Biology : Cell & Microorganisms
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is Cell Theory?
All living things are made up of cells. All cells come from pr-existing cells. Cells are the building block of life.
Unicellular cell
Single cell like bacteria
Multicellular cell
Made up of multiple cells like animal cells
Light Microscope
Uses light, has colour, only shows some organelles when stained.
Electron Microscope
Has much stronger magnification and does not have colour.
Prokaryotic Cells
Have no membrane, are extremely small, contain sub-cellular components that don't have a membrane and are a unicellular cell.
Example = bacteria
Eukaryotic Cell
Well organised, contain membrane bound organelles, quite large, and carry DNA in a nucleus where it is organised into chromosomes
Example = animal cells
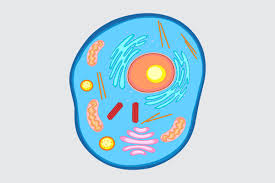
What cell is this?
Animal Cell
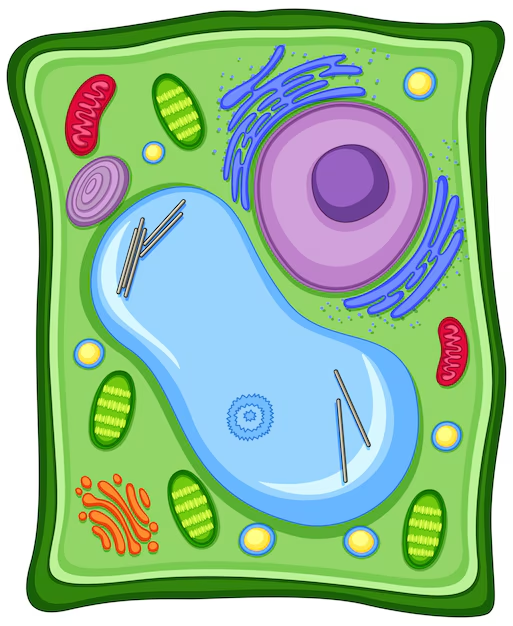
What cell is this?
Plant Cell
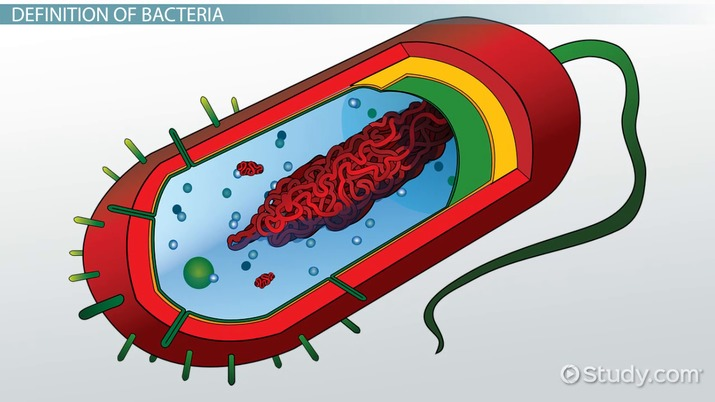
What cell is this?
Bacteria Cell
What does the Nucleus do?
Stores genetic information.
What does the cell membrane do?
Control the exchange of material between the cell and the external environment.
What does the cell wall do?
Strengthens the cell and helps maintain its shape (only in plant cells)
What do Ribosomes do?
create proteins for the cell or remove them from the cell.
What does the Golgi body do?
Package proteins and send them to the cell membrane.
What does the Mitochondria do?
Carry out aerobic respiration to create ATP
What do Chloroplasts do?
Carry out photosynthesis
What structure is the Cell Membrane?
Fluid Mosaic Model
What is passive transport?
Movement that does not require energy because it is moving the same way as the consentration gradient.
What are the types of passive transport?
Diffusion - gases floating through
Facilitated Diffusion - large items travel through protein channels
Osmosis - water
What is osmosis?
The movement of water in and out of the cell.
What is Hypotonic?
When the percentage of solute outside of the cell is lower than inside the cell, water will move into the cell, an animal cell will burst, and a plant cell will swell and become turgidity
What is isotonic?
When the percentage of solute is equal inside and outside of the cell meaning there will be no water movement in or out of the cell causing it to stay the same.
What is Hypertonic?
When the percentage of solute outside the cell is higher meaning water will move out of the cell causing it to shrivel up.
What is active transport?
Requires energy (ATP) to move molecules because it is movie against the concentration gradient.
What are the types of active transport?
Endocytosis - in
Exocytosis - out
What are the 2 types of Endocytosis?
Phagocytosis - cell eating
Pinocytosis - cell drinking
What is mitosis?
a process that allows cells to split into identical daughter cells.
What are the phases of mitosis?
Interphase - cell preparing for splitting, starts to grow and copy DNA
Prophase - DNA condenses into chromosomes, the nuclear membrane breaks down, and spindle fibers form.
Metaphase - Chromosomes line up in the middle, and spindle fibers attach
Anaphase - Spindle fibers pull chromosomes apart towards the poles of the cell
Telophase - new nuclear membrane form splitting the cell into two
Cytokinesis - cell fully splits and has formed two identical daughter cells.
Mitosis acronym
I Play Monopoly At the Circus
What are Autotrophs?
Create their own energy through photosynthesis
What Are Heterotrophs?
Create energy by feeding on other organisms.
Photosynthesis chemical equation
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Carbon dioxide + water —> Glucose + oxygen
Aerobic Respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Glucose + oxygen —> carbon dioxide + water + energy
Alcohol Fermentation equation
C6H12O6 —> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + energy
Glucose —> alcohol + carbon dioxide + energy
Lactic acid fermentation equation
C6H12O6 —> 2C3H6O3 + energy
Glucose —> lactic acid + energy