7: Production
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Theory of the Firm
Explains how a firm makes cost-minimizing production decisions and how its cost varies with its output.
Production Technology, Cost Constraints, Input Choices
Three steps in understanding production decisions of firms:
Production Technology
Describe how inputs can be transformed into outputs
Cost Constraints
Firms must take into account the prices of labor, capital, and other inputs
Input Choices
Given its production technology and the prices of labor, capital, and other inputs, the firm must choose how much of each input to use in producing its output.
very short run, short un, long run, very long run
Time Horizons
Very short run
all factors of production are fixed (e.g., on one particular day, a firm cannot employ more workers or buy more products to sell)
Short run
one factor of production (e.g., capital) is fixed.
Long run
all factors of production of a firm are variable (eg, a firm can build a bigger factory).
Very long run
all factors of production are variable, and additional factors outside the control of the firm can change, e.g., technology, government policy. A period of several years.
production function
A __for any commodity is an equation, table, or graph showing the quantity that can be produced for each combination of alternative inputs
• Input-output relationship [q = f(K,L)]
• Production process as a “black box”
MP_k = fk = partial derivative of Q with respect to K
Marginal Physical Product (MP) formula
AP_k = Q/K
Average Product (AP) Formula
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
what formula is this:
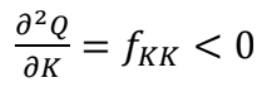
positive
The APL curve usually rises at first, reaches a maximum, and
then falls, but it remains __ as long as the TP is positive.
zero, negative
The MPL curve also rises at first, reaches a maximum, and then declines. Notice that the MPL becomes__ when the TP is maximum and __when the TP begins to decline
law of diminishing returns
The falling portion of the MPL curve illustrates the__
increasing rate
Stage 1 of Production: TP – increasing @__
max
Stage 1 of Production: AP – increasing to __
max then falling
Stage 1 of Production: MP – increasing to__
decreasing rate
Stage 2 of Production: TP – increasing @ __
falling
Stage 2 of Production: AP –___
zero
Stage 2 of Production: MP – falling to __
max to falling
Stage 3 of Production: TP – from__
falling
Stage 3 of Production: AP – __
falling (negative)
Stage 3 of Production: MP –__
Marginal Products
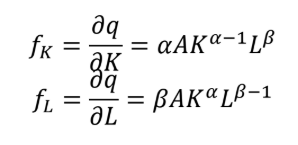
Cobb-Douglas Production Function
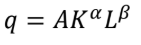
Returns to Scale
Refers to the response of output when all inputs are increased simultaneously and proportionately. Given q = f(K, L)
degree of homogeneity of the production function
Let γ any constant factor by which L and K are increased
γ^hq = f(γK, γL)
Where h – __
alpha + beta = h
For Cobb-Douglas Production Function, RTS is just __
Isoquant
Locus of points, each point representing a combination of inputs which yields the same level of output
IQ that lies above and to the right of another represents higher levels of output, Negatively sloped, Never intersect, Convex to the origin
Characteristics of Isoquants
Isocost
Locus of points, each point representing a combination of inputs that a firm can purchase at the same time given its budget C = wL + rK
C = wL + rK
Constraint/Isocost formula
cost-minimizing choice of inputs
The point of tangency of the isoquant and the isocost line tells us the __, L and K.
Slope of the isocost = slope of the isoquant
Tangency Condition
-w/r
slope of isocost
-MRTS_LK
slope of isoquant
MPL/w = MPK/r
Equimarginal Principle Formula
equivalent amount of output
When cost is minimized, each dollar of input added to the production process will add an __.
Min C = rK + wL
Objective Function:
st q0 = f(K, L)
(Lagrange) Constraint:
Z = rK + wL + lamda[Q_0 − f(K, L)]
Lagrange equation:
Expansion Path
Locus of cost-minimizing tangencies, assuming fixed input prices