SOLUTIONS
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Class 12(Chemistry), Chapter-1.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are the types of solutions(with examples)
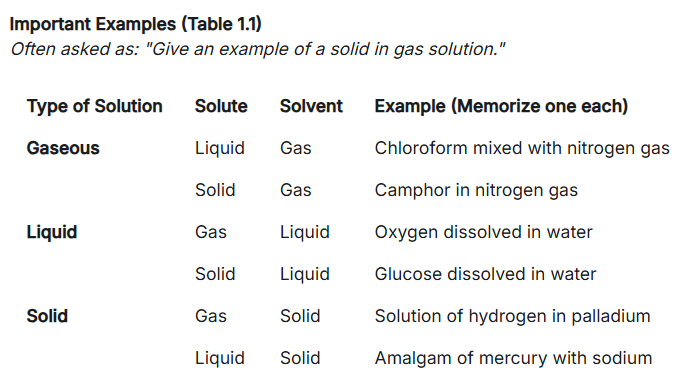
Define the following:
1. Solution
2. Homogeneous mixture(its geneous; not genous)
3. Binary solution
4. Solvent
5. Solute.
Solution: A homogeneous mixture of two or more components.
Homogeneous Mixture: A mixture where composition and properties are uniform throughout.
Binary Solution: A solution consisting of only two components.
Solvent: GENERALLY, the component present in the largest quantity. It determines the physical state of the solution.
Solute: One or more components present in the solution other than the solvent.
What’s the state of the solution if the solvent is:
1. solid
2. liquid
3. gas
Answers:
1. solid
2. liquid
3. gas
Note: The physical state of the solvent always dictates the physical state of the final solution. If the solvent is a gas, the solution is also a gas, regardless of the solute.
Bro, what’s Henry’s Law.
Confusing Version:
"The partial pressure of the gas in the vapour phase (p) is proportional to the mole fraction of the gas (x) in the solution."
Plain English Version:
"The pressure of the gas ABOVE the liquid is directly linked to how much of that gas is DISSOLVED IN the liquid."
Or even simpler:
"More pressure above → More gas dissolves inside"
What are the 3 applications of henry’s law.
NCERT page no.8. class 12 chemistry part 1
What’sthe Partial Pressure
What’s dilution threshold from molefraction
molefraction(x of solute)
x < 0.01 - Dilute
x > 0.01 - Non-dilute

What’s the vapour phase?
What’s volatile and non-volatile?
Volatile: Easily evaporates. High vapour pressure
non-volatile: opposite of volatile, duh.

State Raoult’s Law
State Dalton’s law of partial pressures
the answer of dalton stuff is in page no. 10 ncert

Common mistakes card 1 (cmc)

What’s
1. Mass percentage (w/w):
2. Volume percentage (V/V):
3. Mass by volume percentage (w/V):
4. Parts per million (ppm):
and molality, molarity etc. + a cmc 2.
Check NCERT page no. 2-5
What specific component is used as an antifreeze in cars (mentioned in NCERT example)?

Which of these is dependent on temperature and why?
A. Molality
B. MolarityWhat’s the symbol of each?
Molarity, because molarity depends on VOLUME.
Symbols:
A. Molarity: M
B. Molality: m
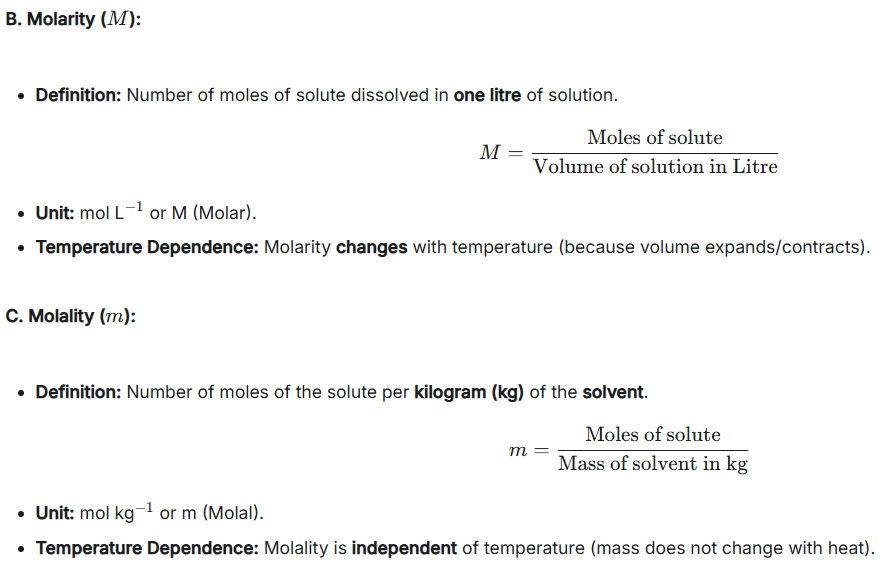
Common mistakes card 3 (cmc)
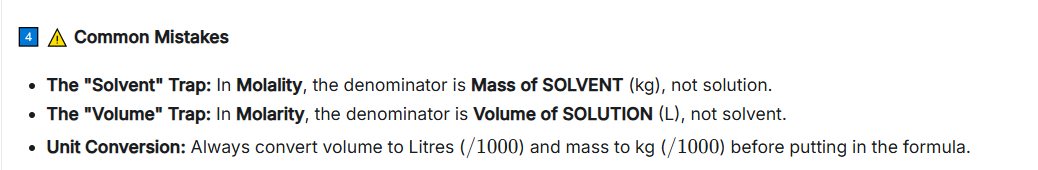
REMINDER
I highly suggest you reread till before, colligative property, as most of it is not covered in flashcards.
reread: 1.3 - 1.5
from Google AI Studio and Claude AI.
you know what, learn full, dont rely on flashcards for this. too risky.
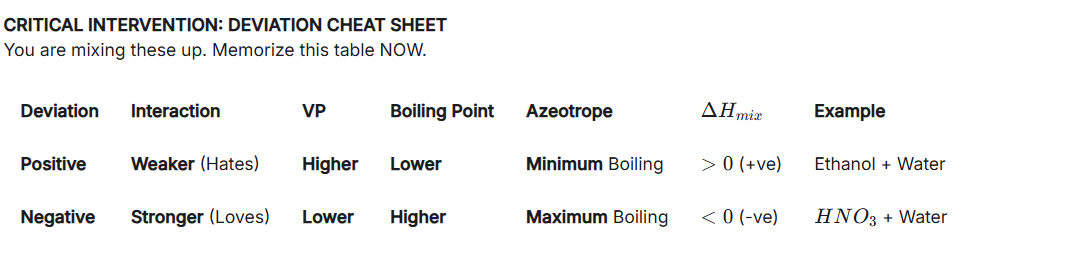
Differentiate between, positive and negative deviation
very important.



The subscript of the outermost bracket is taken as the n of that term
Answer: 3.
whats:
1. hypotonic
2. hypertonic
3. isotonic
the formula, whats the one at higher conc in each case.
Hehe, check it for yourself.
what’s tetramerization.