Unit I Test List (Chapter 17 & 18)
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Name the order of the cardiac conduction system (MC)
1. Sinoatrial Node- RA wall; sets pace of heart = pacemaker; activates atrial syncytium->spreads depolarization to both atria
2. Atrioventricular Node- in inferior intratrial septum above tricuspid; slowest conduction because of smaller diameter of the nerve fibers to allow atria to contract before ventricles
3. Atrioventircular Bundle/Bundle of His- connects atria & ventricles (no gap junctions); insulation of signal by fibrous skeleton
4. Right/Left Bundle Branches- down interventricular septum toward apex
5. Subendocardial Conduction Networks/Purkinje Fibers- spread into ventricular walls ; activate ventricular syncytium->ventricular contraction
Know what cardiac output is and ______x________=Cardiac Output (MC)
• CO: Amount of blood pumped by each ventricle/minute
• Heart rate x Stroke volume
Know the difference in Preload and Afterload (MC)
• Preload: Amount of stretch at the end of diastole; measured by EDV or amount of blood at the end of diastole before ejection
• Afterload: Resistance the heart must overcome to open SL valves; measured by ESV or amount of blood at the end of systole after ejection
What is the function of the chordae tendineae? (MC)
Fibrous cords that project from papillary muscles to AV valves
Why is a shot given after baby blood and mother blood mix during birth? (MC)
If an Rh- mother has an Rh+ child, antibodies develop at the end of pregnancy during blood mixing & second child may have RBC's destroyed
Know the function of blood proteins in the body (MC)
• Albumin: ~60% of plasma proteins and functions as a carrier of lipids/steroids, a pH buffer, and an osmoregulating protein
• Fibrinogen- 4% blood cotting
• Globulins- 35% many different proteins with a wide variety of functions
• Regulatory Proteins- 1%
• Hemoglobin: Transfers oxygen
Know the different leukocytes...if they are granulocytes or agranulocytes....if they are phagocytic or nophagocytic (MC)
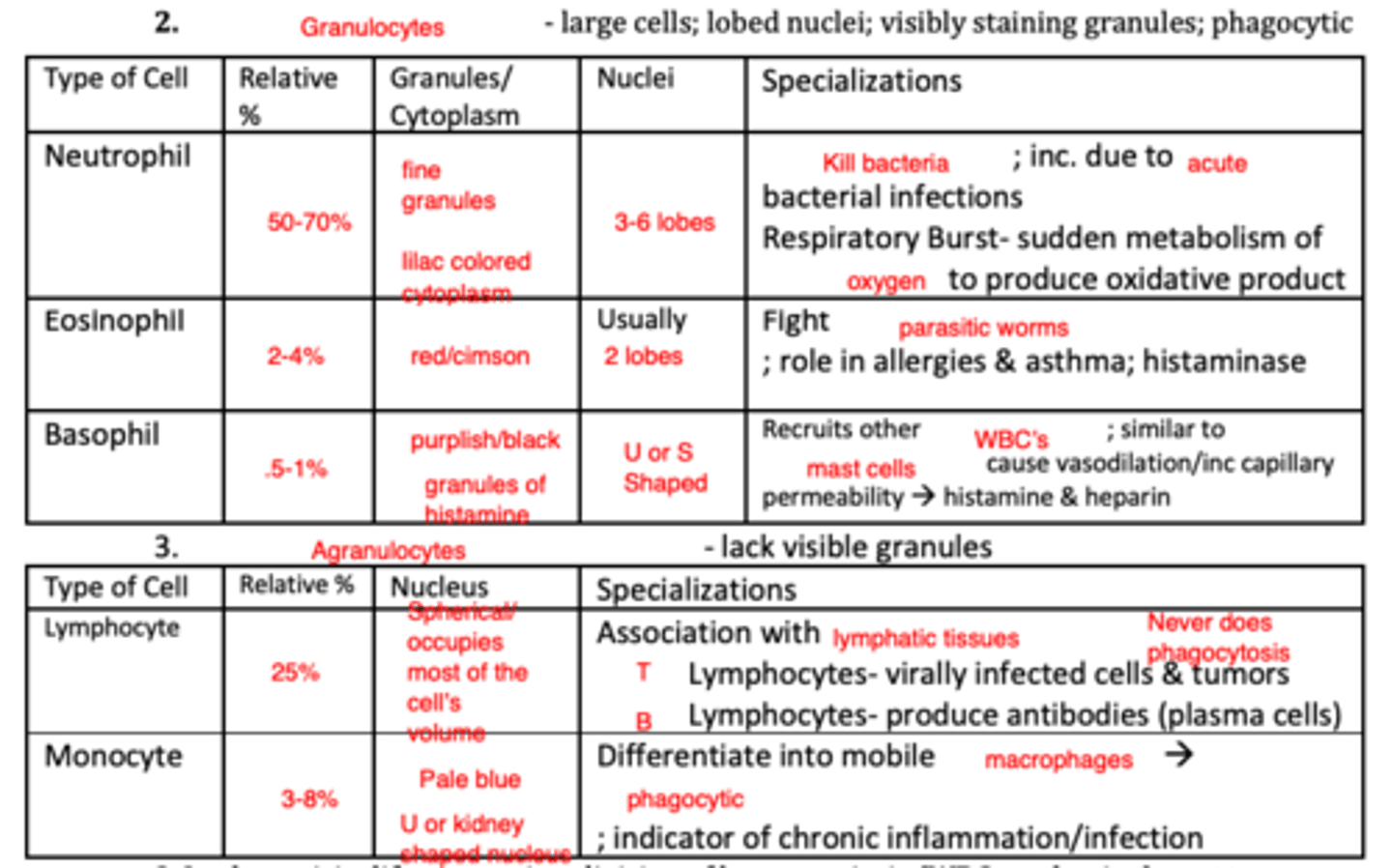
Know the role of platelets....be able to pick out what is NOT (hint: platelets do not do phagocytosis) (MC)
Blood coagulation, inflammation, & immune defenses
What is the route of blood flow in the heart (MC)
1. Unoxygenated blood enters right atria through superior & inferior vena cava
2.Right atria pumps blood to right ventricle via tricuspid valve (atriovenricular valve)
3. Right ventricle contracts-> pulmonary trunk->R/L pulmonary arteries thought Pulmonary valve: semilunar valve (PSL)
4. Unoxygenated blood is sent to the lungs & blood is oxygenated (pulmonary); Gas exchange occurs in the capillaries of lungs
5. Blood returns to left atrium by L/R pulmonary veins
6. Left atrium pumps blood to left ventricle via mitral (bicuspid) valve
7. Left ventricle pumps blood to the aorta through the aortic semilunar valve
8. Oxygenated blood is sent to the body tissues (systemic) & deoxygenated
What makes up the majority of plasma? (MC)
Water (~90%)
If you take a blood smear and look at it under a microscope, what cell type will you see most often? (MC)
Erythrocytes
What is the difference between oxyhemoglobin and carboxyhemoglobin? (MC)
• Oxyhemoglobinbright: red; gained O2
• Deoxyhemoglobin: dark red; lost O2
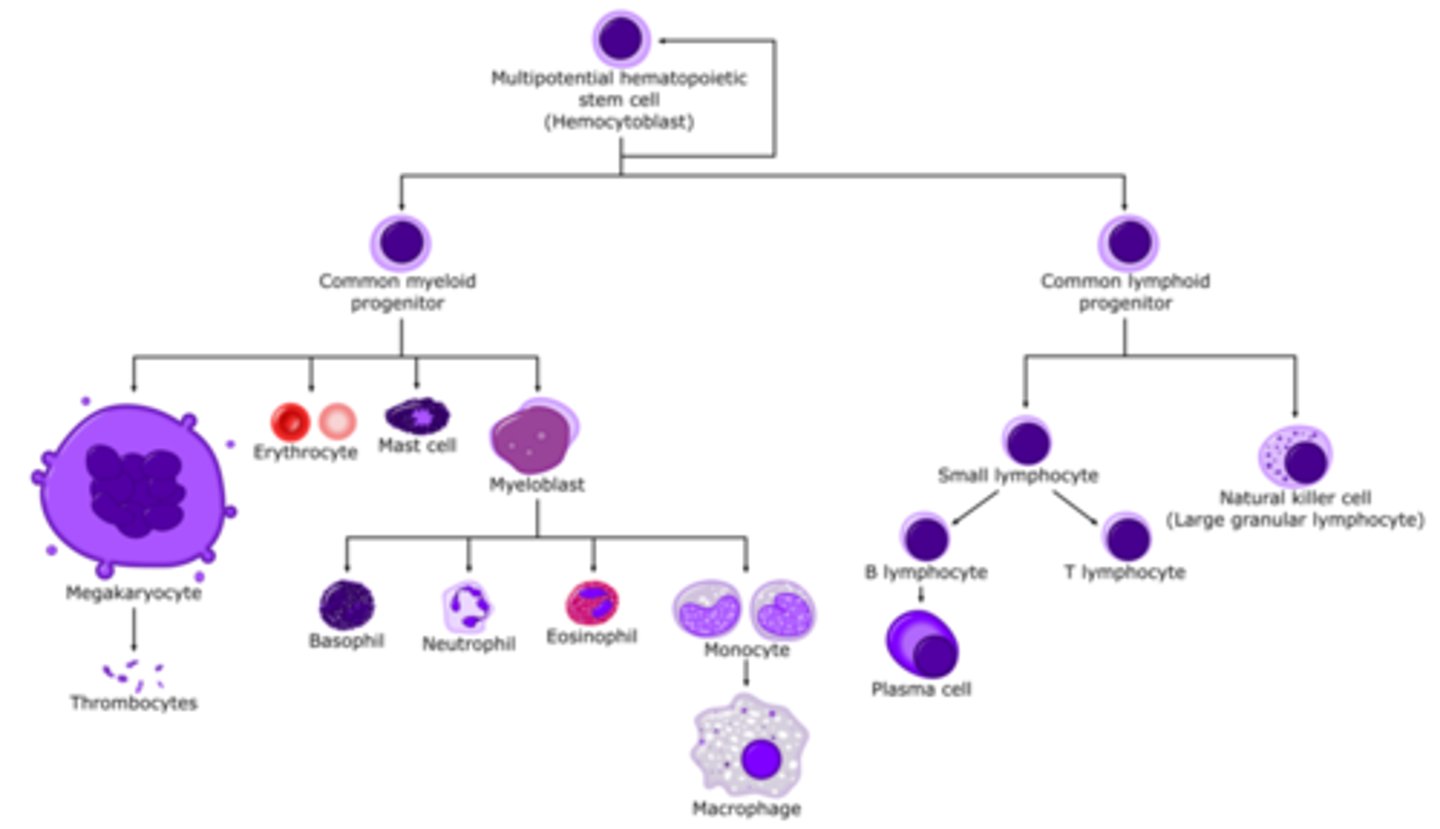
Become familiar with the process of erythropoiesis and where it takes place (MC)
• Occurs in the red bone marrow of axial skeleton, girdles, & proximal epiphysis of the femur/humerus
• Hemocytoblast or Hematopoetic Stem Cell matures into committed stem cells; development process includes: 1. Accumulation of hemoglobin->Red color
pluripotent 2. Ejection of nucleus and organelles late in development
Why is erythropoietin secreted? (MC)
Hypoxia: reduction in O2 availability because of reduced RBCs, reduced hemoglobin, or reduced O2 availability
Which layer of the pericardium is synonymous with the epicardium? (MC)
Visceral Pericardium
Know the general flow of breakdown of red blood cells (heme is broken down into ______...the globin is broken down into _______ and ______ ....the remainder is excreted in ______.) (MC)
• Heme->biliverdin->bilirubin excreted as bile pigments in feces, but iron salvaged
• Globin->amino acid subunits and recycled
Know the difference between the walls of the atrium and ventricles (which is thinner and thicker) (MC)
• Atrium: Thinner myocardium; smaller volume; separated by interatrial septum
• Ventricles: Thicker myocardium; larger volume; separated by inter ventricular septum
Which leukocyte is the most prevalent? How does it kill pathogens? Where does it stem from? (MC)
• Neutrophils are the most prevalent
• Phagocytic; kills bacteria via respiratory burst (sudden metabolism of oxygen to produce oxidative product)
What do papillary muscles do? (MC)
Regulate valve function by pulling chordae tendineae
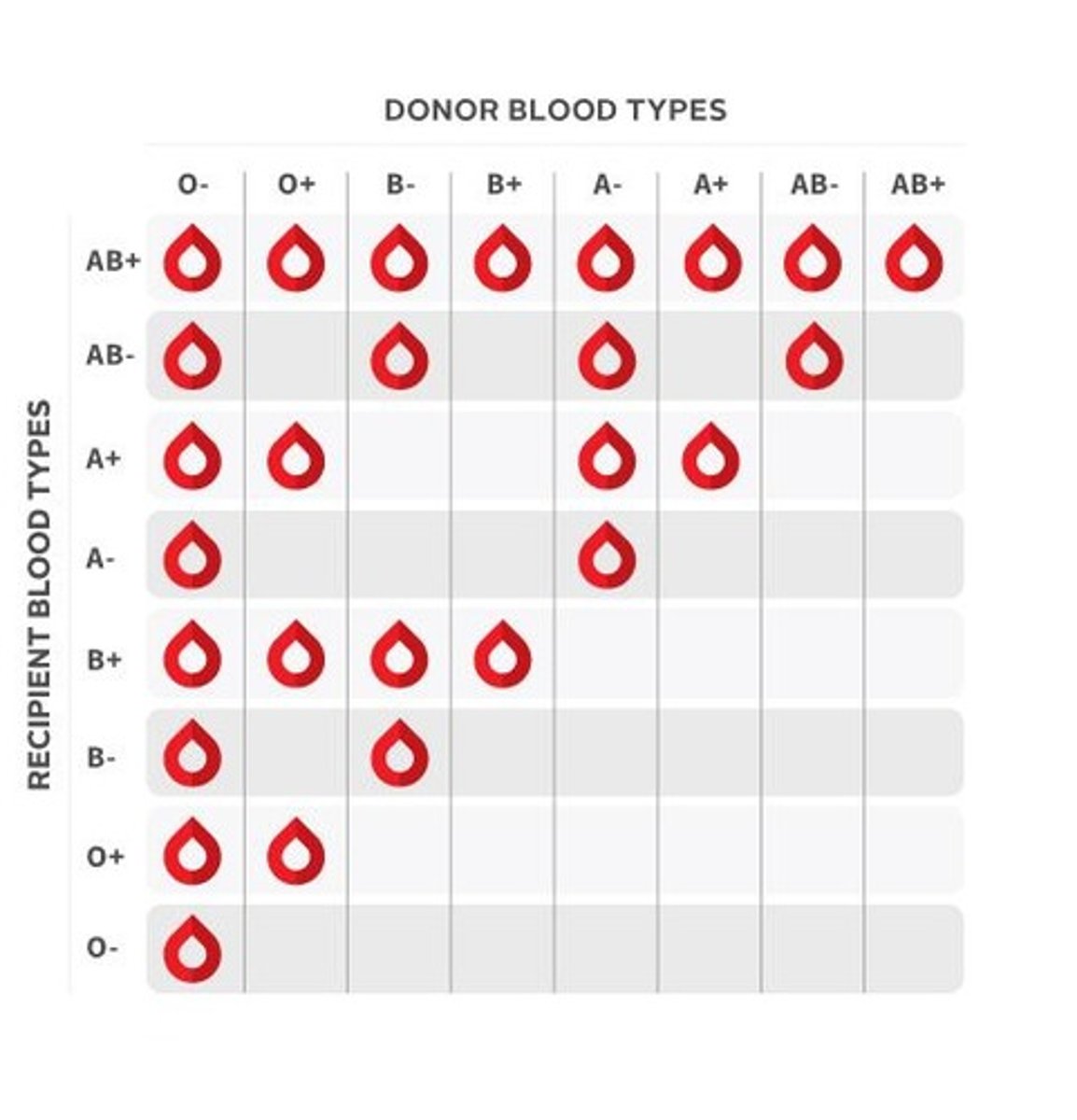
Know who can donate blood to who...know who can receive (MC)
Know the differences in atrial/ventricular systole and atrial/ventricular diastole (MC)
1. Late Ventricular Diastole- atria empty into the ventricles passively (ventricularfilling); AV valves are open ; SL valves are closed
2. Atrial Systole- rest of the blood forced into the ventricles actively
3. Early Ventricular Systole- AV valves are closed as intraventricular pressure increased : isovolumentric contraction- brief period in which ventricles contract, but all valves are closed & volume remains constant
4. Late Ventricular Systole- blood ejected (ventricular ejection); SL valves open
5. Early Ventricular Diastole- SL valves close ; isovolumetric relaxation- brief period in which ventricles relax, but all valves are closed & volume remains constant; ventricles relax; atria fill
After a cut, know the events in order that take place to prevent blood loss and induce clotting (MC)
1. Vascular Spams- Vasoconstriction ; slows blood flow
2. Platelet Plug Formation- normally smooth flow due to prostaglandins & nitric oxide; damage causes release of ADP, serotonin, & thromboxane A2->platelet attachment to collagen under endothelium
3. Coagulation- Fibrin reinforcement of clot; clotting factors cause solidification; Vitamin K required to synthesize some factors; Cascade->protein is cleaved to produce an enzyme (except fibrinogen/fibrin)a. Phase 1- Formation of Prothrombin Activator (factor X, factor V, Ca, & aggregated platelets); two pathways: i. Intrinsic- all factors present in the blood; slower pathway; negatively charged surfaces such as activated platelets, collagen, or glass imitates; begins with Hageman’s factor (factor XII) ii. Extrinsic- requires damage; faster pathway because some steps are skipped; begins with tissue factor (factor III) from damaged cells b. Phase 2- Prothrombin is converted to thrombin through the prothrombin activator (mediator) c. Phase 3- Fibrinogen is converted to allowing it to polymerize->insoluble clot production; if Ca is present factor XIII stabilizes the clot
What happens in excitation-contraction coupling? (how is it electrically stimulated and how does it contract?) (MC)
Pacemaker cells generate APs for contractile cells
1. Gap junctions allow conduction of impulses via the intrinsic cardiac conduction system as non-contractile, autorhythmic pacemaker cells generate depolarizations due to their pacemaker potential (unstable resting potential that allows them to generate depolarizations without external stimulation)
a. Slow Na channels begin to open to cause slow depolarization
b. Once at threshold, Ca channels open and allow Ca influx and we see fast Na channels open to cause more rapid depolarization
c. Repolarization occurs due to K efflux and the pacemaker cells becoming more negative
2. Contractile Myocardial Effects
a. In resting phase only K channels are open to establish a resting potential
b. Upon early depolarization sodium enters & allows the cell to approach threshold rapidly, later K channels open and the cell is slightly repolarized
c. Almost simultaneously with K channels opening, Ca channels open to allow steady Ca influx and create plateau , which maintains the contraction
d. As Ca channels close and K channels open, the cell voltage decreases
Know methods to prevent coagulation and how it works (who binds to thrombin and prevents its action on fibrinogen?) (MC)
• Endothelium: discourages clotting->smooth
• Heparin from mast cells & basophils (anticoagulant)
• Antithrombin: prevents thrombin from acting on fibrinogen
• Warfarin/Coumadin: Vitamin K antagonist->prevents formation of clotting factors
• Aspirin and Ibuprofen: blacks platelet aggregation
• Citrate Phosphate Dextrose: removes Ca2+ (required for clotting)
Just know the following statement: In cardiac muscle, calcium channels inactivate & potassium channels open...repolarization and diastole are initiated (MC)
Just know the following statement: In cardiac muscle, calcium channels inactivate & potassium channels open…repolarization and diastole are initiated
What is the function of plasmin on fibrin? (MC)
Digests fibrin
What activates the ventricular syncytium? (MC)
Subendocardial Conduction Networks/Purkinje Fibers
What is the relationship between hematopoiesis, erythropoiesis, thrombopoiesis, and leukopoiesis? (MC)
• Erythropoiesis, thrombopoiesis, and leukopoiesis are all subdivisions of hematopoiesis
• Originates from Hemocytoblast (Hematopoetic Stem Cell)
Which part/chamber of the heart do you expect to be the thickest and why? (MC)
Left ventricle because it has to pump the blood further around the body, and against higher pressure, compared with the right ventricle
What is the function of intercalated disks? (MC)
Desmosome & gap junction; allow anchorage & communication; allows electrical coupling for the functional syncytium
Why do erythrocytes eject their nucleus and organelles? What is the benefit? (MC)
• Doesn't need a nucleus or organelles
• Lack of nucleus/organelles=Larger surface-to-volume ratio- more gas carrying capacity
What does atrial systole mean? (TF)
Rest of the blood (that didn't passively fill) forced into the ventricles actively via atrial systole
What neurotransmitters are associated with sympathetic and parasympathetic and what are their functions as it relates to slowing/increasing cardiac output? (TF)
• Parasympathetic: slows CO; decrease in Ca influx; input from vagus nerve->acetylcholine
• Sympathetic- increases CO; accelerator nerves release epinephrine which act on AV nodes->spontaneous depolarization by opening Ca channels; emotions->sympathetic(hypothalamic input)
Does the intrinsic cardiac conduction system contain contractile cells? (TF)
No
Where is the cardiac conduction system the slowest? (TF)
Atrioventricular Node
Know this statement: The intrinsic clotting mechanism is initiated using Hageman's factor (TF)
The intrinsic clotting mechanism is initiated using Hageman's factor
Know the difference between Angina Pectoris and Myocardial Infarction (APP)
• Angina Pectoris- thoracic pain; caused by occlusion of coronary artery or stress induced coronary spasms from an inc. in oxygen demands; lack of oxygen to myocardium leads to weakened cells, but no death
• Myocardial Infarction- heart attack; occlusion of a coronary artery; O2 deficiency leads to myocardial death ; myocardium replaced with scar tissue causing loss of function; most significant damage->left ventricle
Hemolytic Anemia
RBC lysis , premature removal from circulation, or pathogenic disease
Aplastic Anemia
Destruction/inhibition of red marrow
Hemorrhagic Anemia (APP)
Loss of blood
Microcytic Anemia (APP)
Small, pale RBCs->microcytes; Fe deficiency
Athlete's Anemia (APP)
Inc in blood volume during stress->dilution of hemoglobin content
Pernicious Anemia (APP)
B12 deficiency; progenitor RBCs grow, but don't divide or develop->large/pale RBCs or macrocytes
Thalassemia (APP)
Thin, delicate RBCs b/c of absent/faulty globins (reduced Hb)
Sickle Cell Anemia (APP)
RBCs are crescent shaped due to abnormal Hb gene & associated proteins; obstruct small BVs
Know what is associated with Lubb Dupp (which valves) (APP)
• Lubb: Ventricular systole; atrioventricular valves close/semilunar valves open
• Dupp: Ventricular diastole; semilunar valves close/atrioventricular valves open
Know what type of leukocyte is associated with a viral infection....Is it phagocytic? (APP)
T Lymphocytes; not phagocytic
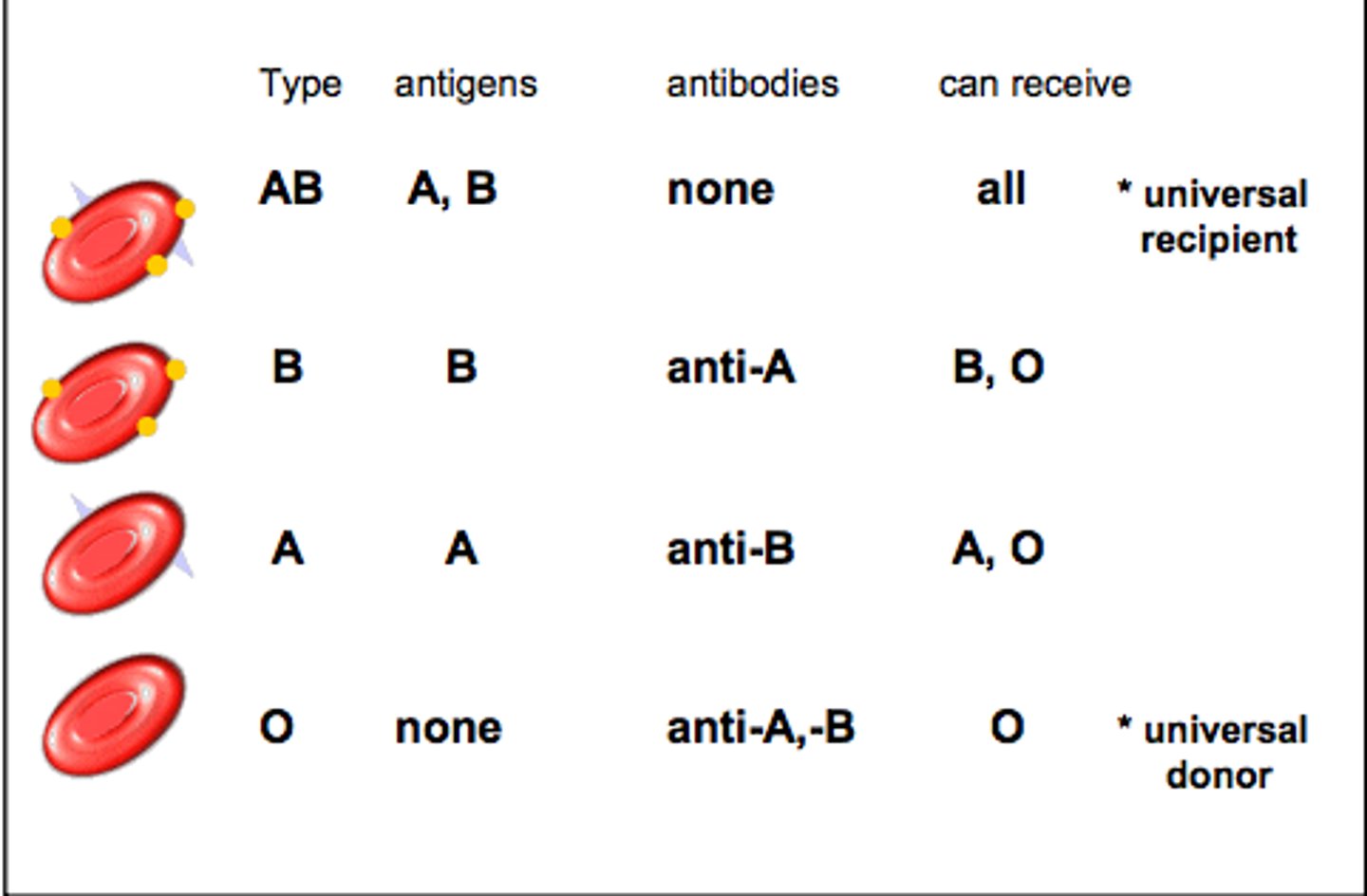
Know what antigens and antibodies are associated with a blood type (APP)
Arrhythmia
Irregular rhythm
Fibrillation
Irregular contraction; lack of ability to pump blood effectively
Tachycardia
Rapid heart beat
Bradycardia
Slow heart beat
Flutter
Rapid atrial or ventricular repolarization
Murmur
Improper closing of valves
Asystole
No pulse
Why is O- the universal donor? Be able to describe in terms of antigens (SAQ)
O- red blood cells have no A, B or Rh antigens so no antibodies will act against the new blood
What is the difference between extrinsic and intrinsic blood clotting pathways? (SAQ)
• Intrinsic- all factors present in the blood; slower pathway; negatively charged surfaces such as activated platelets, collagen, or glass imitates; begins with Hageman’s factor (factor XII)
• Extrinsic- requires damage; faster pathway because some steps are skipped; begins with tissue factor (factor III) from damaged cells
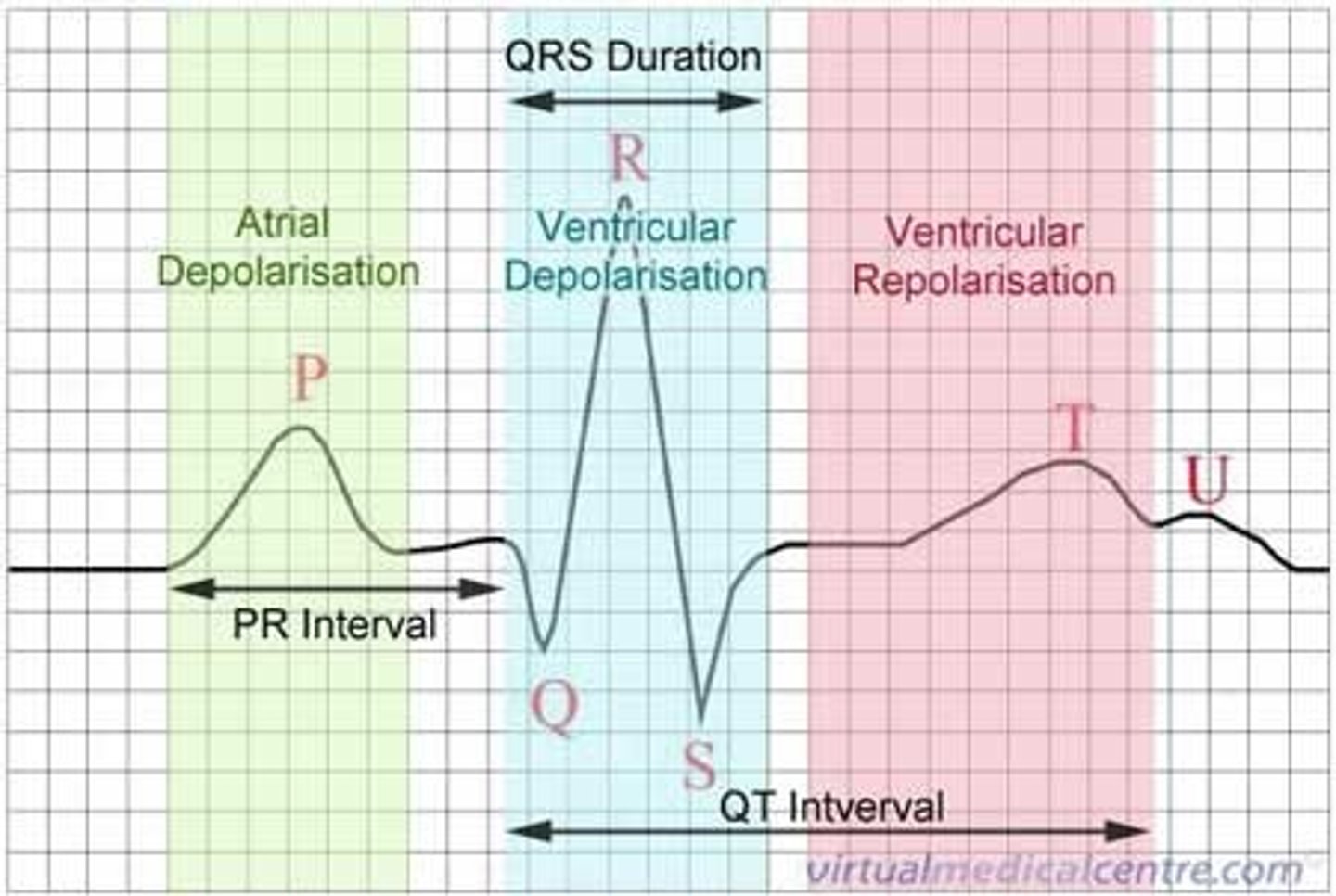
ECG labeled (SAQ)
• P Wave: Atrial depolarization
• QRS Wave: Ventricular depolarization (hides atrial repolarization)
• T Wave: Ventricular repolarization
What is consistent with congestive heart failure in terms of cardiac output? (APP)
Inability to maintain normal CO
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic congestive heart failure? (SAQ)
• Systolic Heart Failure: large, dilated heart that cannot eject blood efficiently
• Diastolic Heart Failure: LV walls cannot relax properly and LV does not fill properly; may see LV hypertrophy, but otherwise normally sized heart
What hormone causes erythrocyte levels to increase (blood doping) and what is it called when we have too many red blood cells? (SAQ)
• Erythropoietin (EPO)
• Polycythemia
What white blood cell is associated with parasites? (SAQ)
Eosinophil
What is the difference in leukocytosis and leukemia/lymphoma? (SAQ)
• Leukocytosis- increased WBC count
• Leukemia & Lymphomas- grossly inc numbers with abnormal forms & loss of function
What is the origin of the ligamentum arteriosum? Why is this vessel necessary? (SAQ)
• Ductus Arteriosus
• Connects the aorta and the pulmonary artery
How can liver failure affect blood clotting? (SAQ)
Liver failure prevents the synthesis of clotting factors->inability to clot; lipid absorption disorders affect vitamin K absorption->inability to produce clotting factors
What is hematocrit? What makes it up? (SAQ)
• Relative percentage of RBCs
• Blood that has been centrifuged separates into three layers: erythrocytes 45% , buffycoat<1%, and plasma 55%