lecture 4 - MHC and antigen presentation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
intracellular pathogens vs extracellular pathogens
intracellular pathogens reside and replicate inside a cell, extracellular pathogens replicate outside of cells.
intravesicular pathogens reside where?
they are degraded by? why?
antigens/peptides bind to MHC class __?
they are presented to what cells?
= activation to ___ intravesicular bacteria/parasites
vesicles within a cell
endocytic vesicles. they have a low (acidic) pH
II
effector CD4 T cells
kill
cytosolic pathogens reside where?
the pathogen is degraded where?
the peptides bind to MHC class __
the peptides are presented to which cells?
the effect on the presenting cell?
cytosol
cytosol
I
effector CD8 T cells
cell death due to cytotoxic T cells
extracellular pathogens and toxins reside where?
they are degraded where?
the peptides bind to MHC class __
they are presented to what cells?
what is the effect on the presenting cell?
outside of a cell
endocytic vesicles (they have a low (acidic) pH)
II
effector CD4 T cells
activation of B cells to secrete Ig to eliminate the pathogen
whilst MHC class I molecules are translated, they are _______ into the __ membrane
pathogens are being degraded by the ________ in the cytosol
the peptides are ______ transported from the cytosol to the ER by the ___ complex
embedded
ER
proteasome
actively
TAP
steps of MHC class 1 to be expressed on cell membrane.
partially folded MHC class I binds to calnexin for B2-microglobulin to bind
MHC class I aB2m complex binds to calreticulin, ERp57 and tapesin
this complex binds to TAP via tapesin
defective ribosomal products (DRiPs), old proteins and degraded peptide from proteasome are delivered to ER by TAP
peptide binds to MHC class I - full complex is released from TAP and exported to cell membrane
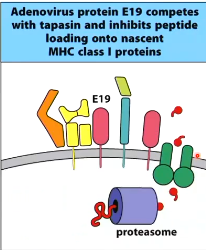
adenovirus protein ___ inhibits peptide loading onto MHC class I by _________
E19
competing with tapasin, blocking the complex from binding to TAP
where are MHC class II molecules presented?
vesicles
steps of extracellular antigens being presented onto MHC class II peptides
antigen taken up into intracellular vesicles
as endosome matures, pH decreases
low pH activates proteases to degrade antigen into peptide fragments
MHC class II is synthesised in ER and binds to an invariant chain (Ii)
Ii is cleaved in acidic endosome leaving CLIP (Class-II associated Invariant chain Peptide)
vesicles containing peptides fuse with vesicles containing MHC class II
HLA-DM binds to MHC class II releasing CLIP
peptide fragments can bind to MHC class 11 groove
MHC class II travels to cell surface
what is Invariant Chain (Ii)?
what does it bind to?
what is it’s purpose?
a trimer which binds to 3 Class II aB molecules in the ER
binds to MHC class II’s groove
prevent premature peptide binding

what happens if virus doesn’t infect APCs?
Class I (normally presents intracellular antigens) → what if antigen is outside of the cell?
Class II (normally presents extracellular antigens) → what if antigen is within the/invaded cell?
partially degraded antigens in endosomal pathway can be translocated to cytosol
cytosolic proteins can be loaded by autophagy
cross-presentation of exogenous antigens
extracellular antigen uptake by phagocytosis into endosome
antigen degraded into peptides in cytosol OR antigen is loaded into preformed MHC class I in an endosomal compartment
degraded peptides loaded into ER to load onto MHC class I
presentation of cellular antigens by MHC class II
antigen broken down in autophagosome then enters MHC Class II pathway
HLA (_______ ______ _______) encodes for ___ region
class I section is made up of ____, ____ and, ____
class II section is made up
DP, DQ and ___ which make up the MHC II protein chains
DOA and DOB which make ______ which kicks out CLIP
TAPBP and TAP which are involved in ______
human leukocyte antigen
MHC
HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C
DR
HLA-DM
MHC class I binding
MHC restriction is?
T cells only recognising specific antigens when bound to self-MHC molecules
superantigens circumvent normal recognition. how? and why so dangerous?
they bind outside of MHC and to the T cell receptor (TCR)
non-specific binding regardless of antigen causes massive T cell activation/inflammatory response - e.g. toxic shock syndrome
what characteristic enable MHC antigen diversity?
MHC class I and II genes are highly polymorphic - many allelic variation between each genes (i.e. DRB in MHC Class II, HLA-A in MHC Class I)
inherit two MHC class regions from each parent - haplotype
6 versions of MHC I
6-8 types of MHC II
they are polygenic - inheriting multiple genes that encode for MHC class 1
so I inherit 6, only 1 is required for 1 MHC 1 molecule but each 1 has many different alleles