% CO2, 3% N2
HIgh wind speeds
Causing greatly varying temperatures: 35oC to -143oc
So cold water and carbon dioxide freezes out of the atmosphere
Dust Devil
Dust-filled vortices, created by strong surface heating, are generally smaller and less intense than a tornado
Global Dust storms
Caused by the winds
Runaway refrigerator effect
less elements in the atmosphere so the planet is a lot colder
Mars Composition
Mainly made of silicates, with a small solid metal core
Solid core: due to mars being smaller and cooled off quicker
No global magnetic field due to no ionic movement in the core
Low density
Mars Localized magnetic fields
Possibly had a global magnetic field that caused this
the crustal rocks on Mars were magnetized long ago → Leaving magnetic patches
Mars terrain:
Heavily created south
Young volcanic plains on the north
Tharsis Bulge
olcanic system on mars containing the highest peak in the solar system (olympus)
south of mars
Valles Marineris
Caused by the upwelling from the Tharsis bulge creating tectonic cracking of the crust
Has experienced water and wind erosion
south part of mars
Mars Rotation:
Rotation period (sidereal day): 24 hours 37 minutes 23 seconds
Determined by tracking permanent surface markings over many years (very long time) → using optical wavelengths
Orbital period: ~2 Earth years, 687 Earth days
Rotational axis tilt: ~25°, similar to Earth’s.
Causes seasons on Mars.
Due to Mars’ longer year , each season lasts ~6 Earth months
Historical Speculation of Martian Civilization
Controversy began in 1877 with Giovanni Schiaparelli:
Observed faint, straight lines on Mars called “canale” (channels).
English translation “canals” suggested artificial origin.
Imagination led to the idea of canals as irrigation systems from
Percival Lowell and the Martian Canal Hypothesis
Lowell (American astronomer, 1855–1916) strongly promoted the idea of intelligent Martians → Claimed canals were constructed to preserve Martian civilization amid deteriorating climate.
Martian Channels and Gullies:
Outflow channels: from catastrophic flooding from heating
Runoff Channels: From ancient storms
Gullies: From underground sources, on the steeples of valleys and craters - Underground lakes on Mars: extremely salty water
Gullies recurring slope linea
Dark lines found on gullies, changing by seasonal patterns and temperature flow of surface water
Halophile
the only kind of life that would be possible in mars salty water since they love salt
Ancient Lakes and Glaciers on mars
Dried out Lake beds: now seen as layered sedimentary rock and hematite spheres
Hematite Spheres
Iron oxide compounds that only form in water
Sojourner/ curiosity:
A mars rover → use solar cells for energy
Martian Rocks
Come to us from meteorites and not from any return missions
Has a smaller escape velocity → more escapes
Has traces of water and carbon → possibility of life in the past
Escape velocity
Minimum speed needed for a projectile to be free of the gravitational influence of a massive object like a planet
Kinetic energy is = to potential energy
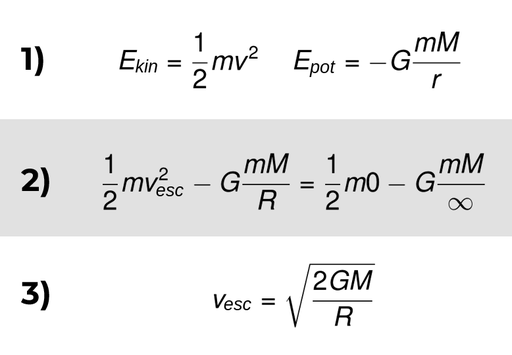
Kinetic energy:
changes from the maximum when it is fired from the surface of the planet to zero when it has escaped the gravitational influence
Gravitational energy
Is gained as an object moves further from the planet
Therefore kinetic energy = potential energy
KEY IDEA
More massive objects have a higher escape velocity → they can hold onto lighter gases a lot easier even when they are heated up