Personal Finance: Money Management, Budgeting, and Financial Statements
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
Money management
The day-to-day financial activities necessary to manage current personal economic resources while working toward long-term financial security.
Personal financial records
Documents that help you plan the use of your resources.
Personal financial statements
Documents that measure and guide your financial position and progress.
Spending plan
Also known as a budget, it is the basis for effective money management.
Receipts
Proof of purchase that is part of financial recordkeeping.
Credit card statements
Monthly summaries of credit card transactions that are part of financial recordkeeping.
Insurance policies
Documents that outline the terms of insurance coverage, part of financial recordkeeping.
Tax forms
Documents required for tax reporting, part of financial recordkeeping.
Home files
Used to keep records for current needs and documents with limited value.
Safe deposit box
A private storage area at a financial institution with maximum security for valuables.

Computer system
An online system, such as 'the cloud', for storing financial records.
Personal and employment records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to personal and job history.
Money management records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to managing finances.
Tax records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to tax filings.
Financial services records
Category of financial records that includes documents from financial institutions.
Credit records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to credit history.
Consumer purchase records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to consumer goods purchases.
Housing records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to housing and property.
Insurance records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to insurance coverage.
Investment records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to investments.
Estate planning records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to estate planning.
Retirement records
Category of financial records that includes documents related to retirement planning.
Birth certificates
Documents that should be kept permanently.
Wills
Documents that should be kept permanently.
Social Security data
Documents that should be kept permanently.
Federal tax documents
Should be kept for three years from the date you file your return, consider keeping for six years.
Real estate documents
Should be kept indefinitely related to the purchase and sale of real estate.
Balance Sheet
A financial statement that reports what an individual or family owns and owes.
Liquid Assets
Cash and items of value that can easily be converted to cash.
Real Estate
Property consisting of land and the buildings on it.
Personal Possessions
Items owned by an individual that have personal value.
Investment Assets
Assets that are held for the purpose of generating income or appreciation.
Current Liabilities
Debts that must be paid within a short time, usually less than a year.
Long-term Liabilities
Debts that you do not have to pay in full until more than a year from now.
Net Worth
The difference between total assets and total liabilities.
Insolvency
The inability to pay debts when they are due because liabilities exceed the value of assets.
Cash Flow
The actual inflow and outflow of cash during a given time period.
Cash Flow Statement
A statement that summarizes cash receipts and payments for a given period.
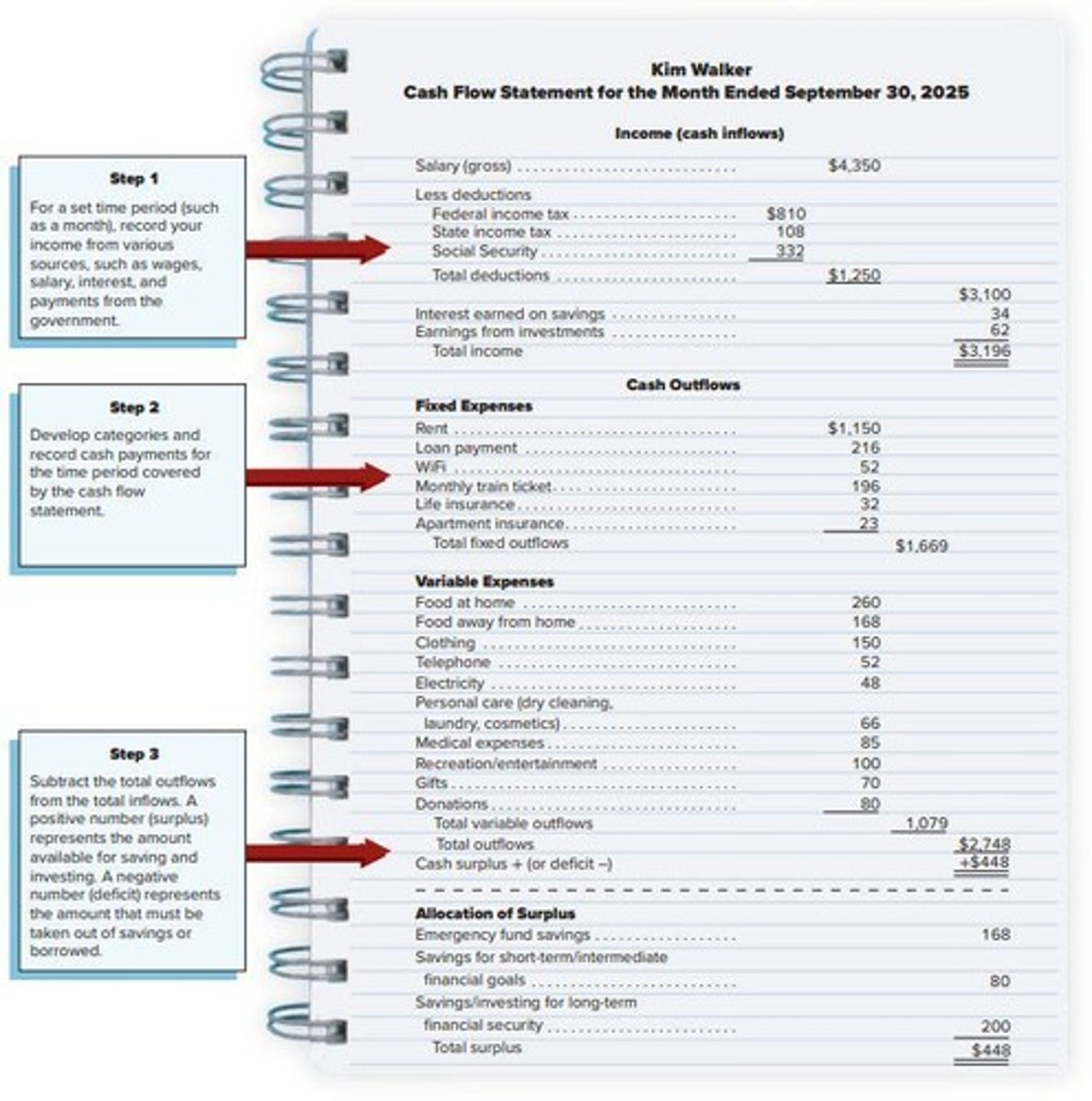
Inflows
Deposits made into your account, including income from employment and interest earned.
Outflows
Checks written, cash withdrawals, and debit card payments, including expenses like rent and food.
Take-home Pay
Earnings after deductions for taxes and other items; also called disposable income.
Discretionary Income
Money left over after paying for housing, food, and other necessities.
Fixed Expenses
Regular, recurring costs that do not change in amount.
Variable Expenses
Costs that can fluctuate in amount from month to month.
Budget
A specific plan for spending income.
Financial Goals
Objectives that individuals aim to achieve through financial planning.
Financial Emergencies
Unexpected financial situations that require immediate attention and resources.
Financial Management Habits
Practices that promote effective handling of financial resources.
Short-Term Goals
Goals that are set to be achieved in less than 2 years.
Immediate Goals
Goals that are set to be achieved in 2 to 5 years.
Long-Term Goals
Goals that are set to be achieved over 5 years.
Single person financial goals
Complete college, take a vacation to Europe, buy a vacation home in the mountains, pay off auto loan, pay off education loan, provide for retirement income, donate to charity, attend graduate school, take an annual vacation, remodel home, buy a retirement home.
Married couple (no children) financial goals
Build a stock portfolio, provide for retirement income, buy a new car, increase life insurance, increase investments, accumulate a college fund for children.
Parent (young children) financial goals
Increase savings, buy a new car, move to a larger home.
SMART approach
A method for setting financial goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Budget variance
The difference between the amount budgeted and the actual amount received or spent.
Mental budgets
Budgets that exist in a person's mind.
Physical budgets
Budgets that involve envelopes, folders, or containers.
Written budget
A budget that can be kept in a notebook.
Digital budget
A budget that may involve spreadsheets or software.
Typical After-Tax Budget Allocations
Budget allocations for different life situations, including housing, transportation, food, clothing, personal and health care, entertainment, reading and education, personal insurance and pension payments, gifts, donations, and contributions, and savings.
Housing budget allocation
0 to 25% for a couple over 55, 30 to 35% for a couple with no dependents, 20 to 30% for a working single, 25 to 30% for parents with children over 18 in college.
Transportation budget allocation
5 to 10% for a couple over 55, 15 to 20% for a couple with no dependents, 10 to 18% for a working single, 12 to 18% for parents with children over 18 in college.
Food budget allocation
15 to 20% for a couple over 55, 15 to 25% for a couple with no dependents, 13 to 20% for a working single, 15 to 20% for parents with children over 18 in college.
Clothing budget allocation
5 to 12% for a couple over 55, 5 to 15% for a couple with no dependents, 5 to 10% for a working single, 4 to 8% for parents with children over 18 in college.
Personal and health care budget allocation
3 to 5% for a couple over 55, 3 to 5% for a couple with no dependents, 8 to 12% for a working single, 4 to 6% for parents with children over 18 in college.
Entertainment and recreation budget allocation
5 to 10% for a couple over 55, 5 to 10% for a couple with no dependents, 4 to 8% for a working single, 6 to 10% for parents with children over 18 in college.
Reading and education budget allocation
10 to 30% for a couple over 55, 2 to 4% for a couple with no dependents, 3 to 5% for a working single, 6 to 12% for parents with children over 18 in college.
Personal insurance and pension payments budget allocation
0 to 5% for a couple over 55, 4 to 8% for a couple with no dependents, 5 to 9% for a working single, 4 to 7% for parents with children over 18 in college.
Gifts, donations, and contributions budget allocation
4 to 6% for a couple over 55, 5 to 8% for a couple with no dependents, 3 to 5% for a working single, 4 to 8% for parents with children over 18 in college.
Savings budget allocation
0 to 10% for a couple over 55, 4 to 15% for a couple with no dependents, 5 to 8% for a working single, 2 to 4% for parents with children over 18 in college.
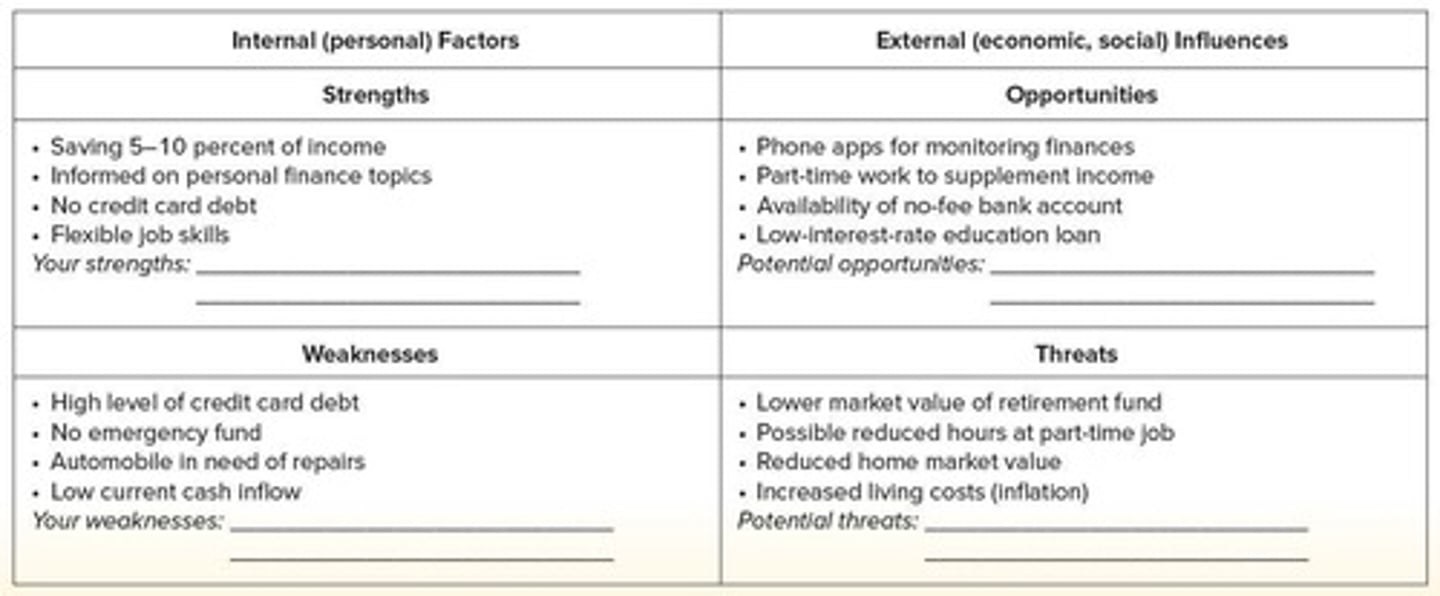
SWOT analysis
A planning tool used by companies that can also help with money management and budgeting activities.
Changes in net worth
Result from cash inflows and outflows.
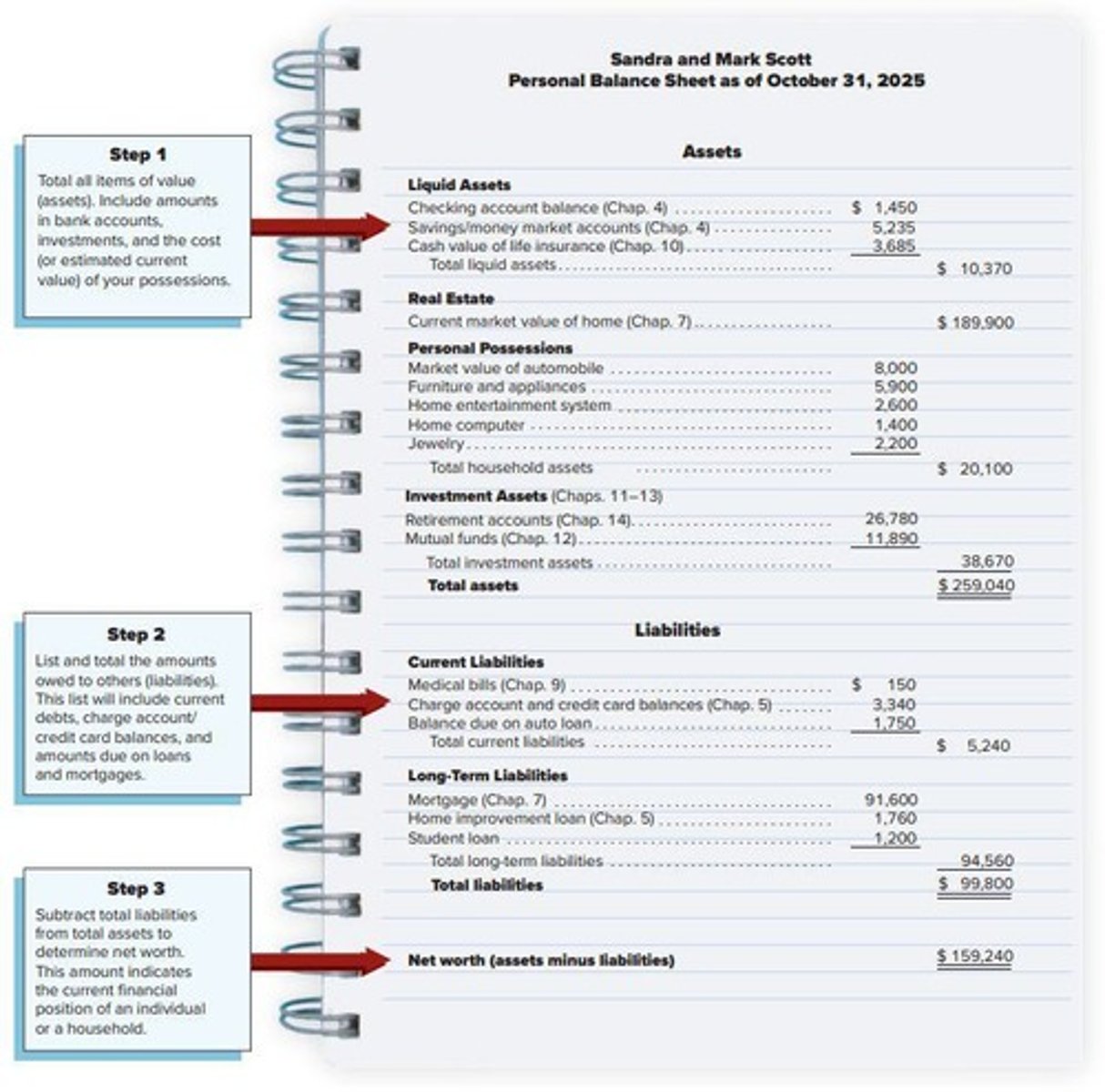
Personal Balance Sheet
A statement that lists all items of value (assets) and amounts owed (liabilities).
Savings Rate
The percentage of income that is saved, often suggested as 5 to 10 percent.
Employer Matching Contributions
Additional funds contributed by an employer to an employee's retirement account, matching the employee's contributions.
Emergency Fund
Savings set aside to cover unexpected expenses.
Budgeting Process
A series of steps including setting financial goals, estimating income, and reviewing spending patterns.
Financial Records
Documents that provide information about an individual's financial activities and status.
Savings Goals
Specific amounts of money that one aims to save for future needs or objectives.
Future Value Calculations
Mathematical computations used to determine the value of an investment at a future date based on a specified rate of return.
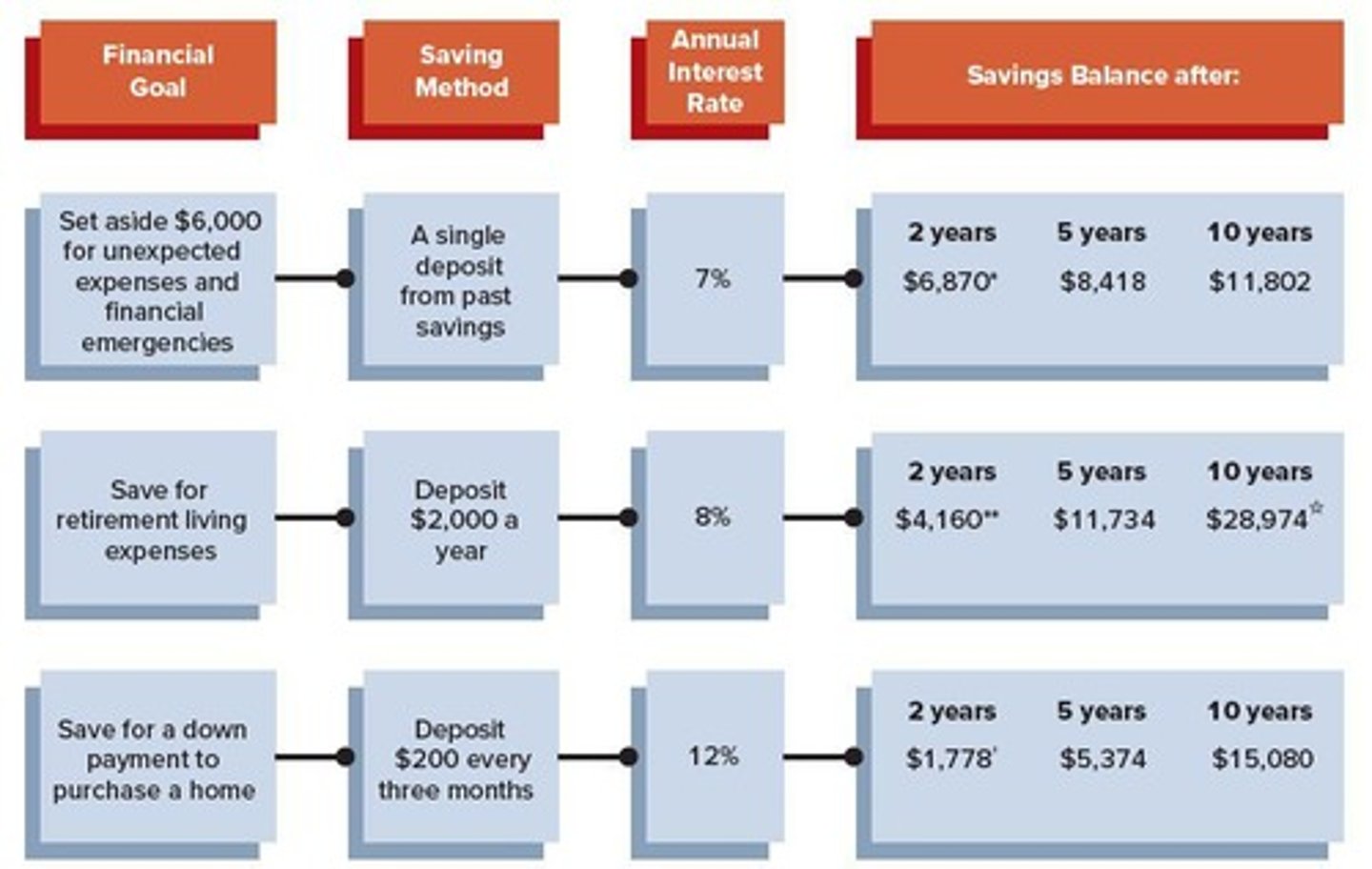
Present Value Calculations
Mathematical computations used to determine the current worth of a future sum of money or stream of cash flows given a specified rate of return.
Fireproof Home Safe
A secure safe designed to protect contents from fire damage.
Certificates of Deposit
A savings certificate with a fixed maturity date and specified fixed interest rate.
Insurance Policy Numbers
Unique identifiers assigned to insurance policies for tracking and management.
Estate Plan
A plan for managing an individual's assets and responsibilities in the event of their death or incapacitation.
Digital Records
Electronic versions of important documents stored on computers or devices.
Budget Summaries
Overviews that outline expected income and expenses over a specific period.
Assets
Items of value owned by an individual or household, including liquid assets, real estate, personal possessions, and investment assets.
Liabilities
Amounts owed to others, including current debts, charge account and credit card balances, and amounts due on loans and mortgages.
Income (cash inflows)
Money received from various sources, such as wages, salary, interest, or payments from the government.
Deductions
Amounts subtracted from gross income, including federal income tax, state income tax, and Social Security.
Total Assets
The sum of all assets owned, which in the example is $259,040.
Total Liabilities
The sum of all liabilities owed, which in the example is $99,800.
Total Current Liabilities
The sum of all current debts, which in the example is $5,240.
Total Long-Term Liabilities
The sum of all long-term debts, which in the example is $94,560.
Total Liquid Assets
The sum of all liquid assets, which in the example is $10,370.
Total Investment Assets
The sum of all investment assets, which in the example is $38,670.
Market Value of Home
The current market value of a home, which in the example is $189,900.
Market Value of Automobile
The market value of an automobile, which in the example is $8,000.