forensic exam 3
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
the three classifications of substances by CH, bonding and formats
the inner structure of substances
protons, neutrons and electrons
the modified griess test
a nondestructive test of GPR that is sprayed onto the skin or clothing; if it turns pink it is positive
five types of gunpower
2 kinds of flakes, balls, discs, cylinders
the SEM examination
can enlarge GSR half million- a million times
GSR
Gun shot reside; made of lead, antimony and barium
GPR
gun powder reside; multiple kinds
organic materials
carbon based compounds
inorganic materials
compounds that dont contain carbon
element
the building blocks of all matter
compound
substances that are composed of two or more elements chemically combined
mixture
matter consisting of two or more pure substances that retain their individual identities and can be separated
alloy
a mix of metals in different ratios
protons
Positively charged particles
neutrons
the particles that have no charge
electrons
Negatively charged particles
atomic number
the number of protons in the atom
atomic mass
sum of protons and neutrons
atomic weight
weight average of all isotopes
contusion ring
soot or smoke around the bullet wound
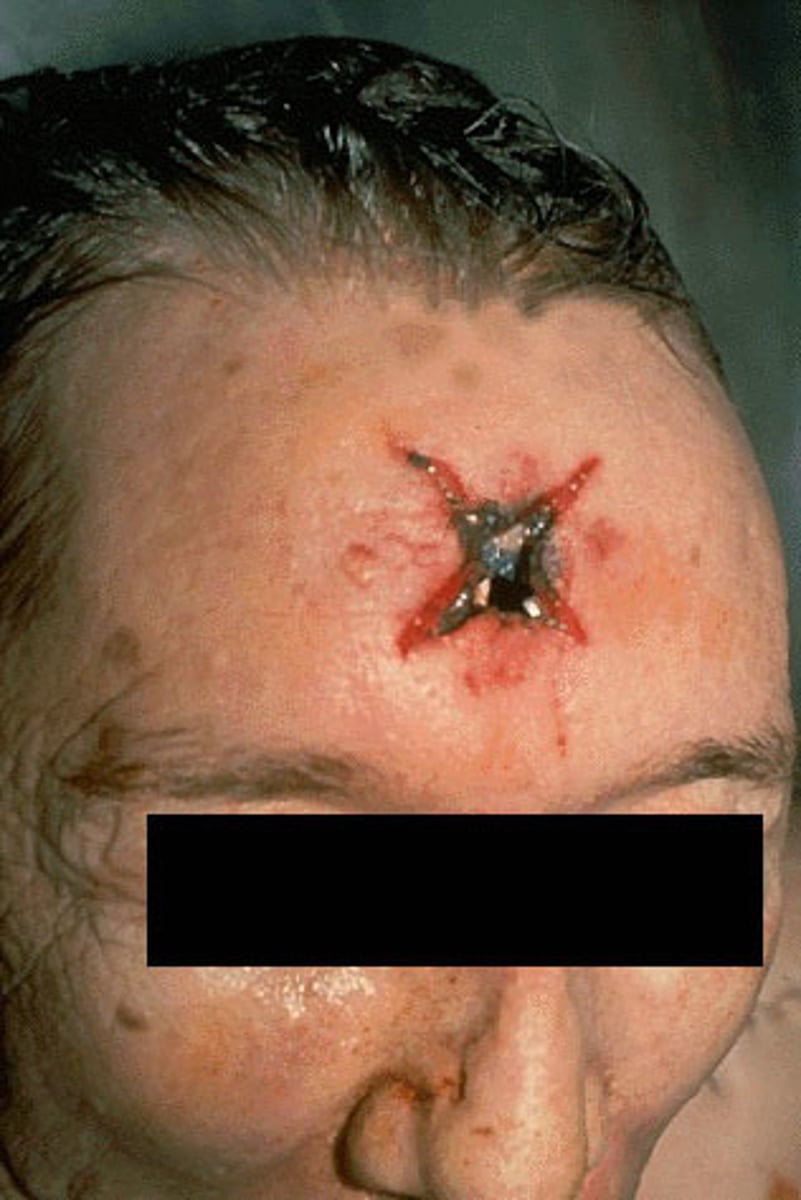
abrasion ring
cone shaped, star, torn, from contact or close to contact shot
isotopes
same carbon property of an element but different atomic mass
ions
positively and negatively charged atoms
burned poweder
part of GPR, can be used for testing
unburned powder
allows for chemical testing, part of GPR, griess test can be conducted on
soot
burned powder
stippling
comes from close range; little dots on the skin
particles
small amount; typically from unburned powder
micrometer
how SEM is measured
quality analysis
confirms the presence of a molecule or element
quantity analysis
determines the compound present and its concentration
the major components of human blood and its testing steps
erythrocytes, leukocytes and thrombocytes
the principles of luminol and seratec tests
testing of body fluids through spray
the ABO typing system
broad classifications based on antigen A or antigen B
the principle of the pythagorean theorem on the blood angle calculation
cos (angle)= shorter angle/ longer angle
the principle of saliva and semen tests
presence of salivary amylase and seminal stain
erythrocytes
red blood cells
leukocytes
white blood cells; carry DNA
non human blood samples
blood samples from animals
non blood samples
spinach, horseradish, bleach, metals, etc.
presumptive tests
a preliminary test to determine if the red stain is a human blood with a possible mistake but good for plea bargain
confirmatory tests
refer to a second test by advanced techniques
luminol
can detect the iron in blood from mixes as low as 1-1 million mixtures; dark blue light is positive
seratec tests
tests on blood, saliva and semen
hemoglobin in blood
can be detected by luminol and seratec
iron element in blood
in hemoglobin and can be detected by luminol
sine
used to determine the angle of blood spatter
cosine
inverse of sin
false positive tests on blood
a positive test when it should be negative; could be caused by horseradish, spinach, bleach, and certain metals and plants
false negative tests on blood
a negative test when it should be positive
type AB blood
3% of people have; master receiver because they have both A and B antigens
type O blood
43% of people have; master donor because they have neither A or B antigens
spinach by luminol
can produce a false positive
blood by luminol
a test that detects the iron in blood, can be applied to large areas, is very sensitive and cheap
n-DNA
nuclear DNA; can be used to pin down an individual
the brief DNA history
the DNA roadmap
the flow from largest part of the genome to the smallest part
the pitchfork syndrome
believing you can get away with murder after leaving DNA on the scene
the two DNA comparison methods (the sequential order and the allele)
DNA coding- sequential order; number of repeats; allele method
the supreme court decisions on DNA examination
50 states require samples to be collected from those convicted of felonies; 28 states and the federal government currently collect DNA samples from arrestees for felonys
the coded gene
only 1 percent of genes
non-coded gene
99 percent of the genes
genome
the entirety of the human makeup; the world
chromosome
A specific part of the genome, CA
gene
a region of DNA that helps determine a characteristic; Long Beach
locus/loci
a specific spot on a chromosome occupied by and repeats vary by individuals; a neighborhood in Long Beach
alleles
number of repeats by STR in the junk area; number of same looking houses in a neighborhood
TA base pair
2 hydrogen bonds
GC base pair
3 hydrogen bonds
the letter order
a sequence of expression
the alleles methods
two numbers of the repeats at each locus from two parents for 26 numbers
PCR
polymerase chain reaction; can amplify a partial DNA by two steps
STR
short tandem repeats; locations/markers on genes; less likely to degrade
f-DNA
familial DNA
m-DNA
mitocondrial DNA that can narrow down a suspect to siblings of a mother; 1,000 per cell
Y-DNA
DNA found in the Y chromosome and is therefore inherited through the paternal line; looking at gender
CODIS
DNA database
NGI
Next Generation Identification; using palm print, iris color, facial freckles, hair color, etc. to identify individual
forensic genealogy
using genetic information to identify suspects
genotyping
the genetics of an individual
phenotyping
observable characteristics resulting from the interaction between genotype and the environment
degredation
starting to break down
cross contamination
the process by which bacteria or other microorganisms are unintentionally transferred from one substance or object to another
mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information