Emotion and Stress (week 11)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the characteristics of emotions?
Emotions involve strong reactions of most bodily systems, are triggered by our interpretation of events, can disrupt ongoing activity, are adaptive, communicate information about feeling states, affect survival, and are based on genetic processes affecting brain function.
How do affect, mood, and feeling differ?
Affect is a general hedonic tone (positive/negative),
mood is a prevailing state lasting longer than an emotional state and is less intense,
while feeling is the subjective experience accompanying an emotion.
What is the James-Lange theory of emotion?
The James-Lange theory suggests that emotions arise from physiological responses to events.
What is the traditional view of basic emotions according to Russell (2003)?
The traditional view posits that there are a limited number of basic emotions, which can vary in number from 5 to 15.
What are the five basic emotions identified in the traditional view?
Fear, anger, sadness, happiness, and love.
What are some of the additional emotions included in the broader view of basic emotions?
Amusement, contempt, contentment, disgust, embarrassment, excitement, guilt, pride in achievement, relief, satisfaction, sensory pleasure, and shame.
What are the criteria for basic emotions according to Ekman (1999)?
Basic emotions have distinctive universal signals, specific physiology, an automatic appraisal mechanism, universal antecedent events, distinctive appearance during development, are observable in other primates, have fast onset, short duration, uncontrollable onset, and are associated with distinct subjective experiences.
What are the problems with the basic emotion approach?
There is no agreement on the number of basic emotions, and it is difficult to meet the criteria for defining them.
What is the emergent construct approach to emotions?
This approach views emotions as constructs that emerge from various psychological and physiological processes rather than as fixed entities.
What is the significance of facial expression processing in emotion research?
Facial expression processing examines how different facial expressions are recognized and whether some expressions are processed preferentially.
What is the 'happy face advantage'?
In speeded recognition tasks, individuals tend to recognize happy faces faster than other expressions.
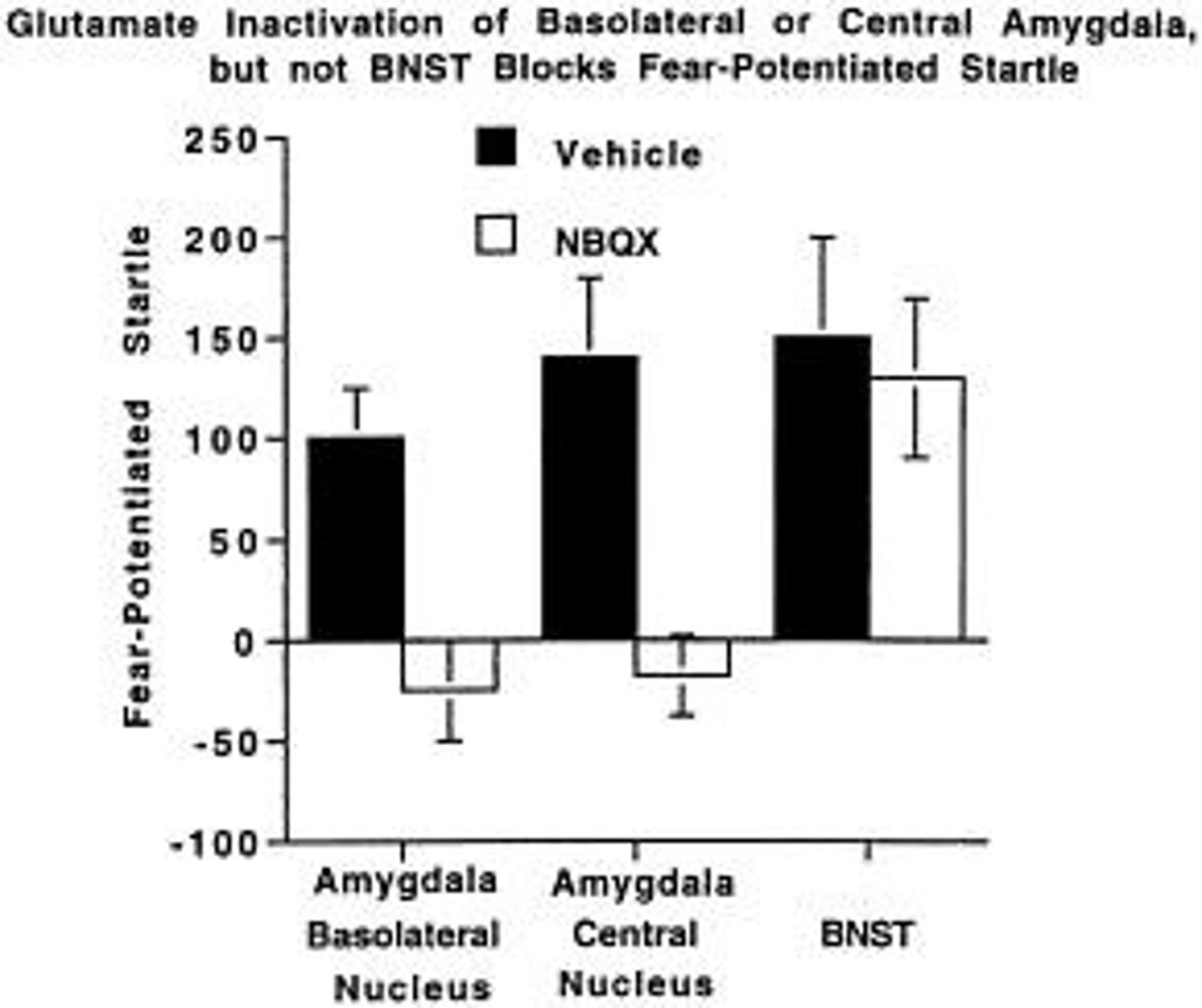
What is the role of the amygdala in fear?
The amygdala is crucial for processing fear and other emotions, with lesions disrupting fear responses.
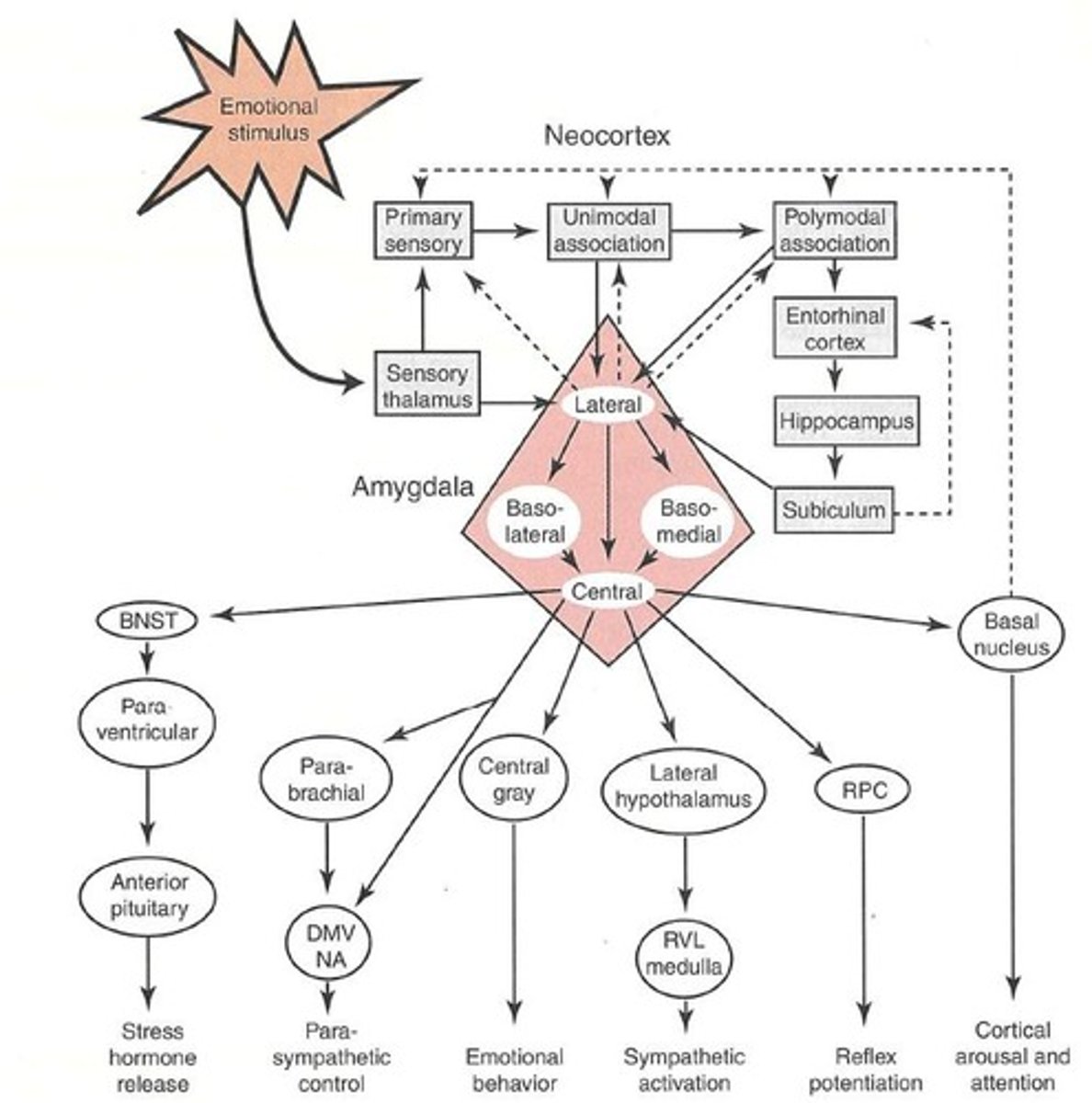
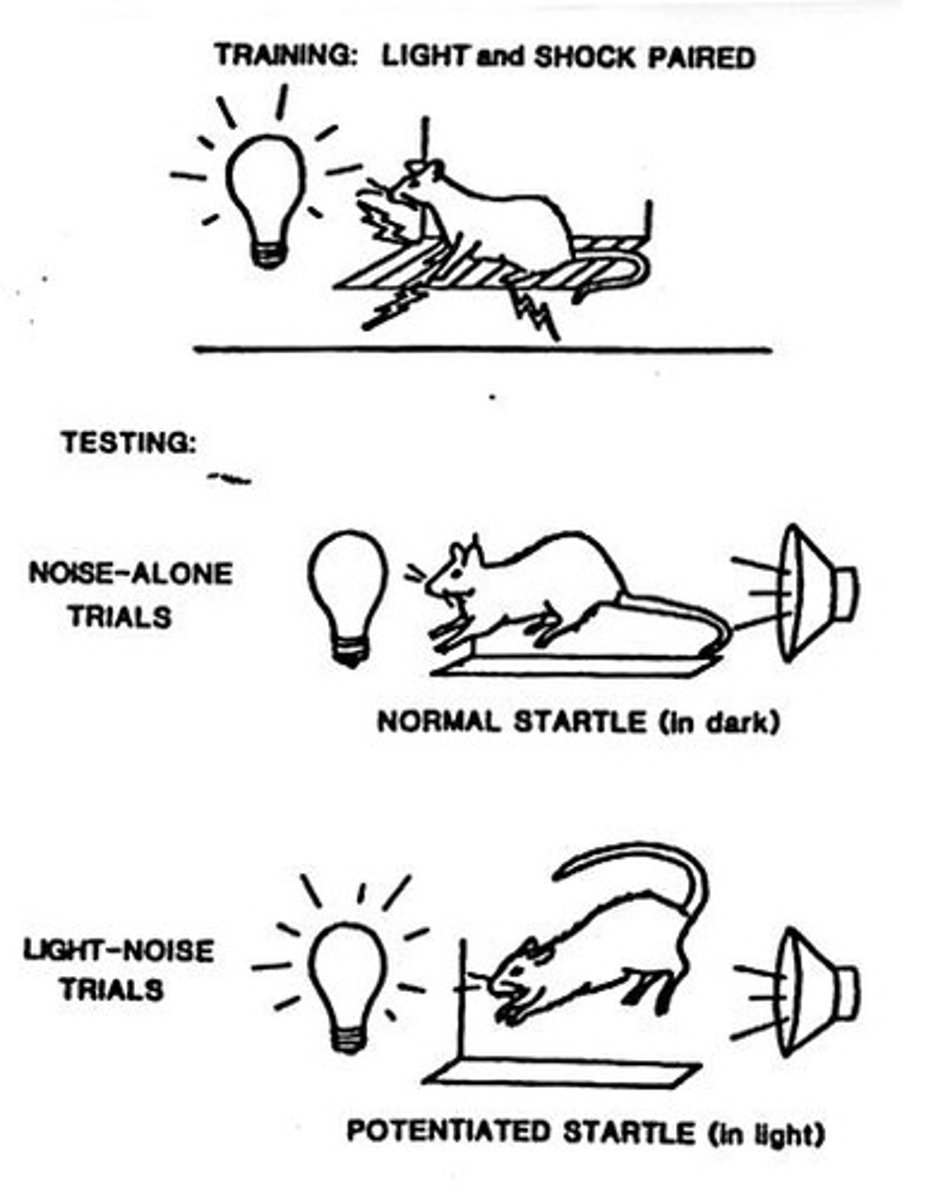
What is fear conditioning?
Fear conditioning is a behavioral neuroscience method to study fear responses, involving fear-evoking situations and learned fear.
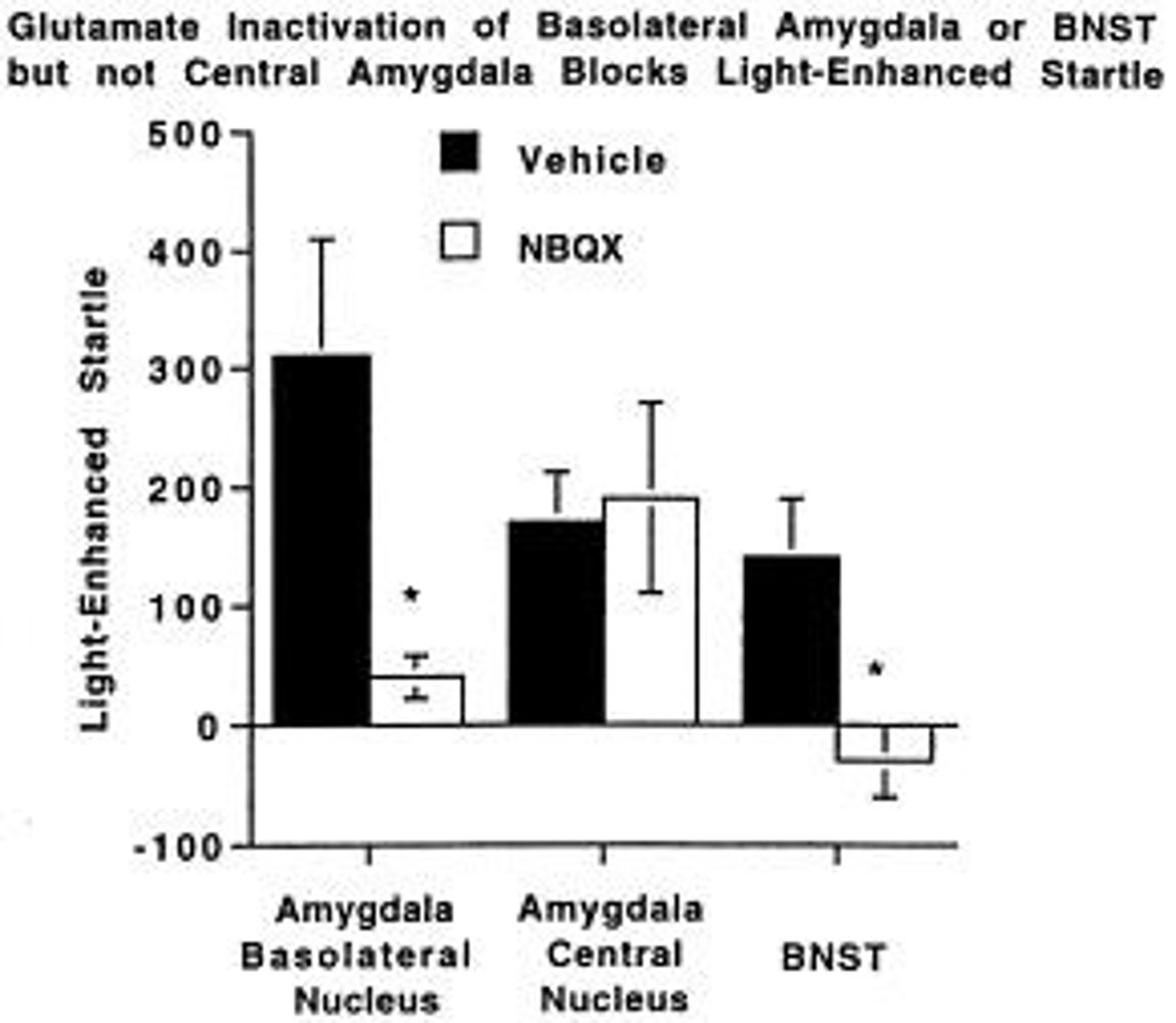
What neurochemical processes are involved in fear conditioning?
Glutamate and NMDA-receptor activity are involved, with NMDA antagonists reducing and agonists enhancing fear learning.
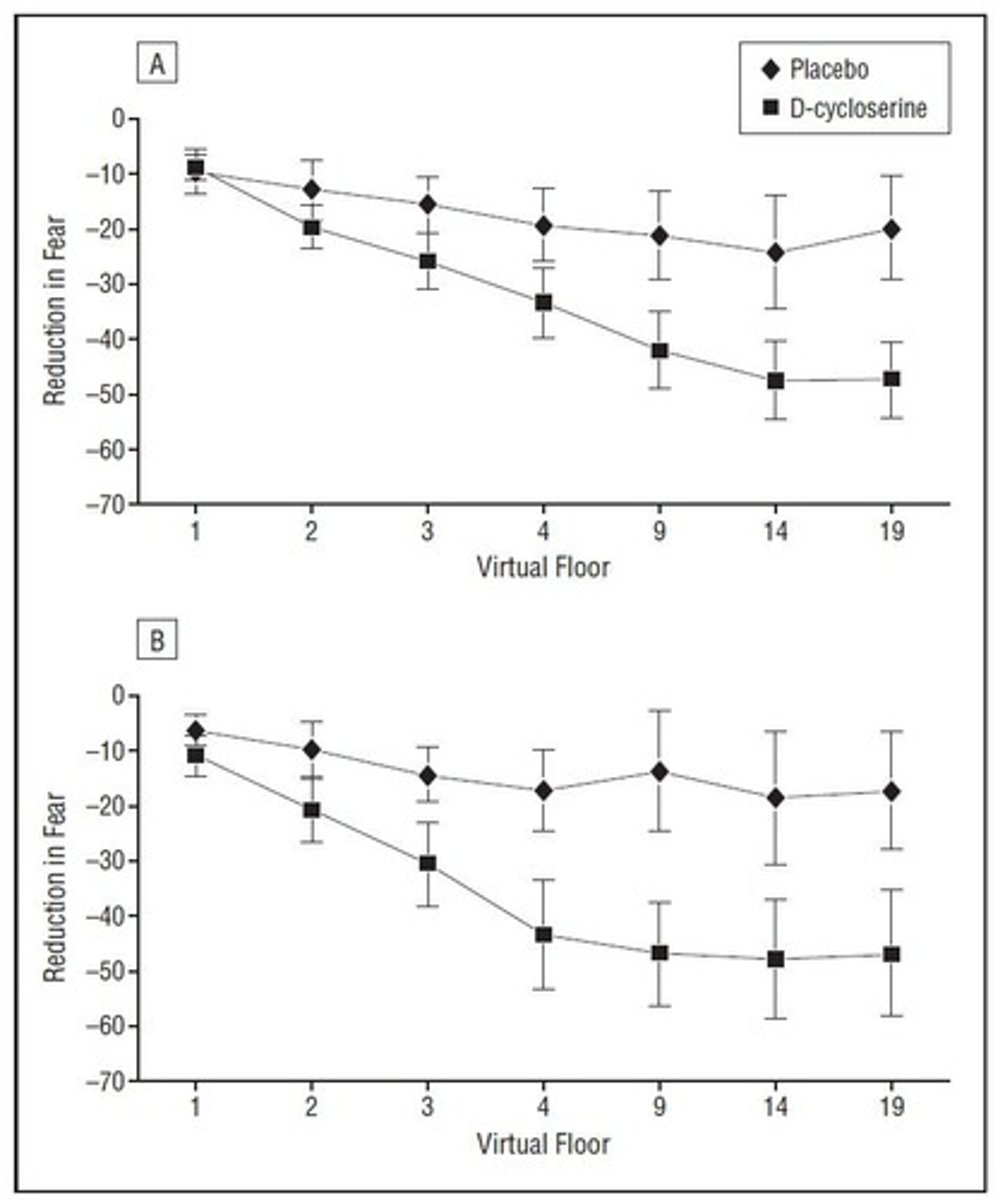
What is the potential application of D-Cycloserine in fear treatment?
D-Cycloserine, a partial NMDA agonist, may speed up fear extinction and enhance exposure treatment in phobias.
What is the difference between fear and anxiety?
Fear is a basic emotion that is adaptive, while anxiety is a more generalized response that can manifest as disorders such as phobias and generalized anxiety disorder.
What is the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS) according to Selye?
GAS describes the body's response to stress in three stages: alarm reaction, resistance/adaptation, and exhaustion.
What happens during the alarm reaction phase of GAS?
The alarm reaction phase involves initial defense mechanisms, which may fail, leading to increased heart rate and decreased temperature and blood pressure.
What are the effects of prolonged stress according to GAS?
Prolonged stress can lead to exhaustion, collapse of reproductive and immune functions, and enlargement of adrenal glands.
What is psychoneuroimmunology?
Psychoneuroimmunology studies the interaction between psychological processes, the nervous system, and the immune system.
What are the components of the immune system?
The immune system includes cells like lymphocytes and killer cells, and antibodies such as immunoglobulins.
How does stress affect immunity?
Stress can substantially affect functional parameters of the immune system, with objective stressful events having a larger effect than subjective ones.
What is the NPU paradigm used to assess human fear and anxiety?
The NPU paradigm presents cues in different contexts to measure startle responses during fear conditioning.
What is the role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) in anxiety?
The BNST is involved in anxiety responses, with its activation leading to unconditioned startle enhancements in both rats and humans.
What are the effects of alprazolam in separating fear and anxiety?
Alprazolam, a benzodiazepine, is used to assess fear and anxiety responses in experimental settings.
How would you research fear?
use fear evoking situations (unconditioned fear)
acquired fear (fear conditioning)