Eng Vocab 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Analysis
Identifying features of the text and explaining how the author uses them to develop a meaning or have an effect.
Ex: He analyzed the text message to see if his mom was mad.

Allegory
Fictional work in which the characters represent ideas or concepts.
Ex: Tortoise and Hare- Slow and steady wins the race

Alliteration
The repetition of consonant sounds. (Usually in the beginning of words,
Ex: Clary closed her cluttered clothes closet

Allusion
A reference to another thing
Ex: Chocolate was her Achilles’ heel

Anaphora
Repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of a successive phrase
Ex: I will not mock teacher’s outdated cell phones, II will not mock teacher’s outdated cell phones

Diction
Contract- specific words that describe physical qualities of conditions
Abstract- the language that denotes ideas, emotions, conditions, or concepts that are intangible
Denotation literal definition of a word
Connotation- implicit meaning not explicit meaning
Ex: I’m hot (atractive or temperature)

Figurative Language
all language that implies imaginative comparison
Ex: Its as cold as ice

Image/imagery
The mental picture created by words/associations. Also include auditory and sensory components
Ex: The loud neon blue shirt that hung above the quiet stairwell.

Metaphor
Compares two unlike things for dramatic effect
Ex: She is an angel

Mood
The feeling of a work, scene, or event.
Ex: A piece of art makes you happy

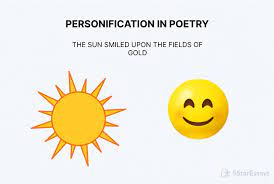
Personification
Objects are described as having human qualities or personalities.
The wind whistled.
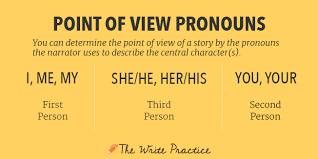
Point of View
The perspective from which a story is told
Ex: I love cars- First person
Shift/Turn
A change or movement in a piece resulting in an epiphany, realization, etc.
Ex: He loves cars however…

Simile
Compares one thing to another using like or as.
Ex: his eyes were as blue as the ocean

Structure
The framework/organization of a literary selection
Ex: Poetry-Rhyme scheme

Symbol
Something that stands for something else

Syntax
The way words are arranged in a sentence
Ex: The sun blinded her. She was blinded by the sun
Tone
The way an author presents a subject
Ex: Serious, ominous, ect.

Declarative Sentence
Makes a statement
Ex: She is sick.

Imperative Sentence
Gives a command
Ex: Go clean your room

Interrogative Sentence
Asks a question
Ex: Is she sick?

Exclamatory Sentence
Provides an emphasis/ expresses strong emotion
Ex: I am so mad!

Compound Sentence
contains two independen clauses joined by a coordinating conjuction or by a semicolon
ex: I like blue, but she likes red.
Complex Sentence
Contains an independent clause and one or more subordinate clauses
Ex. Because she was tired, she went home

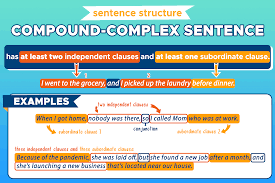
Compound-Complex Sentence
contains two or more independent clauses and one or more subordinate clauses
Ex: She was talking while the class was quiet, but no one heard her.