viruses & fungi
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1
New cards
host range, narrow & broad
How many diff kinds of species a virus can infect
narrow = very few (1-2)
broad = many
narrow = very few (1-2)
broad = many
2
New cards
Tissue tropism
what kind of cells a virus can infect (respiratory, etc)
3
New cards
parts of virus structure (2 parts)
\-capsid surrounds genome. Made of protein
\-some have envelope with spike protein for attachment
\-some have envelope with spike protein for attachment
4
New cards
what kinds of viral genomes are there (how genetic info stored)
RNA or DNA
single stranded (ss) or double stranded (ds)
(-) oriented 3’-5’ or (+) oriented 5’-3’
single stranded (ss) or double stranded (ds)
(-) oriented 3’-5’ or (+) oriented 5’-3’
5
New cards
Icosahedral virus
\-radial symmetry (circle)
\-fixed size
\-naked or envelope
\-some have spike proteins for attachment
\-fixed size
\-naked or envelope
\-some have spike proteins for attachment
6
New cards
filamentous virus
\-helical symmetry
\-helical tube around genome
\-variable size → flexible
\-size can increase based on genome
\-helical tube around genome
\-variable size → flexible
\-size can increase based on genome
7
New cards
amorphous virus
\-no symmetrical form
\-most flexible
\-NO capsid, but HAS envelope
\-has “core wall” under envelope (similar to cytoplasm in cells)
(example: flu)
\-most flexible
\-NO capsid, but HAS envelope
\-has “core wall” under envelope (similar to cytoplasm in cells)
(example: flu)
8
New cards
tailed bacteriophage virus
\-only infects bacteria
\-DNA stored in head, tail used to attach & inject
\-ALWAYS HAS *DS DNA GENOME*
\-DNA stored in head, tail used to attach & inject
\-ALWAYS HAS *DS DNA GENOME*
9
New cards
antigenic drift
when a virus evolves and mutant proteins no longer recognized by host antibodies → generates new strands of virus
10
New cards
3 levels viruses evolve in
\-community: evolve to infect diff species → increase host range
\-within a species: evolve to be more infectious → antigenic drift
\-within an organism: evolve variants that resist meds → infect tissue
\-within a species: evolve to be more infectious → antigenic drift
\-within an organism: evolve variants that resist meds → infect tissue
11
New cards
5 steps to ALL virus life cycle
1) attachment to cell
2) penetration
3) synthesis of new material in cell
4) assembly of virus in cell
5) release virus
2) penetration
3) synthesis of new material in cell
4) assembly of virus in cell
5) release virus
12
New cards
what is lytic infection vs lysogenic infection
lytic = normal infection cycle
lysogenic = bacteriophage NA into host DNA during replication. slower. then a stimulus activates it and all cells with viral genes in DNA become infected suddenly
*PROK ONLY*
lysogenic = bacteriophage NA into host DNA during replication. slower. then a stimulus activates it and all cells with viral genes in DNA become infected suddenly
*PROK ONLY*
13
New cards
prokaryote viral infection steps (image)
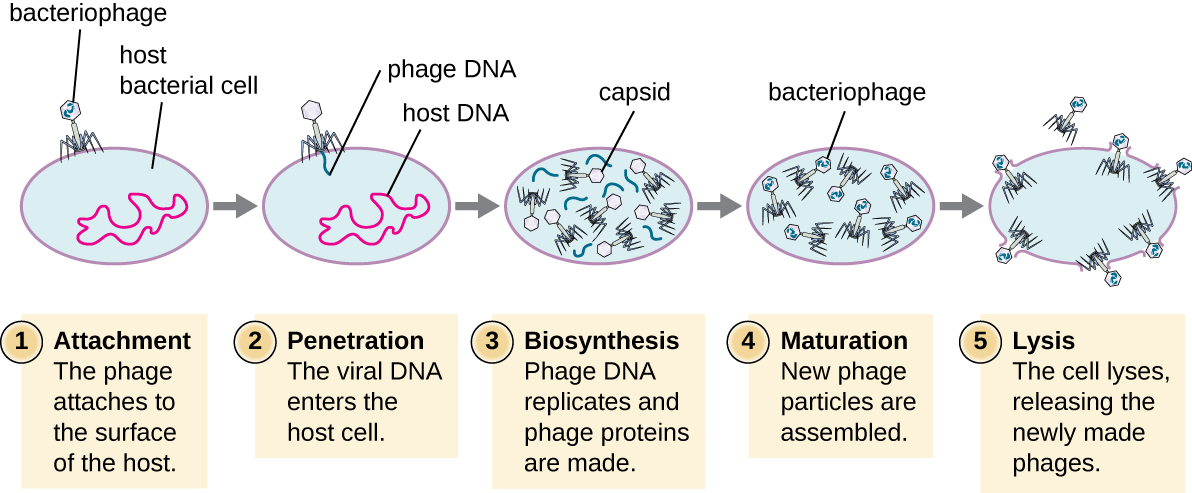
14
New cards
euk viral infection steps (image)
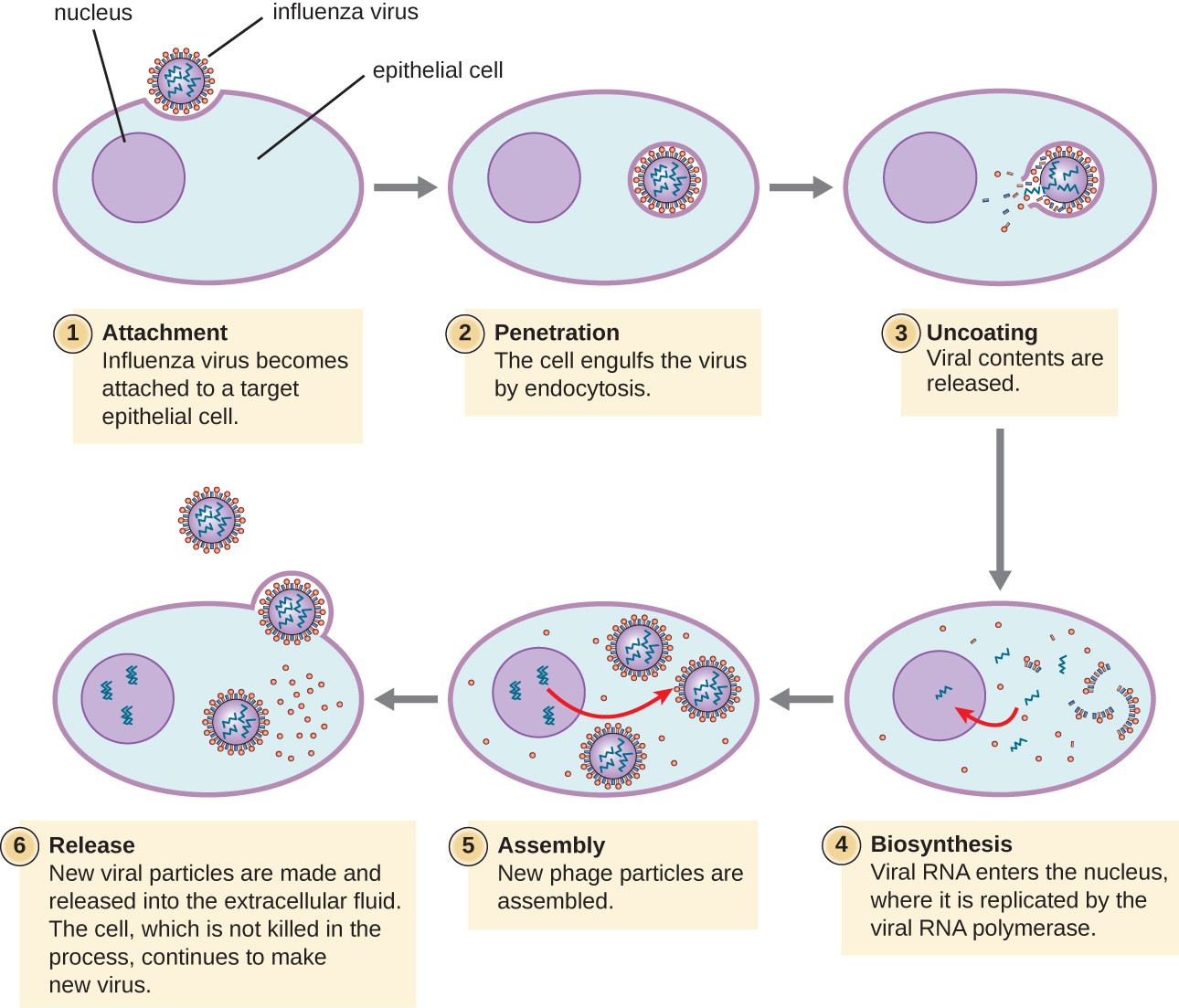
15
New cards
ss and ds go to the _____ for replication
nucleus
16
New cards
DNA virus goes to the ______
nucleus
17
New cards
RNA virus goes to the _____
cytoplasm
18
New cards
persistent infection
when cell doesn’t die and lyse, instead virus keeps being made and released out of cell. *EUK ONLY*
19
New cards
Latent infection (latency period)
when virus doesn’t produce virions for long periods. (ex. HIV or herpes). *EUK ONLY*
20
New cards
LATENT infects ____ cells, while LYSOGENIC infects ____ cells
(prok or euk)
(prok or euk)
latent = EUKARYOTIC infection
lysogenic = PROKARYOTIC infection
lysogenic = PROKARYOTIC infection
21
New cards
Antigenic shift
when a host picks up a disease from 2 diff species at the same time. the 2 strains combine and make a new variant thats highly infectious
(ex. when a pig gets the flu from humans and bird at the same time)
(ex. when a pig gets the flu from humans and bird at the same time)
22
New cards
antivirals work best if _____
if taken 24-48 hr after symptom onset
23
New cards
are fungi prokaryotic or eukaryotic
eukaryotic
24
New cards
4 structures unique to fungi
cell wall =chitin, glucan (sugar), mannoprotein
cell membrane = ergosterol
cell membrane = ergosterol
25
New cards
filamentous
multicellular, mold (& spores)
26
New cards
filaments are called ____
hyphae
27
New cards
hyphae make spores called ____
conidia
28
New cards
aspergillus
\-lung infection
\-breathe in from spores
\-greater affect ppl with lung problems (COPD, smoker, allergies)
\-grows everywhere = soil, produce, mold on walls
\-breathe in from spores
\-greater affect ppl with lung problems (COPD, smoker, allergies)
\-grows everywhere = soil, produce, mold on walls
29
New cards
nonfilamentous
single cellular, yeast
30
New cards
yeast in bread is called ____ while infectious yeast is called ____
bread = saccharomyces
infectious = candida
infectious = candida
31
New cards
thrush
yeast mouth infection
32
New cards
many antifungals target
ergosterol & chitin since they are not found in humans