HLA-B, RYR1, CACNA1S, G6PD, mtRNR1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
class I MHC molecules: HLA-A and HLA-B polymorphisms
class I MHC (HLA) genes are amongst the most polymorphic human genes
nomenclature of HLA gene polymorphism:
name (HLA-A or HLA-B) * and four numbers separated by colon
first 2 digits denote the antigen type and second two subtype
e.g. HLA-B * 15:01
drugs impacted by HLA-B polymorphism
HLA-B*15:02
carbamazepine (also HLA-A*31:01)
oxcarbazepine
eslicarbazepine
phenyoin
fosphenytoin
HLA-B*57:01
abacavir
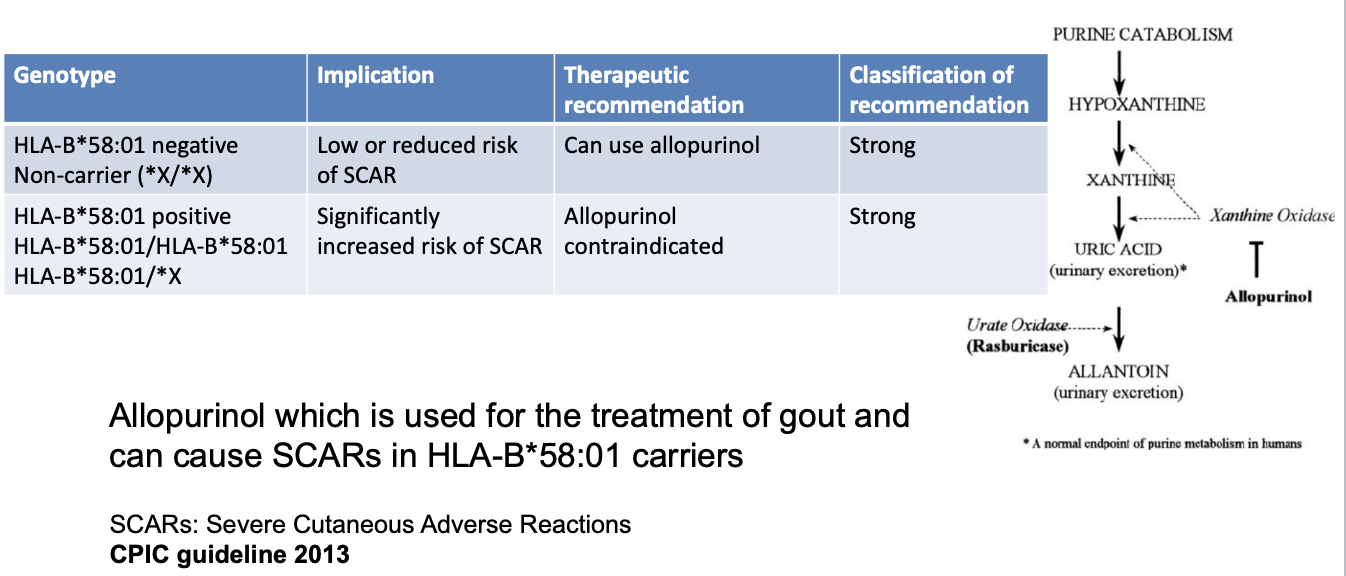
HLA-B*58:01
allopurinol
HLA-B genotype reporting

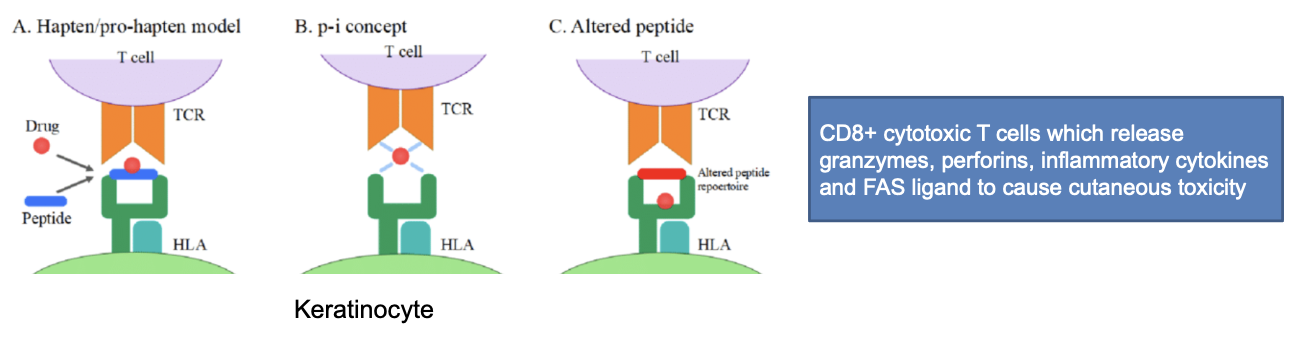
how does HLA-B polymorphism cause hypersensitivity reaction
physical interaction concept:
drugs can interact with HLA allele or TCR leading to their docking and initiation of immune response
altered peptide repertoire:
drugs can interact with HLA allele binding pocket so that a peptide becomes immune reactive and docks to TCR leading to initiation of immune reponse
HLA-B*15:02
strong correlation between incidence of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) & Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) in pts carrying HLA-B*15:02 and use of phenytoin, fosphenytoin, carbamazepine, oxycarbazepine
a severe hypersensitivity reaction
typically occurs within first 3 months of therapy
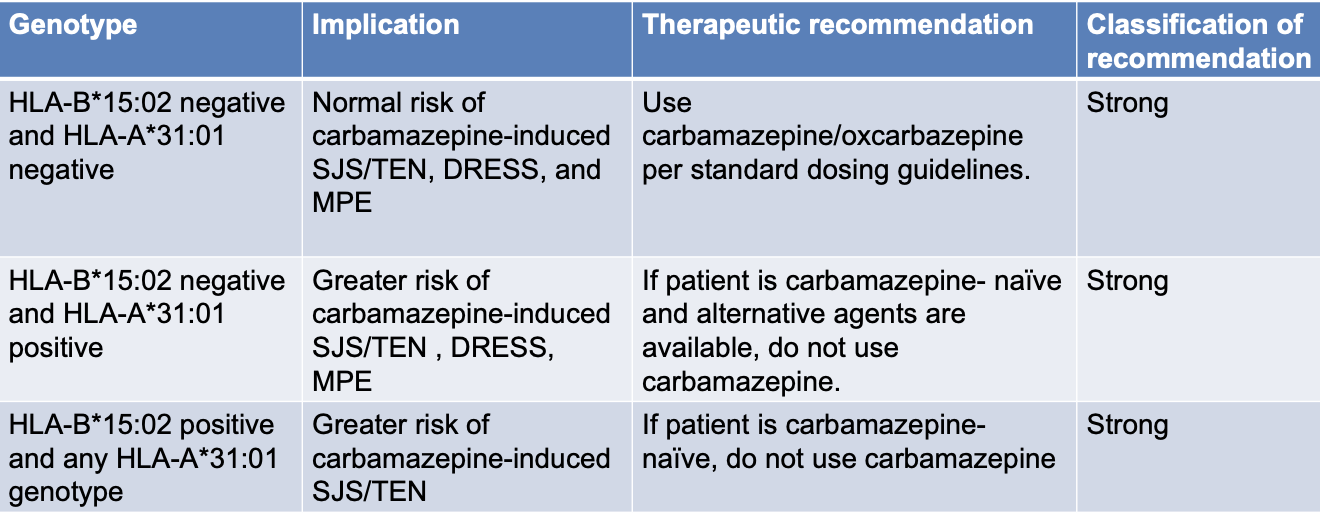
HLA-A*31:01
correlation between incidence of Mild Maculopapular Eruptions (MPE) and Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) in pts carrying HLA-A*31:01 and use of carbamazepine
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) & Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
a medical emergency
fever and flu-like symptoms
unexplained widespread skin pain
red or purple skin rashes that spreads tot he mucous membranes of mouth, nose, eyes, and genitals
shedding of skin within days after blisters
epidermal detachment affecting up to 10% of body surface area SJS, > 30% of the body surface area TEN
mortality < 5% SJS, but TEN > 30%
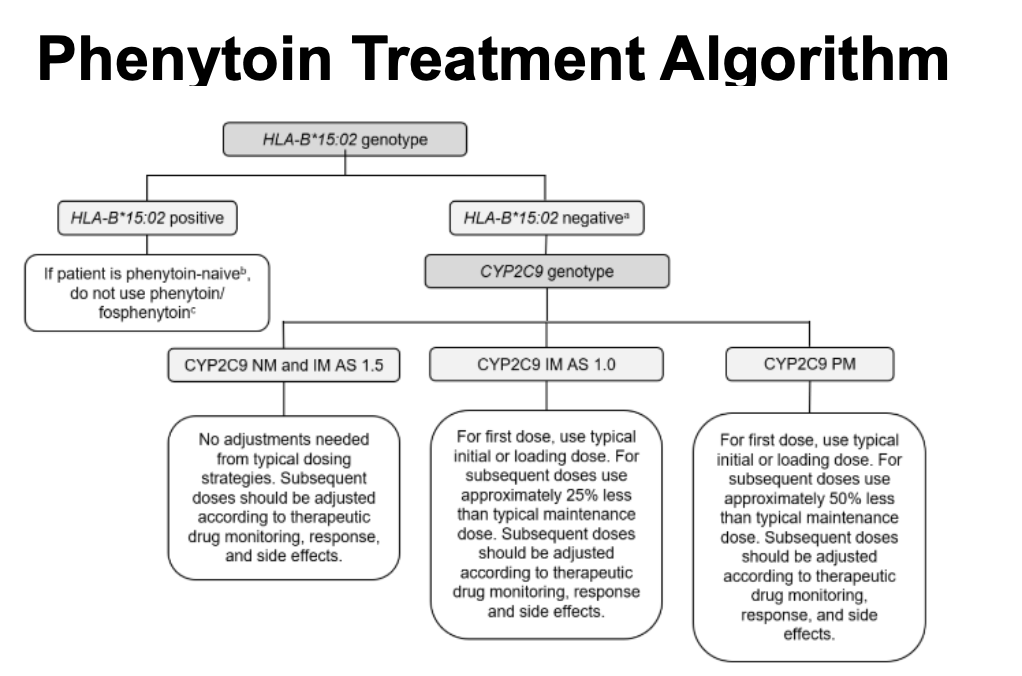
HLA-B*15:02 CPIC recommendations for phenytoin, fosphenytoin, and oxcarbazepine

phenytoin treatment algorithm
carbamazepine: hypersensitivity reaction
higher prevalence in HLA-A*31:01 with carbamazepine:
mild maculopapular eruptivo (MPE) in 10% patients which is a milder reaction without mucosal or organ invovlement
drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) is severe hypersensitivity reaction characterized by generalized cutaneous eruption with systemic manifestations that can be life threatening
FDA label warning on carbamazepine
FDA issued Health Alert in 2007 to include in carbamazepine label recommendations for genetic testing in patients with at-risk ancestry should be screened for the presence of HLA-B*15:02 allele prior to starting carbamazepine
individuals at highest risk are those of Han Chinese descent, followed by those in Vietnam, Cambodia, the Reunion Islands, Thailand, India (specially Hindus), Malaysia, and Hong Kong
CPIC recommendations for carbamazepine
not all of ADEs associated with anticonvulsant hypersensitivty syndrome explained by PGx
a triad of fever, skin eruptions (mild to severe), and lymphadenopathy within 1-8 weeks of exposure of aromatic anticonvulsant
phenytoin/fosphenytoin
carbamazepine/oxcarbazepine
cutaneous eruption in 3% of patins with or without organ involvement
HLA-B*58:01 CPIC recommendations for allopurinol
abacavir
abacavir is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) for HIV treatment
abacavir inhibits viral reverse transcriptase, suppressing HIV’s ability to convert its RNA genome into DNA before insertion into a host cell’s genome
used in combination with other HIV medications, as part of highly active antiretroviral therapy
commercially available as a single agent, Ziagen, or as a fixed dose combination with other nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, lamivudine (Epzicom/Kivexa) and lamivudine/zidovudine (Trizivir)
abacavir HSR
generally well toelrated
~5-8% of pts may experience hypersensitivity reaction (HSR) during the first 6 weeks of treatment
abacivr HSR symptoms (at least 2 of the following):
fever, rash, gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain), fatigue, cough, and dyspnea
suspicion of a HSR warrants immediate discontinuation of abacavir. If the symptoms of clinically diagnosed HSR resolve after discontinuation of abacavir, drug-rechallenge is contraindicated because of immediate and life-threatening reactions, including anaphylaxis and even fatalities
recommended that an allergy to abacavir should be noted in the patient’s medical record
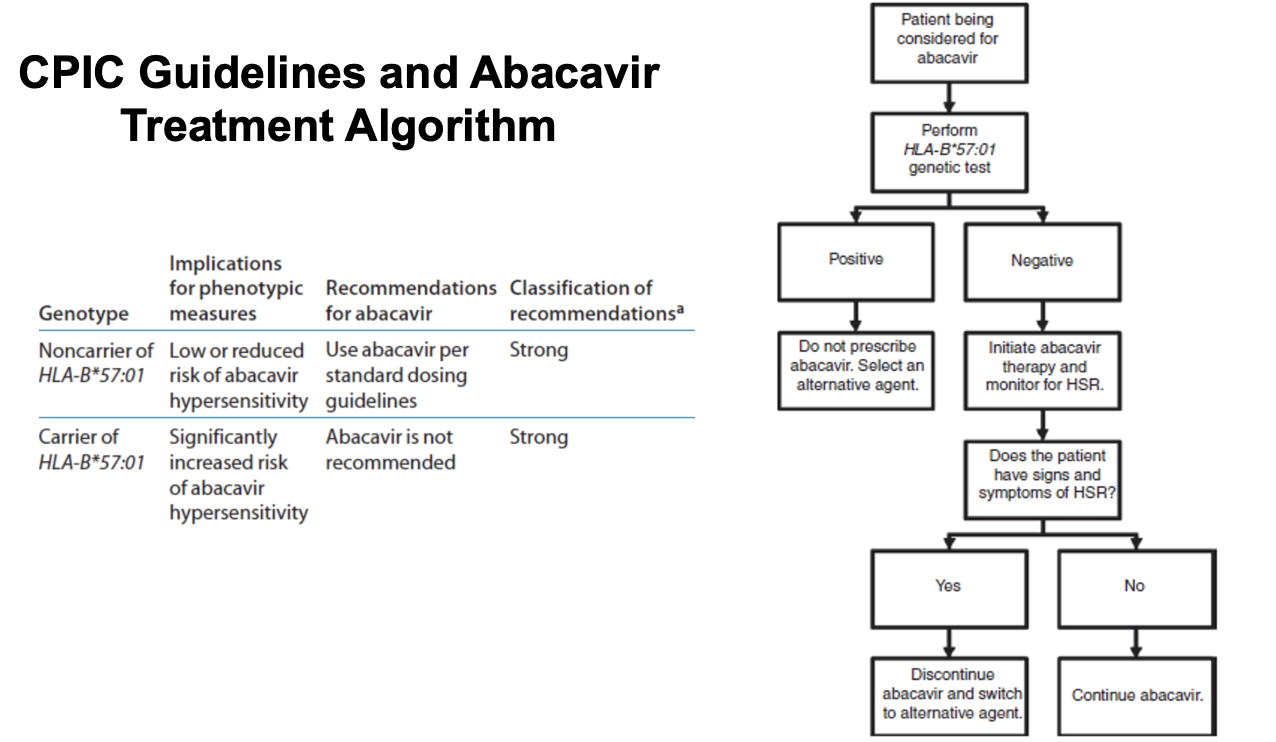
abacavir FDA recommendations
PREDICT trial prompted FDA to implement a black box warning in 2008
recommended that all patients be screened before being treated with abacavir (including those who had previously tolerated the drug and were beings restarted on the therapy) and that abacavir SHOULD NOT be imitate din carriers of HLA-B*57:01
abacavir is one of a limited number of drugs for which the FDA has recommended genetic testing prior to use, and it remains one of the best examples to date of pharmacogenetics being integrated into routine medical practice
CPIC guideliens and abacavir treatment algorithm
RYR1 and CACNA1S in malignant hyperthermia susceptibility (MHS)
potent volatile anesthetic used in general anesthesia
sevoflurane, halothane, enflurane, isoflurane, methoxyglurane, desflurane
depolarizing muscle relaxant, succinylcholine
MHS diagnosis
inherited autosomal domino pattern fro both RYR1 and CACNA1S
“MHS causative” variants
upon exposure to a triggering agent, MHS patient can have:
sustained increase of cytoplasmic calcium within skeletal muscle leading to uncontrolled muscle contraction
other indications of MH:
tachycardia and an increase in end-tidal CO2 followed by skeletal muscle rigidity, metabolic and respiratory acidosis, and hyperkalemia, hyperthermia, and arrhythmia
if left untreated, an MH reaction can result in cardiac arrest and death
one of 2 criteria:
positive response to a muscle biospy (fresh) by caffeine-halothane contracture test (CHCT) —> gold standard
presence of pathogenic variants in RYR1 or CACNA1S
absence of causative mutation does NOT rule out MH susceptibility
safe anesthetics for MHS patients
all local anesthetics (lidocaine)
IV anesthetics:
propofol
benzos
ketamine
etomidate
inhaled non-volatile general anesthetic such as nitrous oxide
non-depolarizing muscle relaxants
rocuronium
atracurium
cis-atracurium
barbiturates and opioids
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) enzyme polymorphism
gene encoding for G6PD enzyme is present on X chromosome
males can be either function or loss of function
females can be homozygous normal function, heterozygous normal function (carrier), or homozygous loss of function
more than 2 dozen SNPs reported
all alleles are loss of function
prevalence is high in Africa, Asia, the Mediterranean, and the Middle East
G6PD Function
to generate NADPH for antioxidant defense
RBCs are esp susceptible to oxidant stress acne they have no nucleus and cannot synthesis damaged proteins
G6PD polymorphism
foods (fava beans)
some drugs can cause oxidative stress
results in RBCs rupture leading to hemolytic anemia in individuals homozygous for loss of function G6PD
signs and symptoms: weakness, fatigue, breathlessness, brown urine, jaundice
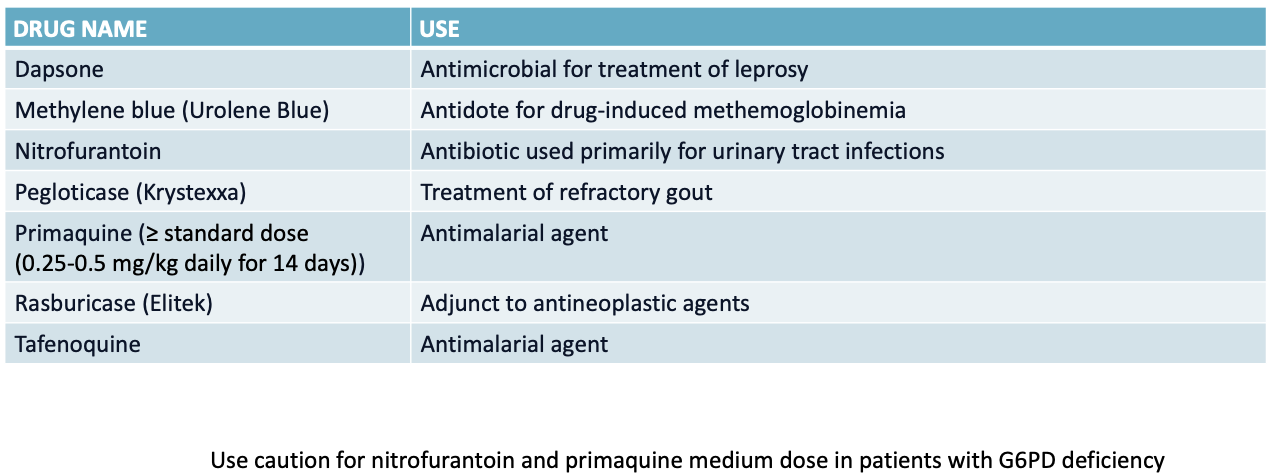
medications that should be avoided in G6PD deficiency
aminoglycosides
aminoglycosides are a large class of antibiotics
amikacin, gentamicin, kanamycin, paromomycin, plazomicin, streptomycin, tobramycin
typically administered IV/IM for serious Gram(-) bacterial infections or as synergistic treatment for Gram (+) bacterial infecitons
MOA: inhibit protein synthesis by binding to 16s rRNA of bacterial 30S ribosome
side effects: nephrotoxicity (overall reversible), hearing loss (permanent)
aminoglydoside-induced hearing loss (AIHL) even with single dose
MT-RNR1 in AIHL
variants in MT-RNR1 that predispose to AIHL cause the 12s rRNA subunit to more closely resemble the bacterial 16s rRNA subunit
amino glycoside bind more readily —> increased risk of AIHL
mitochondrial DNA is encoded for the genetic information required by mitochondria whereas nuclear DNA is encoded for the genetic information required by the entire cell
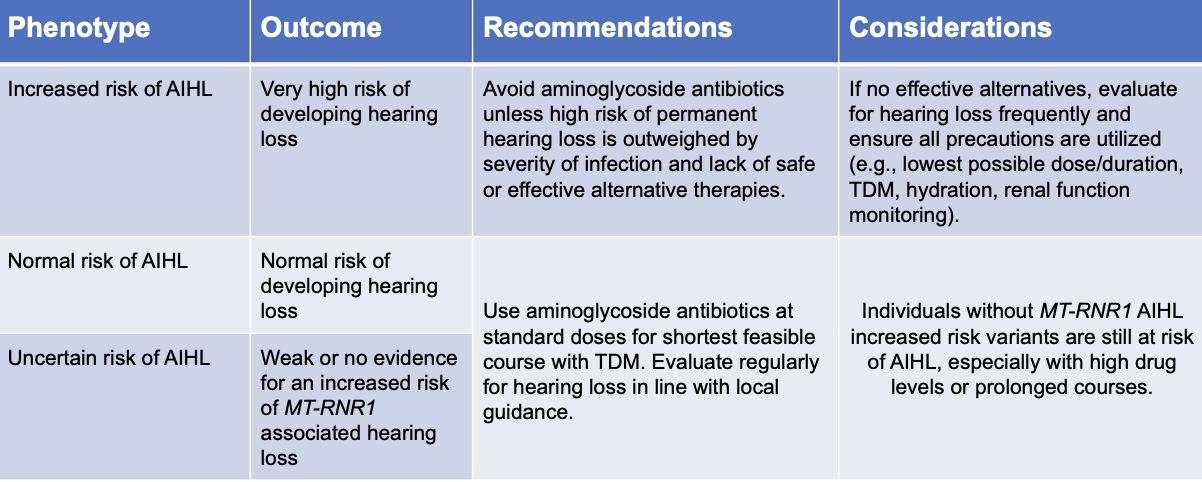
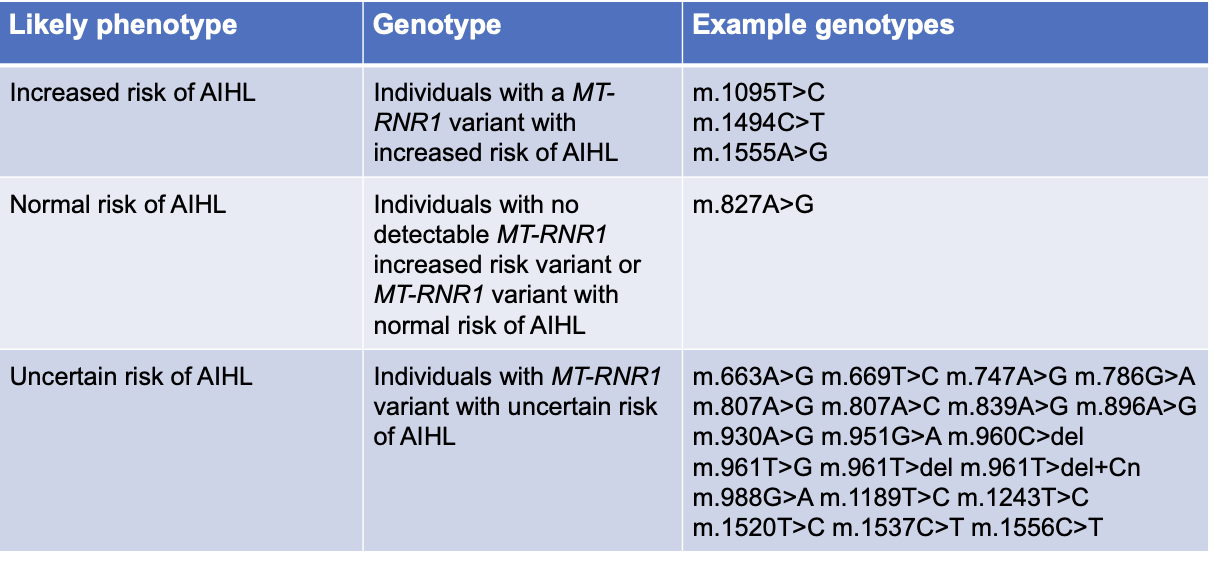
assignment of MT-RNR1 Phenotype based on genotype
CPIC recommendation for aminoglycosides in children and adults