Praxis 5001 (Reading) (186 Questions and answers with diagrams ) 2025-2026
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
alphabetic principle
an understanding that letters and letter patterns represent the sounds of spoken words.

phonics
teaching reading by training beginners to associate letters with their sound values
声学

pragmatics
the study of language use such matters as deixis, taking turns in conversation, text organization, presupposition, and implicature.
语用学
fast mapping
The process by which children map a word onto an underlying concept after only one exposure to the word.

morpheme division
study of word formation and structure of words - dividing syllables
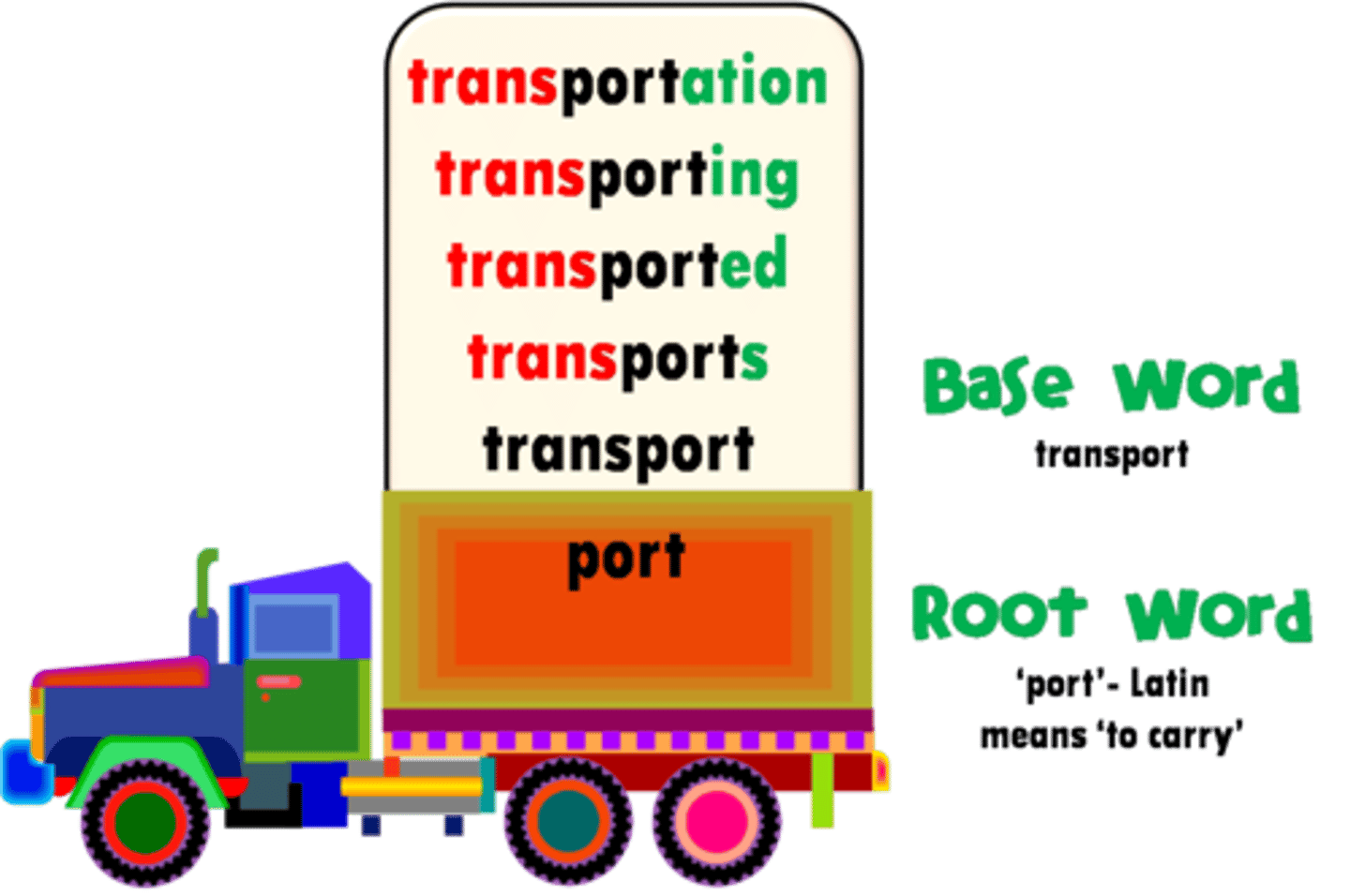
phonic construction
The putting together of the sounds to make the whole word

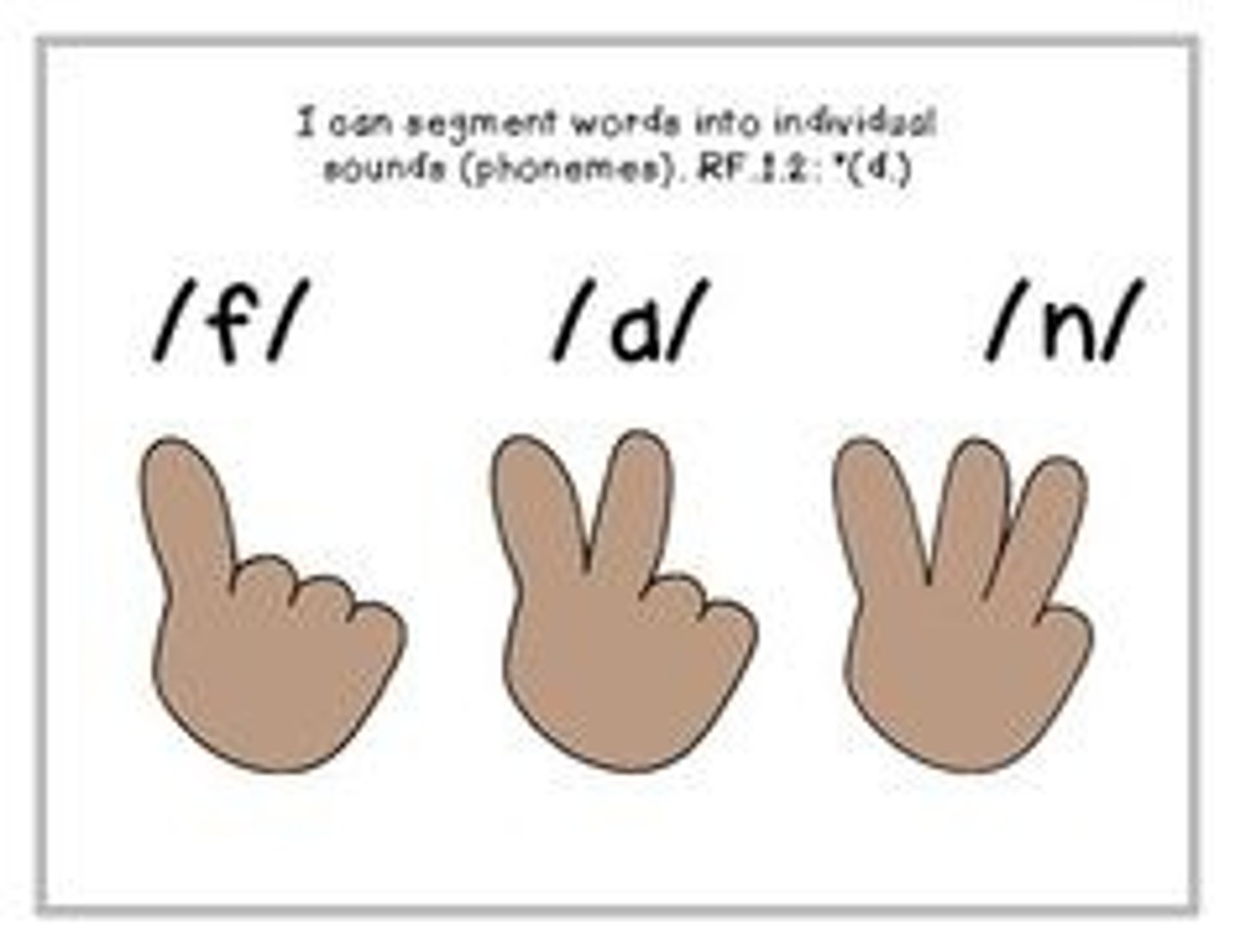
phonemic segmentation
ability to break word down into basic sound units.
syllabication
forming or dividing words into syllables

habituation
a general accommodation to unchanging environmental conditions
习惯化
underextension
occur when a child incorrectly uses a word to describe a narrower set of objects or actions than it is meant to
telegraphic speech
early speech stage in which a child speaks like a telegram--'go car'--using mostly nouns and verbs and omitting 'auxiliary' words

dipthong
a speech sound that consists of either two vowels or a vowel and a semivowel contained in a single syllable ie snout; boy

affixes
parts added to the beginning (prefix) or end (suffix) of a root word to create new words.
etymology
the study of the sources and development of words
词源学

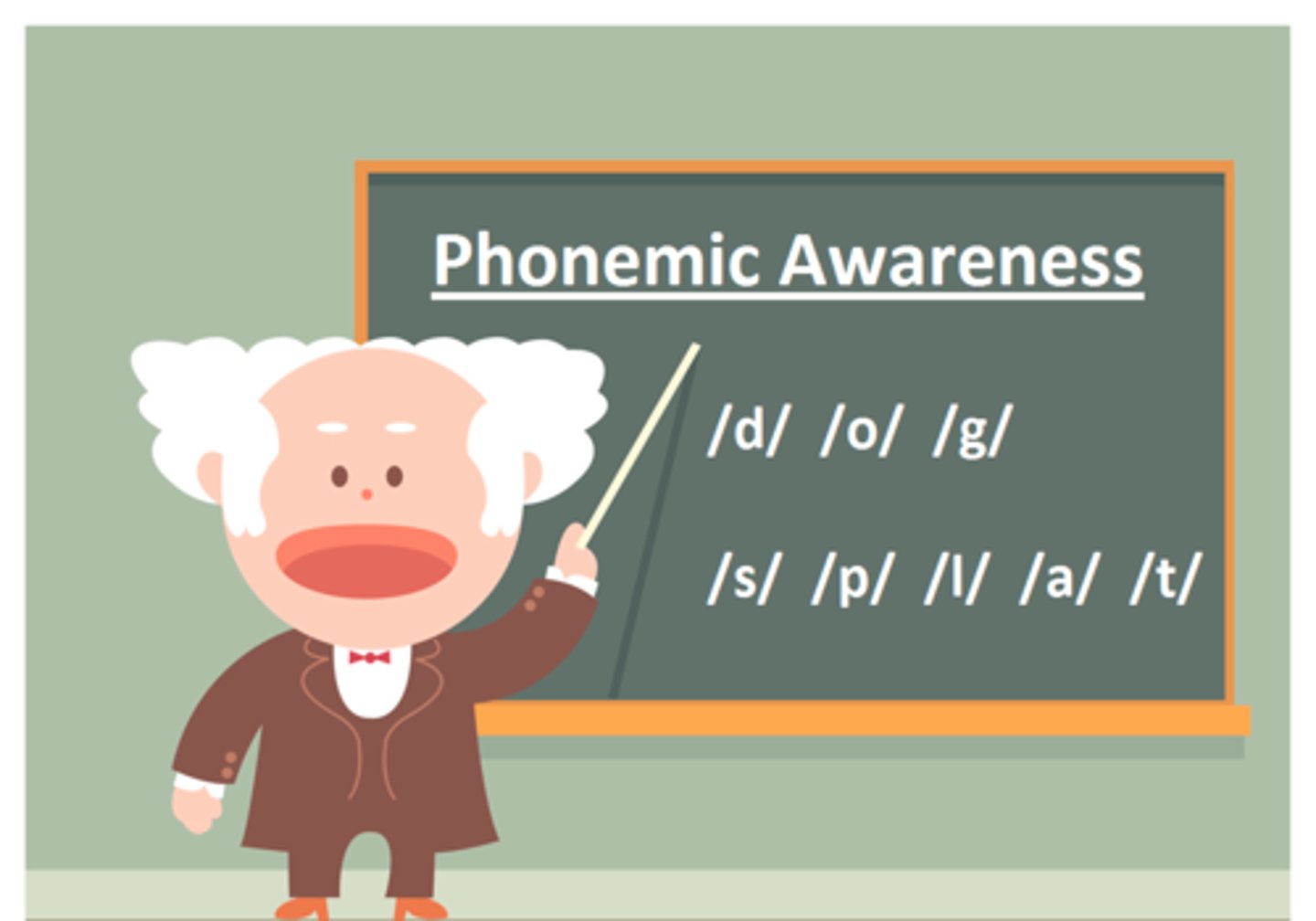
phonemic awareness
The ability to hear, identify,and manipulate the individual sounds, phonemes, in oral language.

oral vocabulary
Words that we use in speaking or recognize in listening

analytical skills
the ability to identify relevant issues, recognize their importance, understand the relationships between them, and perceive the underlying causes of a situation
分析能力

Pre-alphabetic phase
Not connecting the letters and sounds of the logo.

Early alphabetic phase
students recognize some letters of the alphabet and can use them together with context to remember words by sight.
Late alphabetic phase
readers possess extensive working knowledge of the graphophonemic system, and they can use this knowledge to analyze fully the connections between graphemes and phonemes in words. They can decode unfamiliar words and store fully analyzed sight words in memory.

Orthographic phase
Students are able to sound out familiar and unfamiliar words. Know letter sounds and read most common words automatically. At this point students are most able to enjoy and obtain knowledge from reading.

Semantics
the study of language meaning
语义学

Literal comprehension
refers to the understanding of information that is explicitly stated in a written passage. (main idea, sequence of events, knowlege of vocabulary)
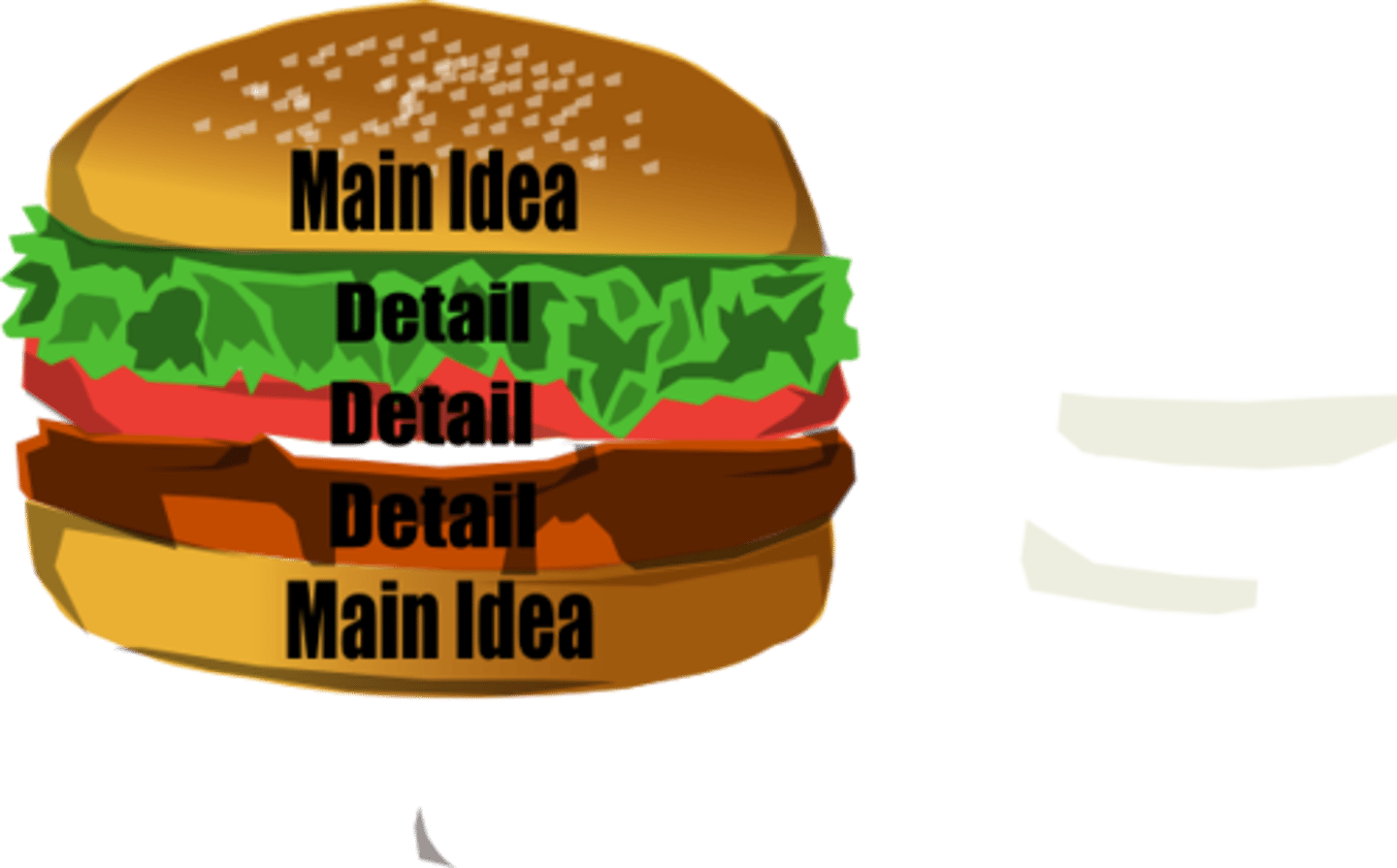
Critical comprehension
One of the highest levels of understanding. Requires readers to think beyond the printed page. Ex. indicating whether text is true or false, distinguishing between fact and opinion, detecting propaganda, judging whether the author is qualified to write the text, recognizing bias and fallacies, identifying stereotypes, making assumptions.

Metacognition
an explicit understanding of how learning works and an awareness of yourself as a learner. AKA Thinking about thinking.
元认知
syntactic clues
grammatical cues like word order, function words, and word endings

morphological rules
a set of rules that indicate how morphemes can be combined to form words

connotative meaning
The meaning suggested by the associations or emotions triggered by a word or phrase

blends
two letters that are pronounced together with each letter retaining it pronunciation (dr, bl, sm, rst)
onomatopoeia
using words that imitate the sound they denote
拟声
rhyming couplets
a pair of rhyming lines that usually have the same meter and length
internal rhyme
a rhyme between words in the same line

alliteration
use of the same consonant at the beginning of each stressed syllable in a line of verse
n. (诗歌的)头韵

satire
witty language used to convey insults or scorn
讽刺诗,讽刺文学:literary ridicule

paradox
a statement that at first seems to be absurd or self-contradictory but which may in fact turn out to be true
n.矛盾;似矛盾而正确的说法
悖论

metaphor
comparison not using like or as; Josh was a volcano ready to blow!
暗喻
n.隐喻,暗喻

simile
a figure of speech that expresses a resemblance between things of different kinds (usually formed with 'like' or 'as')
n.明喻

digressive
(of e.g. speech and writing) tending to depart from the main point or cover a wide range of subjects
a.离题的,枝节的
jargon
specialized technical terminology characteristic of a particular subject
行话
n.暗语;行话

anthropomorphic
attributing human characteristics or qualities to objects, animals, or gods
拟人化的

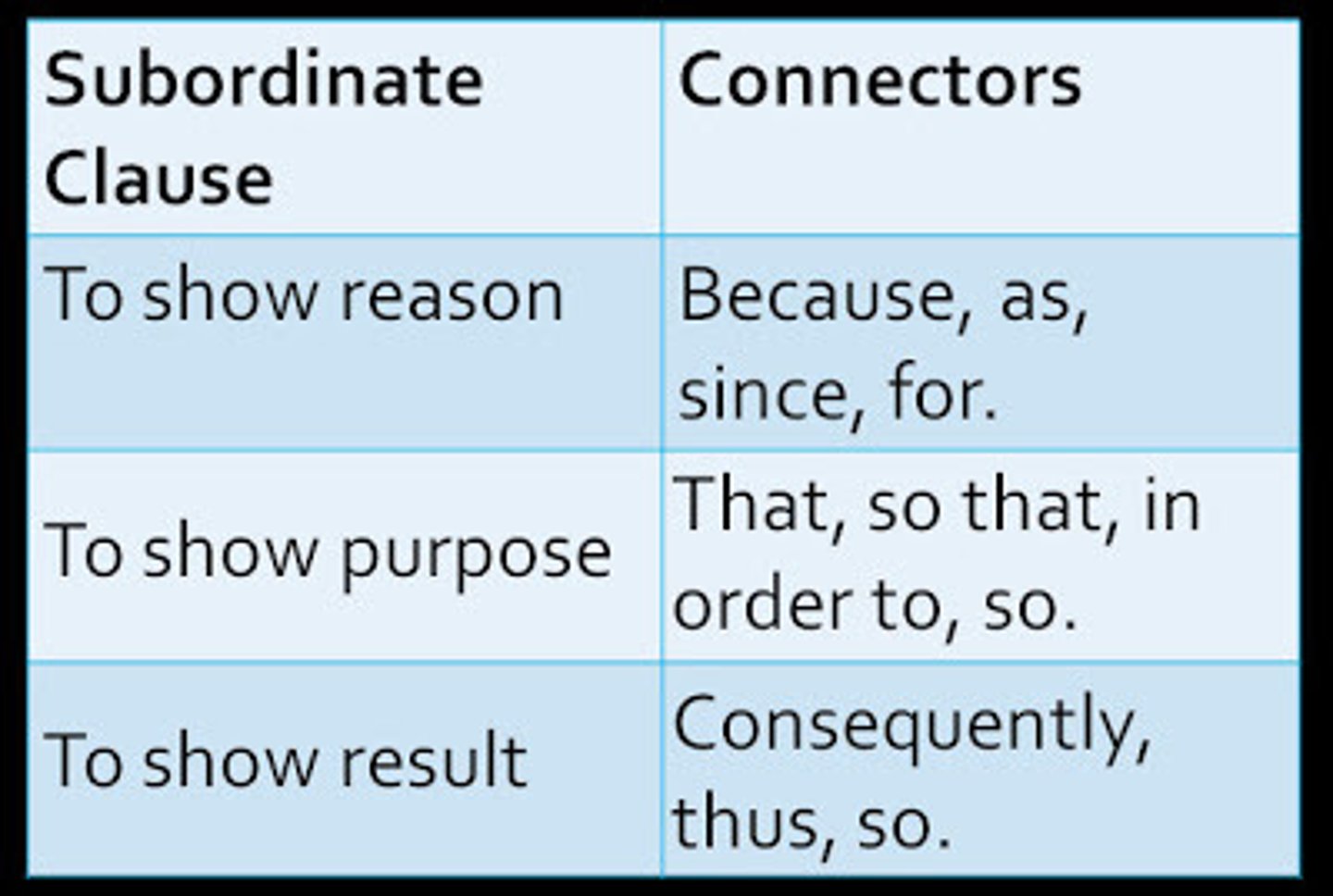
complex sentence
a sentence composed of at least one main clause and one subordinate clause
复合句

main clause
a clause in a complex sentence that can stand alone as a complete sentence
主句
subordinate clause
a clause in a complex sentence that cannot stand alone as a complete sentence and that functions within the sentence as a noun or adjective or adverb
从句
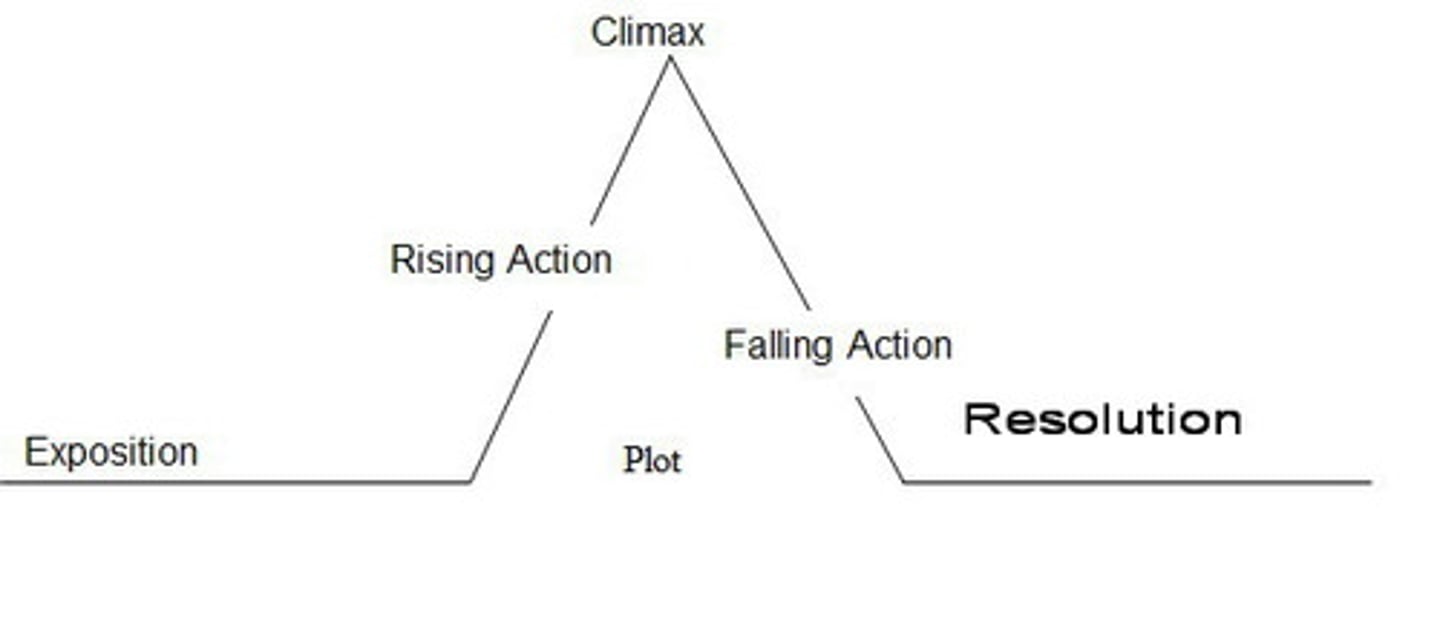
literary elements
The essential techniques used in literature (e.g., characterization, setting, plot, theme).
narrative tone
the basic sense of the story:
optimism: comedy, romance
pessimism: tragedy, irony
that comes from attachment: secure vs. insecure
and a sense of self: clearly defined vs. amorphous

Colloquial
characteristic of informal spoken language or conversation rather than formal speech or writing
口语的
MLA format
Stands for Modern Language Association--An accepted formatting for essays, in-text citations, and bibliographic information. It is a way to efficiently standardize formatting.

phrase structure
links all the parts together in a structure like that of a family tree. Example: The Noun Phrase Sidney Bechet combines with the Verb Phrase played the soprano, to get the sentence: Sidney Bechet played the soprano.
phonemes
Smallest units of sound in the human language, like consonants or vowels
head word
a word that had the same grammatical function as the phrase that has been built around it e.g. in a noun phrase, the head word is a noun
Analytical
using or skilled in using analysis (i.e., separating a whole--intellectual or substantial--into its elemental parts or basic principles);
intending to understand the nature of something
a.分析的,解析的

Expository
explanatory; serving to explain; N. exposition: explaining; exhibition
解释的

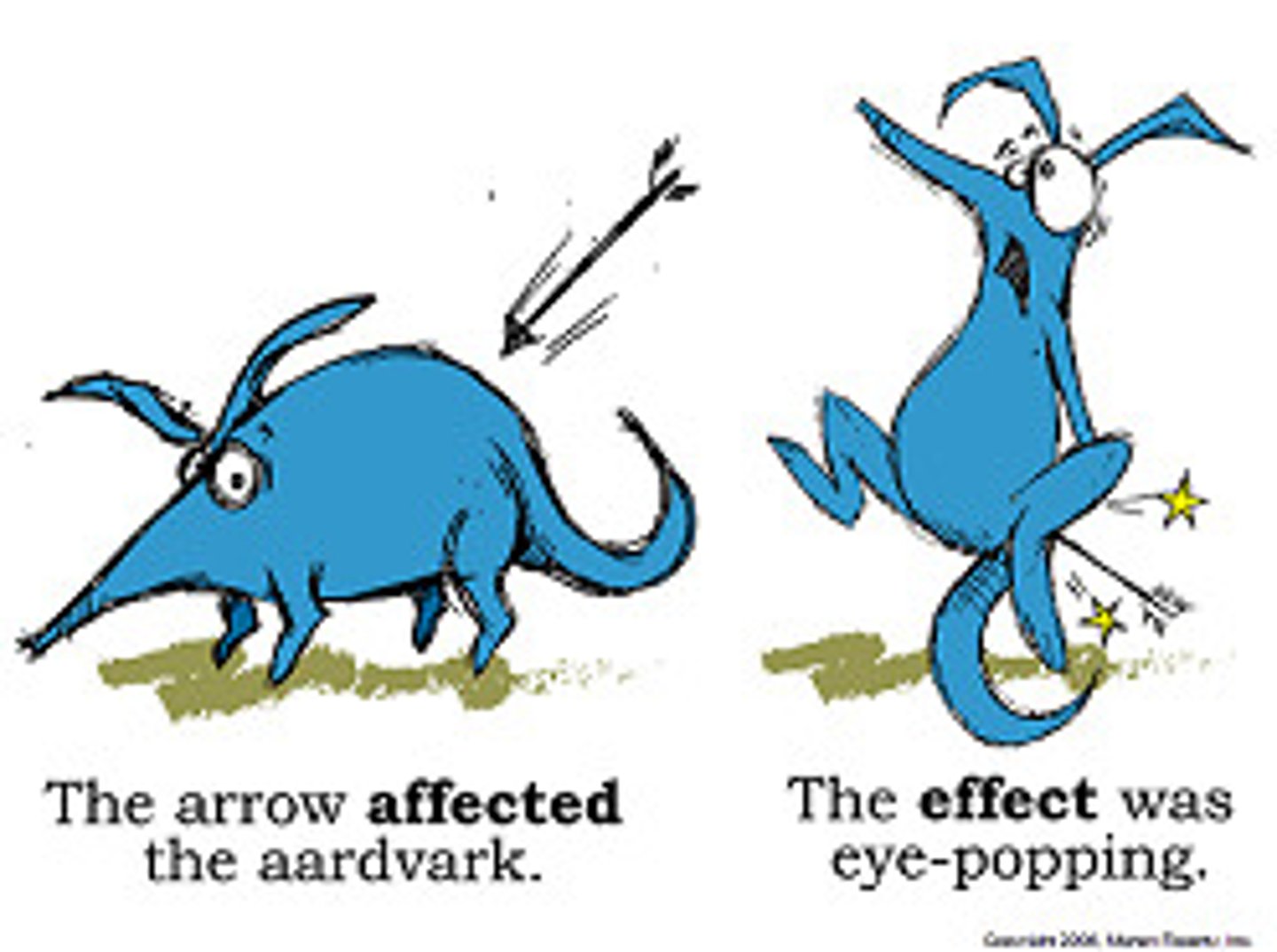
affect vs effect
"Affect" usually a verb meaning "to influence"
The drug did not affect a disease.
"Effect" is noun mean "result"
The drug has many adverse side effect.
"Effect" also a verb mean "to bring about"
The government effected many positive changes., AFFECT: verb EFFECT: noun
Aardvark is "a very easy noun" or "affect verb effect noun"
AFFECT: to influence or to change: "The rain affected my hair."; to act in a way that you don't feel as in "He affected an air of superiority".
EFFECT: as a result. "The rain had no effect on my hair."
* The arrow affected aardvark. *
* The effect was eye-popping. *
amphiboly
an ambiguous grammatical construction
Ex. e.g., 'they are flying planes' can mean either that someone is flying planes or that something is flying planes

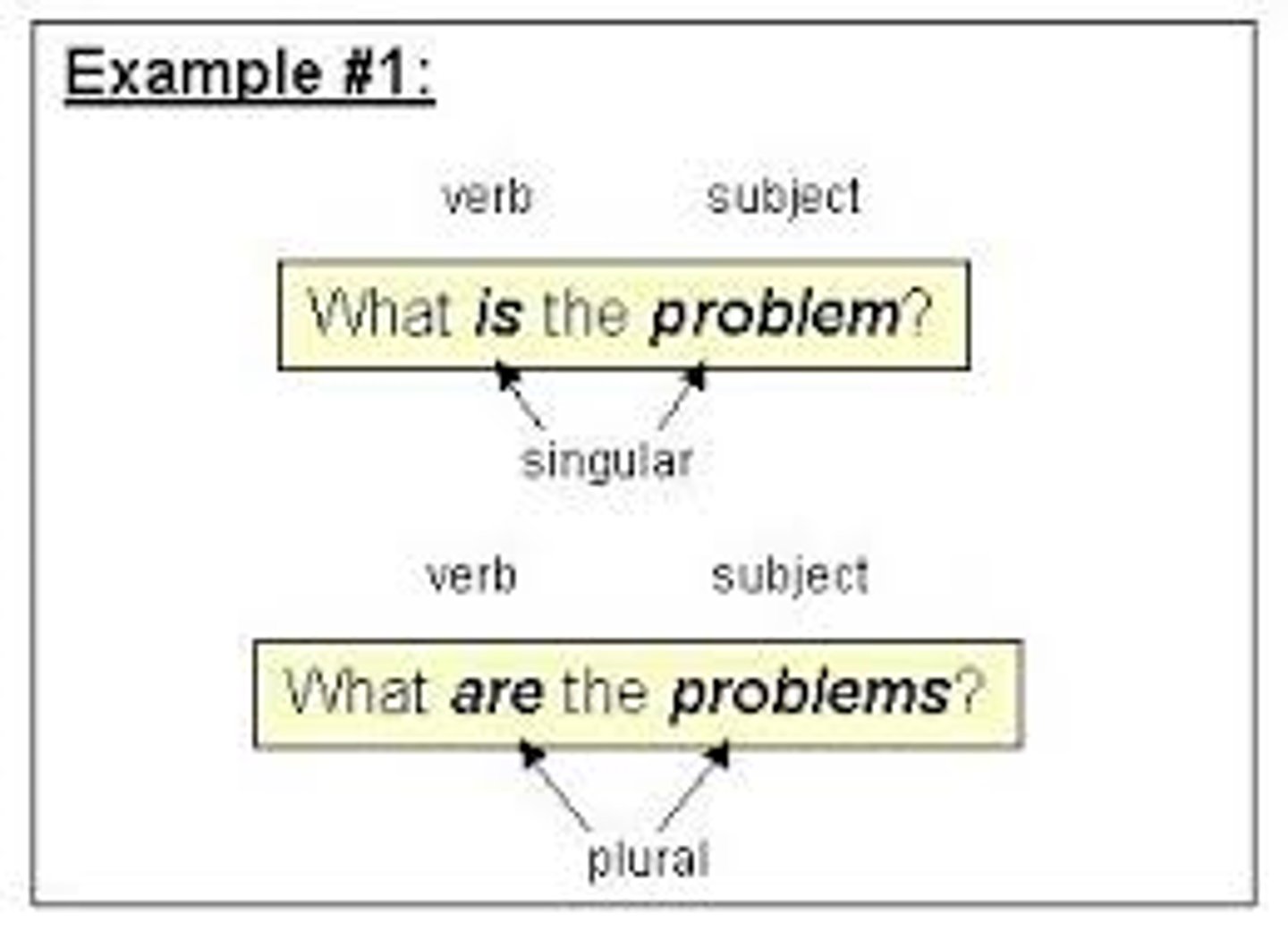
Subject-verb agreement
subject stays the same; verb must be singular or plural to match the subject
webbing
A visual grouping of ideas with connections to other ideas
copy editing
The processing of proofreading copy and making necessary corrections and changes
independent clause
a clause in a complex sentence that can stand alone as a complete sentence
独立分句

Anaphora
repetition of a word or phrase as the beginning of successive clauses
首语重复法

four key elements to good listening
Hear the message
Interpret the message
Evaluate the message
Respond to the message
Decoding
the process of translating the symbols contained in a message into meaning and interpreting the message

Letter-Sound Correspondence
The matching of an oral sound to its corresponding letter or group of letters.

Sight Words
words children identify quickly, accurately, and effortlessly. are high-frequency words introduced to children vicually for easy recognition.

Compound Words
Two or more words combined to create a new word.
Over-regularization
occur when grammatical rules are incorrectly generalized to irregular cases where they do not apply. (I hitted the ball, the girl goed home)
Formulaic speech
Also known as the Intermediate Language Proficiency stage. The learner knows about 6,000 receptive words and begins to make complex statements, state opinions, ask for clarification, share thoughts, and speak at greater length.
Fluency
the quality of being facile in speech and writing
n.流利,流畅,雄辩

orthographic stage
uses spelling patterns to recognize famliar words
silent period
The first stage of the process of second language acquisition, the preproduction stage, the CLD students may not communicate during this period except in nonverbal ways.

nativist approach
the theory that a genetically determined, innate mechanism directs language development

phonics approach
teaching reading by first teaching the sounds of each letter and of various letter combinations

alphabetic approach
Teaching reading by teaching the letters then putting the letters together to words
whole language approach
An approach to reading instruction based on the idea that instruction should parallel children's natural language learning. Reading materials should be whole and meaningful.

morphemes
smallest meaningful units of speech; simple words, suffixes, prefixes; examples: red, hot, calm, -ed, pre-

past participle
a participle that expresses completed action
过去分词

participle
a verb form that can be used as an adjective
n.分词

metacognitive reader
awareness of our own knowledge and ability to understand, control and manipulate our own cognitive processes. ie. thinking about thinking
Prose
ordinary speech or writing without rhyme or meter; referring to speech or writing other than verse
散文

Non-fiction
writing that tells about real people, places, and events

Poetry
literature in metrical form
n.诗歌,诗集

Unreliable first-person narration
a narrator, whether in literature, film, or theatre, whose credibility has been seriously compromised

Omniscient third-person narration
the narrator tells what all the characters are thinking,feeling, and doing
Reliable second-person narration
Another person tells the observations thoughts and feelings about the one character. Most sentences start with you.
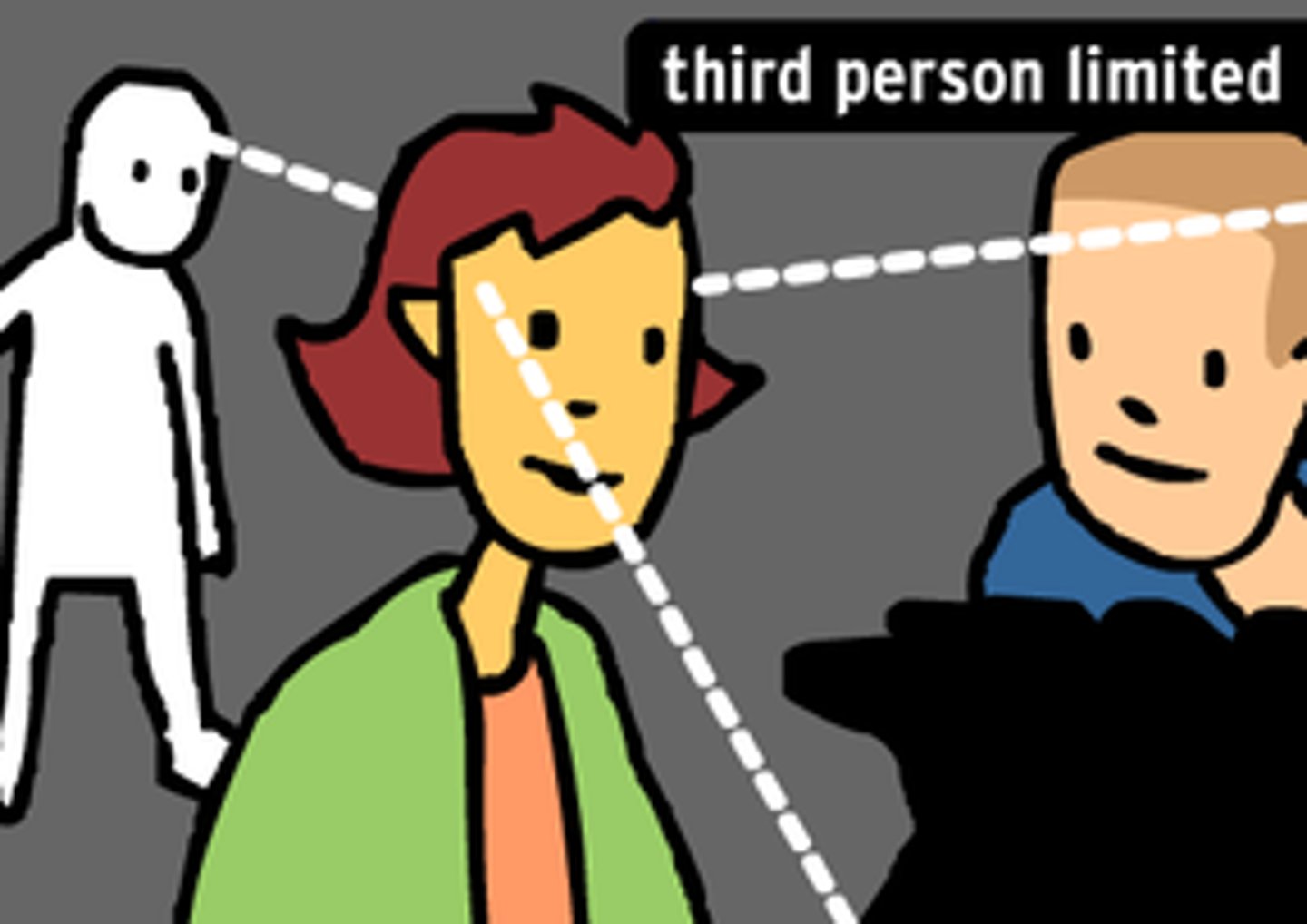
Limited third-person narration
the narrator tells the story from a limited viewpoint of only one character,referring to the character as he or she
pictograph
a graph that uses pictures to show and compare information
象形文字

adjective
the word class that qualifies nouns
形容词
adverb
the word class that qualifies verbs or clauses
n.副词 a.副词的

conjunction
something that joins or connects
n.联合;连词

interjection
A word or phrase sometimes inserted between other words, often expressing emotion; a word not linked grammatically to other words in a sentence
n.插入语;感叹词

imperative sentence
A sentence that requests or commands
祈使句

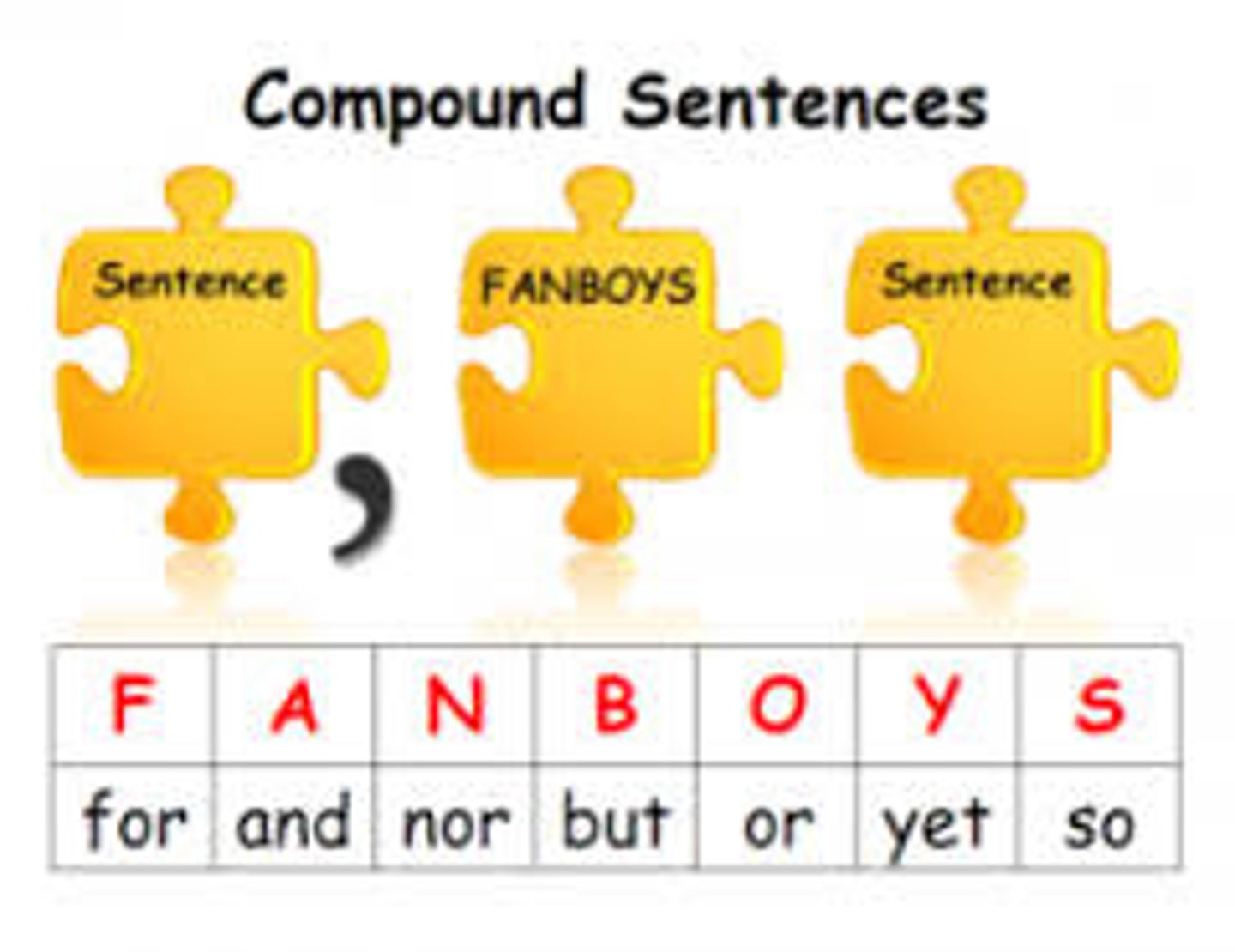
compound sentence
A sentence is composed of at least two independent clauses. It does not require a dependent clause. The clauses are joined by a coordinating conjunction (with or without a comma), a correlative conjunction (with or without a comma), a semicolon that functions as a conjunction, or a conjunctive adverb preceded by a semicolon.
复合句
interrogative sentence
a sentence of inquiry that asks for a reply
疑问句

Expressive skills
Speaking and Writing
Receptive skills
listening and reading
Selectivity
You must determine what is most important, and select those parts to begin the process of studying and learning.
选择,选择性
Rhetorical skills
(修辞技巧)
Heighten followers' emotional levels and inspire them to embrace the vision
Current research on emergent literacy states
(关于新兴文化状态的研究现状)
reading and writing develop concurrently in inter related ways
single best predictor in academic success in ESL students
vocabulary knowledge
most effective activity to develop students' concepts of print
listening to teachers read aloud
L.S. Vygotsky's exemplary instruction in literacy
implements a variety of grouping practices based on student's strengths and weakeness