4.2 Electricity
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Adding electrons to an uncharged atom makes it
negatively charged, more electrons than protons
Removing electrons from an uncharged atom makes it
positively charged, more protons than electrons
How are electrons transferred?
by friction
Uncharged objects
equal no. of protons and negative charges
charged objects
more + than - or more - than +
How can an insulator become charged with static electricity
Rub 2 insulators together, friction transfers electrons. One insulator will have a positive charge, and the other insulator will have a negative charge
How to get a balloon to stick to a wall
balloon & wall has no charge. rub balloon, it gains electrons by friction. put the balloon near the wall, electrons are repelled from the wall. balloon and wall attract.
What is an electric field?
area around electric charge
Force of a field
force of the field is strongest closer to the surface
SPARK
P.d between the charged object & earth, air becomes ionised, electrons jump between charged object and the earth, energy is released as jumping heat.
Conductors
allow electron charged to flow through them
Insulators
Don't allow electron charges to flow through them
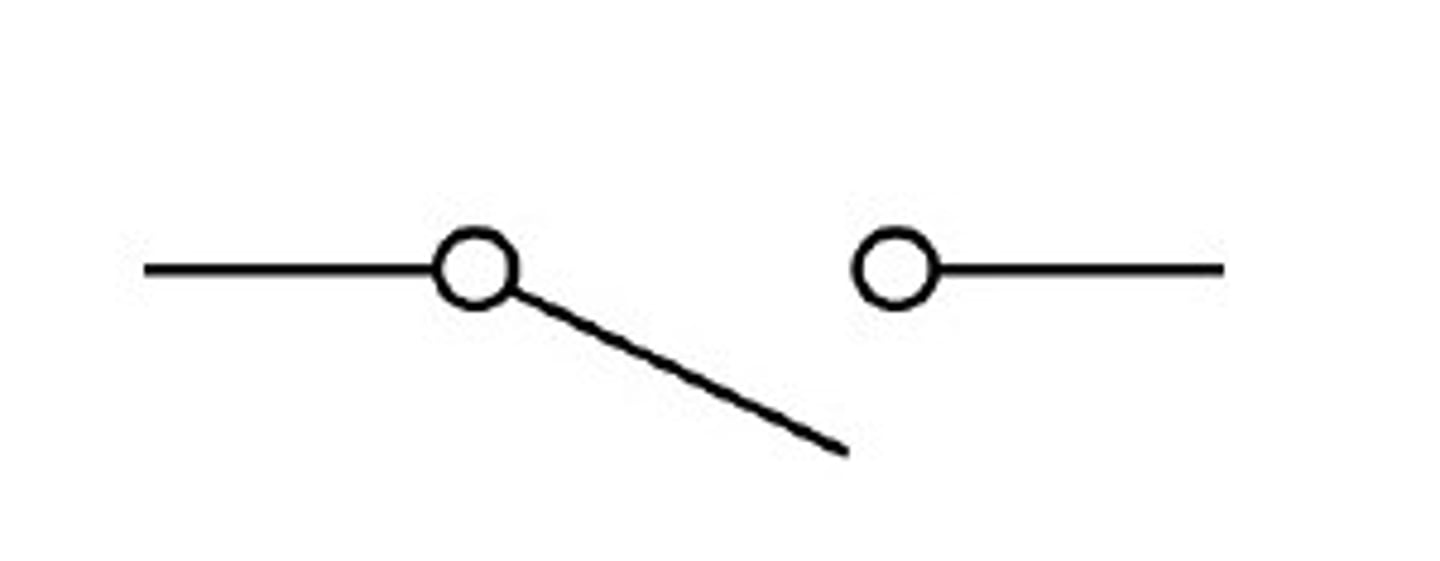
Switch (open)
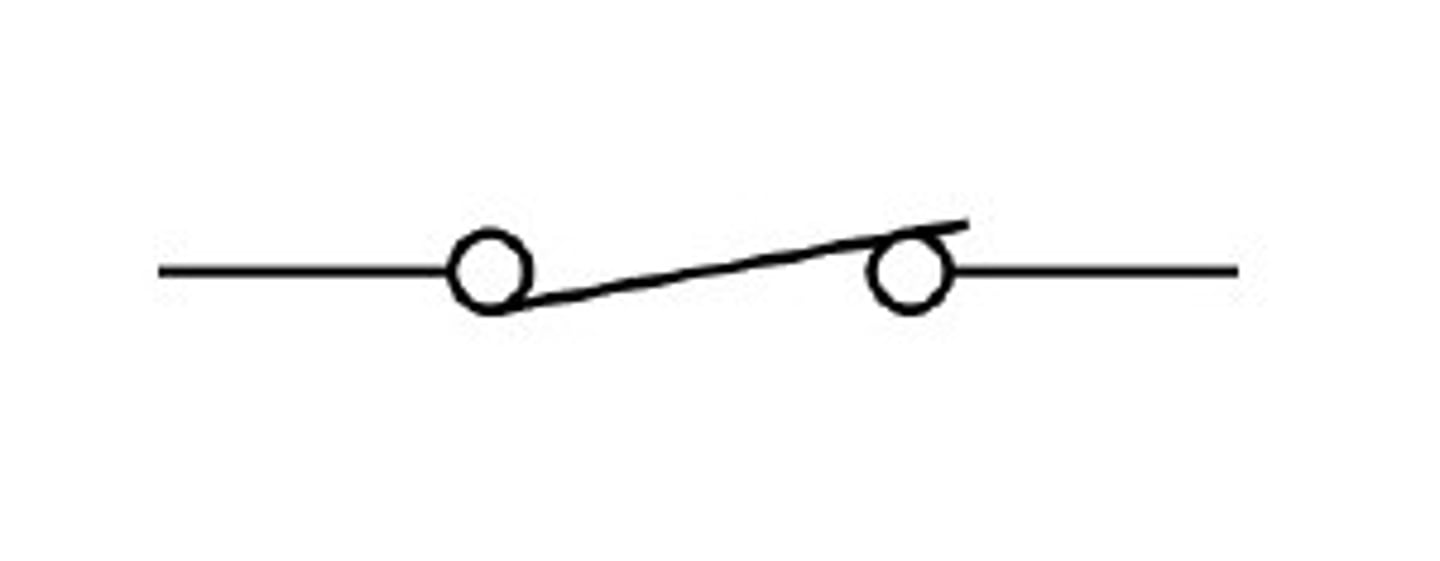
Switch (closed)
Cell

Battery
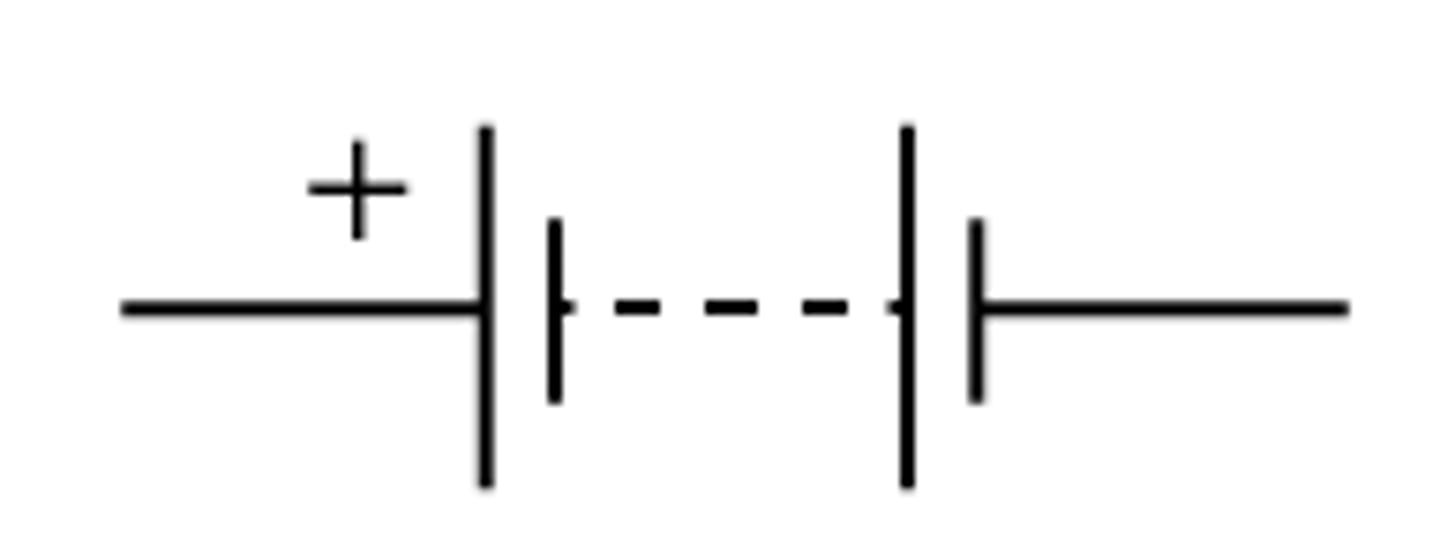
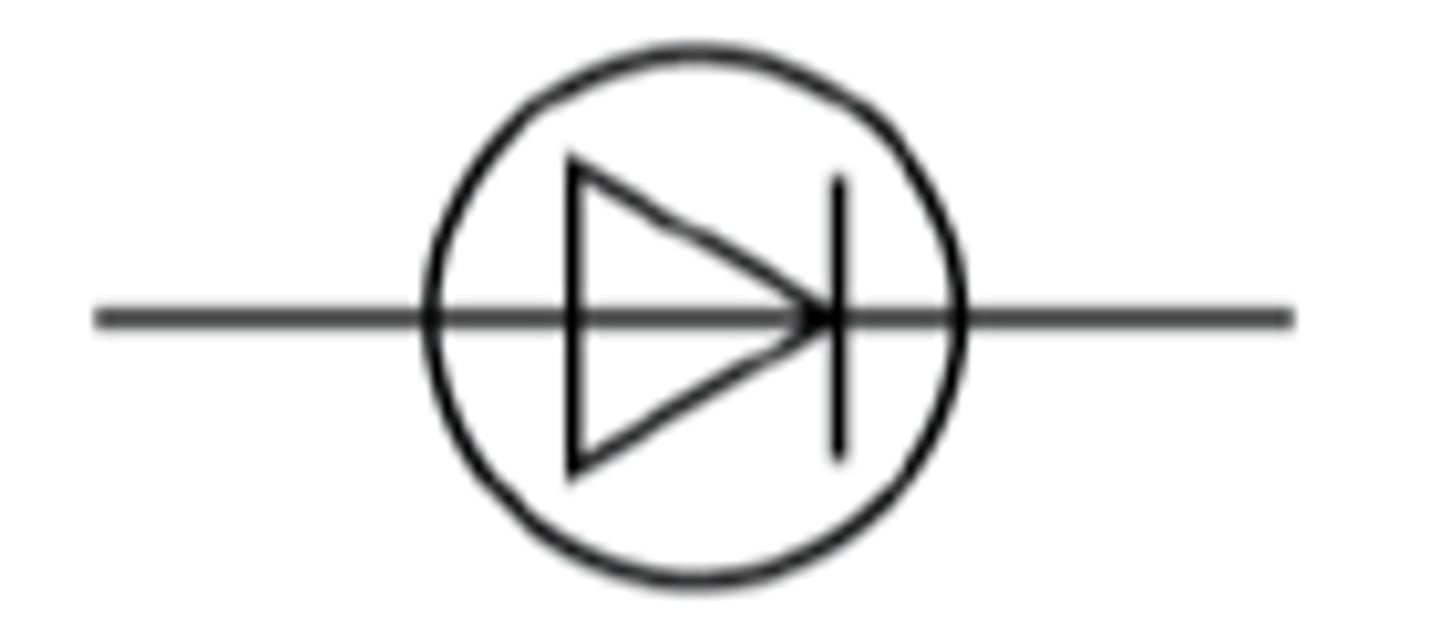
Diode
Resistor
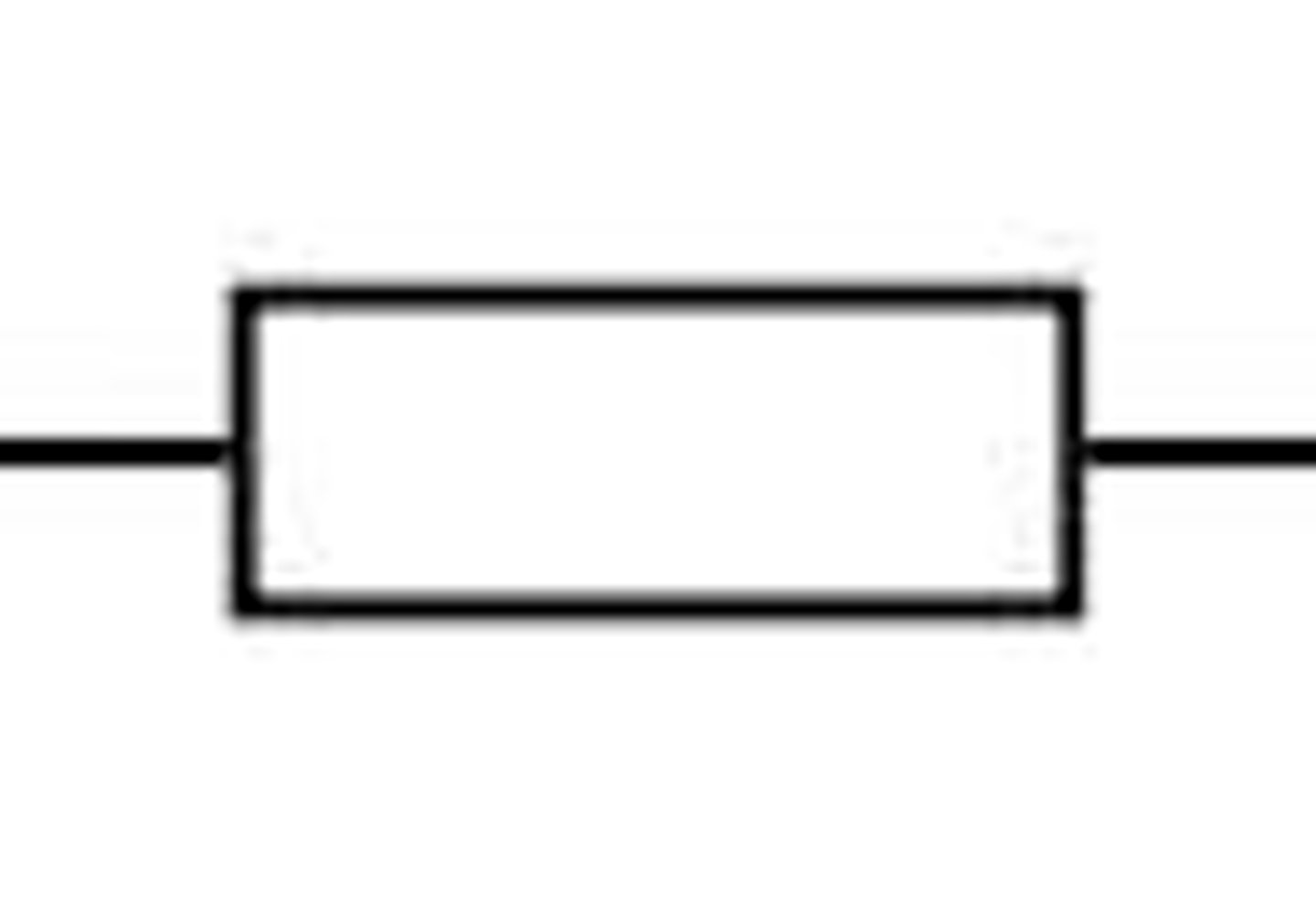
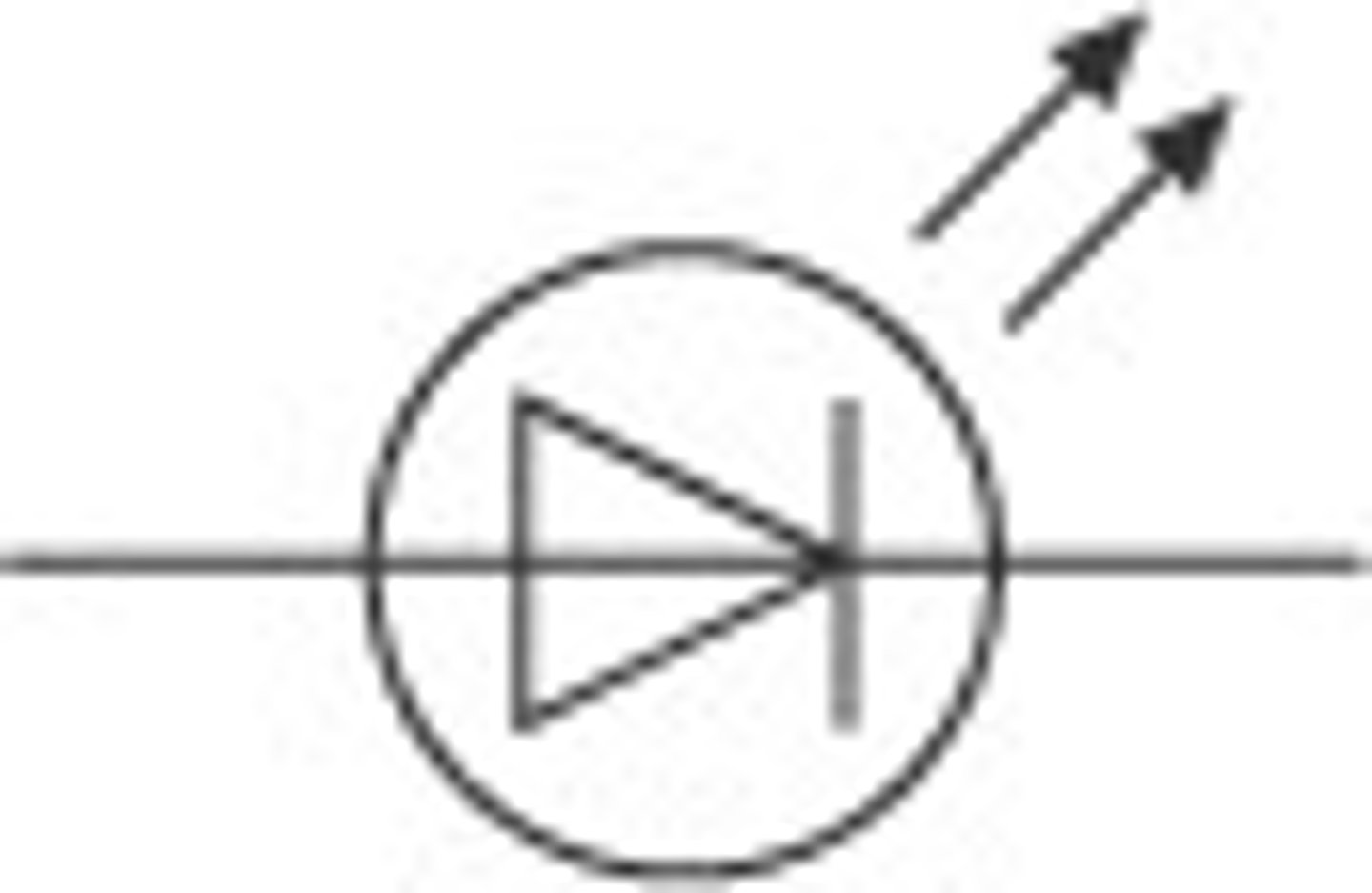
LED
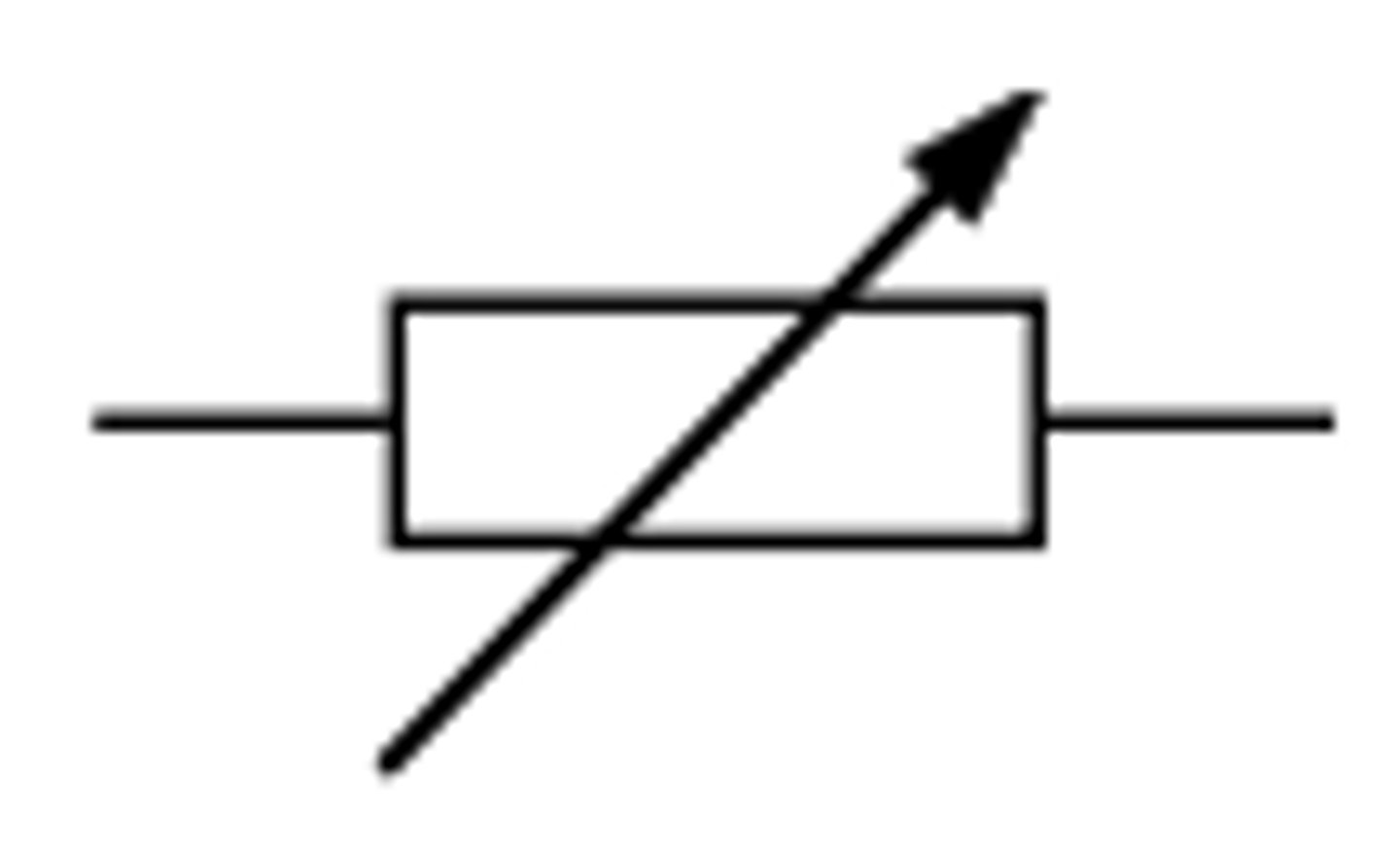
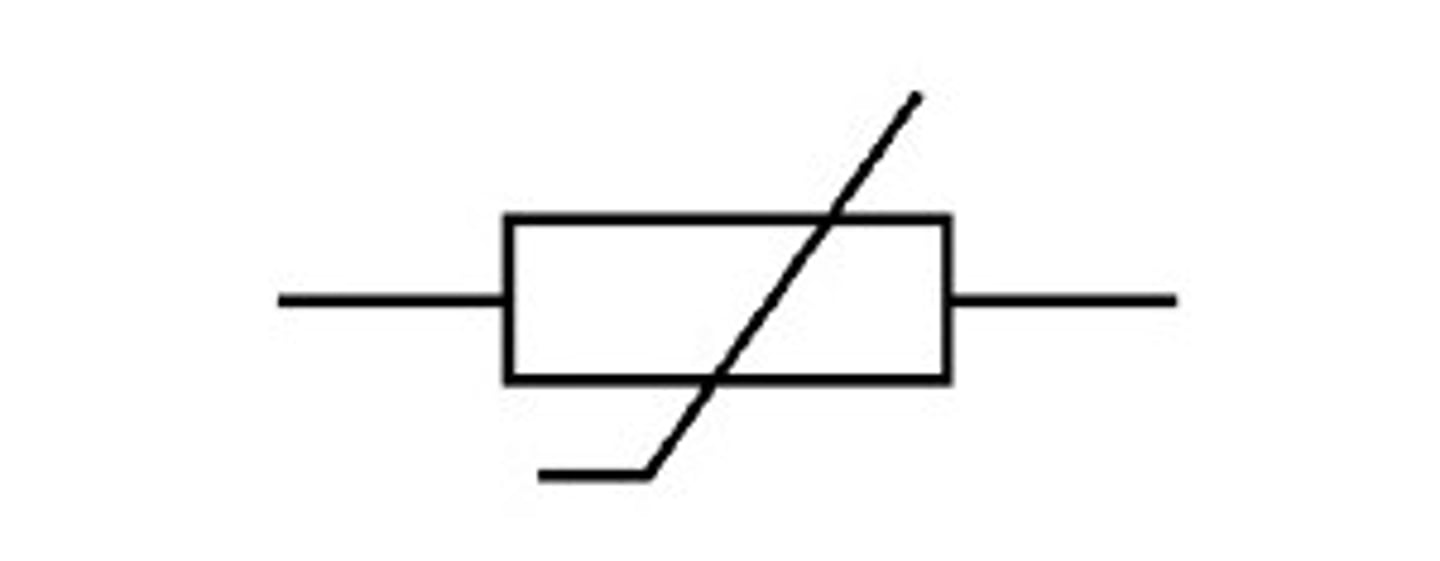
Variable resistor
Lamp

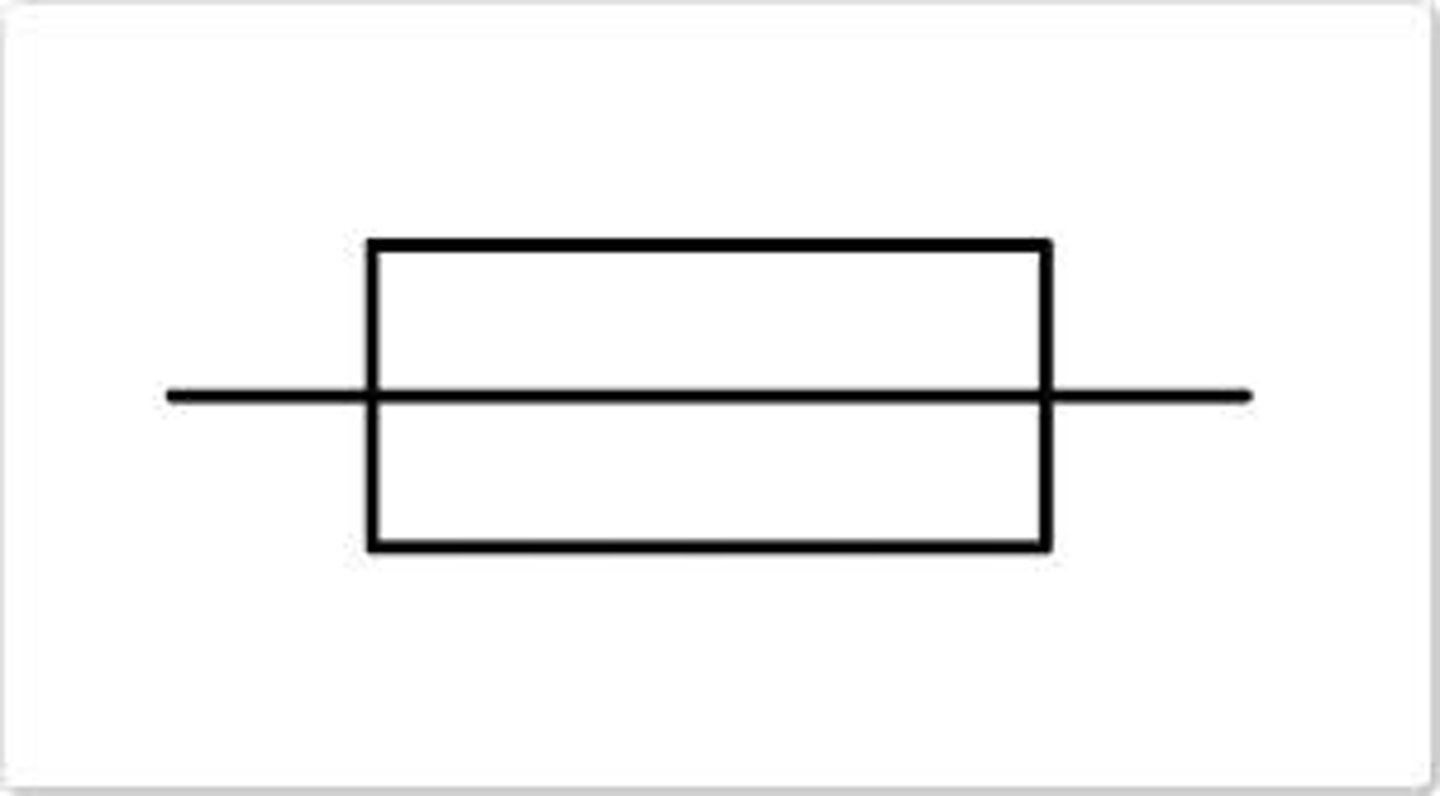
fuse
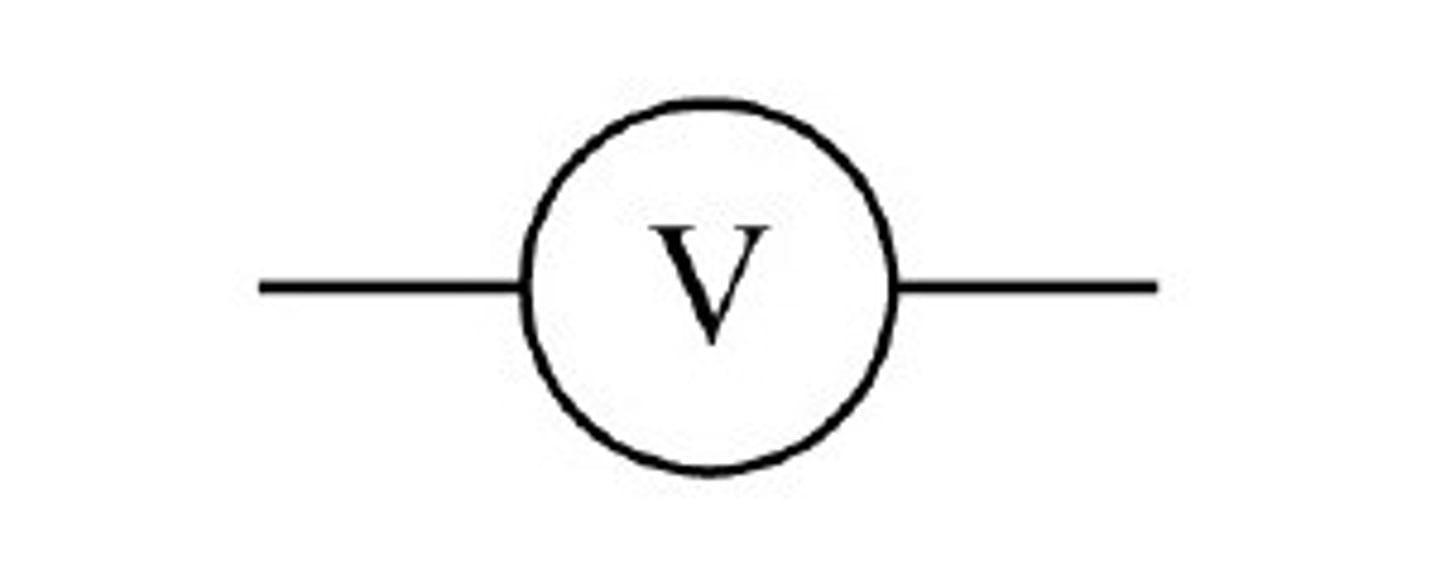
Voltmeter
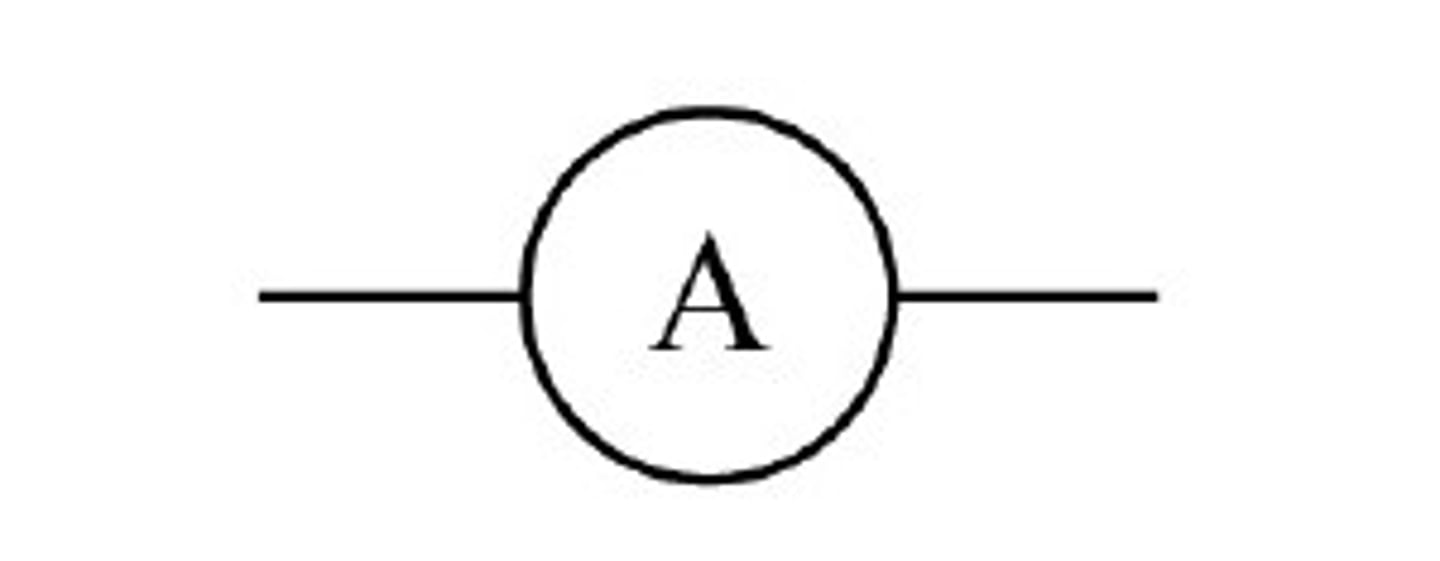
Ammeter
Thermistor
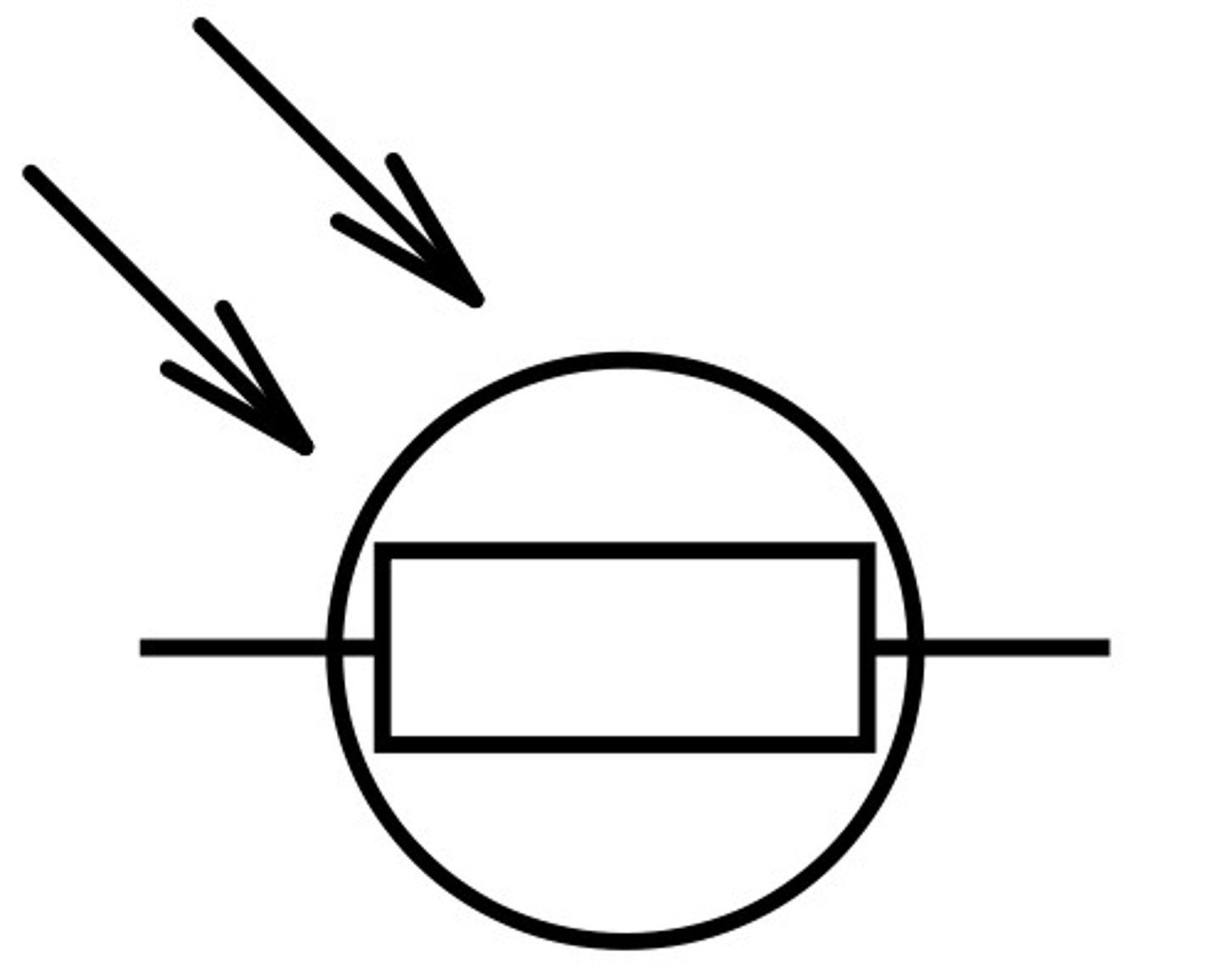
LDR
What is current?
rate of flow of charge around a circuit. Measured in amps
Current (A) =
Charge (C) / time (s)
Potential difference (V)
Work done (J) / Charge transferred (C)
What is potential difference?
Energy transferred per unit charge
Resistance (Ohms) =
Pd (V)/ current (A)
Thermistor
Resistance increases as temp decreases
Light dependent resistor
Resistance decreases as light intensity increases, less current with flow
What is potential difference?
Energy transferred or the work done per unit charge.
pd = energy/charge
Volts
What is current?
Rate of flow of charge.
Current = Charge/time
Amps
What is resistance?
Ratio of pd to current.
Resistance = p.d/current
Ohms
Rules in a series circuit
Total resistance - adds up
Current - stays the same
Pd - is shared
Rules in a parallel circuit
Total resistance - gets less with more branches, its always less than the smallest register.
Current - shared between branches
Pd - same across branches
What are LDRs?
Light dependant resistors, resistors that values depend on conditions. When light intensity increases, resistance of LDR decreases.
What are Thermistors?
Resistors whose values depend on conditions. Temp increases, resistance of thermistor decreases.
V = IR
pd = current x resistance
Resistance
Current is directly proportional to p.d. This relationship is called ohm's law. Resistance of resistor is fixed and does not change.
Filament bulb
As p.d increases, so does the temp of filament. Higher temp increases vibrations of ion in filament, makes it harder for electrons to get past- resistance increases. Current goes up, temp goes up.
Diode
current only flows in 1 directions. Resistance is very large at low pd but at higher pd, the resistance drops & current begins to flow.
Resistor
Current through an ohmic conductor (at constant temp) is directly proportional to pd across the resistor. This means that the resistance remains constant as the current changes.
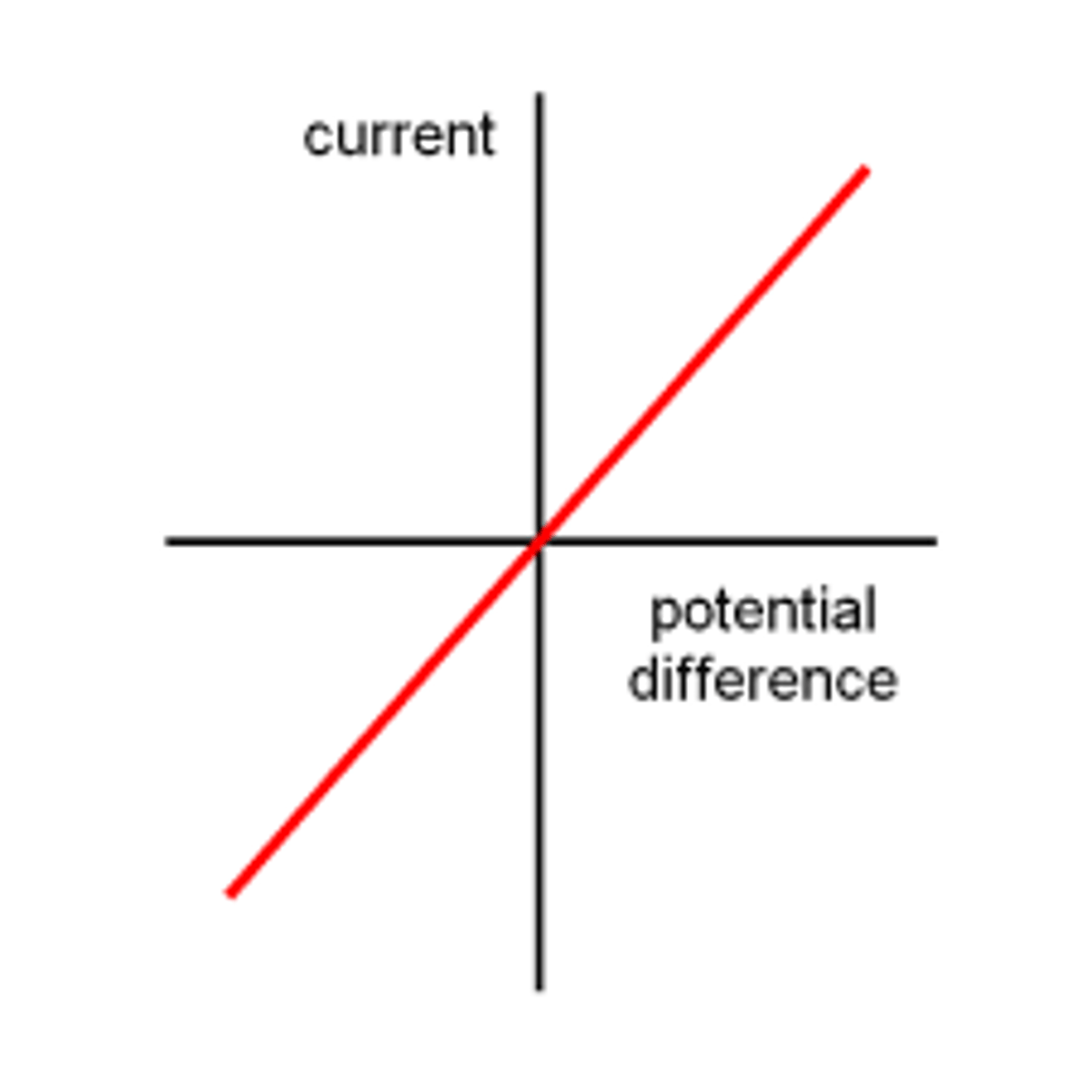
Filament lamp/bulb
The resistance of a filament lamp increases as the temperature of the filament increases.
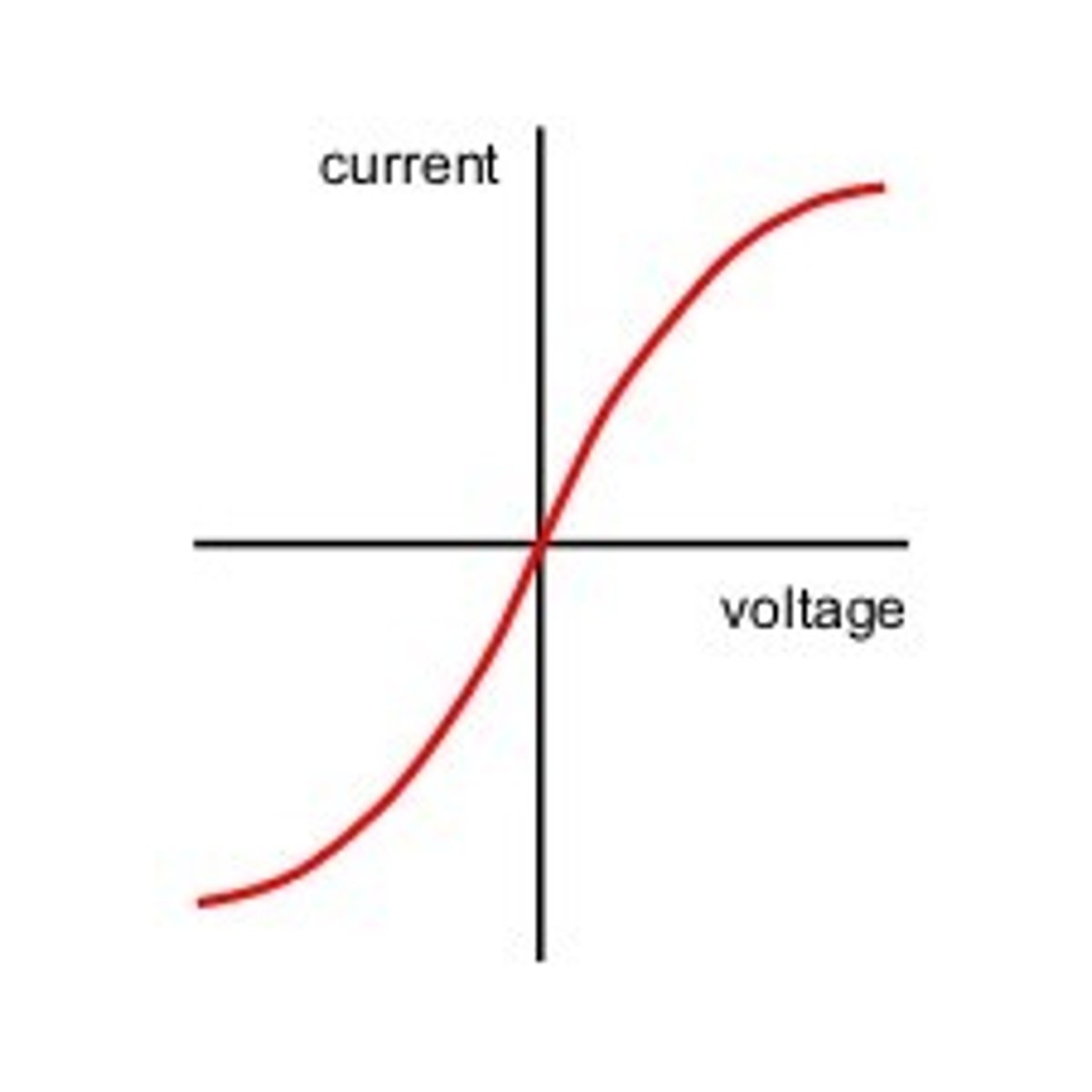
Diode
The current through a diode flows in one direction only. The diode has a very high resistance in the reverse direction.
Direct Current (DC)
Electric current that flows in only one direction, positive or negative. From a cell or battery.
Alternating Current (AC)
A flow of electric charge that regularly reverses its direction; changing constantly. From plugs and sockets.
What is the UK domestic supply?
230 V (DC), has a frequency of 50 Hz.
Calculating frequency of AC electrical supply
Frequency (hz) = 1/ time (s)
Example of calculating frequency of AC electrical supply
Y- gain = 0.2V/cm
Time base = 20ms/cm
20ms = 0.02 s
Wave = 4 squares high
4 x 0.02 = 0.08s
f = 1/0.08
f = 12.5 Hz
Increasing pd on the AC source =
new peak P.d will be higher
AC on an oscilloscope:
- Adjusting pd, increase/decrease no. of waves.
- Time base can change no. of cycles/waves that appear
- Connecting battery pack to oscilloscope, horizontal line as trace.
- Reversing connections from battery pack, line goes to other side of x-axis
What is half-wave retification?
Of an AC supply, where a diode is used to stop current flowing in 1 direction
Plugs
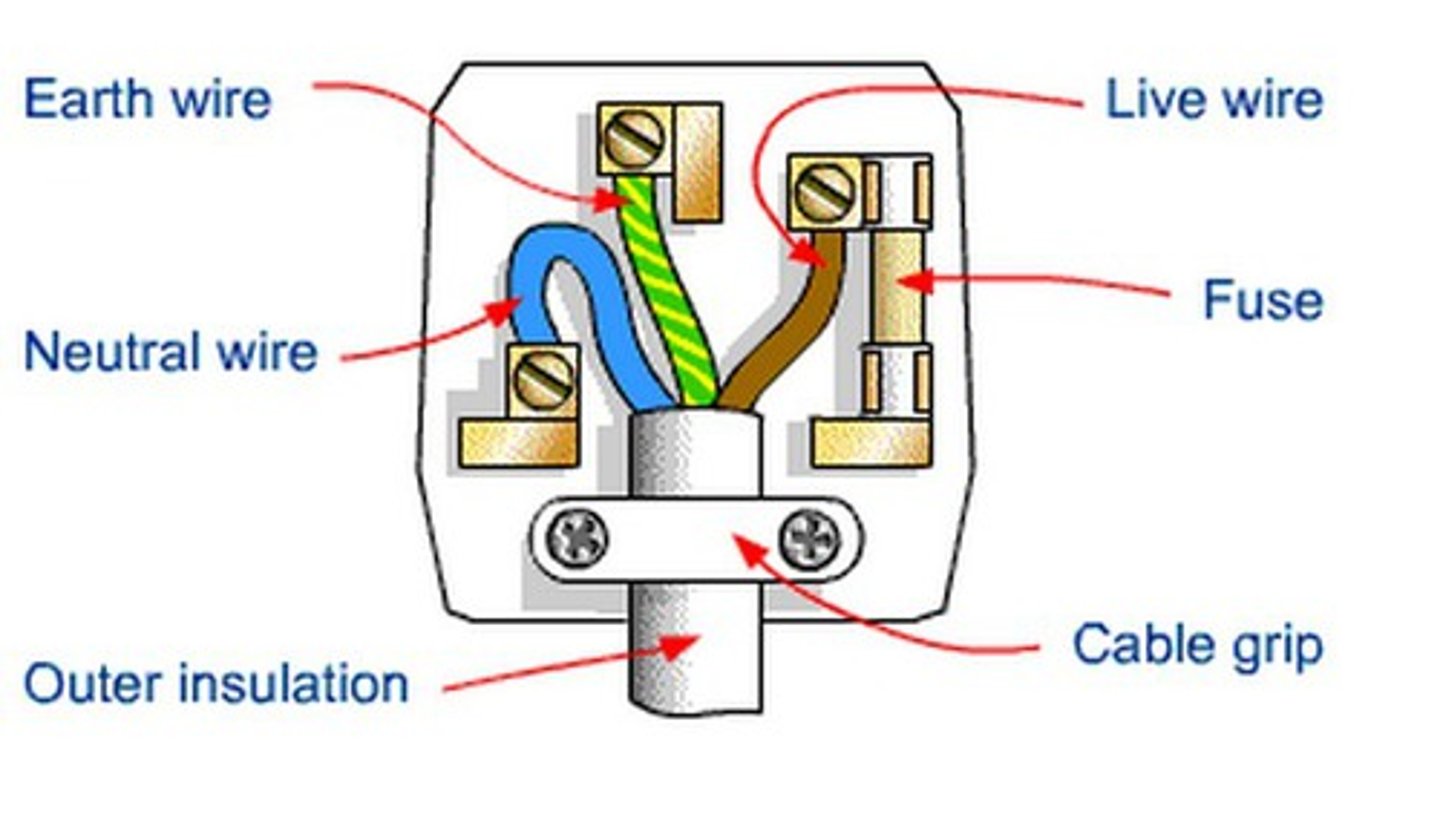
Earth wire
green & yellow wire, prevents casing becoming live, at 0V. The earth pin is longer then the other 2 pins bc it uncovers live and neutral sockets.
Fuse
melts if too much current flows
Neutral wire
Completes the circuit, close to 0V, blue wire, bottom left
Live wire
Brown wire, bottom right, alternates between +325V and -325V.
Cable grip
grips outer cable
How earth wires work
Creates safe route for current to flow through if live wire becomes loose & touches the casing.
Electrical shock if live wire came loose and touched the metal casing, there will be a large pd.
Earth wire connected to metal casing so current goes through earth wire instead. Strong current surges through earth wire bc it has low resistance, this breaks fuse & disconnects appliance
Double insulation
Some appliances like straighteners don't have an earth wire, this is bc they have plastic casing, or live wire can't touch casing. Casing can't give an electric shock, even if wires are loose.
Double insulation - case & cable are insulated.
Why is the case of a plug made of stiff plastic?
For electrical insulation to prevent electric shock, to give plug stability.
Why should the pins of a plug be made of hard material?
To prevent them from getting deformed, resistant to corrosion
Why is brass used to make the pins of a plug?
It's resistant to corrosion, stronger than copper, so less likely to get deformed.
Why are electric cables made of copper?
It has a good electrical conductivity, easier to install
Why is the outside of electric cables made of plastic?
To prevent electric shocks
What is energy?
measure of no. of electrons passing through an electric appliance every second
Power supplied (W) =
Current (A) x P.d (V)
P.d (V) =
Current (A) x Resistance (Ohms)
Power (W) =
Current^2 (A) x Resistance (Ohms)
Energy (j) =
Power (W) x time (s)
What are kilowatt hours?
Amount of energy transferred when a 1kW device is used for 1 hour.
1 kW into joules
1000W into joules
1000 x 60(minutes) = 60,000
60,000 x 60 (seconds) = 36,00,000J
What is the National Grid?
system of cables and transformers linking power stations to consumers.
What are step-up transformers?
Used to increase P.d from the power station to the transmission cables then step-down transformers are used to decrease p.d, to a much lower value, the pd for domestic use.
Two actions performed by a step-up transformer:
Increases voltage and decreases current. If current is too high, it produces heat, thermal energy lost -> efficiency is less.
Two actions performed by a step-down transformer:
Decreases voltage and increases current. For safety.
Why is it beneficial to transmit electricity through cables to out homes at a high P.d?
High p.d means low current, so less thermal energy losses.