Lecture 19.1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What lipid is responsible for protection?
Waxes
What lipid is responsible for energy stores?
Triacylglycerols
What lipid is responsible for membranes?
glycerophosoholipids and steriods (cell structure)
What lipid is responsible for Nerve Insulation?
sphingolipids
What lipid is responsible for hormones?
steriods
What lipid is responsible for Messengers (immunity, inflammation & CNS)?
eicosanoids and glycolipids(nerves)
Characteristics of Saturated Fatty Acids
no double bonds
chains packed together as a result of hydrophobic attraction
solid at room temp (higher melting point)
Characteristics of Unsaturated Fatty Acids
a long chain of carboxylic acid containing one or more carbon-carbon double bonds
due to the kinks, chains cant pack together as effectively
lower melting point, liquid at room temp.
What is a cis unsaturated fatty acid
naturally occurring
Determining Melting Temperature of a Fatty Acid
1) Chain Length: the longer the carbon chain is the higher the melting temp
2) Degree of Saturation: the more double bonds the lower the melting temperature
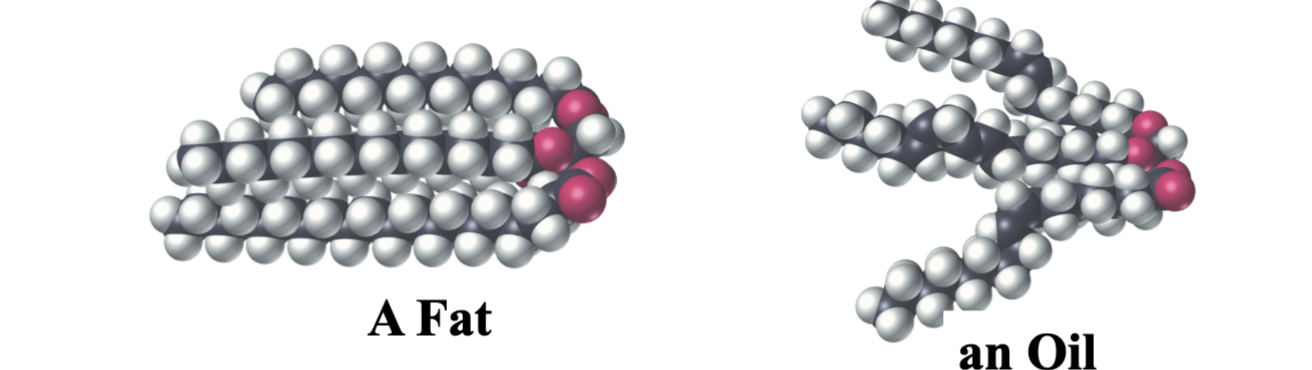
Characteristics of TAGs
two types: fat and oil
non polar, hydrophobic, and not ionic
animal fat contains more sat fats than plant oils
because of high degree saturation in animal fat, it is a solid at room temperature
because of higher content of unsaturated fatty acids in plant oil, it is commonly liquid at room temp
double bonds in naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids are always cis in configuration
neutral charge
three fatty acid chains
What is the biochemical reaction for TAGS?
main energy storage molecule for animals
What is the hydrolysis reaction for TAGS?
Saponification - process of making soaps
What is the hydrogenation reaction for TAGS?
process of making sat fats from poly unsat fats
Iodine number
the number of grams of iodine which will react with 100g of fat or oil
Trans fatty acid
increases LDL
decreases HDL
do not exit is nature
can pack as densely as sat fats
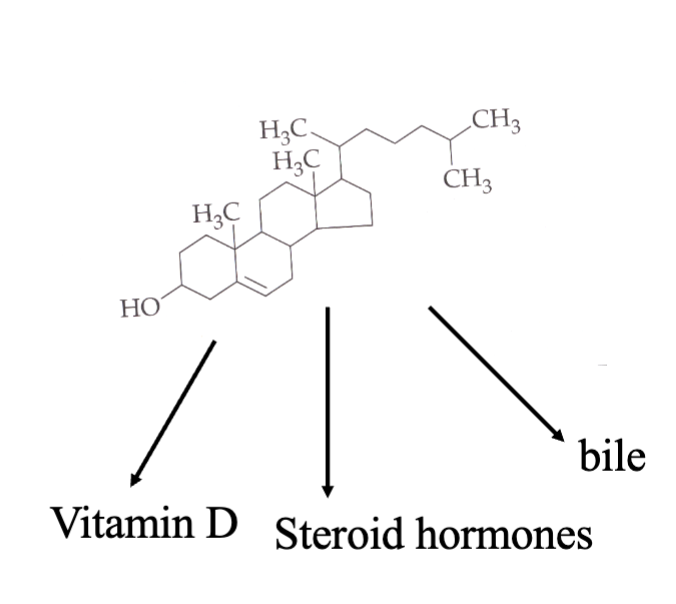
Cholesterol
four fused rings
our bodied can synthesize cholesterol from Acetyl CoA
precursor for steroid hormones, Vitamin D and bile
50% found in cell membranes
Simple diffusion
small uncharged molecules pass through the lipid bilayer from high gradients to low gradients (CO2 and O2
passive tranpsort
Facilitated Diffusion
the issue of embedded integral carrier proteins to transfer molecules
passive transport
glucose
Sodium Potassium Pump
a protein that has been identified in many cells that maintains the internal concentration of potassium ions [K+] higher than that in the surrounding medium (blood, body fluid, water) and maintains the internal concentration of sodium ions [Na+] lower than that of the surrounding medium.
requires energy
active transport
Characteristics of Prostaglandin
responsible for some of the pain and swelling of inflammation
lower blood pressure
affect blood pressure
stimulate uterine contractions
lower gastric secretions
Characteristics of Leukotriene
trigger allergic reactions
triggers asthmatic response
trigger inflammation
what does aspirin do to prostaglandin?
ultilizes irreversible inhibition to block prostaglandin productions