Developmental Anomalies and Developing Dentition
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
when r the first signs of tooth development
6 weeks
localised epithelial thickening in incisor and molar regions
inititiated by epithelium - that has odontogenic potential and then ectomesenchyme
what is jowett et al
MSx1 and MSx2 has to be switched on to make a tooth
what is hypodontia
absence of teeth due to failure of development
anodontia - total lack of teeth in 1 or 2 dentitions
oligodontia - more than 6 teeth missing primary or perm
what teeth are most likely to be missing
8s then lower 5s then upper 2s then upper 5s
more likelt if missing primary teeth then they will be more likely be missing permanent
what is the aetiology of hypodontia
usually uncealr
likely genetic - autosomal dominant inheritence pattern in some families
occasioanlly envurinmental insult
associted with certain syndromes - ectodermal dysplasia or downs
what is autosomal dominant
if they have a dominant gene it will be presented but if it is recessive then both genes r needed
what is supernumery teeth
Development of one or more extra teeth
mesiodens - in midline usually peg shape teeth
supplemental - normal teeth
conical supernumaries - look like a cone and they can erupt but they can migrate up
tuberculate - dont migrate but can impade eruption of adjecent teeth
what is microdontia
small peg shape teeth
lateral incisors most affected
what is macrodontia
big teeth
double teeth - 2 crowns
dens in dente - invagination
talon cusps - evagination
what is doubl teeth
fusuion - abnromal shape resulting from fusion of 2 seperate tooth germs
gemination - 2 teeth develop from one tooth germ look abnormally wide
can distinguish between no of roots and if there is missing teeth - fusion means less teeth
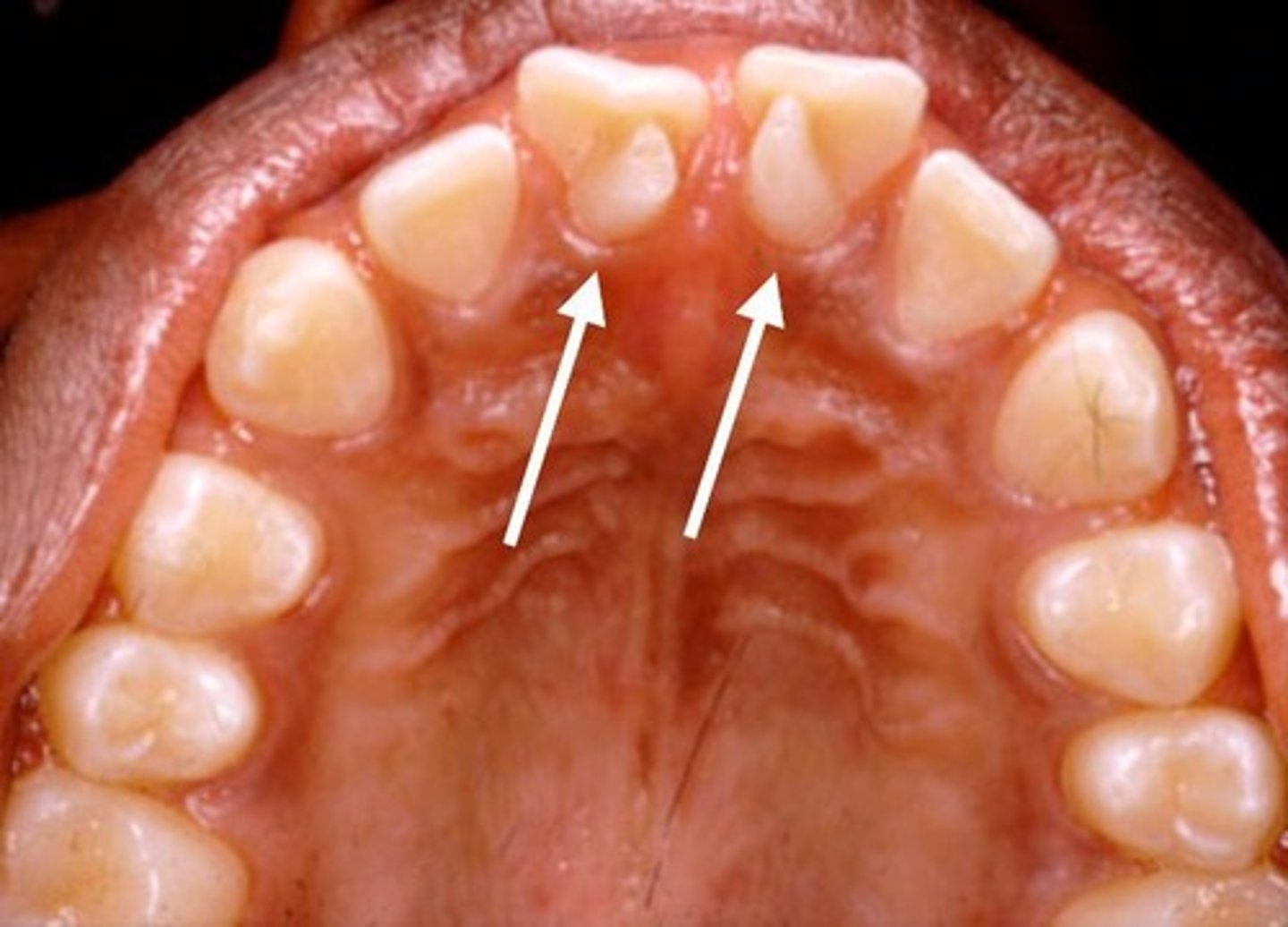
what is dense in dente
tooth wihtin a tooth
localised area of the vrown is folded inwards
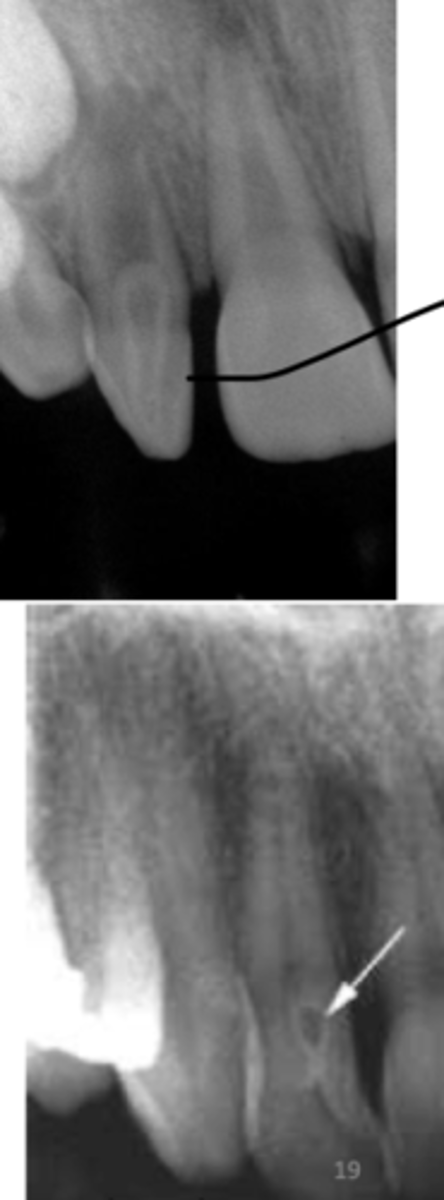
what is a talon cusp
evagination
can have iys own pulp and nerve so hard to do
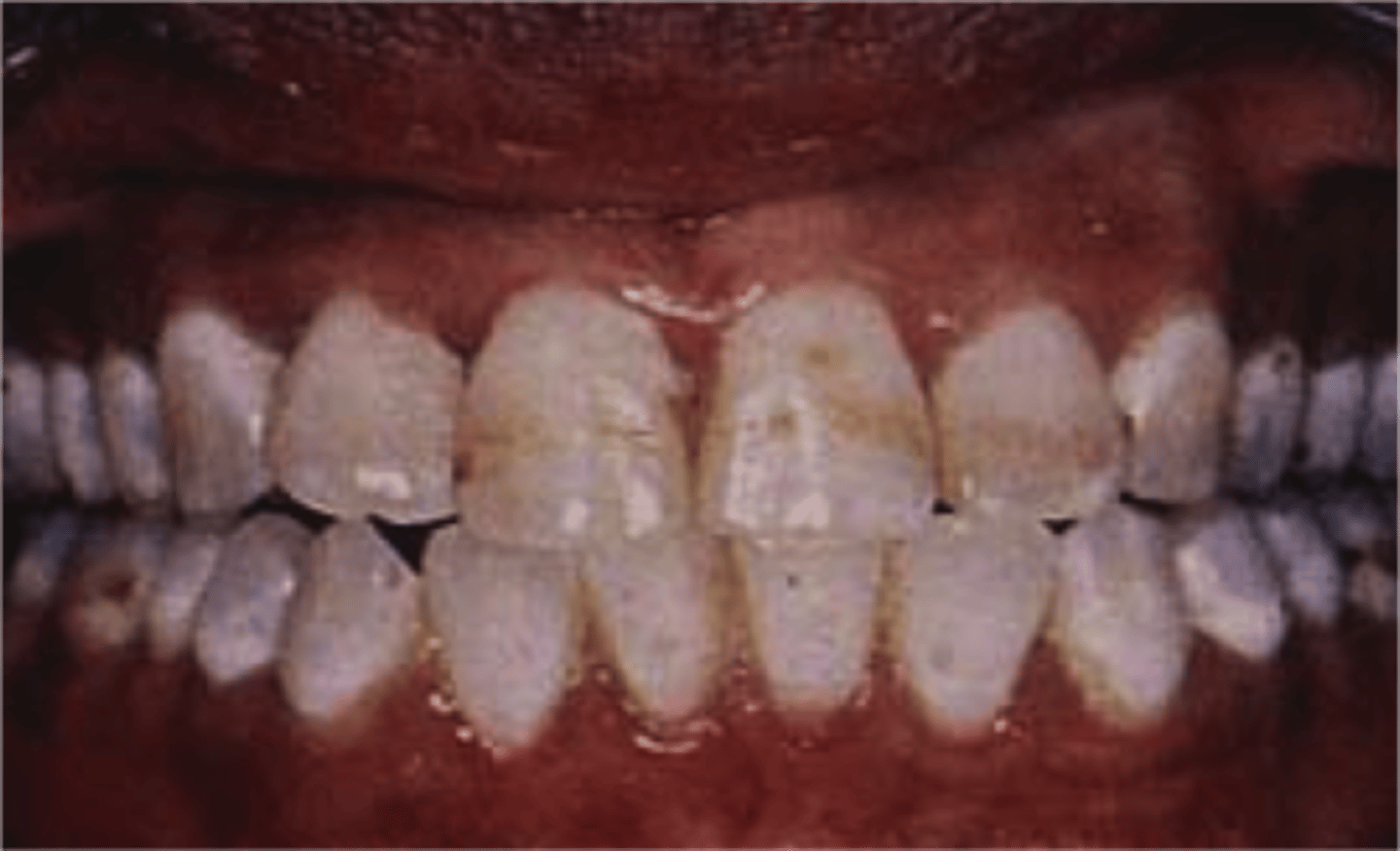
what is amelogenesis imperfecta
effects emalogenesis cycle - affects ameloblast function
affects both primary and perm dentition
2 types - hypomineralised (weak enamel) hypoplastic ( thin but hard)
what do dentinogenesis imperfecta present as
poor OH
pain and infection w necrosis
dentine exposure
enamel breakage
what are non hereditary distrurbances in teeth
what is Molar incisor hypomineralisation
developmental defect in enamel structure
typically 1st perm molars and incisors but can be others
very common - 20%
demarcated enamel opacities and can be from white to yellow/brown
can appear hypoplastic
ot can be axious and fail tx etc
LA is less effective !
what is flourosis
high F conc during amelogenesis
irregular enamel opacities
what is turners tooth
affects successional tooth
allegedly hypoplastic