Cell transportation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the three main ways in which substances move in and out of cells?
-Diffusion
-Osmosis
-Active transport
Diffusion
The spreading out of particles from a high concentration to a low concentration, either in a solution or in a gas. It is a passive process. The molecules move using Brownian motion.
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules from a dilute solution (a high concentration of water) to a concentrated solution (a low concentration of water) through a partially permeable membrane. It is also a passive process.
Active transport
It moves substances against a concentration gradient - from a low concentration to a high concentration. It requires energy, which it gets from respiration.
What is Brownian motion?
The random movement of microscopic particles in liquids or gases.
What is a partially permeable membrane?
A barrier that allows some molecules (such as water) to pass through, but prevents bigger molecules (such as salt or starch) from passing.
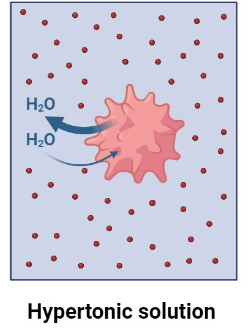
What does hypertonic mean?
High concentration of solutes (for example, salt) compared to a low concentration of a solution or water.
If a cell was put in a hypertonic solution, all of the water from the cell would travel to the hypertonic solution outside, following the laws of osmosis, leaving a plasmolysed cell behind. In this situation, a plant cell wouldn’t burst due to it’s vacuole, but an animal cell might.
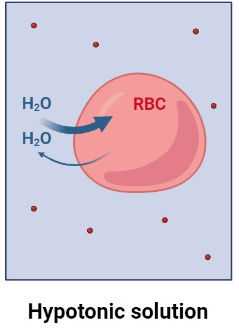
What does hypotonic mean?
Low concentration of solutes (for example, salt) compared to a high concentration of a solution or water.
If a cell was put in a hypotonic solution, all of the water from the solution would rush to the cell, following the laws of osmosis, resulting in a turgid cell. Plant cells generally want to be turgid, as it allows them to hold a strong structure.
What does isotonic mean?
An equal concentration of solutes (for example, salt) compared to a solution or water.
If a cell was put in a isotonic solution, there would be no net movement of water. The cell would maintain its normal size and shape, resulting in a flaccid cell.
TRUE OR FALSE - The larger the difference in concentration, the slower the rate of diffusion.
False - if there is a large difference in concentration, diffusion will occur faster compared to a minor difference in concentration.
TRUE OR FALSE - The higher the temperature, the slower the rate of diffusion.
False - if the temperature is higher, the particles will have more kinetic energy, allowing them to move faster.
TRUE OR FALSE - The larger the surface area of the membrane, the faster the rate of diffusion.
True - a few specialised cells (root hairs, villi, alveoli, etc) have large surface areas for this specific reason - they want to get the most water as possible.