Kinetics
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is rate of reaction?
How fast reactants are changed into products
What is collision theory and what does it depend on?
Collision theory states that the rate of reaction depends on:
How often reacting particles collide with each other - the more collisions the faster the rate
The energy transferred during a collision. Particles have to collide with enough energy for a collision to be successful
What is activation energy?
The minimum amount of kinetic energy needed for particles to react
What factors affect rate of reaction?
Temperature
Catalysts
Concentration
Surface area
Pressure of gas
How does increasing the temperature affect the rate of reaction?
Increased energy and frequency of collisions
How does adding catalysts affect the rate of reaction?
It lowers the activation energy
How does increasing the concentration, surface area and pressure affect the rate of reaction?
They increase the frequency of collisions
How do you work out the rate of reaction?
Change in concentration of product/reactant
time
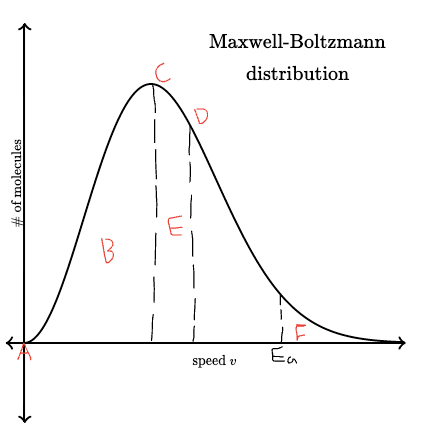
What’s happening at points A,B,C,D,E and F?
A = The curves starts at (0,0) as no particles have 0ke
B = A few molecules are moving slowly
C = The peak of the curve represents the most likely energy of any single molecule
D = The mean energy of all molecules is a bit right of the peak
E = most move at moderate speed
F = These are the only ones that can react?
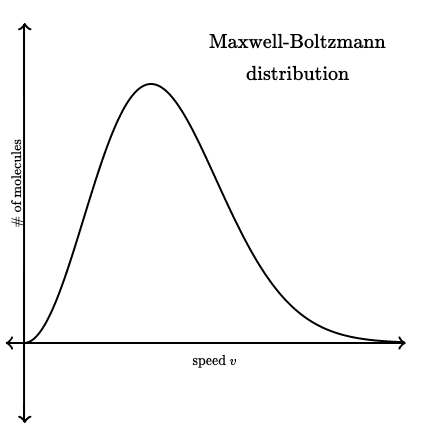
What does the area under the graph represent?
The area is equal to the number of molecules present
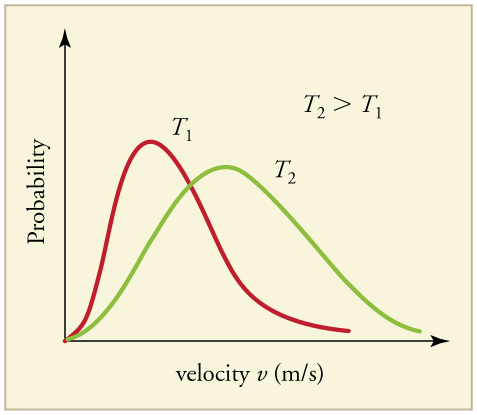
How does temperature affect the distribution?
They only cross once
Peak shifts to the right
Most particles under the activation energy
Height lowers as areas must be equal.
A small change in temperature would lead to more frequent collisions
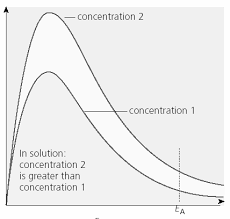
How does concentration affect the distribution?
Shifts it upwards
What factor does not affect the distribution?
Gas pressure
What is a catalyst?
Increases the rate of reaction by providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation rate
They partake in chemical reactions but are put together again at the end of it
How do catalysts affect the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution?
The molecules still have the same amount of energy so the distribution does not change
What is a homogeneous catalyst?
In the same phase as the reactants
What is a heterogeneous catalyst?
In different phase as the reactants
What is adsorption?
Molecules or ions gather on the surface
How do catalysts work?
Reactants are adsorbed onto the surface
Bonds are weakened and broken
New bonds are formed
Desorption (products diffuse away)
What are often used as catalysts?
Transition metals are often used and layed thinly over a ceramic honeycomb
What are the environmental and economic impacts of using a catalyst?
They save money in industrial processes
The reactions can occur at lower temperatures so less fuel is needed hence fewer emissions from fuels
By providing a alternative pathway this gives them a higher atom economy: so less raw materials will be needed and less waste products