Hippocampus Anatomy
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is declarative memory? What can it be broken down into?
It is the conscious, explicit recall of info.
Semantic memory, which is factual knowledge, and episodic memory, which is experiences (flashback esque).
What is the circuit hub for the hippocampal circuit? Where is it located on brain (label it)?
The hippocampus… duh…
Its like the lower seahorse typa structure.
How is the hippocampus like a seahorse? Where is its head relatively oriented in the brain? Tail? Which is rostral and which is caudal?
So its a seahorse with its head towards the front and the tail curling around the back also medially. Rostral = head, Caudal = tail.
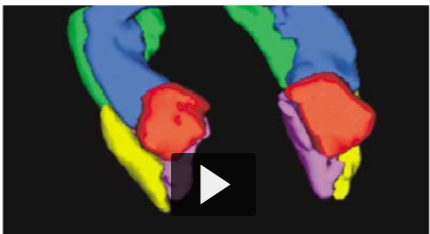
How do you dissect the hippocampal formation? Label each structure and explain the structures going from front to back.
Red = Amygdala
Blue = Hippocampus
Green = Parahippocampal Cortex
Purple = Entorhinal Cortex
Yellow = Perirhinal Cortex
Towards the rostral/front, you have the amygdala, entorhinal cortex, and perirhinal cortex. The entorhinal cortex is more medial/inline with the amygdala, and the perirhinal cortex is more lateral. As you go caudal/to the back, the amygdala is gone and the hippocampus pops up… then parahippocampal.
What does CA stand for? What is the god it is based off of?
Cornu ammonis, named after Amun, and Egyptian god of rams or something (temple guarded by rams).
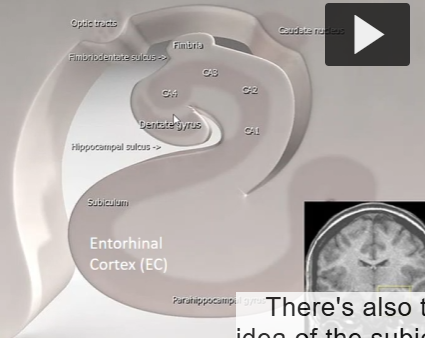
Label this, go from up/in to bottom
Start with dentate gyrus at the rostral/frontal head, then CA4, CA3, CA2, and CA1, then goes downward towards the entorhinal cortex
The hippocampus is generally ____________ throughout life, but then ___________ in later life.
stable, declines
The thickness of the cortex reaches its peak at ___________ years of age. Then, over time, it ___________. Why?
1.7/2
declines/thins/shrinks
Reason is thought to be that brain adapts to experiences… as people grow up, the things that aren’t that useful are pruned away leaving most cortical efficiency for structures that are useful.
Explain how information flows in the HPC.
Sensory information enters to the entorhinal cortex from the neocortical association areas
Info is passed to the dentate gyrus from entorhinal cortex
CA4 → CA3 → CA2 → CA1
Back into Entorhinal Cortex, then back to dentate…
This is a loop!
Where are the neocortical association areas located?
Parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and prefrontal area
Neocortical association areas project to the ____________ and ______________ then to the ____________, and finally the ___________. Can this go backwards?
Perirhinal cortex and Parahippocampal
entorhinal cortex
Hippocampus proper.
It can go backwards too!
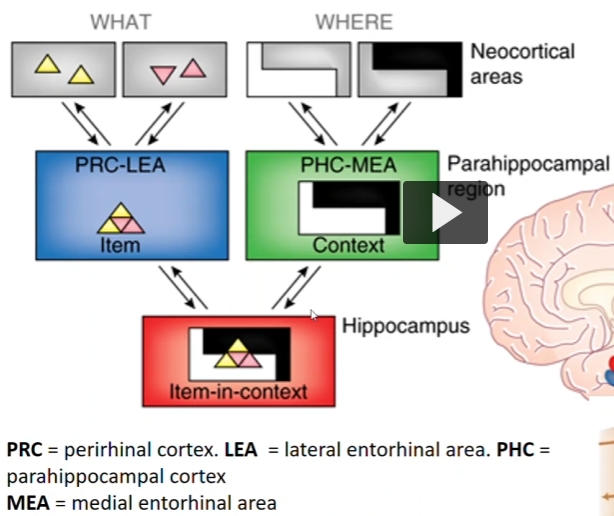
The “what” stream/pathway is what direction, from what structure to what structure? What is it for?
The “where” stream/pathway is what direction, from what structure to what structure? What is it for?
Ventral stream. From Visual Cortex to the temporal lobe neocortical association areas. What objects present/what we see.
Dorsal stream. From Visual Cortex to the parietal lobe neocortical association areas. Where we are relative to our surroundings.
Write out the loop of how info goes throughout the HPC circuit.
Starting at the neocortical association areas, info gets sent to the perirhinal and parahippocampal cortexes, then to the entorhinal cortex, then the dentate gyrus, then CA4 → 3, 2, 1, then to the entorhinal cortex, to the perirhinal and parahippocampal, then to the neocortical.
Go into the “what” pathway in detail… what structures and from what to what?
Starts in visual cortex, info gets sent to the neocortical association areas in the temporal lobe. Then, info gets sent to perirhinal cortex and lateral entorhinal area. Then it gets to the hippocampus.
Go into the “where” pathway in detail… what structures and from what to what?
Starts in visual cortex, info gets sent to the neocortical association areas in the parietal lobe. Then, info gets sent to parahippocampal cortex and medial entorhinal area. Then it gets to the hippocampus.
Where is the info all united?
The hippocampus, where the what and where pathways meet so we get the item in-context (item from what in-context from where).
What is long-term potentiation? What does it require?
If you are constantly activating certain circuits, strengthens synapses.
Requires the convergence of the where and what pathways in the hippocampus.
The hippocampal formation is about __________ and __________, not ___________________. Storage is likely in the _________ and ____________ areas.
Encoding and Retrieval, not Memory storage!
Sensory and polymodal association areas.
What is the role of the DLPFC in the Hippocampal circuit?
Maintain focus to prioritize the relevant information.
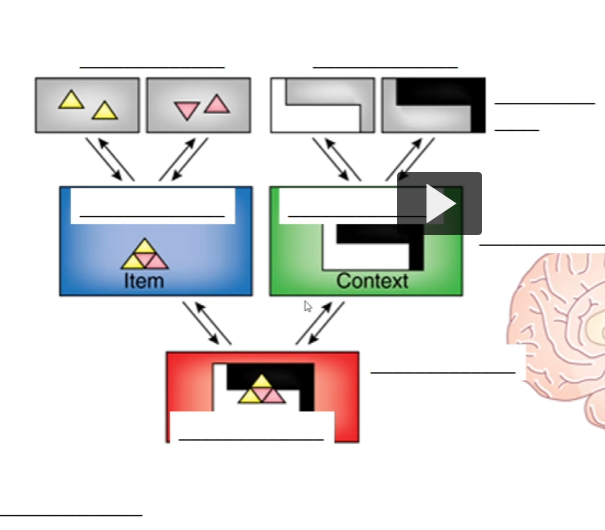
Fill this out
The Hippocampus is like a _____________, not a book.
librarian - helps us find it
What are the forms of declarative memory?
Short-term and Long-term memory.
What is STM governed by (structurally)? Also describe it
DLPFC.
It is the short term maintenance of info in mind + manipulation of that info!
What is LTM governed by (structurally). Describe it briefly.
The hippocampal circuit.
Retrieve earlier, stored info. Can be episodic or semantic.
What is semantic memory? What is episodic memory?
Semantic: Factual knowledge, memory learned but time and place of original info gathering isn’t known
Episodic: Store and retrieve info about unique personal experiences, time and place, and details involved!
Who is HM?
Had seizures (temporal lobe epilepsy) following a bike accident.
MTL resection occurred to try to cure him of his seizures which were rlly rlly debilitating, which did work for curing him from epilepsy, but resulted in memory issues!
HM had anterograde amnesia, which means that he ________________. He also had retrograde amnesia, which means that he _______________. This allowed researchers to realize that encoding and retrieval _______________.
Anterograde means he couldn’t form new long term semantic or episodic memories. Severely impacted.
Retrograde means he couldn’t recall certain past episodic or semantic memories. Moderately impacted and worse for events within 16 of surgery.
were separate processes/affected by different structures!
There is robust/more activation of the hippocampus in response to ________________ compared to _________________.
Words/images that were later recalled/remembered
words/images that were not recalled/remembered