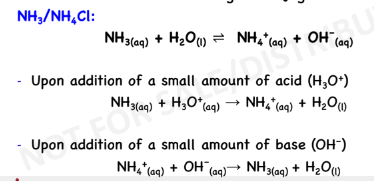ACID BASE EQUILIBRIA | 4.2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
ACIDS (Increase H* in solution). BASES (Increases OH-)
Arrhenius Definition of ACID and BASES
ACIDS (proton H* donor). BASES (proton H* acceptor)
Brønsted-Lowry definition of ACIDS and BASES
ACIDS (electron pair acceptor). BASES (electron par donor)
Lewis Definition of ACIDS and BASES
Arrhenius

Brønsted-Lowry
acid

BASE
must have a pair of non bonding electron (ex. NH3,H20)
Amphiprotic Species (or Amphoteric)
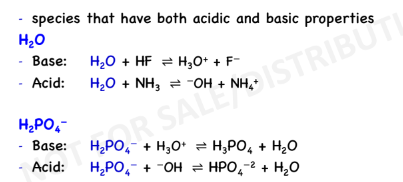
Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases
which acid definition has base, acid, conju acid, and conju base
Conjugate Base
the species produced when an acid gives off its acidic
proton (H+)
Conjugate Acid
the species produced when a base accepts a proton given
off by the acid
Lewis Acid

Lewis Base

P functions

pH – Measure of Acidity
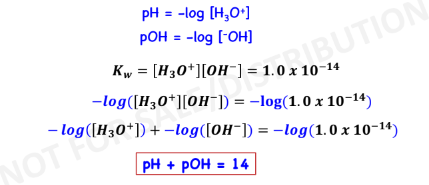
NEUTRAL
[H3O+] = [OH-]
[H3O+] = 1 x 10-7
pH = 7
ACIDIC
[H3O+] > [OH-]
[H3O+] > 1 x 10-7
pH < 7
BASIC

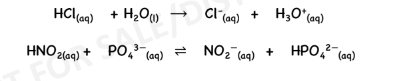
Strong acids and bases
ionize
completely in water.
Weak acids and bases
ionize
only to a limited extent in WATER
Weak Acids & Bases
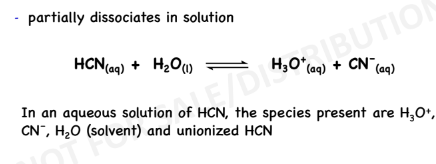
Strong Acids and Bases
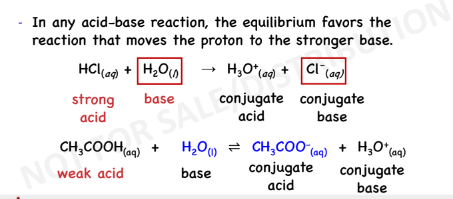
↓strength of its
conjugate base
↑strength acid
Ka
acid dissociation constant
↑higher the Ka value, the stronger the acid
Kb
base dissociation constant
↑higher the Kb value, the stronger the base
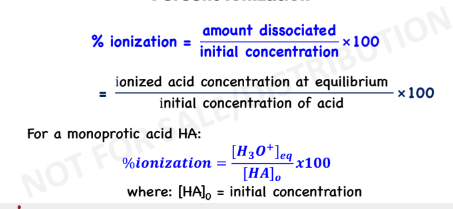
Percent Ionization
BUFFER SOLUTION
solutions that resist drastic changes in pH upon addition of
small amounts of acids or bases
Acidic Buffer:
weak acid + salt containing the
conjugate base
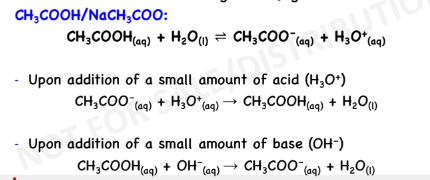
Basic/Alkaline Buffer:
weak base + salt containing the
conjugate acid