Anatomy and Physiology Exam 1
1/341
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
342 Terms
Nucleus
contains genetic material for the cells (DNA)
Cytoplasm
material between plasma membrane and the nucleus
Cytosol
largely water with dissolved protein, salts, sugars and other solutes
Mitochondria
two membranes create two compartments
mitochondrial matrix
unique DNA
intermembrane space
Endoplasmic reticulum
Rough ER and Smooth ER
Rough ER
ribosomes attached, protein assembly and modification
Smooth ER
Synthesis of fatty acids, steroids, lipids
Modified forms in liver, kidney, muscles
Lysosomes
Hydrolytic enzymes to degrade bacteria or old
organellesAcidic interior→ acid hydrolases used to degrade
Peroxisomes
Enzymes, catalases and oxidases, to degrade longchain fatty acids, free radicals, and toxic foreign molecules
Generate hydrogen peroxide
Plasma membrane
separates the cell from the outside world
Extracellular environment
33% of the body water makes up the extracellular compartment
Blood plasma
mostly found inside the blood vessels and makes up 20% of the extracellular fluid
interstitial fluid:
makes up the other 80% of the extracellular fluid
Extracellular matrix
made up of collagen (provides strength), elastin (provides elasticity), and a gel-like ground substance (provides fluidity).
ground substance
composed of glycoproteins, and proteoglycans
Basal laminate or basement membrane
mostly made up of collagen IV.
Forms chemical bonds between the carbohydrates on the surface of cells, and the extracellular matrix
forms a connection between the epithelial cells and the underlying connective tissue.
Transport across cell membranes: plasma membrane is ____
selectively permeable
Passive transport
substances move across cell membranes, without the input of any energy, down their concentration gradient
osmosis
passive movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration (more water) to a region of higher solute concentration (less water).
facilitated diffusion
carrier mediated diffusion
active transport
a cell uses energy, primarily from the breakdown of ATP, to move a substance across the membrane, i.e., against a concentration gradient
Primary active transport example
Na+/K+ pump
intercellular junctions
tight
adherence
desmosomes
gap
Membrane potential
A. Relative abundance of intracellular and extracellular ions
B. Resting membrane potential
C. The Na+/K+ pump and its role in maintaining the resting membrane potential
One of the five important functions of skeletal muscle contraction is heat production.
True
What is found in the Motor End Plate? (neuromuscular junction)
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholine receptors
What is found in the Synaptic Knob (neuromuscular junction)
Synaptic vesicles filled with acetylcholine
Voltage-gated Calcium channels
Myofibrils are composed of protein filaments called
actin and myosin.
A bundle of muscle fibers is known as a
fascicle
A skeletal muscle fiber is…
multinucleated, meaning it contains many nuclei
The muscle cell membrane is called the
sarcolemma
Which connective tissue wrapping separates individual muscle fibers?
endomysium
Rising sarcoplasmic calcium levels results in….
contraction in smooth muscle fibers and skeletal muscle fibers.
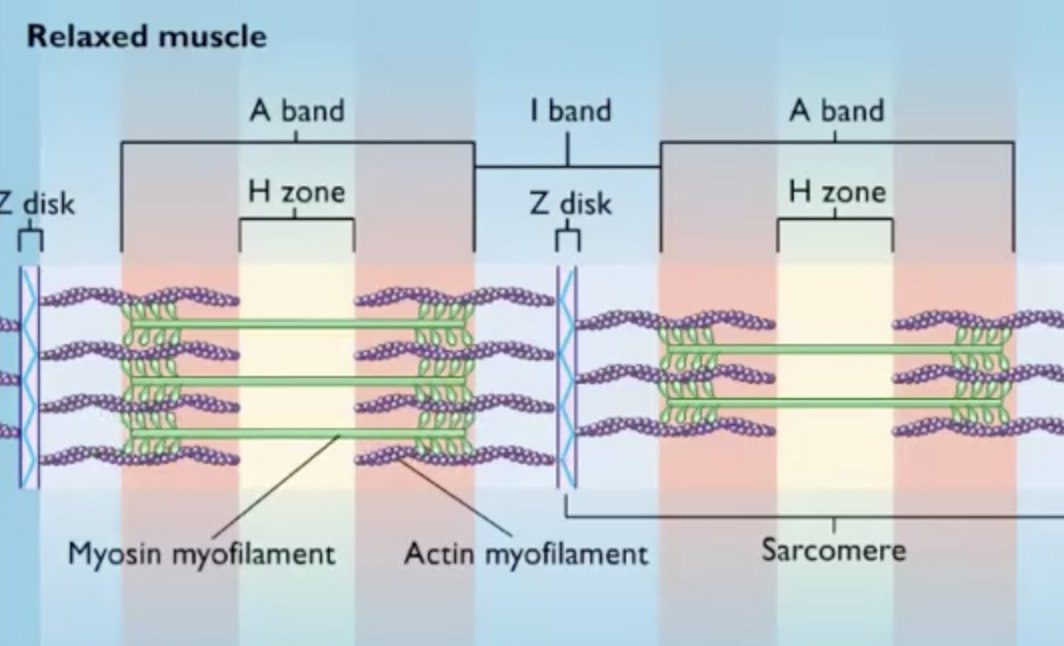
The area of the muscle fiber where the actin and myosin myofilaments overlap is the
A band

During contraction, the actin myofilaments slide toward the
H zone
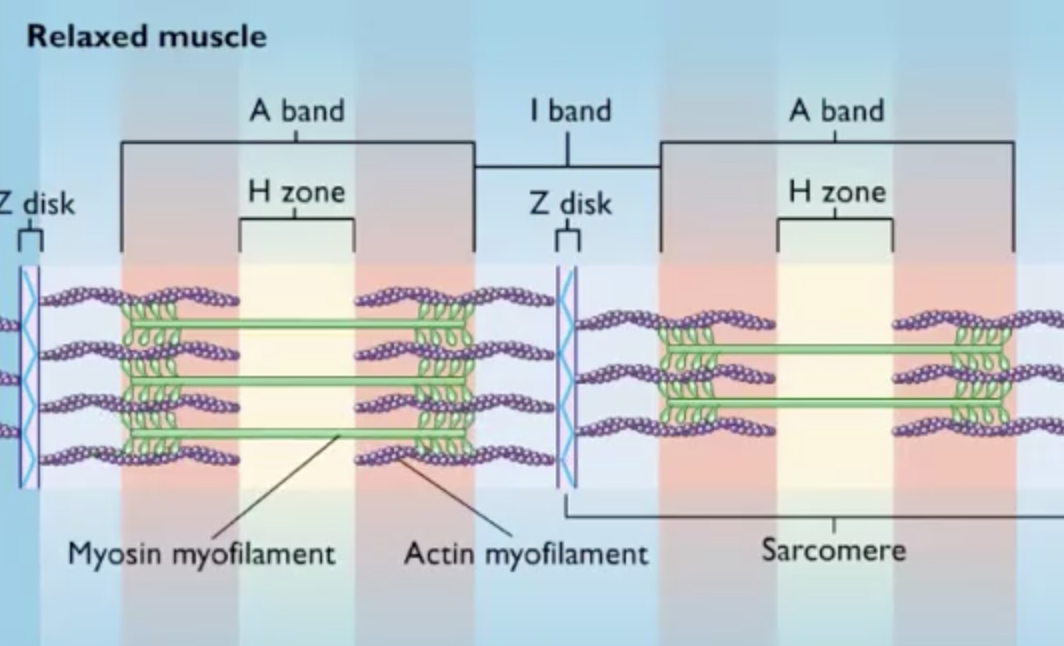
The distance from one Z disk to the next Z disk is called a(n)
sarcomere
In a fully contracted muscle, actin filaments ____myosin filaments, increasing overlap
slide past
In a relaxed muscle, the ends of the actin filaments overlap.
FALSE
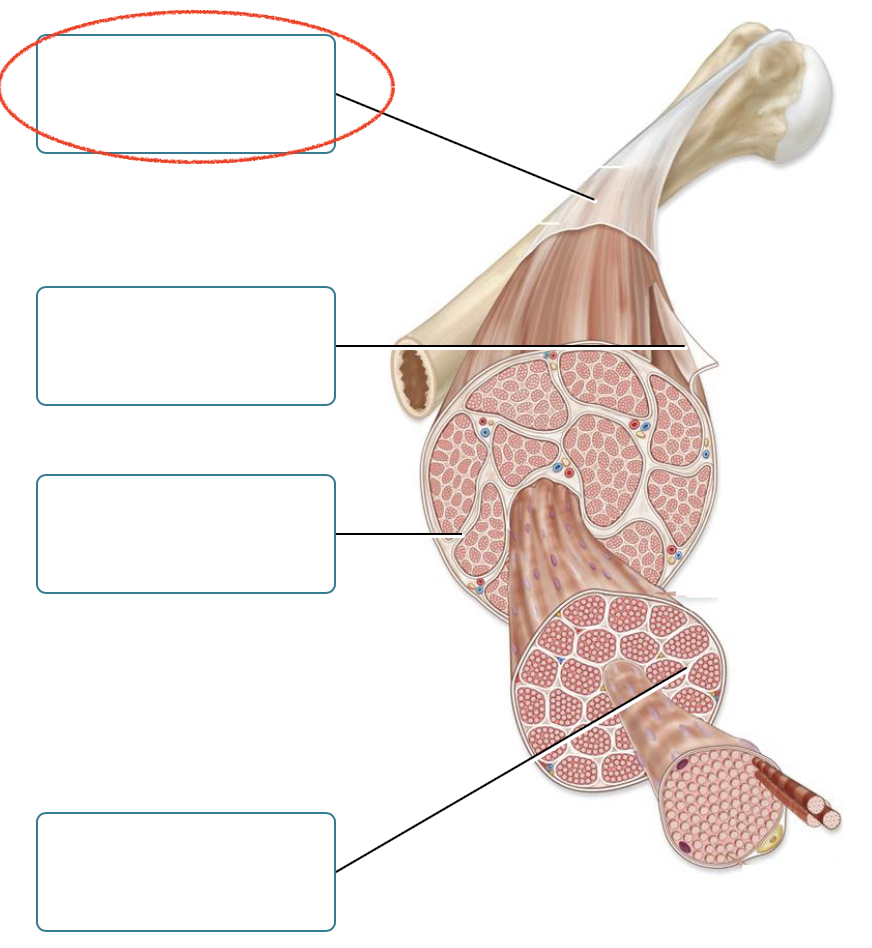
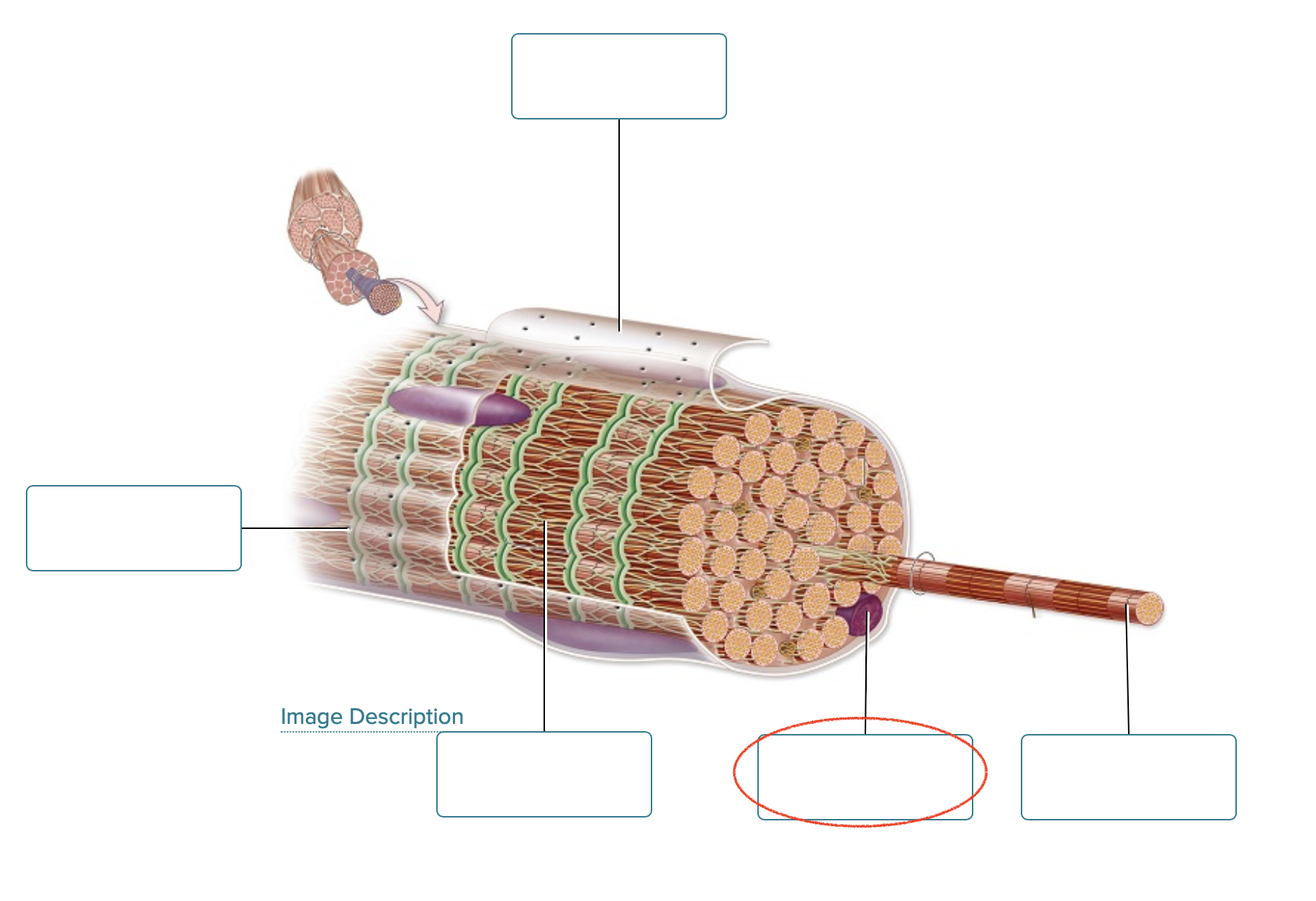
Label the connective tissues associated with skeletal muscle.
Deep fascia
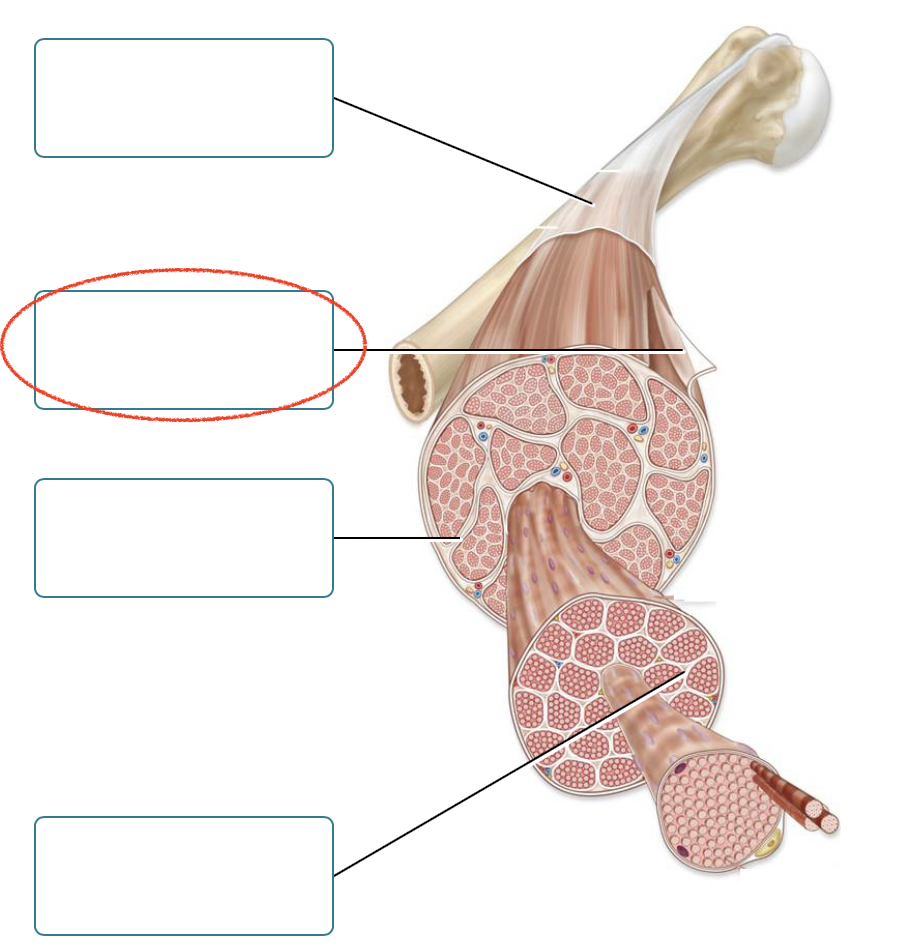
Label the connective tissues associated with skeletal muscle.
epimysium
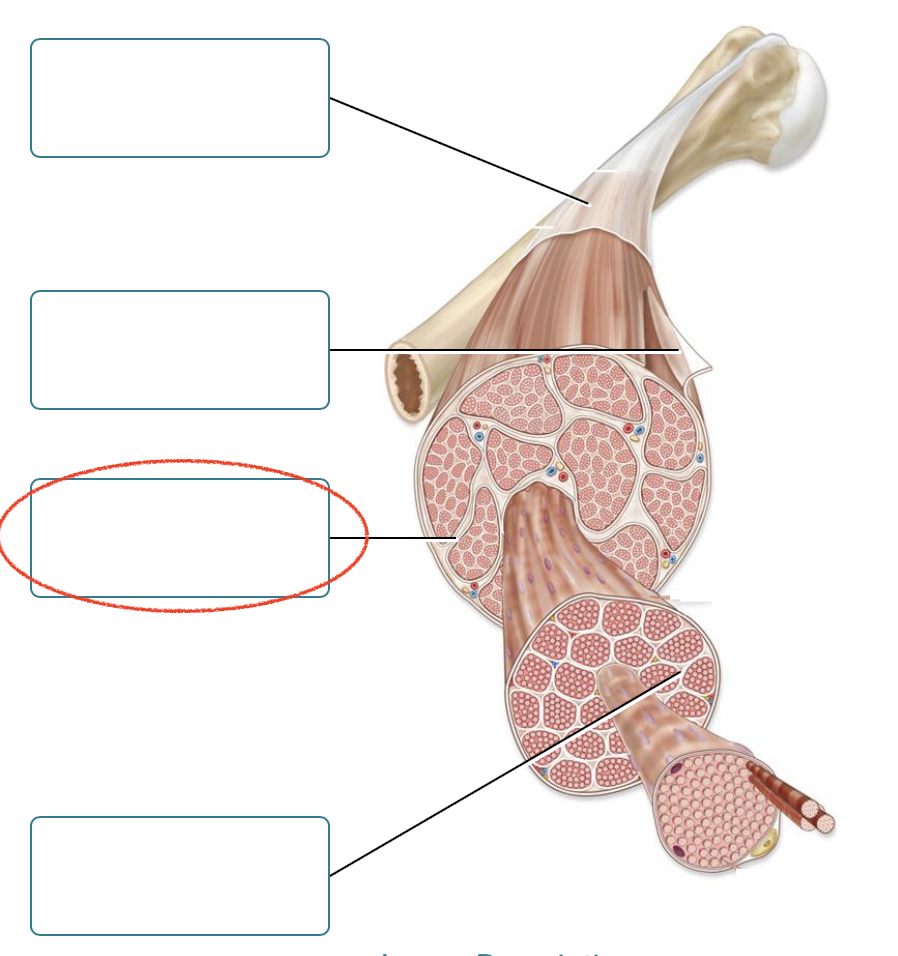
Label the connective tissues associated with skeletal muscle.
perimysium
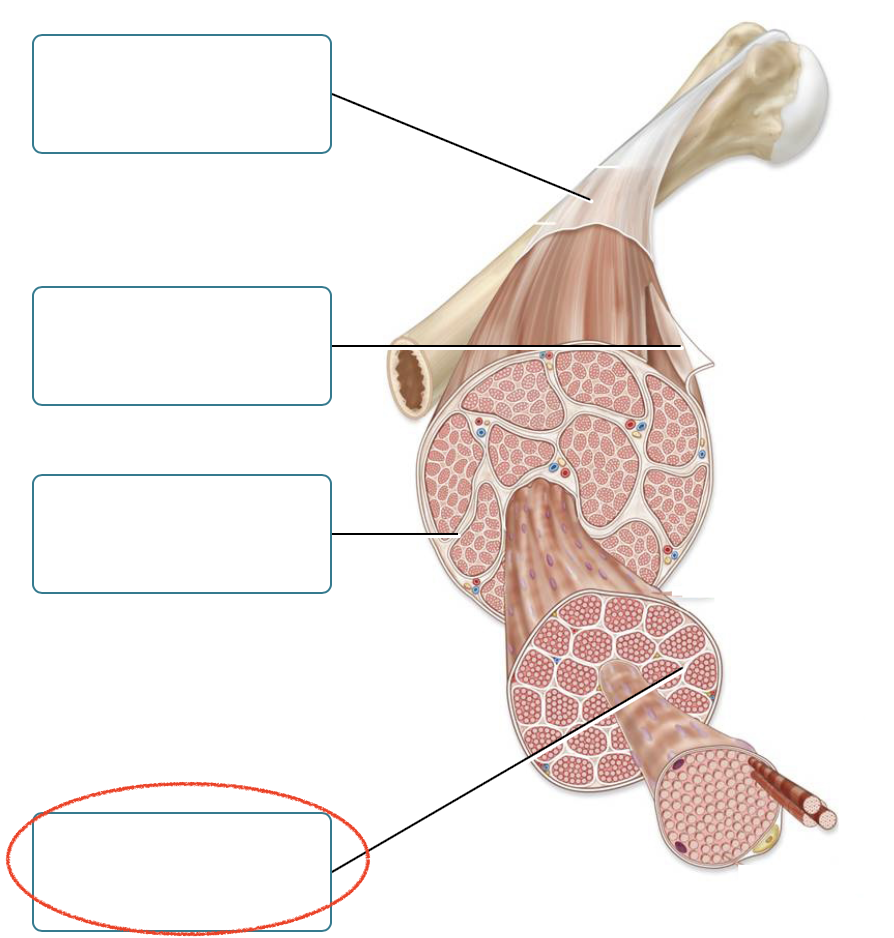
Label the connective tissues associated with skeletal muscle.
Endomysium
At the ends of muscles, the connective tissues merge to form a _________blank, which attaches the muscle to other structures.
tendon
All characteristics of cardiac muscle.
Cells are short and branching.
Cells have one or two nuclei in the center of the cell.
They are composed of thick and thin filaments.
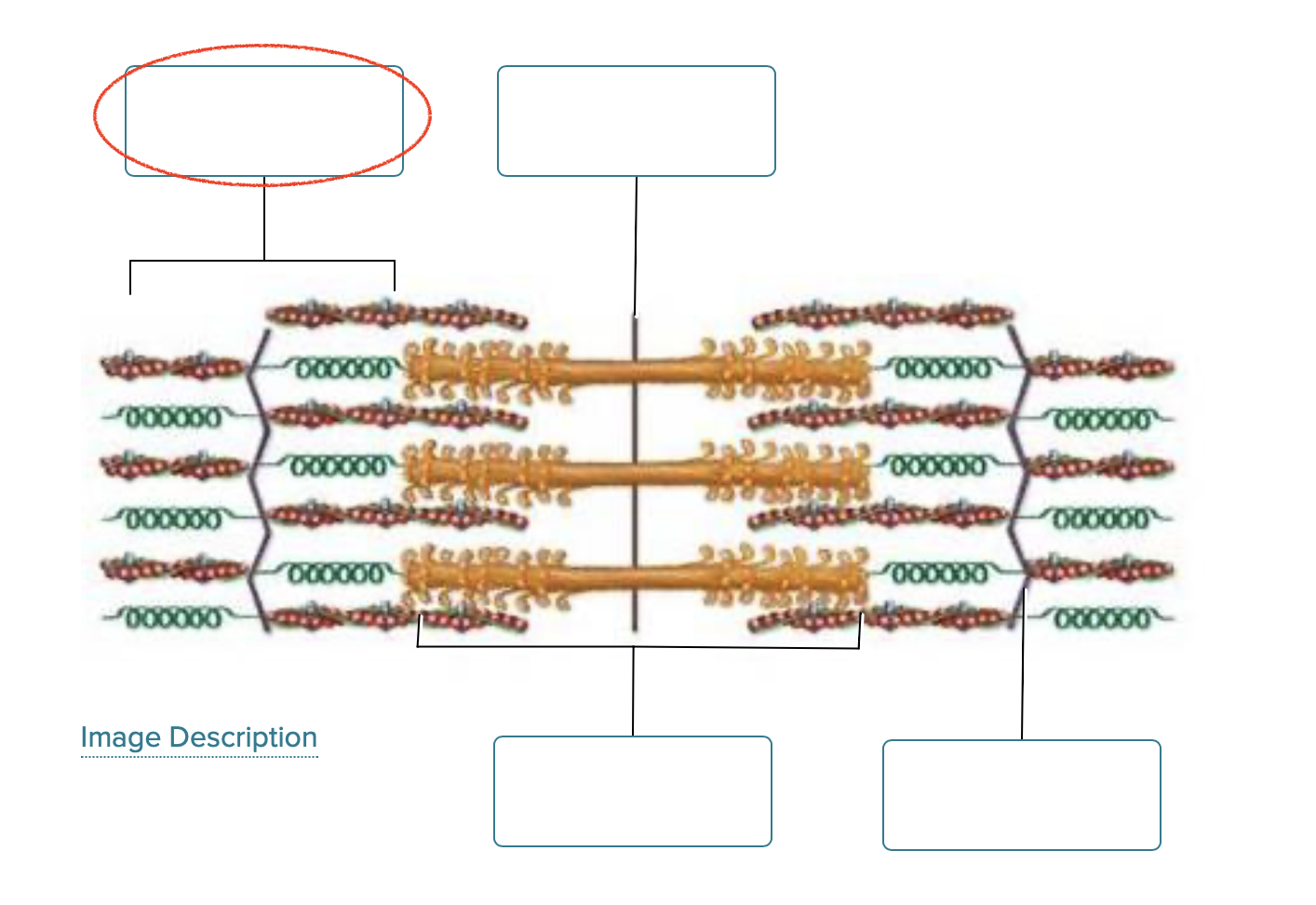
Label the structures of a sarcomere.
I band
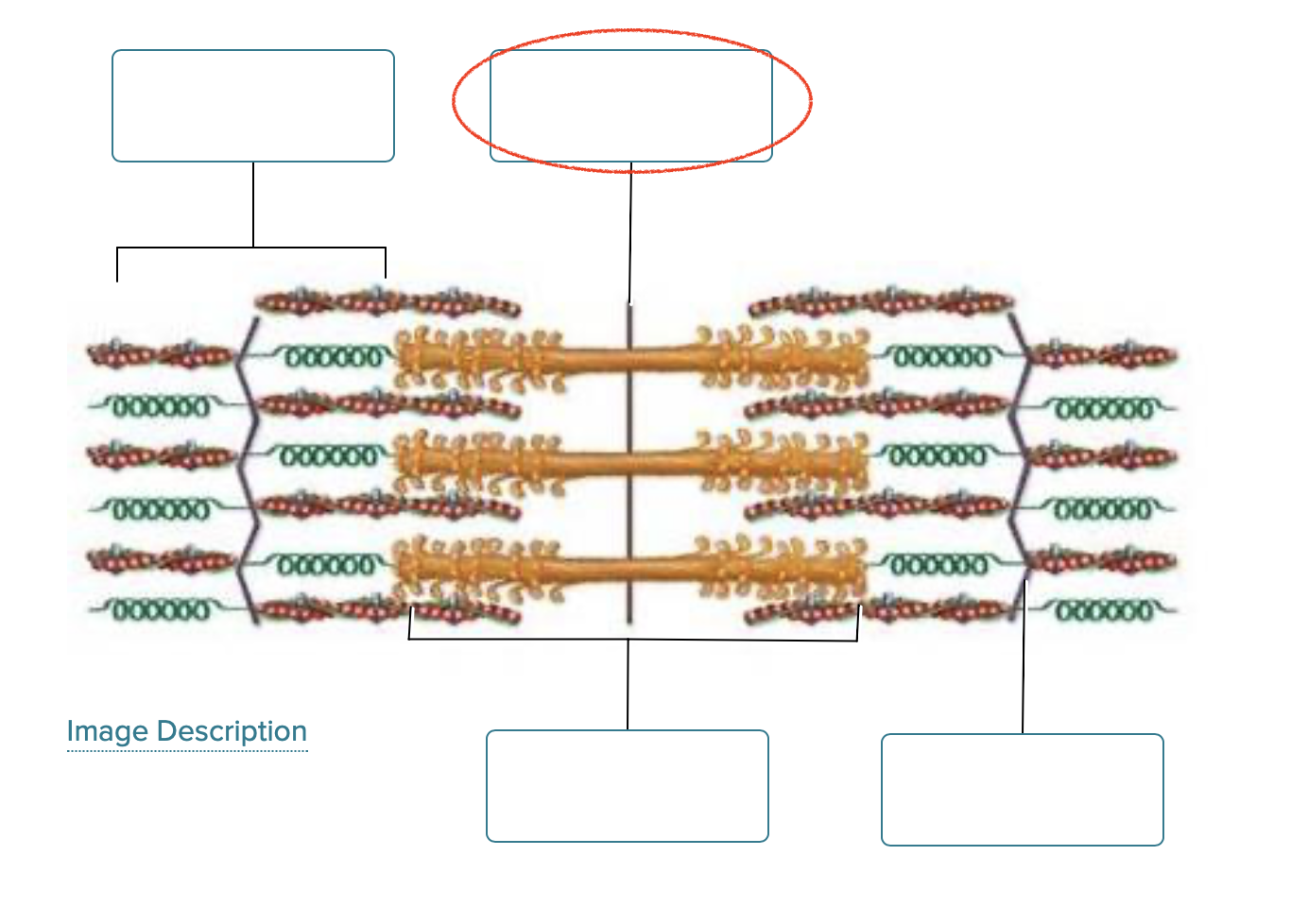
Label the structures of a sarcomere.
M line

Label the structures of a sarcomere.
A band
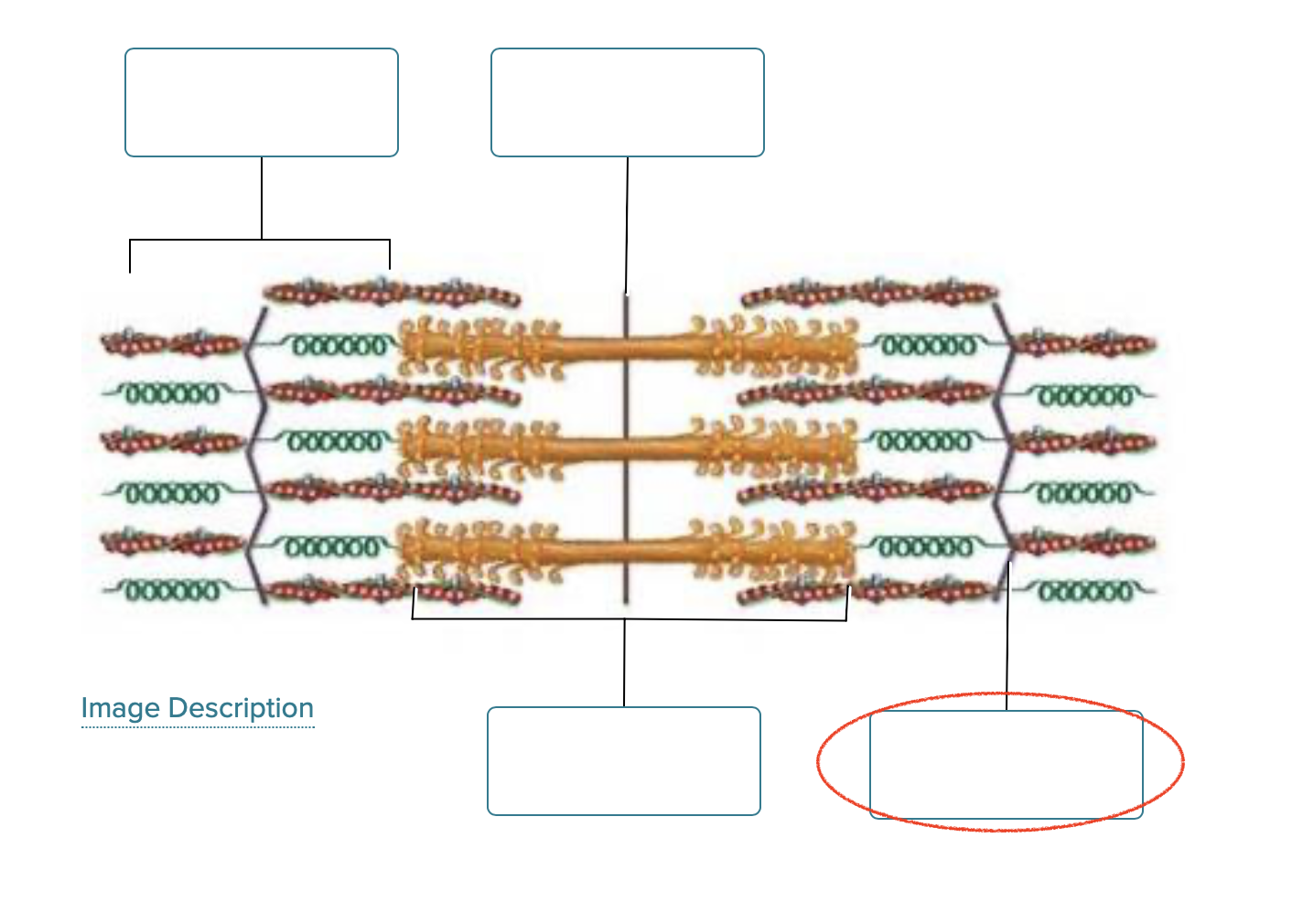
Label the structures of a sarcomere.
Z disc
What are the events involved in smooth muscle contraction?
Initiated by Ca²⁺ binding to intracellular calmodulin.
Ca²⁺/calmodulin complex activates MLCK.
Activated MLCK activates myosin ATPase.
The type of muscle tissue that would be found in the wall of the bladder is _________blank muscle tissue.
smooth
The primary neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction is
acetylcholine
Arrange the following in the proper order in which they occur at the postsynaptic side of a neuromuscular junction.
Action potential is propagated over the muscle cell membrane.
Depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane occurs.
Sodium ions move into muscle cell.
3,2,1
The area between the presynaptic nerve cell and the postsynaptic muscle cell is termed the
synaptic cleft.
Receptors on the postsynaptic cell membrane that bind neurotransmitters (like acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction) are
ligand-gated ion channels
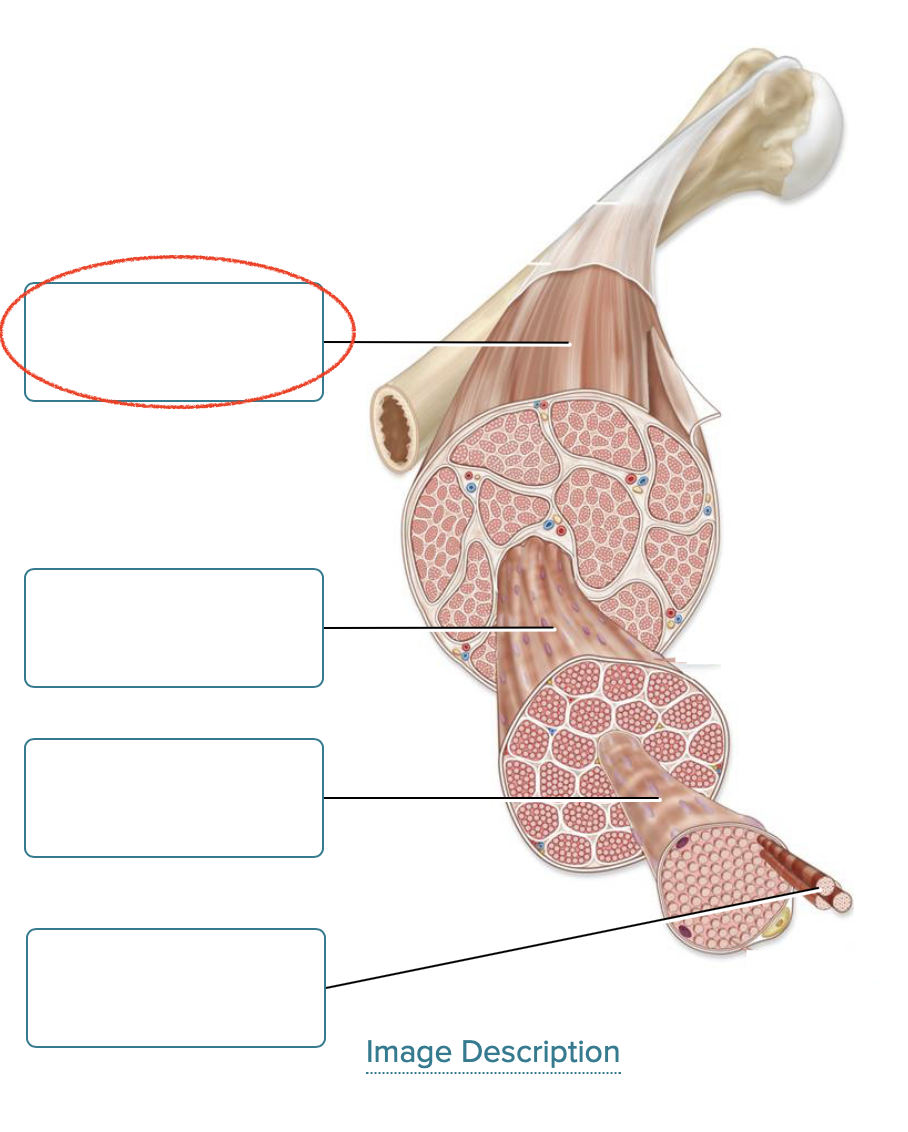
Label the components of skeletal muscle.
skeletal muscle
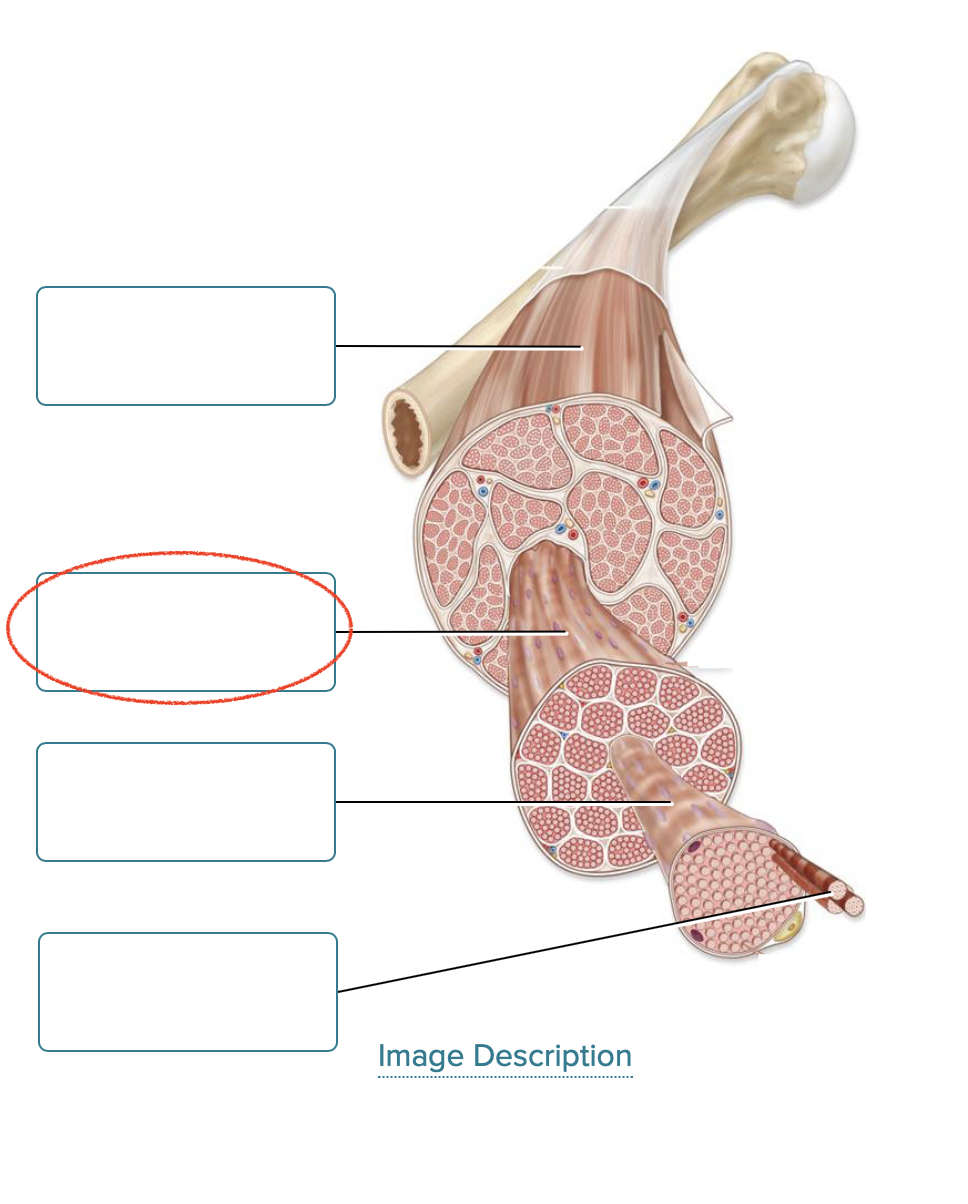
Label the components of skeletal muscle.
fascicle
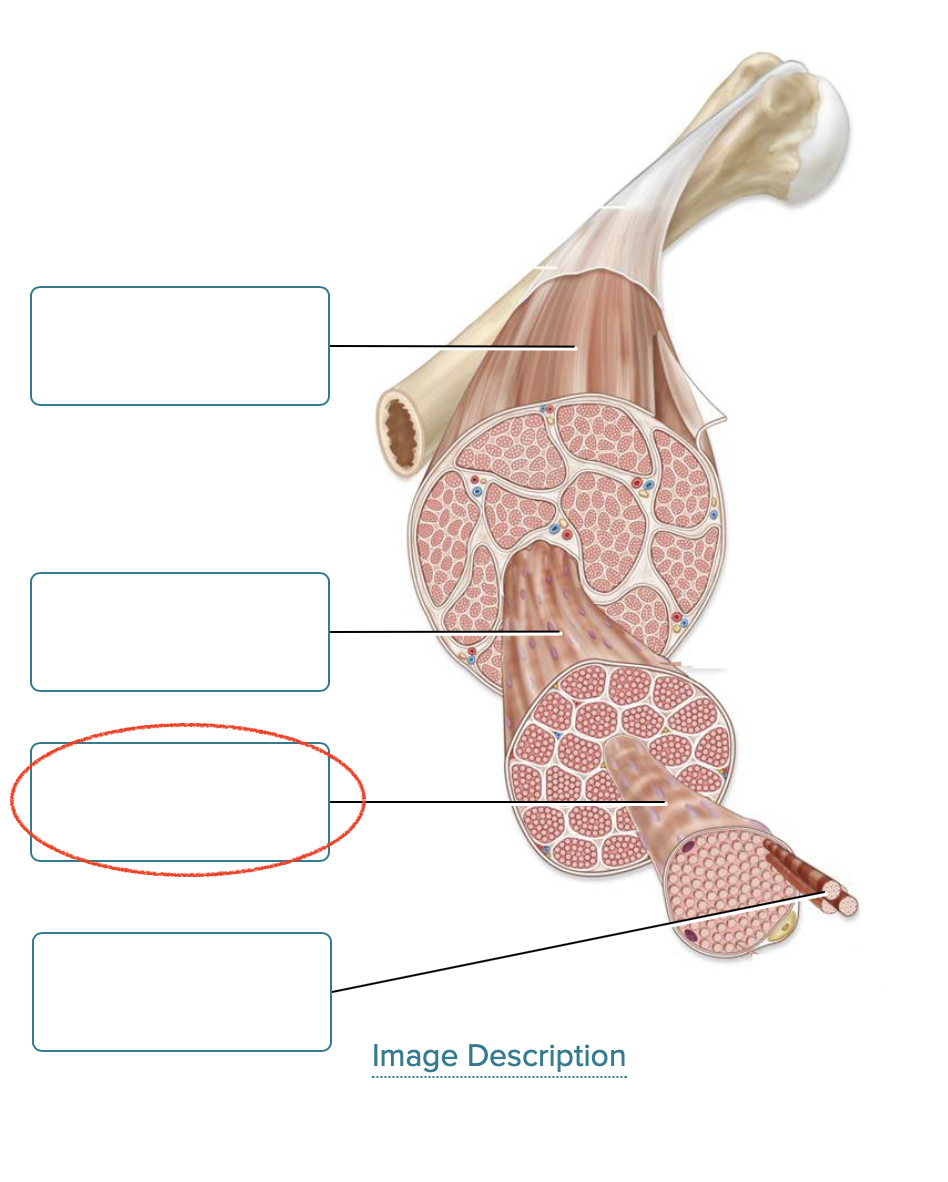
Label the components of skeletal muscle.
muscle fiber
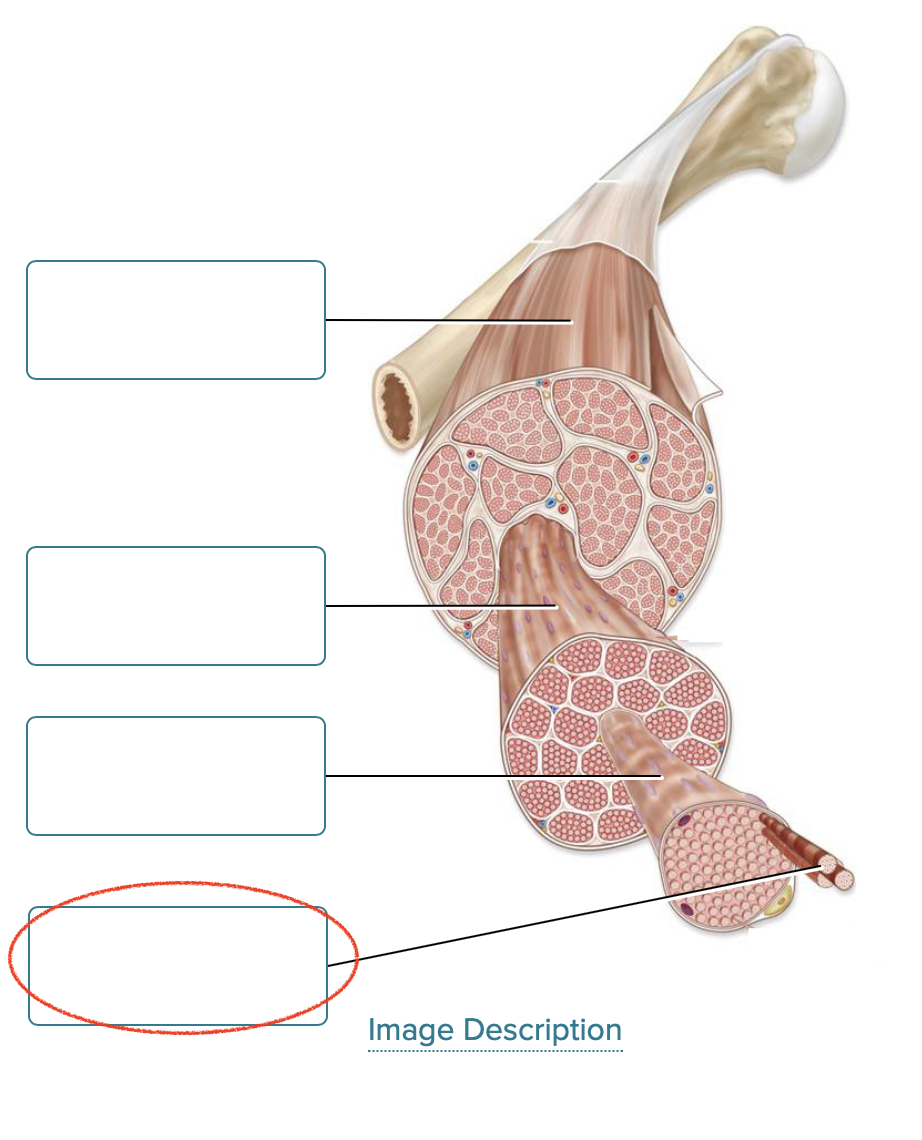
Label the components of skeletal muscle.
myofibril
Check all that are proteins of thin filaments.
actin and troponin
Which is a characteristic of skeletal muscle from the selections below?
mutinucleated
Which of the following connects muscle to bone?
tendons
The component of a muscle fiber that quickly transports a muscle impulse from the sarcolemma throughout the entire muscle fiber is called the
transverse tubule (t-tubule)
A motor neuron transmits the effect of a nerve impulse to the muscle fiber at a _________
neuromuscular junction.
Smooth muscle is not located in the respiratory system.
false- it is found in the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles,
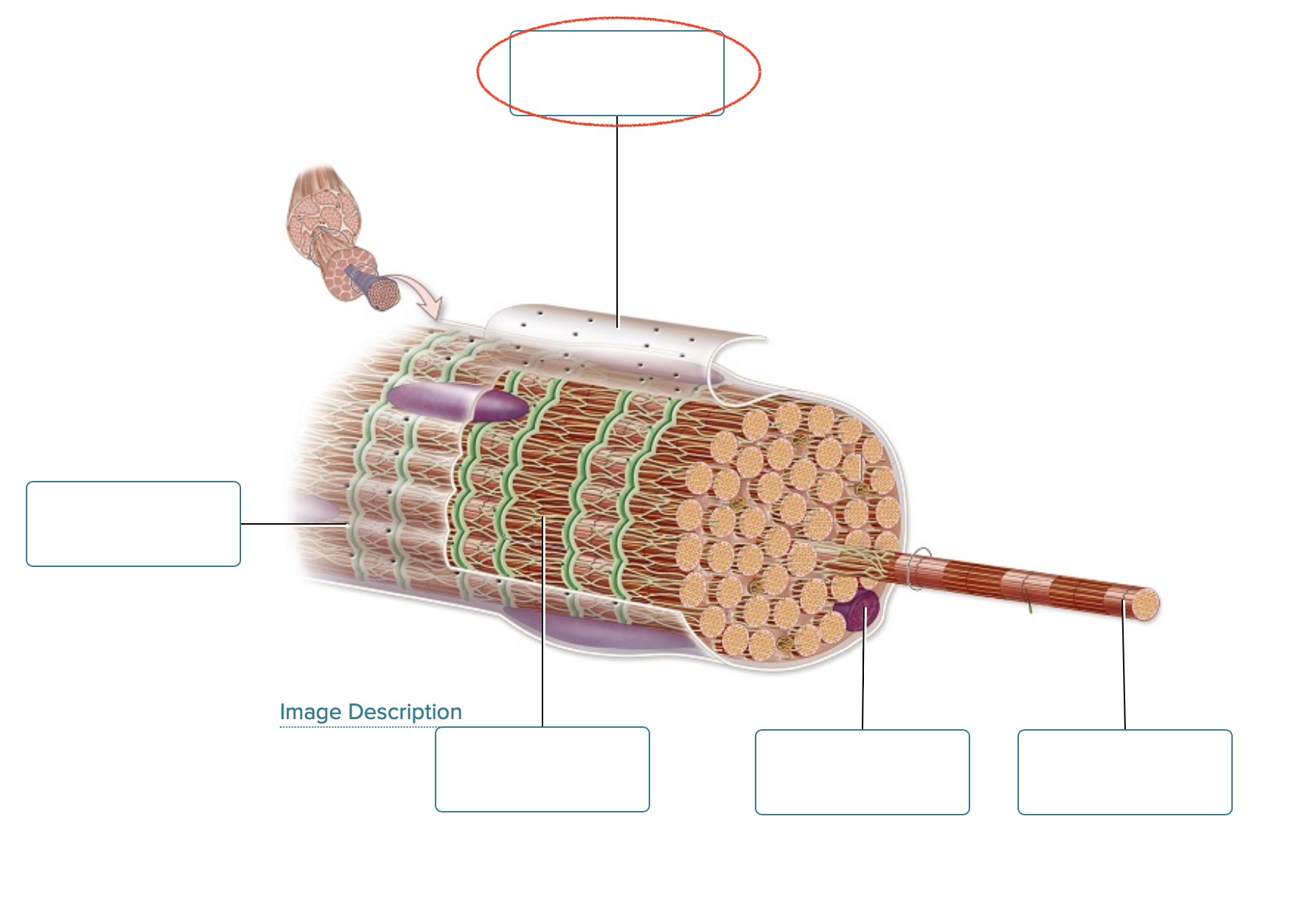
Label the structures of a skeletal muscle fiber.
sarcolemma
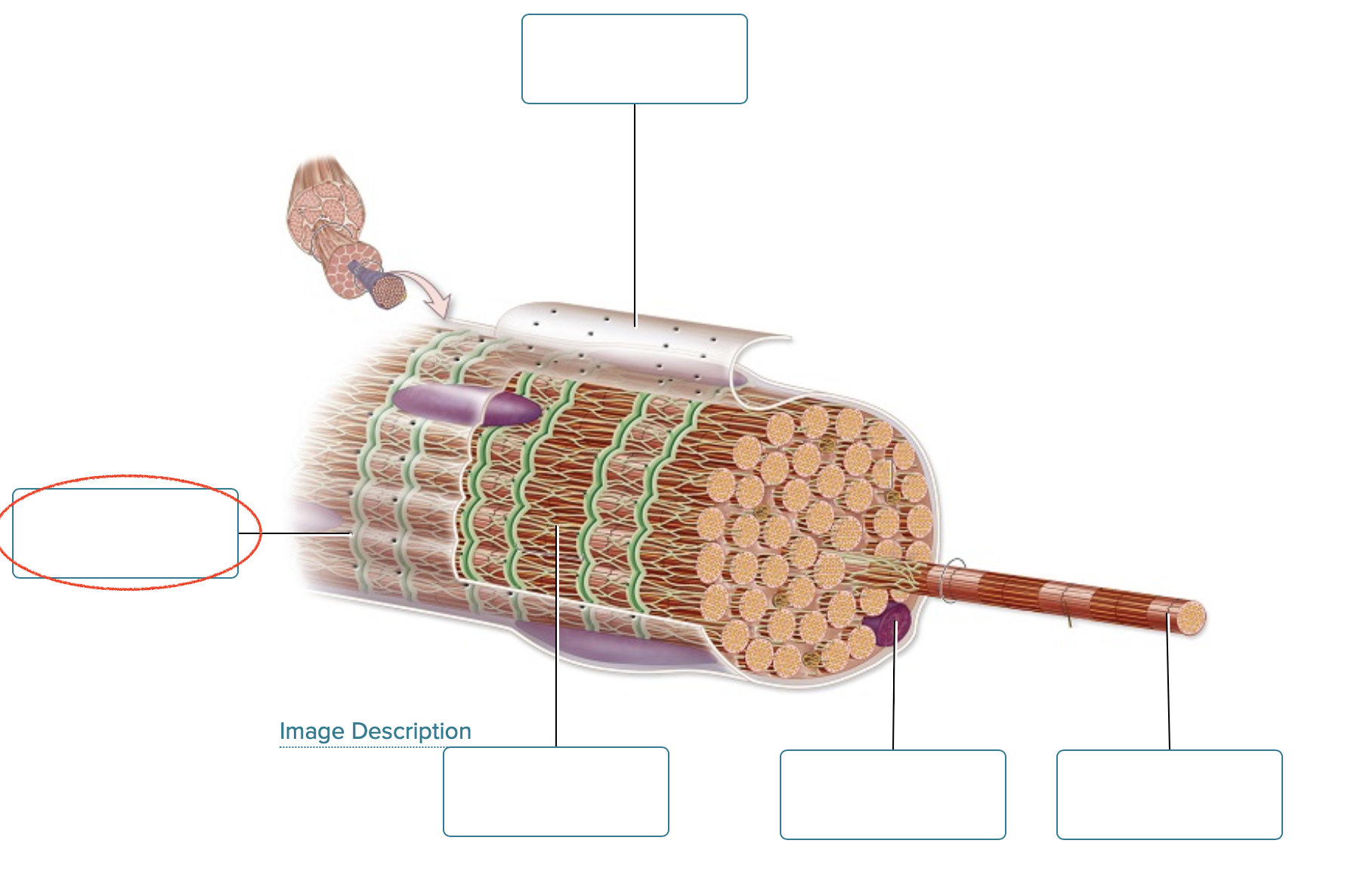
Label the structures of a skeletal muscle fiber.
openings into T-tubules
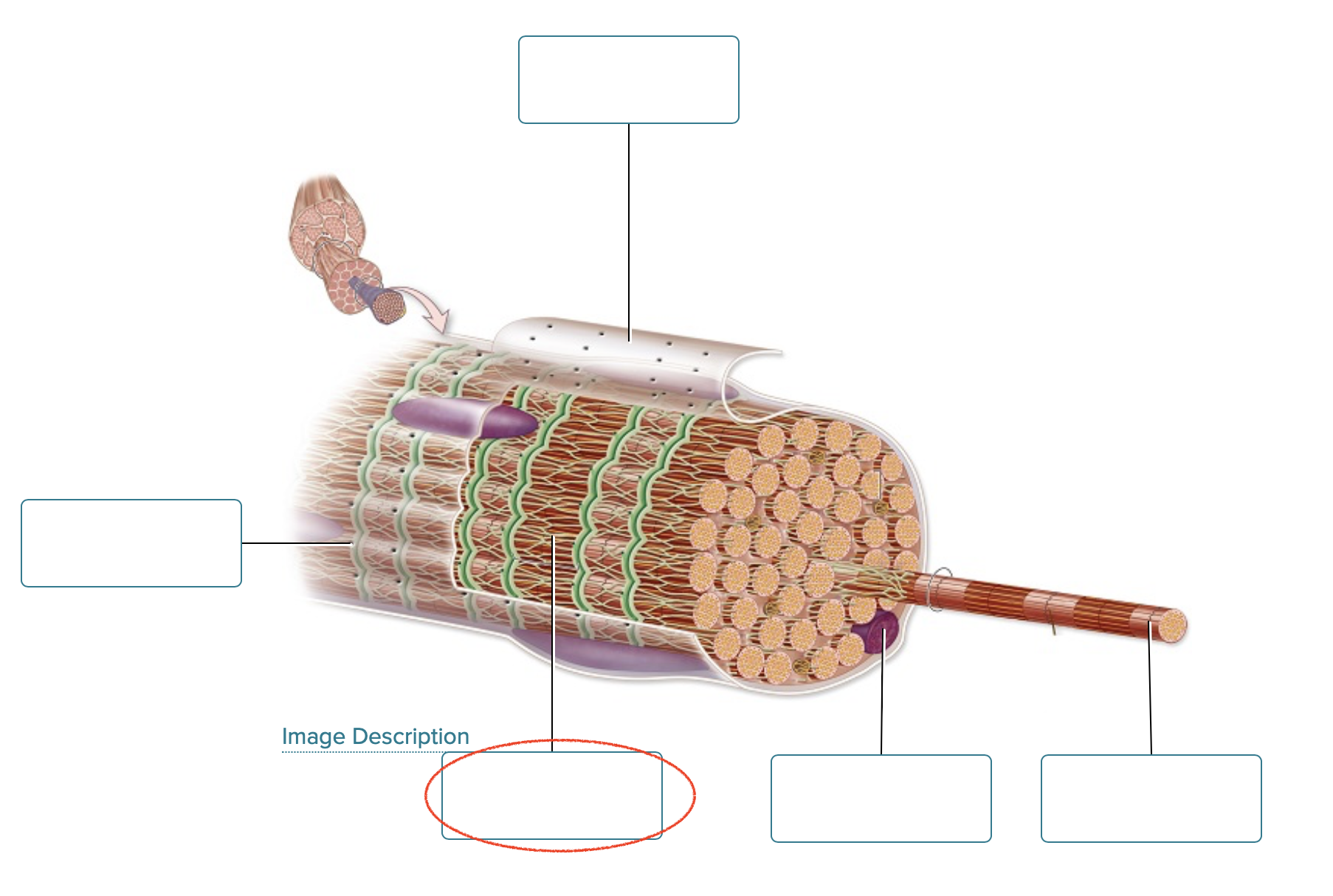
Label the structures of a skeletal muscle fiber.
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Label the structures of a skeletal muscle fiber.
nucleus
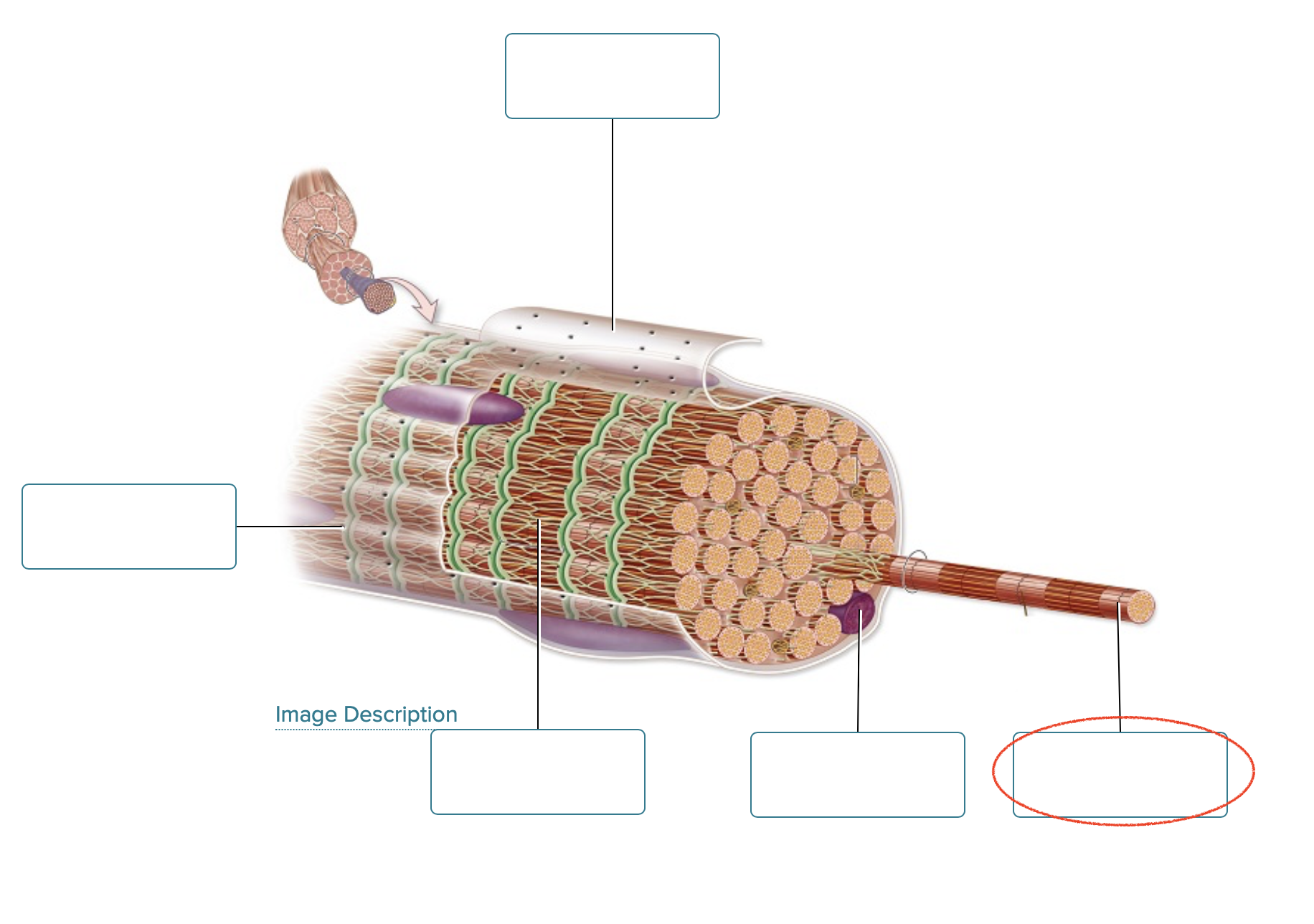
Label the structures of a skeletal muscle fiber.
myofibril
Neighboring cardiac muscle cells in the walls of heart chambers have specialized cell-to-cell contacts that electrically and mechanically link the cells together, permitting the immediate passage of muscle impulses. These cell-to-cell contacts are called _________________
intercalated discs
the specialized region of the sarcolemma that has folds and indentations to increase the membrane surface area covered by the synaptic knob is the
motor end plate
the contractile unit of a myofibril is called the
sarcomere
If you were studying the neurotransmitter released from axon terminals at a neuromuscular junction, you would be studying
acetylcholine
Match each sarcomere region with the filament(s) it contains: THICK FILAMENTS
H band and M line
Match each sarcomere region with the filament(s) it contains: THIN FILAMENTS
I band
Match each sarcomere region with the filament(s) it contains: BOTH THICK AND THIN FILAMENTS
A band
all functions of skeletal muscle tissue.
Body movement – Skeletal muscles pull on bones to produce movement
Maintenance of posture – Skeletal muscles stabilize the body and help maintain posture.
Heat production – Muscle contractions generate heat to help maintain body temperature.
Metabolic regulation – Skeletal muscle stores and uses glucose and other nutrients, contributing to metabolism.
All the muscle fibers under the control of a single motor axon are referred to as
a motor unit
Some reflex arcs (like stretch reflexes) are monosynaptic and do not involve
interneurons—the sensory neuron synapses directly with the motor neuron.
Direct motor pathways are involved in
consciously contracting skeletal muscle.
Which neuron in a sensory pathway is part of the sensory receptor?
primary
Somatosensory pathways process stimuli from
the body's surface (skin, muscles, joints, fascia) for touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception
The space containing cerebrospinal fluid is the _________.
subarachnoid
Upper motor neurons may inhibit
lower motor neurons.
Motor signals to maintain posture and balance pass through a(n) _________ pathway.
indirect
All reflexes share the property of being an
involuntary response.
The spinal cord and spinal nerves are responsible for _________, which are our quickest reactions to a stimulus.
Which portion of a reflex arc is located entirely within the central nervous system?
interneuron
The spinal cord extends from the level of the _________ to the level of the _________
foramen magnum; first lumbar vertebra
A motor command from the brain to signal muscle contraction would pass through a(n)
descending pathway
There are ____ pairs of cervical spinal nerves, but only _____ cervical vertebrae.
eight, seven
Touching a hot object with the right hand will result in withdrawal of the right hand from the object. This is an example of a(n) _________ reflex.
ipsilateral
ipsilateral reflex
an automatic body response where the stimulus and the resulting action happen on the same side of the body
contralateral reflex
an automatic response on one side of the body causes a reflex action on the opposite side; helping with balance and coordination
Water-soluble hormones bind to plasma membrane receptors, which initiate a signal transduction pathway with which of the following processes?
First messenger hormone docking with plasma receptor
Activated protein kinase enzymes
Second messenger pathways including G proteins and phospholipase C
Second messenger pathways including G proteins and adenylate cyclase
The hypothalamus controls the ___ pituitary gland through hormonal regulation, while it controls the ____ pituitary through the hypothalamohypophyseal tract.
anterior; posterior
What is the name of the narrow band of tissue connecting the right and left lobes of the thyroid gland?
isthmus
The endocrine portion of the pancreas produces
insulin and glucagon
As a result of the general stress response, blood concentrations of epinephrine
and cortisol rise
Which organ produces angiotensinogen?
Liver