Astro Lecture 3 - Galaxies
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What are Cepheid variables?
A class of pulsating stars.
These stars had just left the main sequence
Their period of radial pulsation is closely correlated with their intrinsic luminosity
What are 3 main types of galaxies?
Eliptical
Spiral
Irregular
Describe the Hubble Tuning Fork Scheme, including all types and subtypes, and explaining ellipticity
E = 10(1-b/a) where 0<E<7 and an intermediate class of S0. a and b are length of axes

How are spiral galaxies labelled if they have a bar or not?
S - no bar
SB - bar
How are spiral galaxies labelled according to the tightness of the spiral arms?
Tighter in - Sa then Sb then Sc - not tight in
How are spiral galaxies labelled according to the ratio of light in a central redder “bulge” to that in a bluer disk?
Sa - Sb - Sc
SBa - SBb - SBc
Indicating a trend to a lower bulge/disk ratio and hence bluer colours
Why is the Hubble classification still useful?
Despite beiing based on optical appearance there are profound physical differences along the seqeunce
How is 3D shape different for different galaxies?
Spirals are flattened circular disks seen at various orientations.
Elipticals are spherodial systems
How is kinematics different for different galaxies?
Spirals are rapidly rotating
Most large ellipticals are not
How are stellar populations different for different galaxies?
Spirals are actively forming new stars
Elipticals have uniform red colours (old stars and little ongoing new star formation)
What piece of evidence shows spiral galaxies are rotating at high velocities?
Long slit spectroscopy of nearby spiral galaxies using various emission lines reveals Doppler shifts along major axes
Are elliptical galaxies flattened by rotation and why?
Suprisingly, no. If this were the case their rotational velocity would follow the trend that more elongated ellipticals rotate faster. This is not the case.
How would you describe the velocity of stars in an elliptical?
The stars have no coherent systematic velocity
Where does the colour difference between ellipticals and spirals originate from?
Very different stellar populations
Where do blue and red colours originate from for galaxies - and what does colour therefore tell us?
Blue - fully populated MS so plenty of young massive stars (Pop I)
Red - Only old low mass MS stars and red giants (Pop II)
Colours therefore tells us about star formation history
Describe the two population states - I and II
Pop I - Actively forming young stars, heavy element production has continued so metal rich, e.g. spiral disk with plentiful gas for future star formation
Pop II - Old stellar population, no further star formation and metal-poor, e.g. central bulges of spirals, elliptical glaxies, globular clusters
Describe in full the Milky Way as a galaxy
A typical barred SBc spiral
central “bulge” and bar (Pop II)
rotating disk (Pop I)
stellar halo (Pop II)
globular clusters (Pop II)
What is the combined stellar mass of Milky Way?
10^11 to 10^12 M(sun)
How is the stellar halo studied?
Using the stellar motions of stars (Gaia proper motions plus radial velocities)
How does the halo differ from the disk?
It does nto share the systematic rotation of the disk and its stars are on elliptical orbits plunging through our solar neighbourhood so they are easily identified
What are some more important properties of the halo?
Old
Metal - poor
What must every luminous galaxy be surrounded by and where did evidence for this come from?
A dark halo made from dark matter, and ecidence came from rotation curves
How did rotation curves provide this evidence?
Rotation curve remain flat out to radii well beyond the end of the visible disk where light and stellar component is rapidly declining
Due to the fact that M(<r) (mass interior to radius of galaxy) = rv²/G, if v is constant with increasing r, this means M(<r) also increases with radius r, in contrast to declining light
This indicates additional dark material within spherical radius r
Why is rotation curve for Milky Way less well-determined than those for external galaxies?
Because we are embedded within the Milky Way and the distances to sources outside the solar radius are highly uncertain.
How are galaxies usually found in the universe?
Often aggregate in groups and rich clusters of 100-1000 members
What lead to scientists theorizing dark matter must exist in relation to clusters fo galaxies?
In the Coma cluster, Zwicky measured relative motions of galaxies and deduced they were moving too quickly to be bound to the system unless 20-50 times more mass existed somewhere he couldn’t observe
How is cluster mass calculated?
We cannot use KE equation to get cluster mass
We must use the velocity dispersion of the distribution
Assume equilibrium between kinetic and potential energy as in image

What is baryonic matter?
Stuff composed of protons and neutrons, i.e. familiar atoms and molecules
Why can dark matter not be baryonic material/sources in galaxies?
Due to the fact that there is no room dor baryonic matter in the Galactic disk.
Why can dark matter nit be baryonic matter elsewhere (e.g. dark stars/black holes in halo or gas/material inbetween galaxies)?
Can be rejected using abundancies of ligt elements synthesided in Big Bang which deoends on total baryon density
What is dark matter theorized to be then?
A cold, non-interacting particle.
What does this mean simulations suggest about galaxies?
Should be many more tiny galaxies for each large galaxy (dwarf galaxies). These have since been discovered.
What is a typical luminosity of a dwarf galaxy?
10^-3 of that of the Milky Way
Why can spiral arms of galaxies not be permanent features?
Because of differential rotation (angular speed Ω(r) is faster in inner regions). This would quickly wind up the arms.
Describe the density wave theory and give the equation
Stars in orbits with angular frequency k can resonate with this pattern so in each orbital period they encounter succesive crests in the wave.
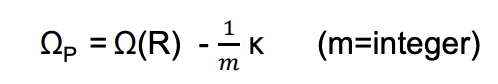
How close are galaxies to each other relative to stars?
Much closer
Can two spirals merge to become an elliptical?
Yes theoretically
What evidence is there for the fact galaxies are continuously accreting fainter satellites?
In the case of the Milky Way, we can see stellar streams which are from stars tidally stripped from infalling satellites
Why are ellipticals bigger and rotating more rapidly today than in the past and how do we know this?
They suffered many mino mergers which “puffed up” their sizes and reduced their angular momentum. We know this due to the Hubble Telescope which can see out to redshifts z=2 corresponding to about 12Gyr ago.
Describe the nature hypothesis for S0 galaxies?
S0 galaxies are a genuine class which formed like that a birth.
Describe the nuture hypothesis for S0 galaxies?
They are “failed spirals” which suffered some environmental catastrophe and lost their gas so they could no longer form stars
Where are S0s dominant and whats does this mean for them?
Dominant in dense cluster of galaxies whereas spirals are not. Spirals could perhaps not survive the cluster environment and lost their gas to become S0.
What does this last point mean for spiral galaxies if correct?
We should see more spirals in clusters if we look back in time
What caused spirals to be transformed into S0s over time?
Tidal effects in the cluster gravitational potential
Hot gas in the intracluster medium
Why does removing gas from the disks cause the change in morphology?
As star formation is truncated
What do most galaxies host in their nuclei?
Suer massive black holes whose mass correlates with that of the galaxy
What does it mean for a black hole to be active?
If it has an accretion disk which fuels material into the black hole.
What type of spectrum does this accretion disk produce?
A non-thermal spectrum with broad emission lines or powerful X-ray and radio jets
What is monolithic collapse?
The faact that galaxies were once considered as isolated systems which formed at once and evolved independantly.
What the hierarchiral picture/
The fact that halos merged first and then more massiev systems were formed later
What is the feedback process?
Teh fact that AGN acitivity can inhibit star formation through heating surrounding gas and preventing it from cooling to form stars.
Describe two ways in which we can look even further back in time?
Ultra-Deep Field - a total of 10 days exposure on one patch of sky only 3 arcmin across.
Gravitational lensing - imaging through foreground clusters which gravitationally magnify background sources otherwise beyond detection.
What is the cosmic dawn and what did it lead to ?
When the first galaxies emerged from darkness, the universe was bathed in light from young stars.
This led to a long process of chemical enrichment in the universe and ultimately to our own existence.