nursing skills and assessment exam 3
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
apnea
temporary cessation of breathing (a - without)
dyspnea
difficulty breathing
hypoxia
low oxygen to tissues
hypoxemia
low oxygen in the blood
tripod positioning
bracing arms in front of you and leaning over a little but to decrease dyspnea and open the airways
barrel chest
anterior and posterior diameter is 1:1 without elliptical shape
dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
hypovolemia
abnormal low blood volume
hypervolemia
abnormal high blood volume
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
sudden episodes of severe shortness of breath that occurs at night 1-2 hours falling asleep, related to congestive heart failure, needs multiple pillows to sleep
supine
laying on back with torso up
fowlers
sitting at a 45-60 degree angle
high fowlers
sitting at a 60-90 degree angle
nocturnal polyuria
excessive urination during the night time
pleural effusion
excessive fluid accumulating in pleural spaces, the area between the lung and the chest walls
hypercholesterolemia
high cholesterol in the blood stream
respiratory assessment expected findings
Equal Rise / Fall Chest
Normal Pattern
No Difficulty Breathing
Normal Rate (10-20) breaths per minute)
Elliptical Shaped Chest
Clear / Auscultable Lung Sounds
respiratory assessment unexpected findings
Dim / Absent Lung Sounds
Adventitious Lung Sounds
Dyspnea / Accessory Muscle Use
Tachypnea / Bradypnea
Clubbing or Pitting of Fingernials
Nasal Flaring / Pursed Lip Breathing
Asymmetrical Chest Expansion
Crepitus
Pain / Tenderness
Lumps
Decreased O2
Alerteed LOC
Increase Anxiety / Confusion
normal breathing ratio
pt should be exhaling double at time they should be inhaling, 1:2 ratio, bases of the lungs are smaller thn apex
respiratory health teaching
dont smoke, avoid exposure to toxins, chemicals, and smoke, use good handwashing technique
dim
lung sounds are hard to hear and dimmer in pitch
dim; whats happening
there is too much fluid at the bases pf the lungs or that the lungs are collapsed (D)
dim; diseases and disorders
pneumonia, pleaural effusion, atelectasis, obesity
absent
lung sounds cant be heard upon auscultation
absent; whats happening
there is too much fluid at the base of the lungs or that the lungs are collaped (A)
absent; diseases and disorders
pneumonia, pleaural effusion, pneumothorax, respiratory fatigue
pneumothorax
air enters the space between the lung and the chest wall
pneumonia
an infection of the lungs that causers inflammation of the air sacs
pleural friction rub
grating, scratching, or creaky sound that is in a specific area of the chest heard in short bursts during inspirations and expirations
pleural friction rub; whats happening
there is inflammation of the lungs covering
pleural friction rub; diseases and disorders
pleuritis, pneumonia, pulmonary edema, trauma, autoimmune disorders
adventitous lung sounds
wheezing, crackles, find crackles, course crackles, rhonchi
wheezing; sound
high pitched, whistling sounds that occors when air moves through a narrowed airway
wheezing; whats happening
means air is being forced through obstructed airways
wheezing; diseases and disorders
asthma, COPD, bronchitis, heart failure, foreign objects
crackles
occurs when air passes through fluid in the small airways of the lungs
crackles; whats happening
means theres fluid in the lungs (C)
crackles; diseases and disorders
pneumonia, pulmonary edema, heart failure
fine crackles; sound
high pitched, short duration that occurs at the end of inspiration
fine crackles; whats happening
means small airways or air sacs are collapsing and reopening
fine crackles; diseases and disorders
pneumonia, pulmonary edema, interstitial lung disease, atelectasis
course crackles; sound
lower pitched, longer duration that occur at inspiration
course crackles; whats happening
means there is fluid in the lungs (CC)
course crackles: diseases and disorders
bronchitis, COPD, pneumonia, pulmonary edema, bronchiectasis
rhonchi; sounds
low pitched, rattling, gurgling heard during expiration
rhonchi; whats happening
upper airways obstruction and is a media emergency due to respiratory distress
ronchi; diseases and disorders
pneumonia, chronic bronchitis COPD, cystic fibrosis
atelectasis
partial or complete collapse of the lung
atelectasis: signs and symptoms
Decreased Breath Sounds / Wheezing
Hypoxemia
Dyspnea / Tachypnea
Fatiuge
Chest Pain
Rapid / Shallow Breaths
emphysema
a chronic lung disease that causes permanent damage to the air sacs in the lungs
emphysema: signs and symptoms
Barrel Chest / Chest Tightness
Finger Clubbing
Dyspnea / Tachypnea / Tachycardia
Pursed Lip Breathing
Tripoding
Shallow Breaths
Chronic Cough
Wheezing
Increased Mucus Production
hypoxia and hypoxemia: signs and symptoms
Confusion
Restlessness
Agitation
Cyanosis
Bradycardia
cardiac assessment auscultation location order
1.) Aortic
2.) Pulmonic
3.) Erb’s Point
4.) Tricuspid Valve
5.) Mitral Valve / Apical Pulse
cardiac assessment expected findings
Normal Rate (60-100 beats per minute)
No JVD / Bounding Pulse
No Rib Cage Deformities
S1 and S2 Present
No Chest Pain
Bilateral +2 Peripheral Pulses
Less 2 Seconds Capillary Refill
cardiac assessment unexpected findings
Tachycardia / Bradycardia
Hypertension / Hypotension
Poor Coloring of Extremities
JVD / Bounding Pulse
S3 / S4 / Murmurs Heard
Swelling of Chest
Sleep / Mental Status Changes
heart valves
tricuspid valve
pulmonic valve
s1mitral valve
aortic valve
s1 lub
heard when the mitral and tricuspid valve closes, loudest at apical pulse
s2 dub
heard when the aortic and pulmonic valve closes, loudest at the bases
s3 ventricular gallop
heard when blood rushes into ventricles that are stiff or dilated, heart failure and hypertension
s4 atrial gallop
heard when heart muscles loses it elasticity and is thickened, heart failure, hypertension, aortic stenosis
heart murrmurs
extra and abnormal heart sounds heard from increases or turbulent blood flow, malfunctioning valves, defect in structures around the heart
cardiac murmur
heard between s1 and s2
diastolic murmur
heard after s2 and before s1 (s4)
risk factors of cardiac diseases
High cholesterol
Eating fatty foods
Obesity
Diabetes
Smoker
pulse grading 0
absent
pulse grading +1
weak
pulse grading +2
normal
pulse grading +3
full/increased
pulse grading +4
bounding
edema grading
accumulation of excess fluid in the tissues, its graded based on its severity and appearance
edema grading +1
less 2 mm
edema grading +2
2-4mm
edema grading +3
5-7mm
edema grading +4
more 7mm
troponin
released by the myocardial muscle when injury has occurred and not present when the body is in normal healthy state
troponin: modifiable risk factors
weight, diabetes control, smoking
troponin: non-modifiable risk factors
age, genetics, family history
fluid overload
too much fluid in the bodt caused by kidney dysfunction, heart failure excessive fluide intake
Tachycardia
Tachypnea
Hypertension
Diluted Labs
BUN
Cr
fluid underload
not enough fluid in the body often caused by dehydration or blood loss
Bradycardia / Weak Pulse
Bradypnea
Hypotension
High Labs
BUN
Cr
right sided heart failure
stops working, causing blood to back up in the body because it can’t move forward
signs and sx - dependent edema, liver and abdominal enlargement, nocturnal urination, JVD< weight gain, puffy face
left sided heart failure
stops working, causing blood to back up in the lungs because it can’t move forward
signs and sx - respiratory congestion (hacking/coughing, pink frothy sputum), wheezing, fatigue, weakness, SOB
venus insufficiency
failure of the veins to adequate circulate blood back to the heart
signs and sx - edema, brawny LE coloring, leg ulcers
tx - elastic stockings
peripheral arterial disease
plaque builds up the arteries that supply blood to the extremities
risk factors:
Hypertension
Smoking
Obesity
Hypercholesterolemia
Hyperglycemia (glucose > 100)
Hypercholesteremia (LDL >130)
Hyperlipidemia (triglycerides > 150)
intermitten claudification
pain in legs when walking due to hypoxia that goes away with rest
peripheral arterial disease: signs and symptoms
Pale / Cool Extremities
Hair Loss on Extremities
Atrophy of Muscle
Thick Toenails
peripheral arterial disease: treatment
Bypass Surgery
Vasodilators
Blood Thinners
Warm Environment
vasodilators
Meds ending in “pril” (ace inhibitors)
Meds ending in “sartan” (arbs)
Nitroglycerine (nitrates)
blood thinners
Aspirin (antiplatelet)
Heparin (anticoagulant)
Warfarin (anticoagulant)
warm environment
Wear Gloves
Warm Clothes
Socks
cardiac assessment procedure
Have the patient sit in supine, fowlers, high fowlers, sitting, or
standing when auscultating the heart
apical pulse
most accurate pulse, 5th intercostal space midclavical line, listen w stethoscope for a full minute
COPD
chronic lung disese that causes progressive damage to the airways and the air sacs in the lungs
interstitial lung disease
a group of chronic lung diseases characterized by inflammation and scarring (fibrosis) of tissues between the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs
cystic fibrosis
a genetic disorder that primary affects the lungs and digestive system
bronchiectasis
abnormal widening of the bronchi or their branches
respiratory assessment procedure
have the pt sit upright
use the diaphram of the stethoscope to listne to lung sounds
move ina. zig zag pattere to compre both lungs
place the stethoscope directly on the skin with firm pressure for clear sound.
cover the posterior chest when listening to the anterior, and vice versa.
ask the pt to take a deep breath in and out as you reposition each stethoscope
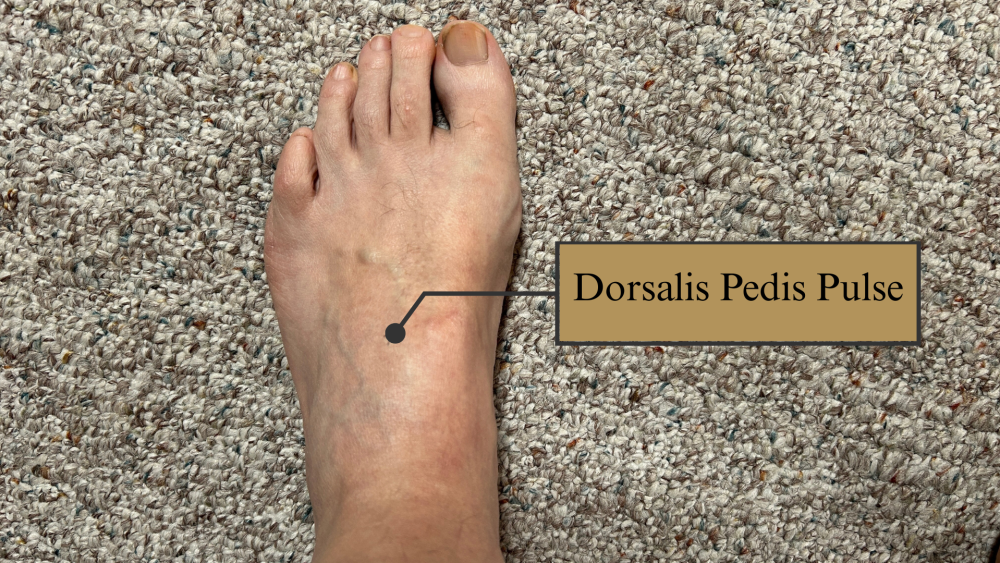
dorsalis pedia pulse
top of your foot been the big and second toe near the center
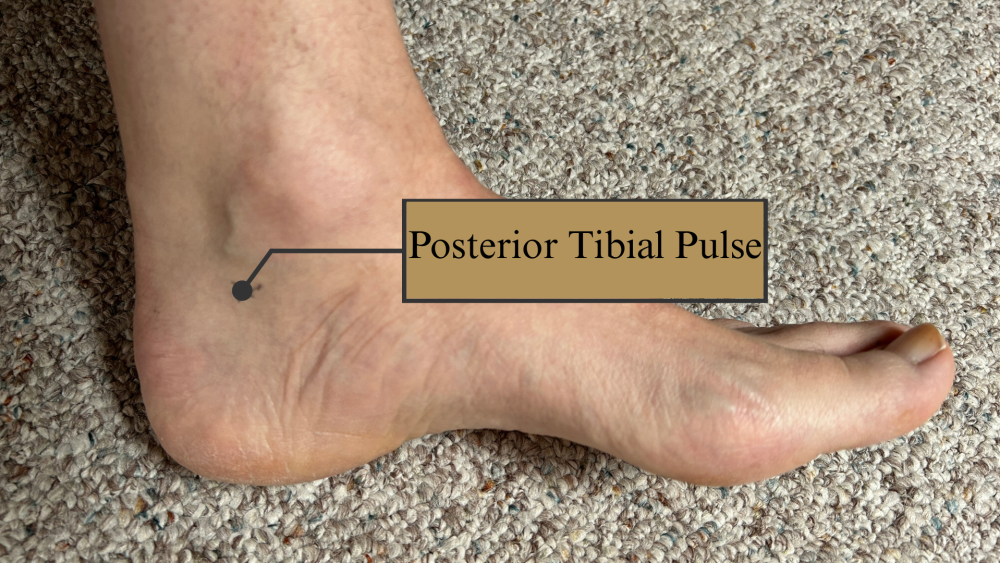
posterior tibial pulse
just behind your anke bone on the inner side of your leg
femoral pulse
groin area
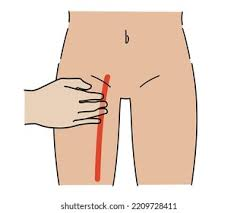
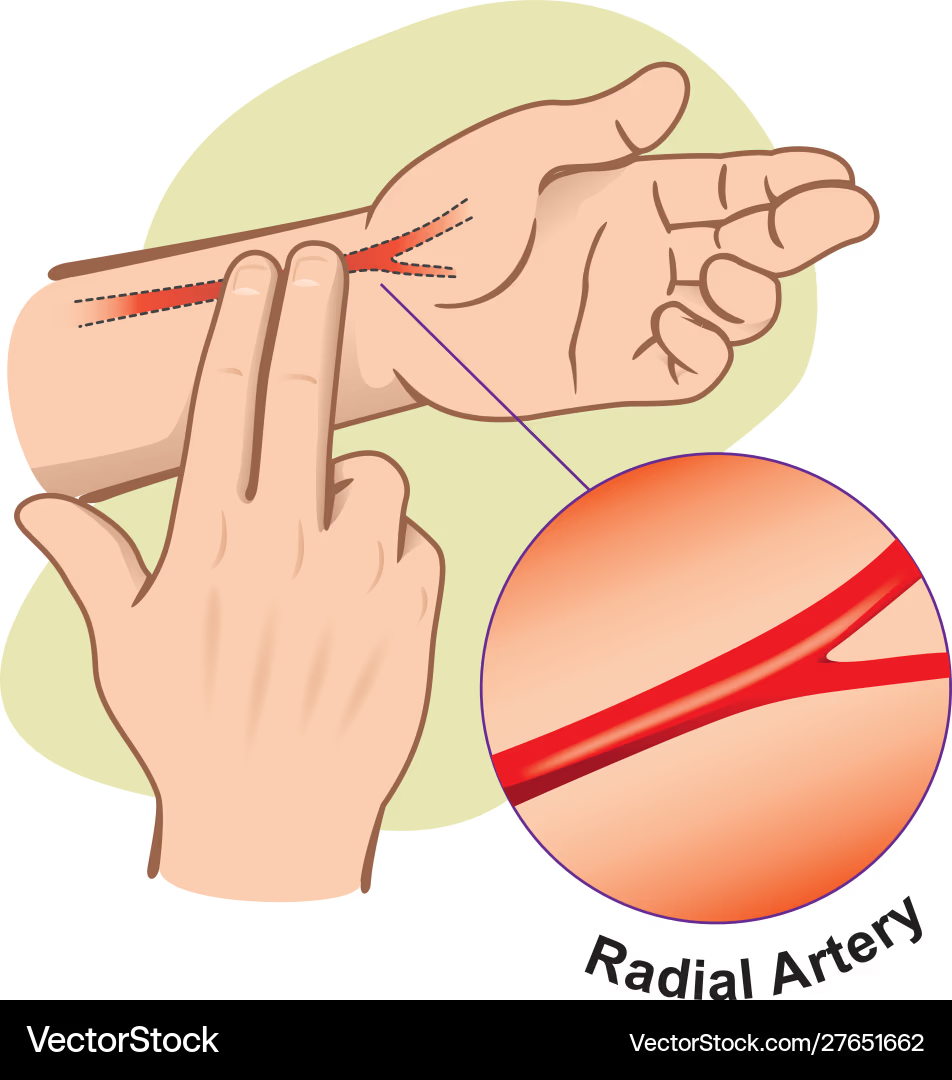
radial pulse
thumb side of your wrist