AP Micro / Elasticity
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What does elasticity measure in economics?
Elasticity measures how much the quantity demanded or supplied of a good responds to changes in price or income.
What is Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)?
PED measures how sensitive the quantity demanded is to a change in price.
What happens to quantity demanded when the price decreases for elastic goods?
Quantity demanded increases significantly when price decreases.
What happens to quantity demanded when the price decreases for inelastic goods?
Quantity demanded increases very little.
What are the general characteristics of inelastic goods?
Few substitutes
Necessities
Small portion of income
Required now, rather than later
Elasticity coefficient less than 1.
What is the distinction between the curvature of elastic and inelastic demand curves?
An elastic demand curve is relatively flat while an inelastic demand curve is steep.
What is the formula for Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand (XED)?
XED = (% change in quantity demanded of Product B) / (% change in price of Product A)
What does a positive (above 0) cross-price elasticity coefficient indicate between two goods?
A positive coefficient indicates a direct relationship, and that two goods are substitutes.
What does a negative (below 0) cross-price elasticity coefficient indicate between two goods?
A negative coefficient indicates an inverse relationship, and that two goods are complements.
What is Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)?
YED measures how sensitive the quantity demanded is to a change in income.
What does a positive income elasticity coefficient suggest about a good?
A positive income elasticity coefficient suggests that the good is normal.
What does a negative income elasticity coefficient suggest about a good?
A negative income elasticity coefficient suggests that the good is inferior.
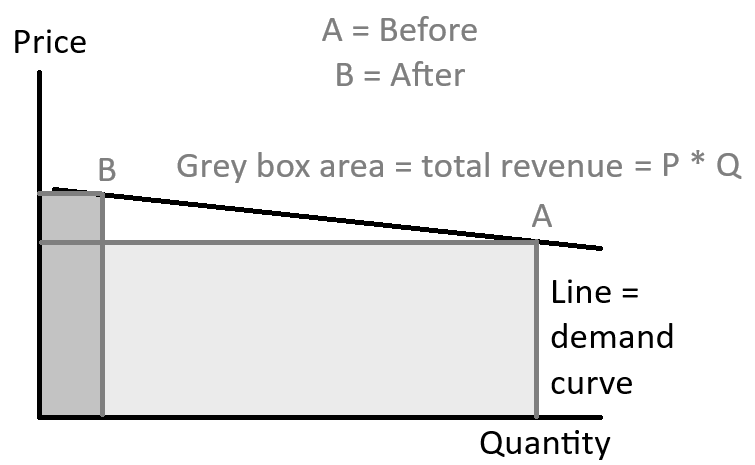
What occurs to total revenue when demand is elastic and the price increases?
When demand is elastic, an increase in price causes total revenue to decrease.
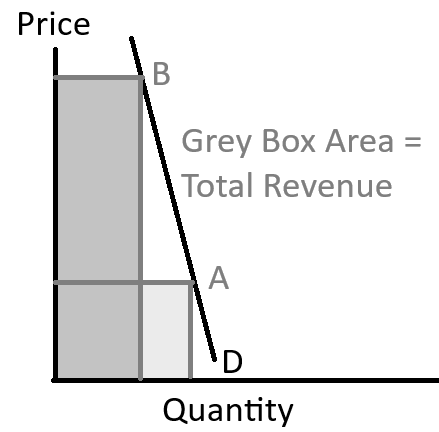
How does an increase in price affect total revenue with inelastic demand?
With inelastic demand, an increase in price causes total revenue to increase.
What does 'unit elastic' mean regarding elasticity?
Unit elastic means that the percent change in quantity demanded equals the percent change in price, resulting in an elasticity coefficient of 1.
What is the effect of time on Price Elasticity of Supply?
Over time, supply often becomes more elastic as producers can adjust their production levels.
What is an example of a perfectly inelastic good (used often in the medical field)?
An example of a perfectly inelastic good is insulin for diabetics, which has a coefficient of 0.
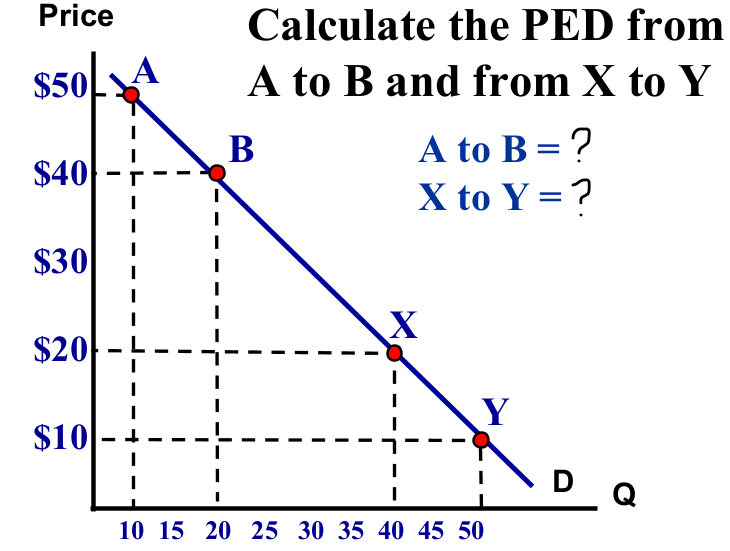
What is the price elasticity of A to B, and X to Y? Which part is more elastic, and how do you know?
The price elasticity from A to B is -5, while from X to Y it’s -0.5. The segment A to B is more elastic because it has a greater absolute value of elasticity.
The equation for price elasticity of demand (PED) of a good
(% change in quantity demanded) / (% change in price)
If % change in quantity > % change in price, then the elasticity coefficient is ﹍ and it’s called ﹍.
>1, elastic demand
If % change in quantity = % change in price, then the elasticity coefficient is ﹍ and it’s called ﹍.
1, unit elastic demand
If % change in quantity < % change in price, then the elasticity coefficient is ﹍ and it’s called ﹍.
<1, inelastic demand
What do you call the elasticity of a good if the coefficient is much greater than 1, or much less than 1?
Very elastic or very inelastic
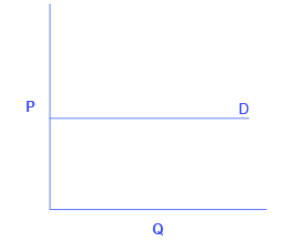
What elasticity does this graph show?
Infinitely/perfectly elastic
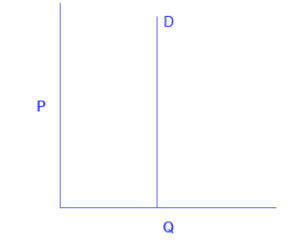
What elasticity does this graph show?
Zero/perfectly inelastic
How do you calculate % change?
(New - Old) / Old
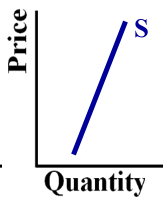
What elasticity does this graph show?
Inelastic
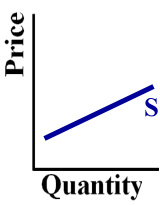
What elasticity does this graph show?
Elastic
What’s the elasticity coefficient of a perfectly inelastic demand and a perfectly elastic demand?
0, ∞
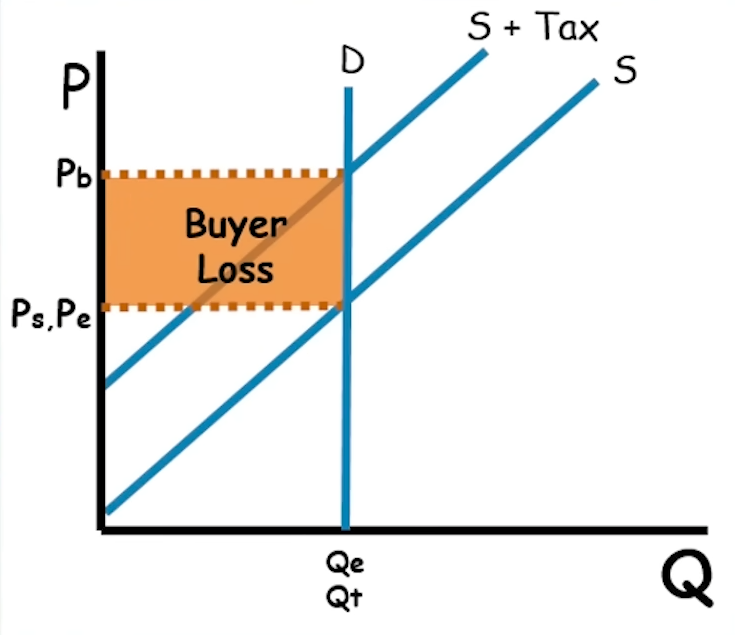
When the demand curve is more elastic than the supply curve, do the buyers or the sellers take on more of the burden of an excise tax?
The sellers take on more burden.
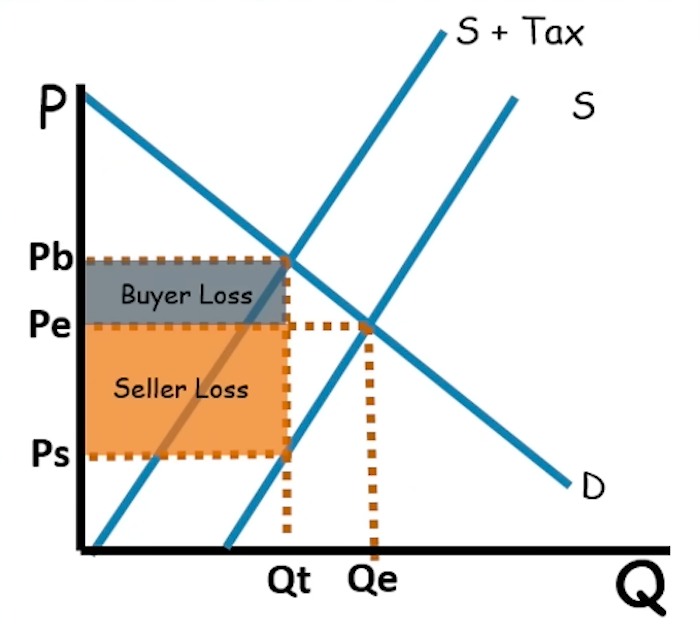
When the supply curve is more elastic than the demand curve, do the buyers or the sellers take on more of the burden of an excise tax?
The buyers take on more burden.
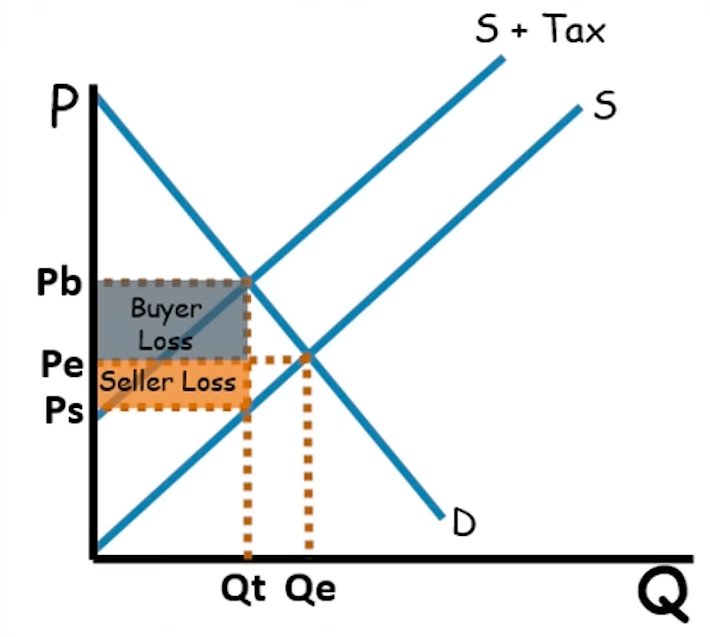
If the supply curve is perfectly elastic, do the buyers or sellers take on more burden of an excise tax?
The buyers take on ALL the burden.
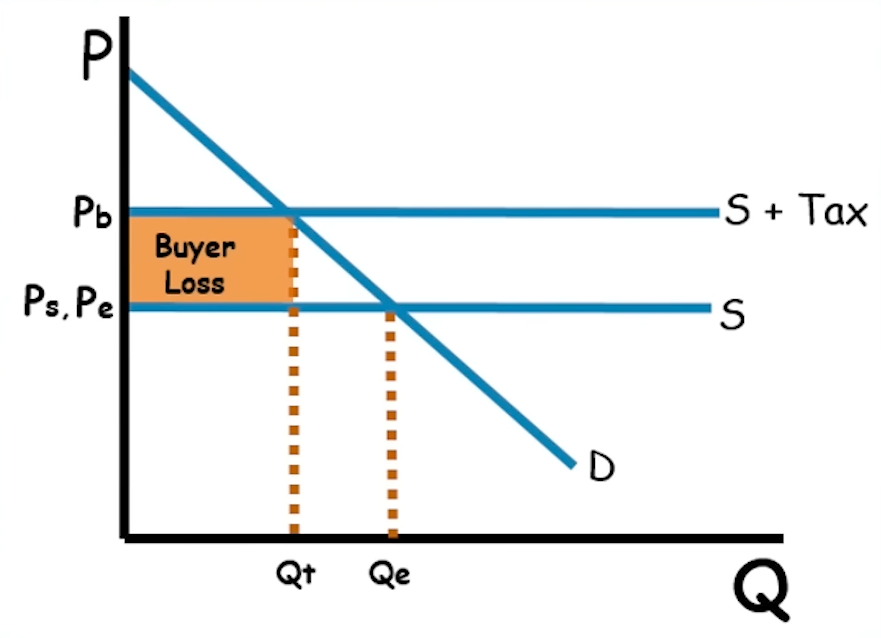
If the demand curve is perfectly inelastic, do the buyers or sellers take on more burden of an excise tax?
The buyers take on ALL the burden.