NSC 837 - Lecutre 6 - photobleaching, autofluorescence labeling, live cell imaging, colocalization
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
fading/photobleaching
irreversible decomposition of a fluorescent molecule
primarily due to the effects of oxygen free-radicals
caused by both the high power, focused beam of confocal system long exposures to the lower intensity mercury lamp systems
if sample is photobleached won’t be able to look at it again
what is fading/photobleaching affected by
intensity of light, duration of light, wavelength of light, pH of embeddng medium (fixed samples)
what can slow the fading process
antifade reagents
difficult for live cells (vitamin c instead)
autofluorescnce
endogenous fluorescence: compounds nnaturally present in cells or tisssue (ex fatty acids, b vitamins, nadh)
fixation-induced fluorescence often the result of aldehyde fixation— glutaraldehyde (worse) to formaldehyde
how to reduce background autofluorescence for fixed cells
image-iT FX signal enhancer - reduces background from non-specific staining by secondary conjugates or antibodies
how to reduce background autofluorescence for live cells
backdrop background suppressor - supressses background in live cells. apply 2 drops per ml directly to live cells
antibodies
5 classes (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE), composed of 2 heavy chaing and 2 light chains
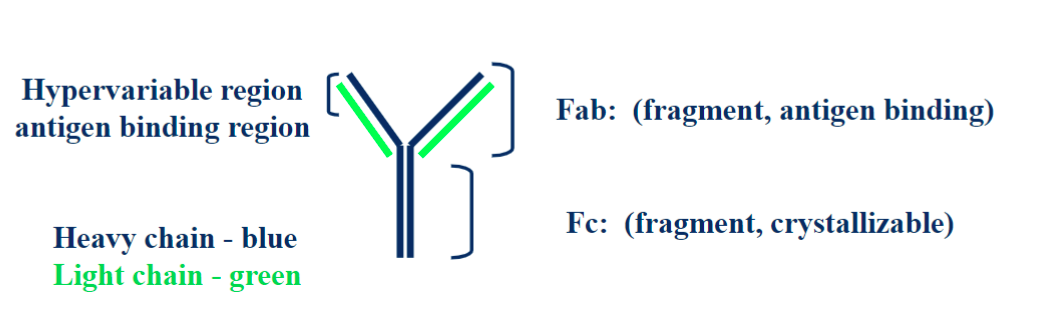
antibodies and imaging
can use to look for component in cell (protein)
usually need to fix sample to use an antibody, it is too big to fit in cell.
nanobodies
isolated from llamas. The consist of a heavy chain and on variable region. It is smaller and can get into smaller regions that regular antibodies can not fit into.
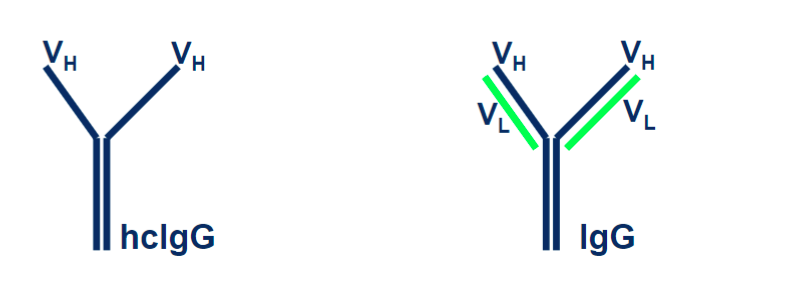
advantages of nanobodies
smalle
enhanced tissue pentration
more easily penetrates small cavities
high affinity and increased specificty
more stable to extreme temps and pH
indirect immunoflourescence
1) add primary (non-fluorescent) antibody to cells tissue
2) incubate
3) wash away excess antibody
4) add secondary antibody with fluorochrome to cells/tissue already labeled with primary
5) incubate
6) wash away excess antibody
controls
1) image fully stained specimen - optimize settings and don’t change
2) image specimen labeled with primary alone -autofluorescence control
3) image specimen labeled with secondary alon (nonspecific binding of secondary antibodies)
fluorescent proteins
GFP is the main one and is a type of fusion protein
fusion proteins
gene of florescent protein is attached to gene of protein of interest
clickable proteins
uses a small sequene that can be encoded with the protein of interest to creat a dusion protein and then snaps an organic dye molecule that reacts (snaps into place)with the target sequnce through a chemical reaction.