Cell Bio Lecture 3
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Alanine
Ala A
Arginine
Arg R
Asparagine
Asn N
Aspartate
Asp D
Cysteine
Cys C
Glutamate
Glu E
Glutamine
Gln Q
Glycine
Gly G
Histidine
His H
Isoleucine
lle I
Leucine
Leu L
Lysine
Lys K
Methionine
Met M
Phenylalanine
Phe F
Proline
Pro P
Serine
Ser S
Threonine
Thr T
Tryptophan
Trp W
Tyrosine
Tyr Y
Valine
Val V
D vs L Amino Acids
Proteins are composed almost exclusively of L-amino acids
D- vs L- refers to the stereochemistry (orientation) around the α-carbon, NOT the amino acid identity
Aspartate (Asp) vs Leucine (Leu) = different amino acids
D vs L = mirror-image forms of the SAME amino acid
Important Notes:
L-amino acids → used in ribosomally synthesized proteins
Some D-amino acids have biological functions, but are NOT incorporated into human proteins
Examples:
Bacterial cell walls (peptidoglycan)
Neurotransmission/modulation (rare in humans)
Exam Tip 🧠:
If the question is about protein structure or synthesis → choose L-amino acids
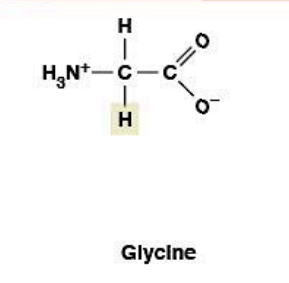
Glycine
(Gly, G) Nonpolar, hydrophobic
R-group: -H (just hydrogen - simplest/smallest amino acid)
Achiral (only amino acid without chirality - has 2 H's on α-carbon, no stereoisomer)
Provides extreme flexibility in protein
Helix breaker - too flexible, lacks side chain for stability
Found at tight turns and loops in proteins
Inhibitory neurotransmitter in CNS
Precursor for heme and purine biosynthesis
Small size + flexibility allow extreme conformational freedom
Enriched in collagen (allows tight packing at center)
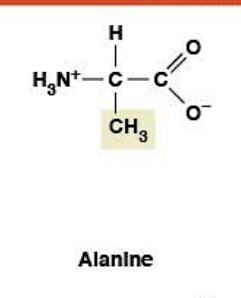
Alanine
(Ala, A)Nonpolar, hydrophobic
R-group: -CH₃ (methyl - smallest side chain after glycine)
Chiral (unlike glycine)
Slightly more bulk → favors α-helices (provides stability)
Precursor for pyruvate (energy production)
Found in extraterrestrial samples
Key difference: Glycine = flexibility (turns); Alanine = stability (helices)
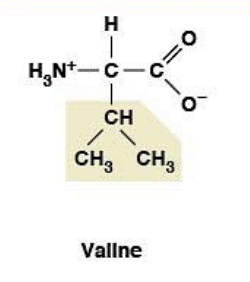
Valine
(Val, V) Nonpolar, hydrophobic
R-group: Branched aliphatic (isopropyl)
Essential amino acid (must come from diet)
BCAA (branched-chain amino acid)
Glucogenic (converts to glucose)
Stabilizes hydrophobic cores
Muscle protein synthesis
Promotes glucose uptake by muscles
Energy production during prolonged exercise
Prevents muscle wasting
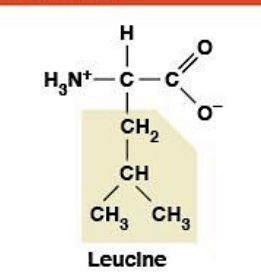
Leucine
(Leu, L) Nonpolar, hydrophobic
R-group: Branched aliphatic (isobutyl)
Essential amino acid (must come from diet)
BCAA (branched-chain amino acid)
Coded by 6 codons (most redundant)
Activates mTOR pathway (muscle growth, autophagy)
Can convert to ketone bodies (ketogenic)
Especially stimulates muscle protein synthesis (key BCAA player)
Used in athletic supplements for performance
Isoleucine
R-group: Branched aliphatic (sec-butyl)
Essential amino acid (must come from diet)
BCAA (branched-chain amino acid)
Dual metabolic role: Glucogenic AND ketogenic (unique!)
Promotes glucose uptake by muscles
Helps maintain blood sugar levels
Energy production during prolonged exercise

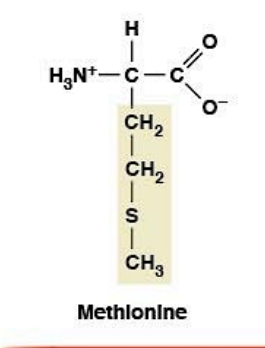
Methionine
Nonpolar, hydrophobic
R-group: -CH₂-CH₂-S-CH₃ (thioether - contains sulfur)
Essential amino acid (must come from diet)
START codon (AUG) for protein synthesis (every protein begins with Met)
Sulfur is polarizable → adaptable interactions
Reversibly oxidized → protective buffer during oxidative stress
Precursor for SAM (S-adenosylmethionine) - main methyl donor in biology
Methylation of DNA, epigenetic regulation
Soft and polarizable sulfur gives flexibility
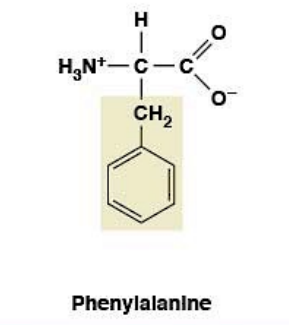
Phenylalanine
Nonpolar, hydrophobic
R-group: Benzyl (benzene ring)
Essential amino acid (must come from diet)
Large, bulky, hydrophobic
Precursor for tyrosine
Protein-protein interactions
Aromatic ring allows π-π stacking
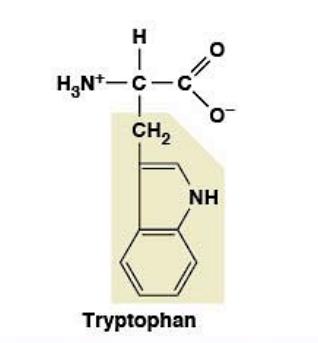
Tryptophan
Nonpolar, hydrophobic
R-group: Indole (largest aromatic side chain)
Essential amino acid (must come from diet)
Bulkiest amino acid of all 20
Precursor for serotonin (mood, sleep)
Precursor for niacin (Vitamin B3)
Pellagra disease (deficiency): 4 D's - Dermatitis, Diarrhea, Dementia, Death
Pathway: Tryptophan → Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Historical: Early 1900s American South - corn-based diets low in tryptophan
Corn's niacin is bound (unavailable)
Lesson: Essential amino acids = public health issue
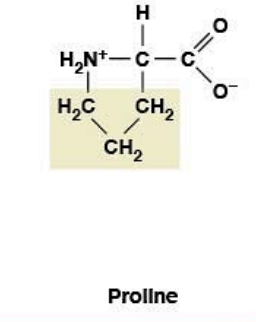
Proline
Nonpolar, hydrophobic
R-group: Cyclic (forms ring back to backbone nitrogen)
α-helix breaker - too rigid, lacks H-bond donor for helix backbone
Restricts phi (φ) rotation - locked position, limits flexibility
Creates rigid kinks in protein structure
Enriched in collagen (provides rigidity)
Can be hydroxylated to hydroxyproline (requires Vitamin C)
Vitamin C deficiency → scurvy (defective collagen)
Cannot be in membrane-spanning helix (breaks helix structure)
Opposite of glycine: rigid vs flexible
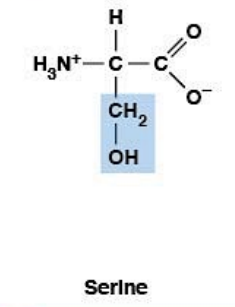
Serine
Polar, uncharged HYDROPHILIC
R-group: -CH₂-OH (hydroxyl)
Small, polar, hydrophilic
Phosphorylation site (Ser-OH → Ser-OPO₃²⁻)
Important in cell signaling cascades
Precursor for glycine and cysteine
Part of "Phosphorylation Trio" (S, T, Y)
Post-translational modification site
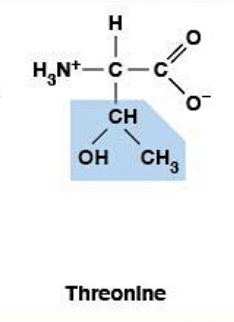
Threonine
Polar, uncharged HYDROPHILIC
R-group: -CH(OH)-CH₃ (secondary alcohol)
Essential amino acid (must come from diet)
Phosphorylation site
Has 2 chiral centers (α-carbon + β-carbon)
Part of "Phosphorylation Trio" (S, T, Y)
Post-translational modification site
Cell signaling regulation
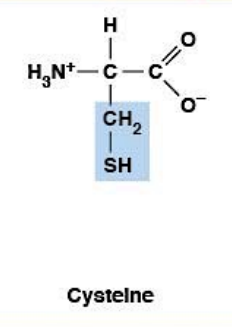
Cysteine
Polar, uncharged HYDROPHILIC
R-group: -CH₂-SH (thiol/sulfhydryl)
Forms disulfide bonds (Cys-S-S-Cys)
Ionizable side chain: pKa ~8.3
At pH 7.4: mostly protonated (free -SH form)
CRITICAL DISTINCTION - Cysteine vs Cystine:
Cysteine: Reduced form (free -SH)
Cystine: Oxidized form (two cysteines linked by -S-S-)
NOT two different amino acids - just redox states
Context trap - Cellular Environment:
Inside cell (cytoplasm): Reducing → favors cysteine (free -SH)
Outside cell/ER lumen: Oxidizing → favors cystine (disulfide bonds)
Disulfide bonds stabilize protein structure (especially extracellular proteins)
Most disulfides form in ER lumen or outside cell
Can break/reform during folding and stress
Hair perm: breaks and reforms disulfides to hold curls
Exam hints:
Oxidation → cystine formation
Protein stability → disulfide bonds
Extracellular protein → assume cystine present
Redox chemistry/metal binding → cysteine
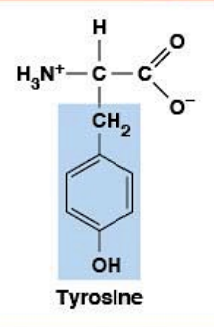
Tyrosine
Polar (aromatic) HYDROPHILIC
R-group: Phenolic (benzene-OH)
Aromatic AND polar (both categories)
Phosphorylation site (receptor tyrosine kinases - RTKs)
Ionizable side chain: pKa ~10.1 (phenol)
At pH 7.4: mostly uncharged (pH < pKa)
Can be hydroxylated
Precursor for neurotransmitters: dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine
Precursor for thyroid hormones (T3, T4)
Part of "Phosphorylation Trio" (S, T, Y)
Critical for cell signaling (kinase cascades)
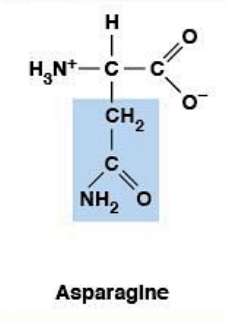
Asparagine
Polar, uncharged HYDROPHILIC
R-group: -CH₂-CONH₂ (amide)
Polar, neutral at all physiological pH
Can form hydrogen bonds
Similar to Asp but uncharged (amide vs carboxyl)
The amide group prevents ionization
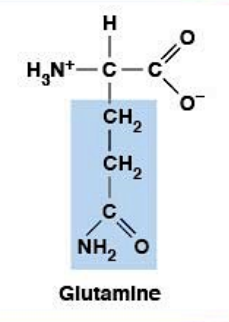
Glutamine
Polar, uncharged HYDROPHILIC
R-group: -CH₂-CH₂-CONH₂ (amide - one more CH₂ than Asn)
Polar, neutral at all physiological pH
Important in rapidly dividing cells (including cancer)
Used in protein synthesis
Enhances fuel metabolism (provides TCA cycle components)
Provides nitrogens for nucleotide synthesis (RNA/DNA)
Similar to Glu but uncharged (amide vs carboxyl)
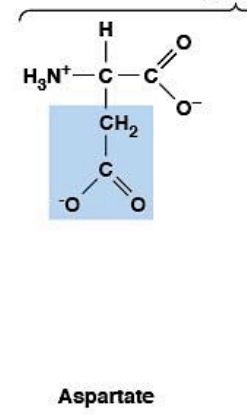
Aspartate
Polar, charged, HYDROPHILIC
Negatively charged (at pH 7.4)
R-group: -CH₂-COO⁻ (carboxylic acid - shorter than Glu)
Ionizable side chain: pKa ~3.9
At pH 7.4: negatively charged (pH > pKa → deprotonated)
Forms salt bridges with Lys, Arg, His
Maintains charge balance in proteins
Enables electrostatic interactions
Central to metabolic pathways (amino acid metabolism)
Hydrophilic - found on protein surfaces
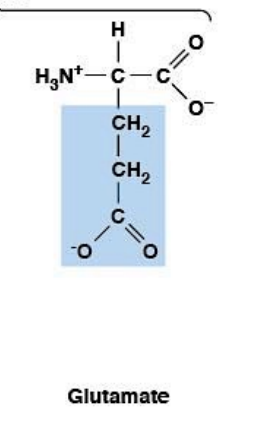
Glutamate
Polar, charged, HYDROPHILIC
Negatively charged (at pH 7.4)
R-group: -CH₂-CH₂-COO⁻ (carboxylic acid - one more CH₂ than Asp)
Ionizable side chain: pKa ~4.3
At pH 7.4: negatively charged (pH > pKa → deprotonated)
Forms salt bridges with Lys, Arg, His
Key player in amino acid metabolism
Neurotransmitter (excitatory in CNS)
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) enhances umami flavor
Umami = one of five basic tastes (sweet, sour, bitter, salty, umami)
Japanese word for "deliciousness" - savory taste in soy sauce, cheese, meats
Sickle cell anemia: Glu → Val mutation at position 6 of hemoglobin β-chain
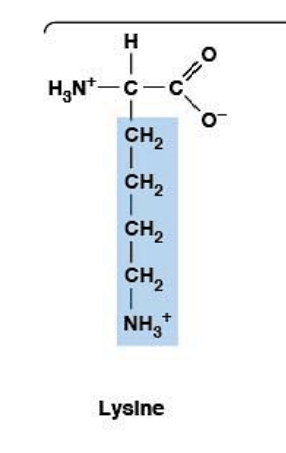
Lysine
Polar, charged, HYDROPHILIC
R-group: -(CH₂)₄-NH₃⁺ (long chain ending in amino group)
Essential amino acid (must come from diet)
Ionizable side chain: pKa ~10.5
At pH 7.4: positively charged (pH < pKa → protonated)
Interacts with negatively charged molecules (DNA, phosphates)
Forms salt bridges with Asp and Glu
Deficiency linked to increased stress and anxiety
Important for physical and mental health
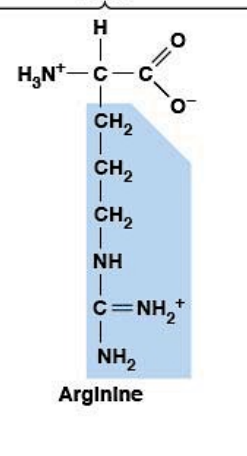
Arginine
Polar, charged, HYDROPHILIC
Positively charged (at pH 7.4)
R-group: Guanidinium group (very basic)
Ionizable side chain: pKa ~12.5 (highest pKa of all amino acids)
At pH 7.4: very positively charged (pH < pKa → protonated)
More basic and more positively charged than lysine
Effective at binding negatively charged molecules/ions
Forms salt bridges with Asp and Glu
Precursor for nitric oxide (NO) - vascular health, immune function
Remains charged across nearly all physiological pH ranges
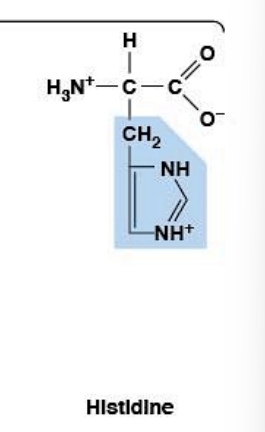
Histidine
Polar, charged, HYDROPHILIC
R-group: Imidazole ring (aromatic)
Ionizable side chain: pKa ~6.0 ⭐ MOST IMPORTANT
Uniquely close to physiological pH (7.4)
At pH 7.4: can be charged (+) or neutral depending on microenvironment
"The exam question amino acid"
"Swiss Army knife of catalysis"
Why Histidine is Special:
Lives on the edge of protonation at physiological pH
Tiny environmental shifts change its charge state
Can both donate AND accept protons (amphoteric)
Workhorse for general acid/base catalysis
Pivot point that shuttles protons around
Used in hemoglobin (Bohr effect - adjusts protonation to tune O₂ affinity)
Ideal for metal binding (Zn²⁺, Cu²⁺ coordination spheres)
Found in active sites of many enzymes
Precursor for histamine (immune response, allergies)
Occasionally used in phosphorylation pathways
Ideal pKa for catalytic residue: Around physiological pH (~6-7) - Histidine is perfect
How pH Affects Amino Acid Side-Chain Ionization
pH determines the protonation state of ionizable side chains
Ionizable amino acids: D, E, R, K, H, C, Y, S, T
Each ionizable group has a pKa
pH < pKa → protonated
pH > pKa → deprotonated
Key Concepts:
Titration curve shows stepwise loss of protons as pH increases
Plateaus = buffering regions (near pKa values)
Isoelectric point (pI):
pH where net charge = 0
Occurs between pKa values surrounding the neutral species
Charge Trends:
Acidic side chains (D, E):
Low pH → neutral
High pH → negative
Basic side chains (K, R, H):
Low pH → positive
High pH → neutral
Exam Tip 🧠:
Compare pH to pKa to predict charge — don’t memorize charge blindly
SUMMARY TABLE - ALL IONIZABLE GROUPS
Amino Acid | Side Chain | Side Chain pKa | Charge at pH 7.4 | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Asp (D) | β-Carboxyl | 3.65 | Negative (-) | Acidic |
Glu (E) | γ-Carboxyl | 4.25 | Negative (-) | Acidic |
His (H) | Imidazole | 6.00 ⭐ | +/Neutral (toggles) | Basic |
Cys (C) | Thiol | 8.00-8.30 | Neutral (mostly) | Weakly acidic |
Tyr (Y) | Phenol | 10.07 | Neutral | Weakly acidic |
Lys (K) | ε-Amino | 10.53 | Positive (+) | Basic |
Arg (R) | Guanidinium | 12.48 | Positive (+) | Basic |
Ser (S) | Hydroxyl | ~13-14 | Neutral (no ionization) | NOT ionizable* |
Thr (T) | Hydroxyl | ~13-14 | Neutral (no ionization) | NOT ionizable* |
*Ser and Thr hydroxyls have pKas so high (~13-14) that they do NOT ionize at any physiologically relevant pH
Essential amino acids VS Non essential amino acid
Essential amino acids cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through diet, while nonessential amino acids are produced internally. The 9 essential amino acids are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Nonessential amino acids include alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine.
Essential Amino Acids (Must be consumed):
Histidine
Isoleucine
Leucine
Lysine
Methionine
Phenylalanine
Threonine
Tryptophan
Valine
Nonessential Amino Acids (Produced by the body):
Alanine
Asparagine
Aspartic acid
Glutamic acid
Serine
Conditionally Essential Amino Acids:
These are typically nonessential, but become necessary during illness, stress, or intense training:
Arginine
Cysteine
Glutamine
Tyrosine
Glycine
Proline
Ornithine