CH 9: The Cardiovascular System (Cardiology)
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
Cardiovascular system
The transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes; composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Four chambers of the heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
-Left side receives blood from the lungs and delivers oxygen-rich blood to body
-Right side receives blood from the body and delivers oxygen-poor blood to the lungs
Valve
Placed between each atrium and ventricle
- right atrioventricular valve (tricuspid valve)
-left atrioventricular valve (mitral valve)
A valve is placed between each ventricle and large artery
-pulmonary valve
-aortic valve
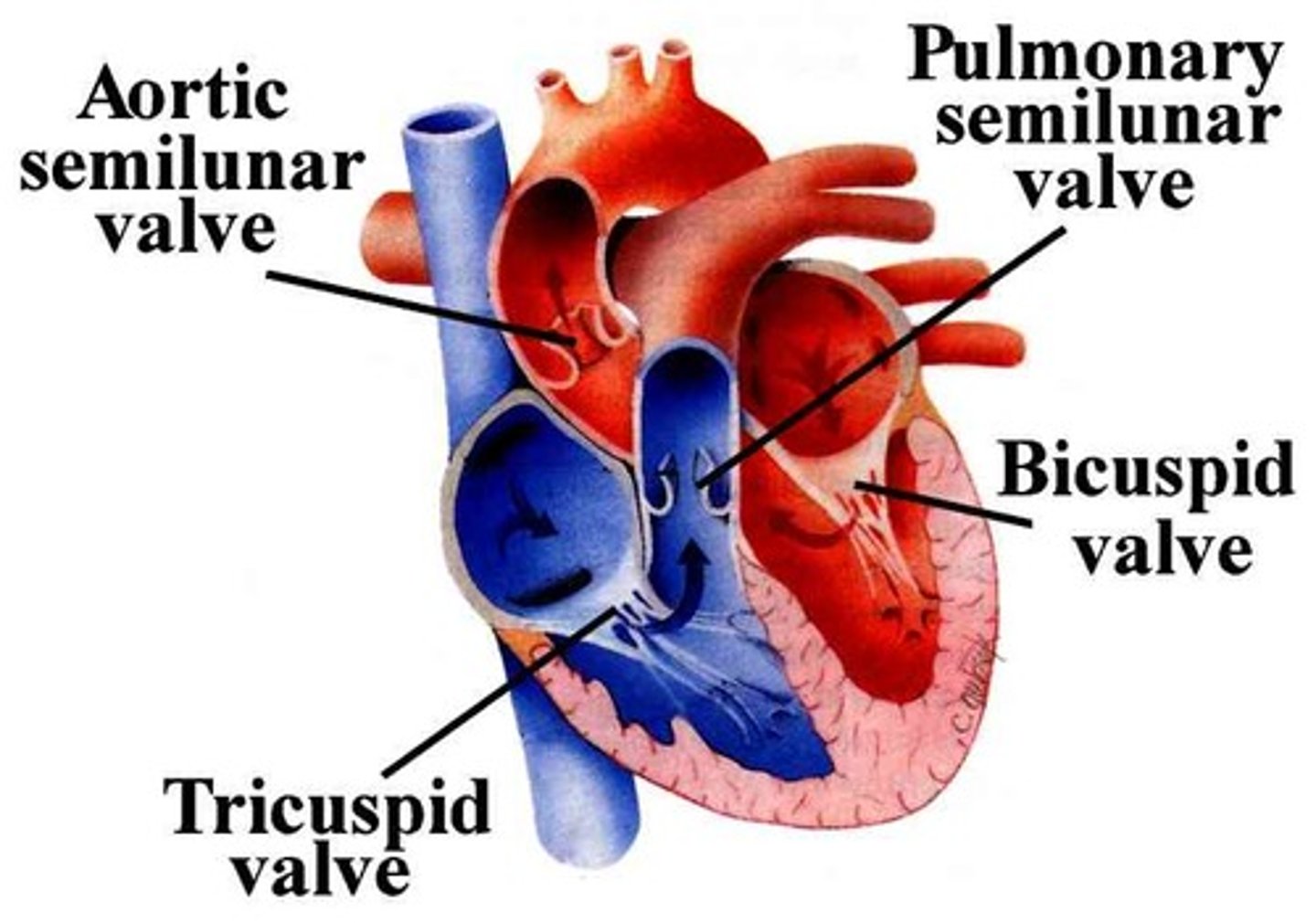
valvul/o
valve
atri/o
atrium (upper chamber)
sept/o
septum (plural: septa)
cardi/o
heart
coron/o
heart
What are the two circulations of the Heart ?
pulmonary and systemic
Three types of vessels
arteries- take blood away from the heart
veins- take blood back to the heart
capillaries- connect arteries and veins
angi/o, vas/o, vascul/o
vessel
aort/o
aorta; main artery leaving the left ventricle
arteri/o
artery
ather/o
fatty plaque
phleb/o, ven/o
vein
What are most common complaints?
-chest pain
-patients express is the feeling of a jumping sensation and odd rhythm
-pain can be felt in blood vessels
angina pectoris
oppressive pain in the chest caused by irregular blood flow to the heart
arrhythmia (ay-RITH-mee-ah)
irregular heartbeat
dysrhythmia
abnormal rhythm
palpitation (pal-pih-TAY-shun)
rapid or irregular beating of the heart
pectoralgia
(PEK-tor-AL-jah)
chest pain
aortalgia
AY-or-TAL-jah
pain in the aorta
diaphoresis
DAI-ah-for-EE-sis
profuse sweating
hemorrhage (HEM-oh-RIJ)
loss of blood
phlebalgia
fleh-BAL-jah
pain in a vein
indicators of how well the heart is pumping or the vessels are circulating blood
skin color, pulse, blood pressure
Signs of heart function
-Heart sounds
-Electrocardiogram
-Echocardiogram
Visualize the blood vessels with an angiogram to see abnormalities
-deposits of fat
-floating material
-cutoff in flow
-dilation of a vessel
endocardium
EN-doh-KAR-dee-um
tissue lining the inside of the heart
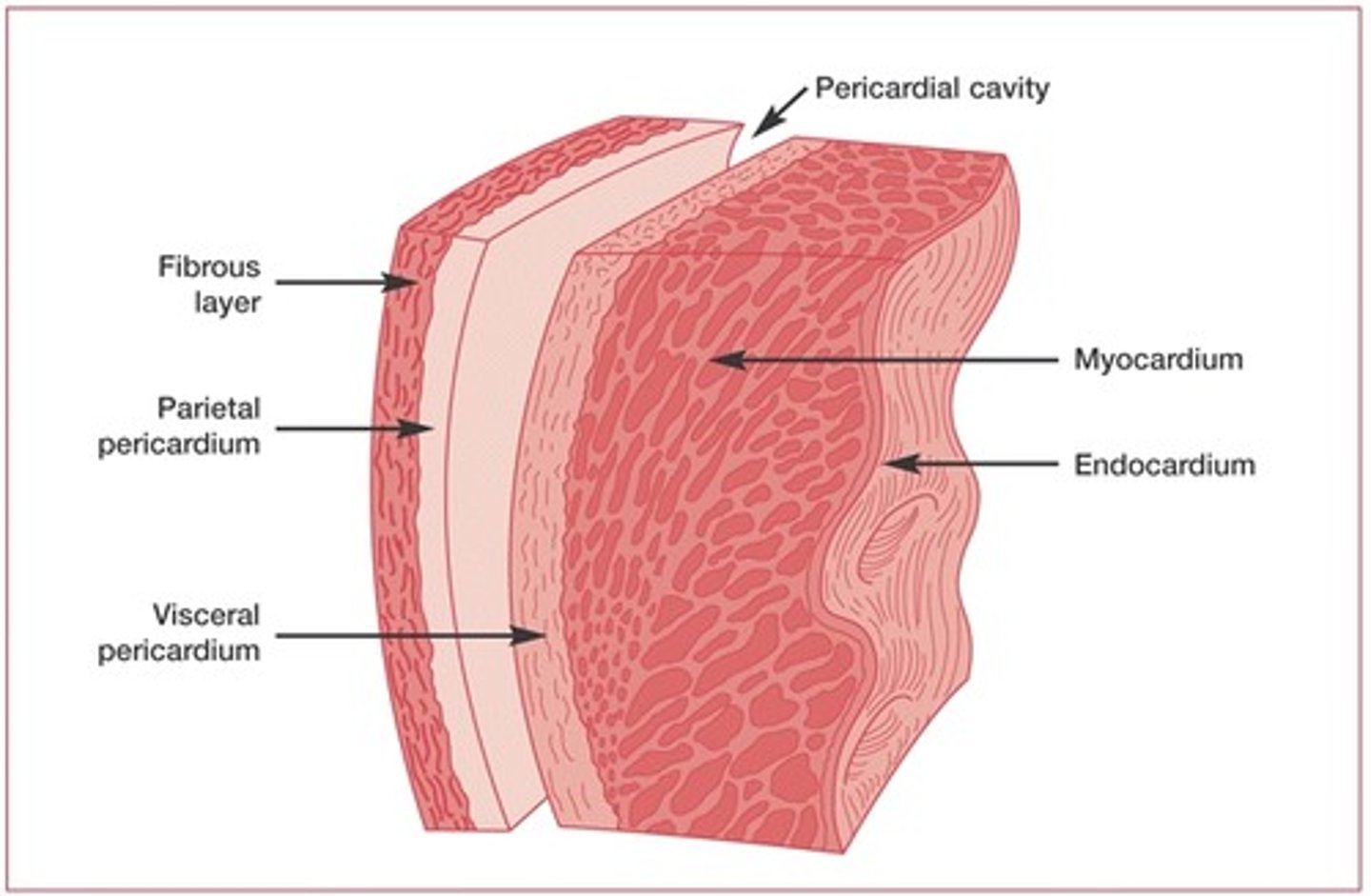
epicardium EH-puh-KAR-dee-um
outer layer of the heart
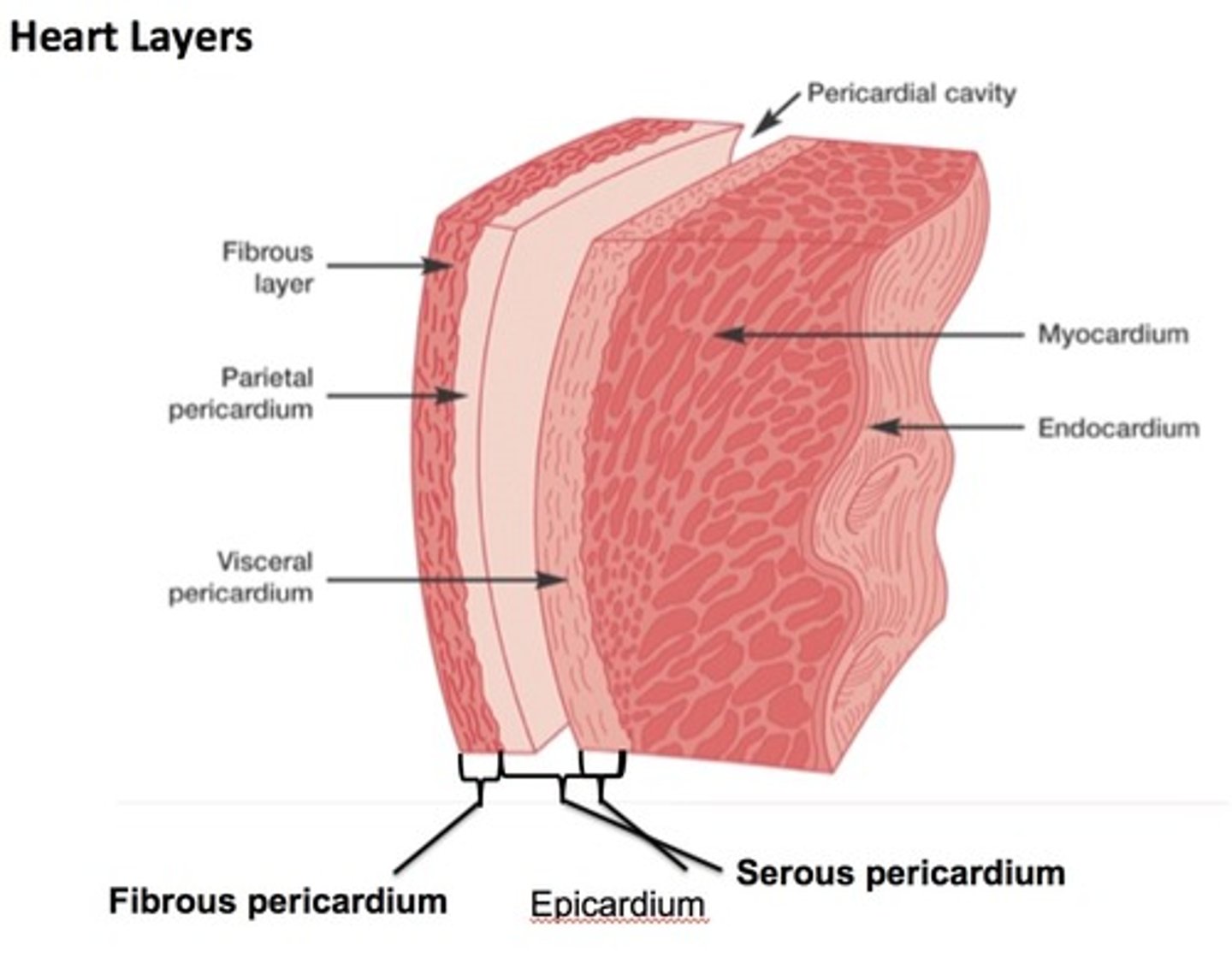
myocardium
MAI-oh-KAR-dee-um
heart muscle tissue
pericardium (PER-uh-KAR-dee-um)
tissue around the heart
bradycardia (BRAY-dih-KAR-dee-ah)
slow heartbeat
cardiomegaly
(KAR-dee-oh-MEH-gah-lee)
enlargement of the heart
cardiotoxic
(KAR-dee-oh-TOK-sik)
poisonous to the heart
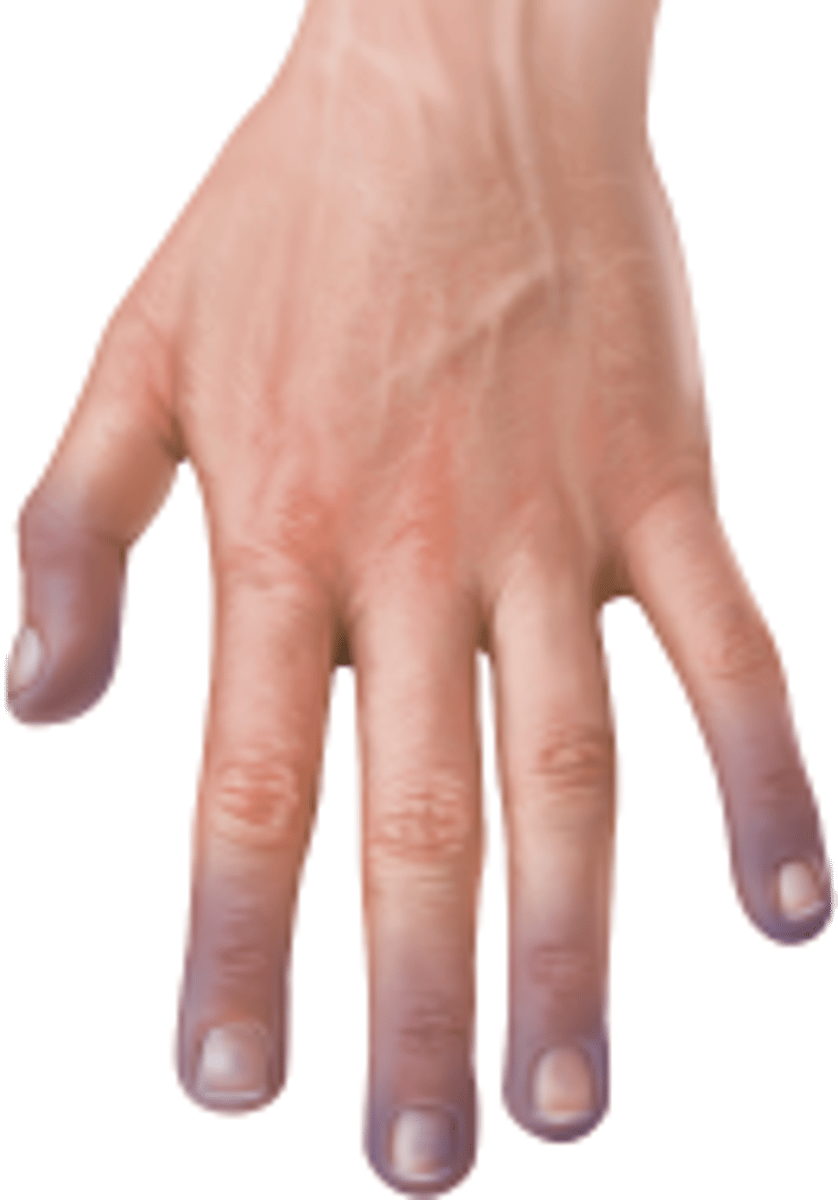
cyanosis (SAI-ah-NOH-sis)
a bluish appearance to the skin; a sign that the tissue isn't receiving enough oxygen
murmur (MIR-mir)
abnormal heart sound
tachycardia (TAK-ih-KAR-dee-ah)
rapid heartbeat
vena cava
large-diameter vein that gathers blood from the body and returns it to the heart; vena hollow
inferior vena cava
portion of the vena cava that gathers blood from the lower portion of the body
superior vena cava
portion of the vena cava that gathers blood from the upper portion of the body (head and arms)
angiogenesis
AN-jee-oh-JIN-eh-sis
development of blood vessels
angiolith
AN-jee-oh-LITH
stone forming in the wall of a blood vessel
angiopoiesis
AN-jee-oh-poh-EE-sis
formation of blood vessels
angiosclerosis
AN-jee-oh-skleh-ROH-sis
hardening of a blood vessel
aortectasia
ay-OR-tek-TAY-zhah
dilation of the aorta
aortic stenosis
narrowing of the aorta
aortolith
ay-OR-toh-LITH
stone deposit in the wall of the aorta
arteriolith
ar-TER-ee-oh-LITH
stone in the artery
arteriorrhexis
ar-TER-ee-oh-REK-sis
rupture of an artery
arteriosclerosis (ar-TER-ee-oh-skleh-ROH-sis)
hardening of an artery
atherogenesis
formation of fatty plaque on the wall of an artery
atherosclerosis
hardening of an artery due to build-up of fatty plaque
embolus
mass of matter present in the blood
embolism
Blockage of a vessel by a clot or foreign material brought to the site by the blood current.
ischemia
blockage of blood flow to an organ
isch/emia=hold back/ blood condition
occlusion
oh-KLOO-zhun
closing or blockage of a passage
phlebosclerosis (FLEB-oh-skleh-ROH-sis)
hardening of a vein
thrombus
blood clot
varicose veins
an enlarged, dilated vein toward the surface of the skin
vasospasm
involuntary contraction of a blood vessel
venosclerosis
VEE-noh-skleh-ROH-sis
hardening of a vein
venospasm
VEE-noh-SPAZ-um
involuntary contraction of a vein
venostasis
VEE-noh-STA-sis
trapping of blood in an extremity due to compression
angiogram
record of a vessel
angiography
procedure to describe the blood vessels
aortogram
record of the aorta
arteriogram
record of an artery
venogram
record of a vein
angioscope
device for looking into a blood vessel
cardiac catherization (CC)
process of inserting a tube (catheter) into the heart
echocardiogram
image of the heart produced using sound waves; the same procedure as an ultrasound performed on pregnant women, but instead it is performed on a heart
echocardiography
use of sound waves to produce an image of the heart
electrocardiogram
record of the electrical currents of the heart
electrocardiography
procedure for recording the electrical currents of the heart
sonography
saw-NAW-grah-fee
use of sound waves to produce diagnostic images; also called ultrasound
stress electrocardiogram
records electrical signals of the heart while the patient experiences increases of exercise stress
transesophageal echocardiogram
record of the heart using sound waves performed by inserting the transducer into the esophagus
vascular endoscopy
procedure to look inside a blood vessel
blood pressure
force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels
diastolic pressure
pressure exerted on blood vessels when heart is relaxed
systolic pressure
Blood pressure in the arteries during contraction of the ventricles.
cardiologist
heart specialist
cardiology
study of the heart
cardiovascular
pertaining to the heart and blood vessels
circulation
movement of substances in body fluids
coronary circulation
circulation of blood through the coronary blood vessels to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle tissue
phlebologist
specialist in veins
Phlebotomist
one who draws blood
phlebotomy
incision into a vein
pulmonary circulation
circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs (to oxygenate it)
systemic circulation
circulation that supplies blood to all the body except to the lungs
abnormalities in the heart at birth
structural defect
Abnormalities of the heart
-electrical defect
-disease heart muscle
-infection of the heart
-lack of blood supply to heart muscle
-heart muscle failure
Abnormal conditions of blood vessels
blockages, weakened area that bulges, inflammation
angiocarditis
AN-jee-oh-kar-DAI-tis
inflammation of the heart vessels
atrial fibrillation
quivering or spontaneous contraction of muscle fibers in the heart's atrium
atrial septal defect (ASD)
flaw in the septum that divides the two atria of the heart
cardiac arrest
cessation of functional circulation
cardiomyopathy
disease of the heart muscle