coagulation cascade
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what is coagulation?
formation of a blood clot
what are the 2 coagulation pathways?
intrinsic and extrinsic
what is the extrinsic pathway triggered by?
external trauma causing blood to escape circulation
what is the intrinsic pathway triggered by?
internal damage to the vessel wall
draw the coagulation cascade
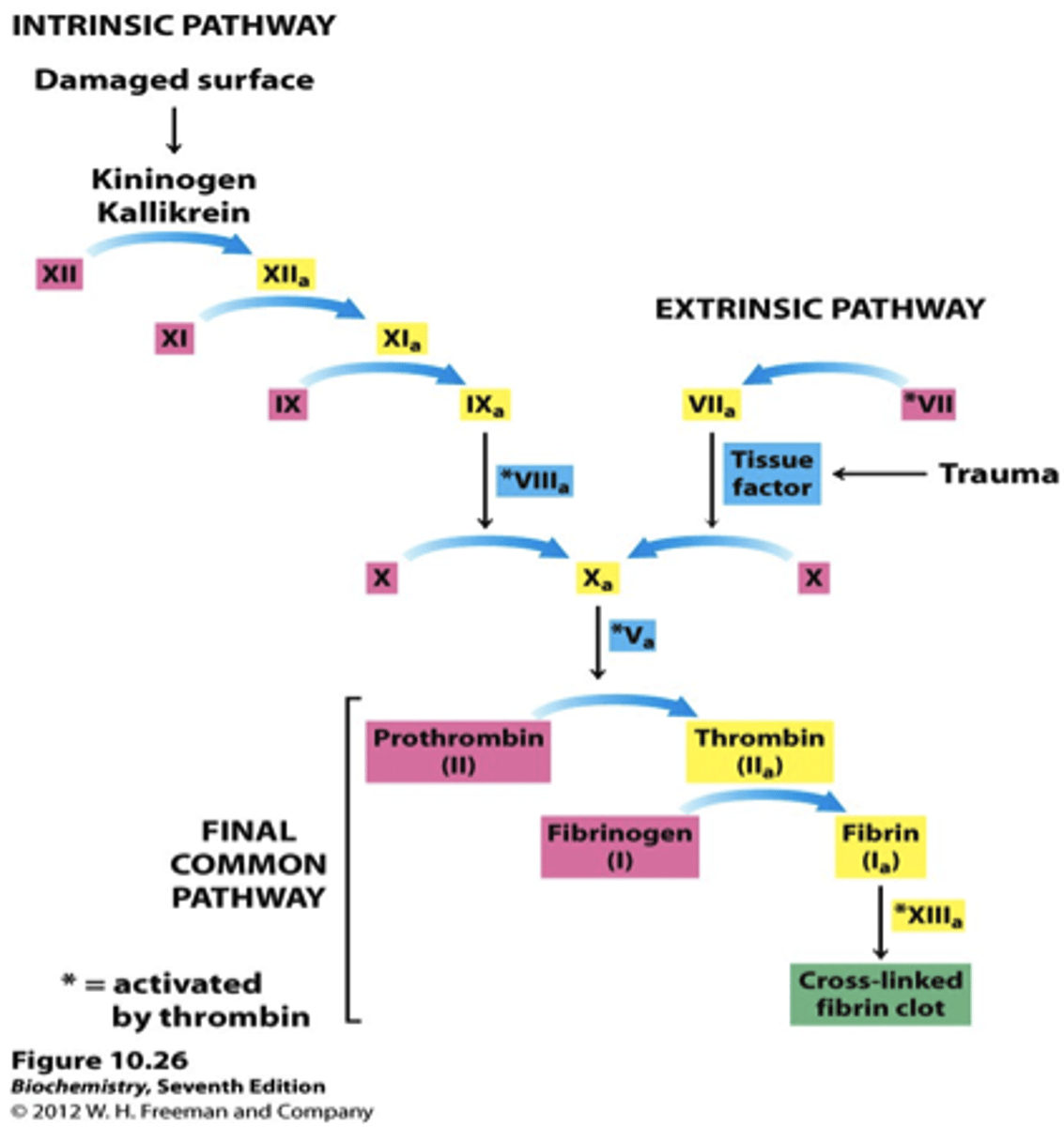
outline the basics of the extrinsic pathway
- factor VII and factor III form a complex called the TF-VIIa complex
- TF-VIIa activates factor X into Xa
outline the basics of the intrinsic pathway
- factor XII activated
- factor XI activated
- factor IX activated
- factor IXa combines with factor VIII to form enzyme complex that activates factor X
what happens to the Xa?
combines with factor Va and stimulates prothrombin to thrombin activation
what does thrombin do?
- stimulates fibrinogen to fibrin activation
- activates XIII to XIIIa
what does XIIIa do?
stimulates fibrin to form cross-link fibrin clots
what regulates the clotting cascade?
- protein C
- protein S
- antithrombin
how is protein C activated?
contact with thrombomodulin which is activated by thrombin
what does protein C do?
degrades factors Va and VIIIa
what does protein S do?
also degrades factor Va and VIIIa
is antithrombin ever inactive?
no, but it can be activated further by heparins
what does antithrombin do?
degrades:
- thrombin (IIa)
- IXa
- Xa
- XIa
- XIIa
how is the blood clot broken down?
fibrinolysis
how does fibrinolysis occur?
- endothelial cells secrete tissue plasminogen activators (tPAs)
- tPAs convert plasminogen into plasmin
- plasmin cleaves the fibrin within the thrombus
which clotting factors require vitamin K for their formation?
II, VII, IX, X (2,7,9,10)
1972
what are 3 examples of anticoagulants?
- warfarin
- heparin
- aspirin
how does warfarin act as an anticoagulant? (3)
- vitamin K antagonist
- competes with vitamin K
- inhibits vitamin K so vit K-dependent factors cannot be synthesised
should warfarin be used in pregnancy?
no
why should warfarin not be used in pregnancy?
teratogenic medication that can cross the placenta
what does teratogenic mean?
can cause developmental and birth defects
how does heparin act as an anticoagulant?
activates antithrombin III
what does antithrombin III do?
- inhibits thrombin by binding to active site
- hence thrombin cannot activate fibrinogen to fibrin and XIII to XIIIa
how does aspirin act as an anticoagulant? (2)
- its is better defined as an anti-platelet
- it inhibits platelet synthesis
what are hirudins?
drugs that are direct thrombin inhibitors
what are some examples of hirudins?
- lepirudin
- bivalirudin