Cardiac muscle
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What’re the general features of cardiac muscle cells?
Contractile
Uni-nucleated
Cells align end to end, can also align parallel
What’re cardiac muscle cells interconnected by and whats within them?
They’re interconnected by intercalated discs and from functional syncytia
Within intercalated discs theres 2 kinds of membrane junctions-
Desmosomes = There for structure to tightly join cardiac muscles so they don’t pull apart when contracted
Gap junctions = Connected by connexins, works like an electrical synapse
What’re the types of cardiac muscle cells?
Myocardial contractile cells (working cells)
Cardiac conducting cells
Explain myocardial contractile cells
99% of cardiac muscle cells
Contractile, MUSCLE part of the heart, do mechanical work of pumping
Joined electrically by gap junctions
Explain cardiac conducting cells
Myocardial Autorhythmic cells = Initiate and maintain electrical activity in the heart, DO NOT CONTRACT
Conducting cells = Conduct electrical signals throughout the heart (Purkinje fibres), DO NOT CONTRACT
What’re the steps of electrical conduction in heart?
Cardiac impulse originates at SA node (AP originates here)
AP spreads throughout right and left atria
Impulse passes from atria into ventricles through AV node (only point of electrical contact atrial and ventricular chambers)
AP briefly delayed at AV node, this ensures atrial contraction precedes ventricular contraction to allow complete ventricular filling
Impulse travels rapidly down interventricular septum by means of bundle of His
Impulse rapidly disperses throughout myocardium by means of purkinje fibres
Rest of ventricular cells activated by cell-to-cell spread of impulse through gap junctions
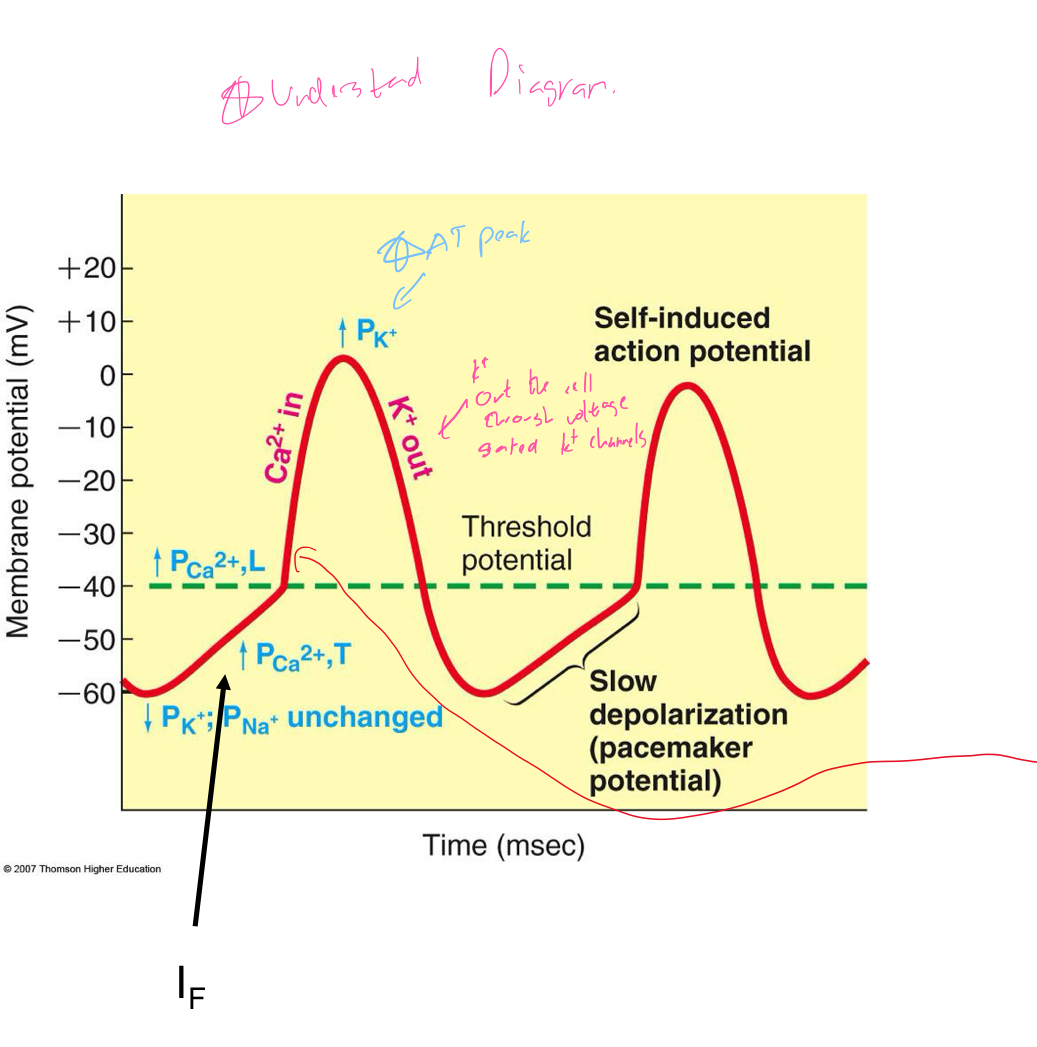
In terms of AP in pace makers explain the intrinsic conduction system
Has autorhythmic cells which initiate action potentials
No real “resting membrane potential”
Pacemaker potential membrane slowly depolarizes “drifts” to threshold, initiates AP, membrane depolarizes to -60 mV
What’re the different kinds of autorhythmic cells and what do they do?
IF = causes pacemaker potential/ where pacemaker current is found, a Na+ current
ICaT = Fast calcium current, turns on and off quickly
ICaL = Slow Ca++ current, responsible for main depolarization
Understand this diagram
What’re the features of AP of contractile cells?
Rapid depolarization
Rapid, partial early repolarization
Prolonged period of slow repolarization called the “plateau phase”
Rapid final repolarization phase
What’re the different phases of AP of contractile cells?
Na+ channels open
Na+ channels inactivate
Ca++ channels open, K+ channels open and balance Ca++
Ca++ channels close; slow K+ channels open
Resting potential
Why is AP of contractile cells so long?
Because plateau is primarily due to prolonged activation of “slow Ca++ channels” (L-type Ca++ channels)
Ensures adequate ejection of blood out of heart
Whats the difference in refractory period of skeletal vs cardiac muscle cell?
Skeletal muscle fast-twitch fiber = The refractory period is very short compared with the amount of of time required for the development of tension, skeletal muscles that are stimulated repeatedly will exhibit summation and tetanus
Cardiac muscle fibers = The refractory period lasts almost as long as the entire muscle twitch, long refractory period in a cardiac muscle prevents tetanus
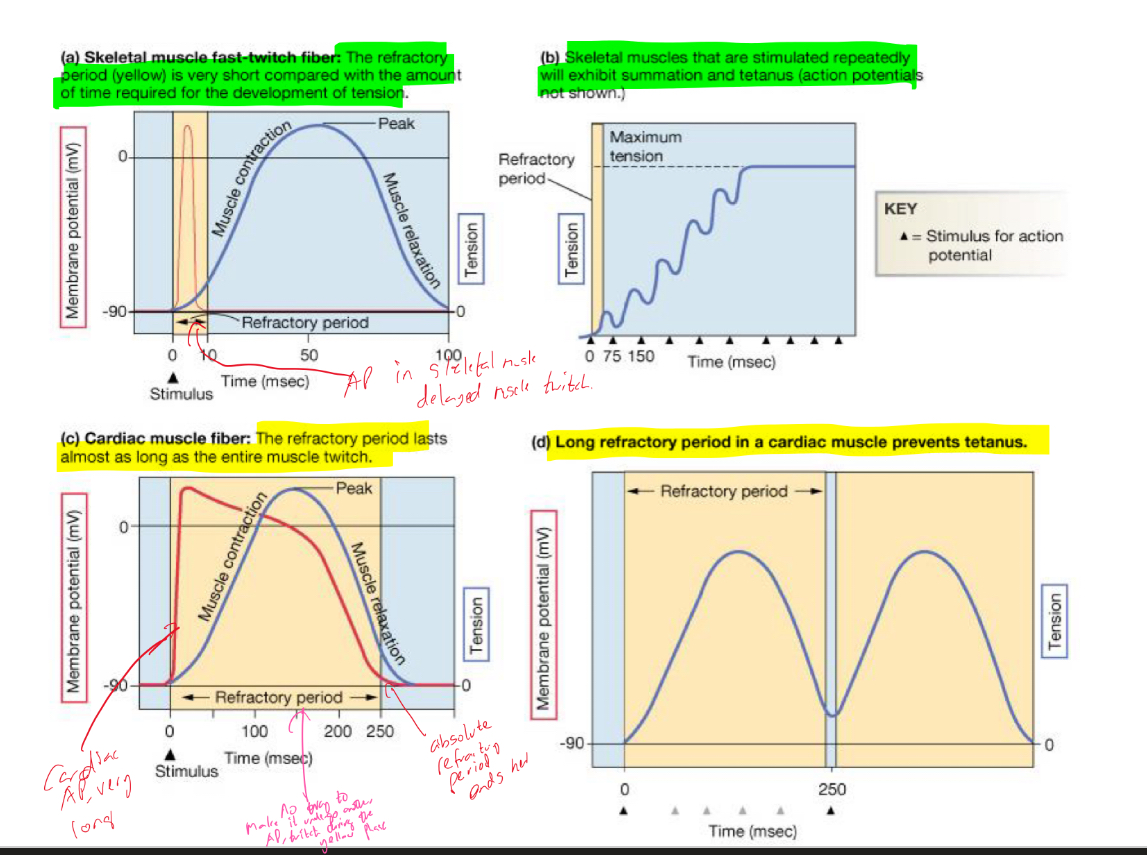
How does the long AP of contractile cells avoid tetanus?
Long AP causes long refractory period and long contraction
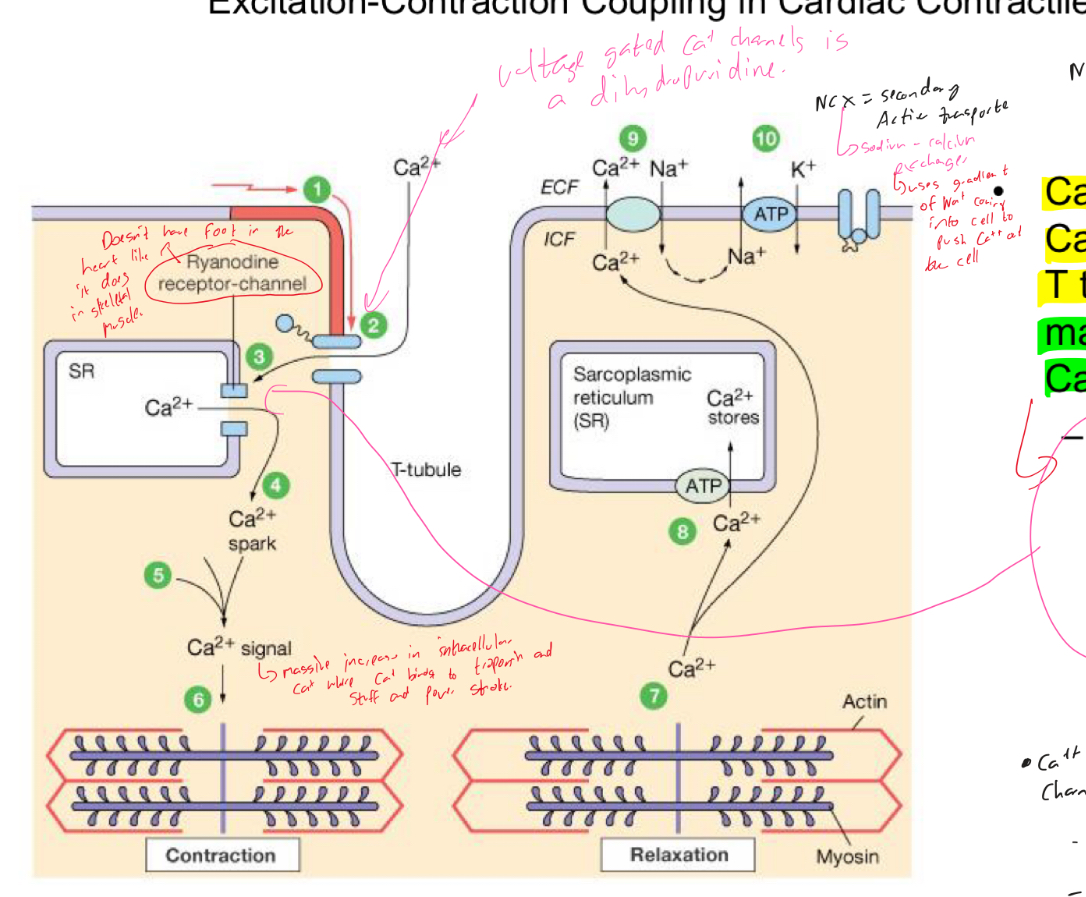
Explain excitation contraction coupling in cardiac contractile cells
Ca++ entry through Ca++ channels in T tubules triggers massive release of Ca++ from SR
Ca++ induced Ca++ release leads to cross bridge cycling and contraction