Unit 2 - Anatomical Organization, Histology, and Maintenance of Homeostasis
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Cells
basic unit structure/function
Cellular organization
cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Tissues
group of specialized cells which perform a specific function
Epithelial Tissue
lining and covering
Basement membrane
forms between the epithelial and connective tissue
Avascular
lacks its own blood supply; nutrients diffuse from neighboring connective tissue
Mitosis
very high rate; renews/repairs itself rapidly
Simple Squamous
Commonly found in alveoli and lining of blood vessels; nucleus is centrally located
Simple Cuboidal
Commonly found in kidney tubules; simple (single layer of cells)
Ciliated Simple Columnar
Commonly found in oviducts/upper respiratory tract
Nonciliated Simple Columnar
Commonly found in ileum, gallbladder, and urinary tract; may contain goblet cells (secrete mucus)
Simple Columnar with microvilli brush border
Commonly found in duodenum; microvilli found at apical surface to increase surface area/absorption
Keratinized Stratified Squamous
Commonly found in superficial skin layer; contains filaments of the protein keratin
Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous
Commonly found in esophagus, oral cavity, vagina, anal canal; no keratin, must be kept moist
Stratified Cuboidal
Commonly found in ducts of mammary, sweat, and salivary glands; rare
Stratified Columnar
Commonly found in lining of developing ovarian follicles
Pseudostratified
appears layered, but is not; nuclei don't line up
Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar
located in respiratory passages
Nonciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
located in prostate vas deferense, No mucus or cilia
Transitional
Commonly found in urinary bladder; cells change shape (from squamous to columnar) as body parts stretch and move
Endocrine Glands
secretions enter the extracellular fluid and diffuse into the bloodstream; no ducts; secretions are called hormones
Exocrine Glands
secrete products into a duct that leads to the surface of the skin or into the lumen of a hollow organ, such as sweat glands and salivary glands, produce digestive enzymes
Merocrine secretion
Cells secrete their substances by exocytosis.
Common locations for Merocrine glands
Salivary and Sudoriferous (sweat) Glands.
Apocrine secretion
A portion of the cell membrane that contains the secretion buds off.
Common location for Apocrine glands
Sebaceous (oil) Glands.
Holocrine secretion
The entire cell disintegrates to excrete its substance.
Connective Tissue
Most abundant tissue used for binding and supporting.
Characteristics of Connective Tissue
Supports/strengthens/protects/insulates and is the major transport tissue (blood).
Stored energy in Connective Tissue
Adipose tissue.
Extracellular Matrix
Material found in space between tissue cells, containing ground substance and fibers.
Ground Substance
Can be fluid/semi-fluid/gelatinous/calcified.
Mesenchymal Connective Tissue
First connective tissue to develop in the embryo from which all connective tissues are later derived.
Mesenchymal stem cells
Clusters scattered throughout adult tissue that supply cells needed for replacement and repair after injury.
Composition of Extracellular Matrix
Composed of ground substance + protein fibers.
Rich nerve and blood supply
Characteristic of connective tissue, except for cartilage.
Collagen Fibers
Very strong and flexible; contain collagen protein
Elastic Fibers
Stretch and recoil; elastin protein
Reticular Fibers
Support and strength; collagen protein with glycoprotein coating
Immature Fibroblasts
Secrete the matrix and produce new cells in loose/dense connective tissue
Chondroblasts
Secrete gelatinous matrix in cartilage
Osteoblasts
Bone formation, secretion of organic fibers and inorganic salts to create crystalline matrix
Mature Fibroblasts
Secrete fibers and ground substance of matrix in loose and dense connective tissue, lots of collagen
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
Transport oxygen
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
Immune response; i.e. plasma cells - secrete antibodies/immune system
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Blood clotting
Mast Cells
Produce histamine, a chemical that triggers inflammatory response which increases vascular permeability and attracts more phagocytic cells to the site
Adipocytes
Fat cells that store triglycerides, found below skin and around organs
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells
Chondrocytes
Mature cartilage cells
Macrophages
Develop from WBC's; move about in connective tissue as scavengers clearing foreign particles
Loose Connective Tissue
Includes areolar, reticular, and adipose; contains fibroblasts, adipocytes, mast cells, macrophages
Dense Connective Tissue
Mainly fibers; little else; includes regular and irregular types
Cartilage
Provides support and flexibility; minimizes friction; forms features and found in joints
Bone
Provides framework; protects organs; supports body
Blood and Lymph
Plays role in immune defenses; found in spleen and lymph nodes
Hemopoietic Blood
Provides transportation, regulation and protection; carries oxygen and nutrients to cells; carries away wastes and carbon dioxide
Muscle Tissue
Types include skeletal, cardiac, and smooth; contract to produce voluntary or involuntary movements.
Skeletal Muscle
Striated and voluntary; attached to bones of the skeleton.
Smooth Muscle
Non-striated and involuntary; located in walls of hollow organs such as blood vessels, intestines, and urinary tract.
Cardiac Muscle
Striated with intercalated discs; involuntary; walls of the heart pump blood.
Nervous Tissue
Initiates and transmits nerve impulses to coordinate activities of the body.
Neurons
Specialized to transmit electrical (nerve) impulses; sense stimuli and convert them into nerve impulses.
Neuroglia
Do not generate or conduct nerve impulses; smaller than neurons and many times more numerous.
Astrocytes
Help provide proper environment for the generation of nerve impulses; provide nutrients to neurons.
Microglial Cells
Engulf invading microbes and clear debris of dead cells.
Oligodendrocytes
Provide support for surrounding neurons; produce myelin sheaths around adjacent neuron axons.
Ependymal Cells
Line cavities of the brain filled with CSF; form CSF and aid with its circulation.
Schwann Cells
Produce myelin sheath around axons of PNS neurons.
Satellite Cells
Form a protective layer around neuron cell bodies in PNS providing nutritional and metabolic support.
Organ
Two or more tissues that work together to perform a specific function.
Organ System
A group of related organs that have a common function.
Integumentary System
The skin and structures derived from it such as hair, nails, and sweat and oil glands; regulates body temperature and protects.
Skeletal System
All the bones and joints of the body and their associated cartilages; supports and protects the body.
Muscular System
Specifically skeletal muscle tissue; powers movements of the body and generates heat.
Cardiovascular System
Blood, heart, and blood vessels; pumps blood carrying oxygen/nutrients to cells and removes carbon dioxide/wastes.
Lymphatic or Immune System
Lymph, lymphatic vessels, and structures containing lymphatic tissue; returns proteins and plasma to the cardiovascular system.
Transport of fats
Transport of fats from gastrointestinal tract to the cardiovascular system.
Nervous system
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sense organs. Regulates body activities in response to internal and external stimuli. Interprets stimuli and responds through muscular contractions or glandular secretions.
Endocrine system
Hormone producing glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, and pancreas. Regulates body activities through hormones, chemicals transported in the blood to target cells.
Respiratory system
Lungs and the airways leading into and out of them. Transfers oxygen from inhaled air to blood and carbon dioxide from blood to exhaled air. Helps regulate pH balance of body fluids.
Digestive system
Physical and chemical breakdown of foods, absorbs nutrients, eliminates solid wastes. Organs of the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines) and accessory organs (salivary glands, pancreas, liver and gallbladder).
Urinary system
Kidneys, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra. Regulates volume and chemical composition of blood. Eliminates metabolic wastes. Regulates fluid and electrolyte balance. Helps maintain pH of body fluids and calcium balance of the body. Secretes hormone that regulate red blood cell production.
Reproductive system
Gonads (testes/ovaries), uterus, vagina, ductus deferens, epididymis, and penis. Produce gametes and release hormones that regulate reproduction. Transport and store gametes.
Homeostasis
Maintenance of a stable internal environment (optimal conditions). Necessary for normal body functioning, to sustain life.
Homeostatic imbalance
A disturbance in homeostasis resulting in disease/breakdown.
Feedback Mechanisms
Mechanisms by which the body senses and responds to internal and/or external stimuli in order to maintain homeostasis.
Negative feedback
Includes most homeostatic control mechanisms. Ex: body temperature, glucose levels. Shuts off the original stimulus, or reduces its intensity.
Positive feedback
The response amplifies the initial stimulus. Not common - only blood clotting and childbirth.
Positive Feedback Example
Alarm or panic can spread by positive feedback among a herd of animals to cause a stampede.
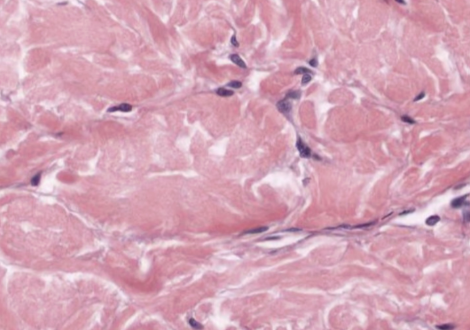
Simple Squamous Epithelium Tissue
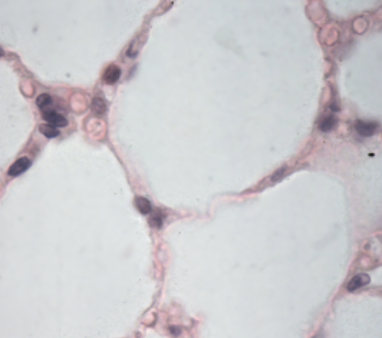
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Tissue
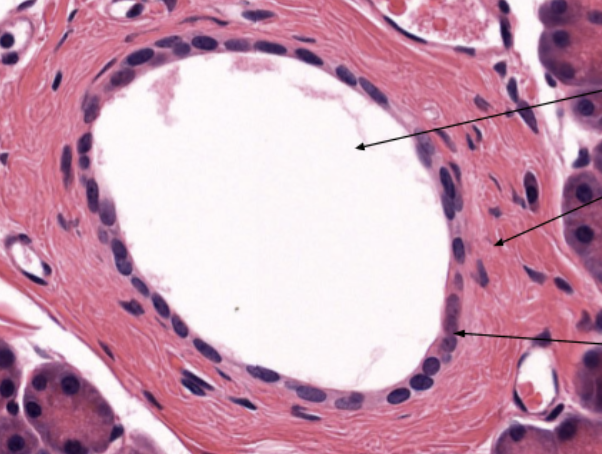
Simple Columnar Epithelium Tissue
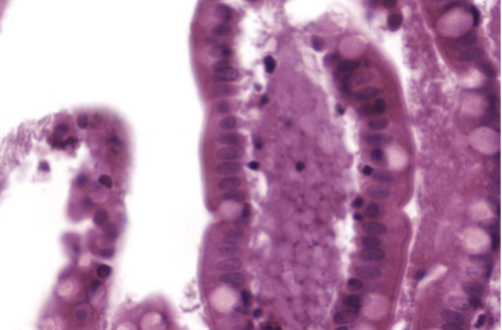
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous epithelial Tissue
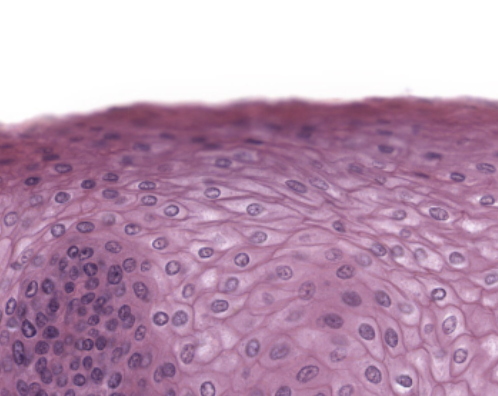
Keratinized Stratified Squamous epithelial tissue
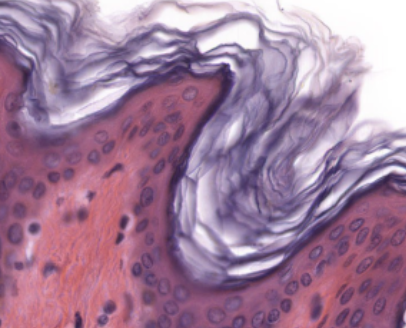
Pseudostratified Columnar epithelial tissue
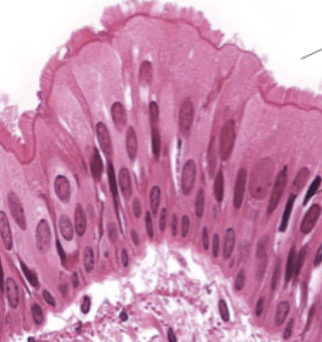
Loose Connective Tissue
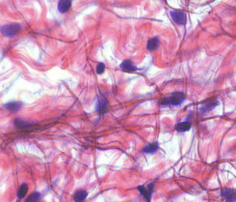
Adipose connective tissue
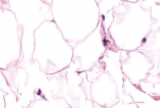
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
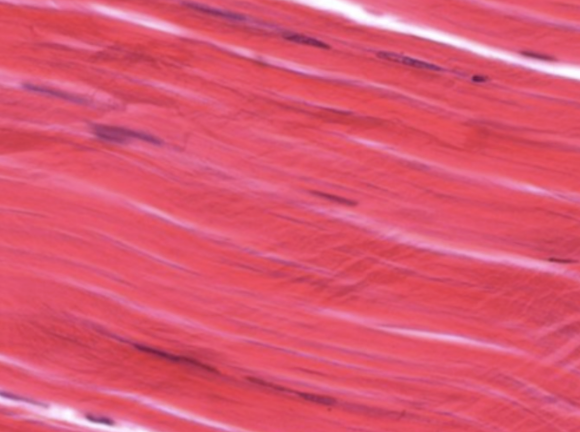
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue