Ethical hacking
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
identification and authentication failure
Identification refers to the ability to identify a user uniquely. In contrast, authentication refers to the ability to prove that the user is whom they claim to be. The online shop must confirm the user’s identity and authenticate them before they can use the system. However, this step is prone to different types of weaknesses. Example weaknesses include
Allowing the attacker to use brute force, i.e., try many passwords, usually using automated tools, to find valid login credentials.
Allowing the user to choose a weak password. A weak password is usually easy to guess.
Storing the users’ passwords in plain text. If the attacker manages to read the file containing the passwords, we don’t want them to be able to learn the stored password.
Broken access control
Access control ensures that each user can only access files (documents, images, etc.) related to their role or work. For example, you don’t want someone in the marketing department to access (read) the finance department’s documents. Example vulnerabilities related to access control include:
Failing to apply the principle of the least privilege and giving users more access permissions than they need. For example, an online customer should be able to view the prices of the items, but they should not be able to change them.
Being able to view or modify someone else’s account by using its unique identifier. For example, you don’t want one bank client to be able to view the transactions of another client.
Being able to browse pages that require authentication (logging in) as an unauthenticated user. For example, we cannot let anyone view the webmail before logging in.
Injection
An injection attack refers to a vulnerability in the web application where the user can insert malicious code as part of their input. One cause of this vulnerability is the lack of proper validation and sanitization of the user’s input.
Cryptographic Failures
This category refers to the failures related to cryptography. Cryptography focuses on the processes of encryption and decryption of data. Encryption scrambles cleartext into ciphertext, which should be gibberish to anyone who does not have the secret key to decrypt it. In other words, encryption ensures that no one can read the data without knowing the secret key. Decryption converts the ciphertext back into the original cleartext using the secret key. Examples of cryptographic failures include:
Sending sensitive data in clear text, for example, using HTTP instead of HTTPS. HTTP is the protocol used to access the web, while HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP. Others can read everything you send over HTTP, but not HTTPS.
Relying on a weak cryptographic algorithm. One old cryptographic algorithm is to shift each letter by one. For instance, “TRY HACK ME” becomes “USZ IBDL NF.” This cryptographic algorithm is trivial to break.
Using default or weak keys for cryptographic functions. It won’t be challenging to break the encryption that used
1234as the secret key.
active reconnaissance
method of information gathering in which the tools actually send out probes to the target network or systems to elicit responses that are then used to determine the posture of the network or system.
These probes can use various protocols and multiple levels of aggressiveness, typically based on what is being scanned and when.
passive reconnaissance
a method of information gathering in which the tools do not interact directly with the target device or network. There are multiple methods of passive reconnaissance. Some involve using third-party databases to gather information. Others also use tools in such a way that they will not be detected by the target.
These tools, in particular, work by simply listening to the traffic on the network and using intelligence to deduce information about the device communication on the network.
DNS LOOKUP
can be used to determine the IP address or addresses used by a website or any other subdomain that might be in use.
Let’s say that those queries reveal that h4cker.org is using the IP addresses 185.199.108.153 for www.h4cker.org, 185.199.110.153 for mail.h4cker.org, and 185.199.110.153 for portal.h4cker.org. Example 3-1 shows an example of the DNSRecon tool in Kali Linux being used to query the DNS records for h4cker.org.
example of using the kali linux dns recon tool —> dnsrecon -d h4cker.org
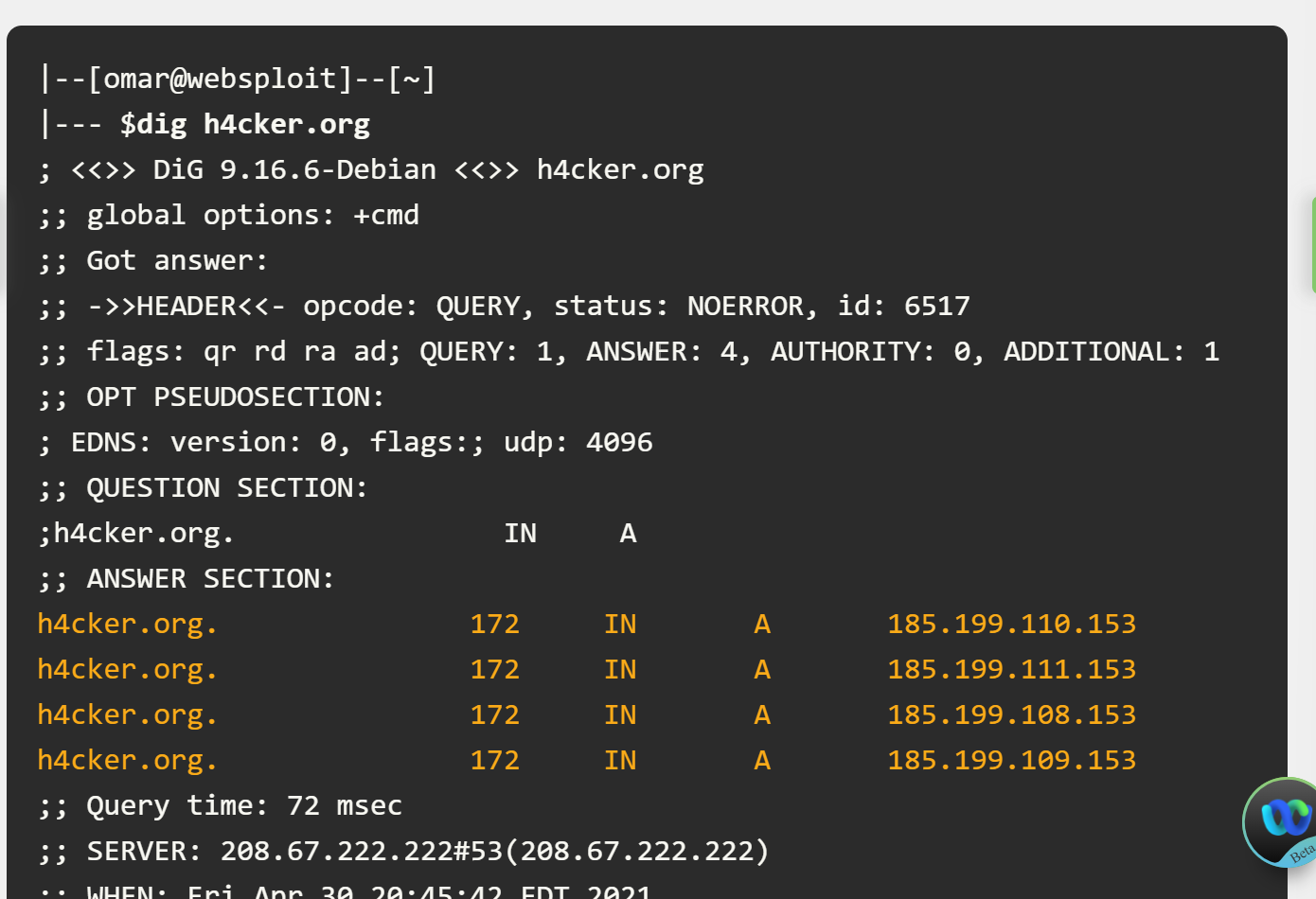
Using DIG to obtain information about a given domain
highlighted lines show the IP addresses associated with h4cker.oeg
can also use dig <domain> mx command to obtain email servers used by h4cker.org MX is mail exchanger record
WHOIS tool
retrieve domain registration information about a website.
Registrant info (who owns it — sometimes redacted for privacy)
Registrar (company used to register the domain)
Registration dates (creation, update, and expiration)
Name servers (DNS servers for the domain)
Contact emails/phones (if not private)
Domain status (e.g., locked, available)