Excitability week 4
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is Gibbs-Donnan Equilibrium?
A state where the concentration of ions is balanced across a membrane, resulting in a net charge (Net Q) of 0.
What is the Nernst Equation used for?
To calculate the equilibrium potential of a single ion.
What is the equilibrium potential for Cl- if [Cl-]r = 3M and [Cl-]l = 1M at 37°C?
Vm = -30 mV.
What is the resting membrane potential (Vm) influenced by?
Interactions of ions and the maintenance of gradients by the Na+/K+ pump.
What are the primary ions involved in resting membrane potential?
Na+, K+, and Cl-.
How does the Na+/K+ pump maintain membrane potential?
It moves 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ into the cell against concentration gradients, requiring ATP.
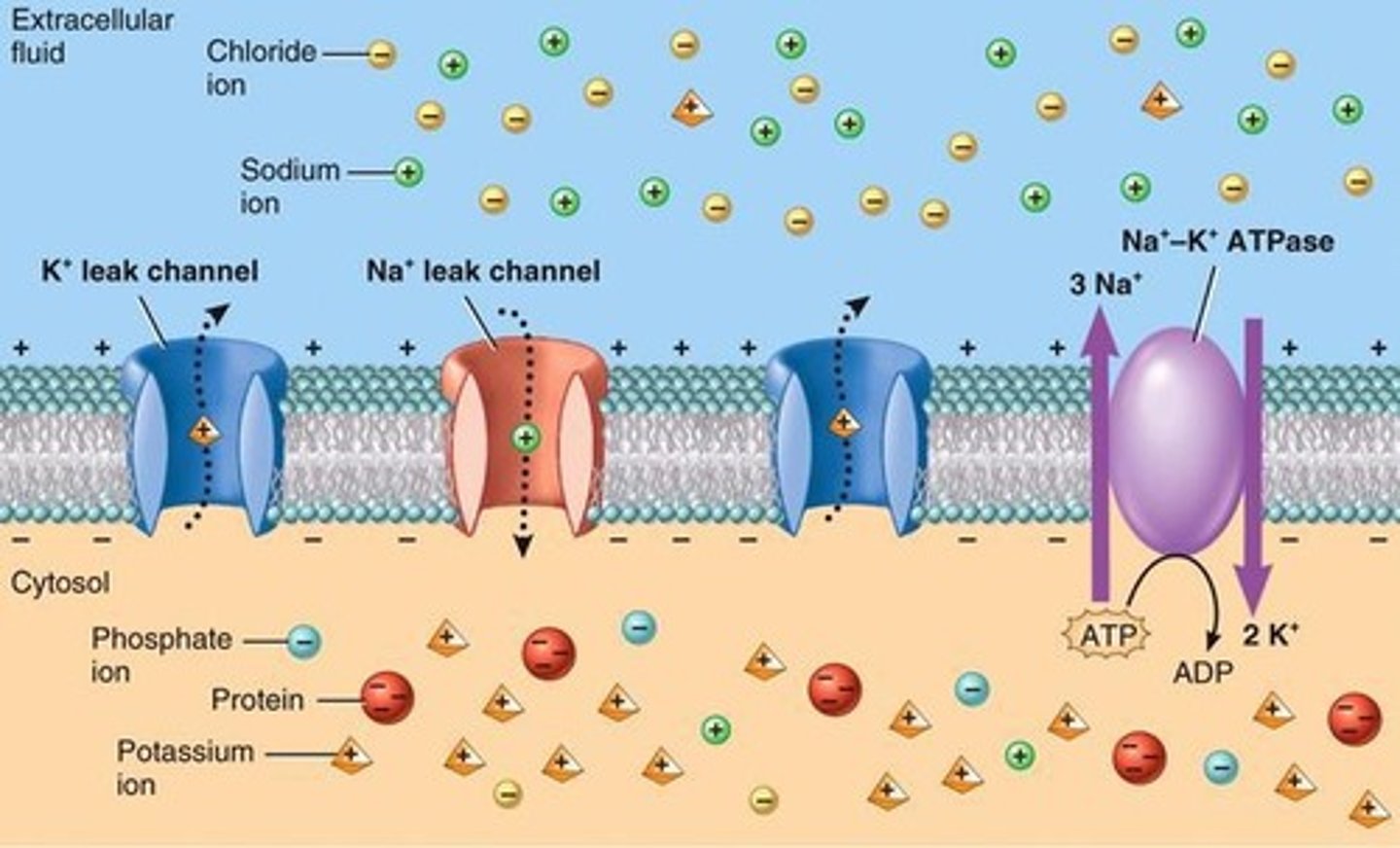
What is the effect of the Na+/K+ pump on Vm?
It slightly lowers Vm by about -4mV.
What does the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz Equation account for?
It includes conductance/permeability factors for ions, unlike the Nernst Equation.
What is the typical resting membrane potential for muscle cells?
Approximately -90 mV.
What is the typical resting membrane potential for nerve cells in the PNS?
Approximately -75 mV.
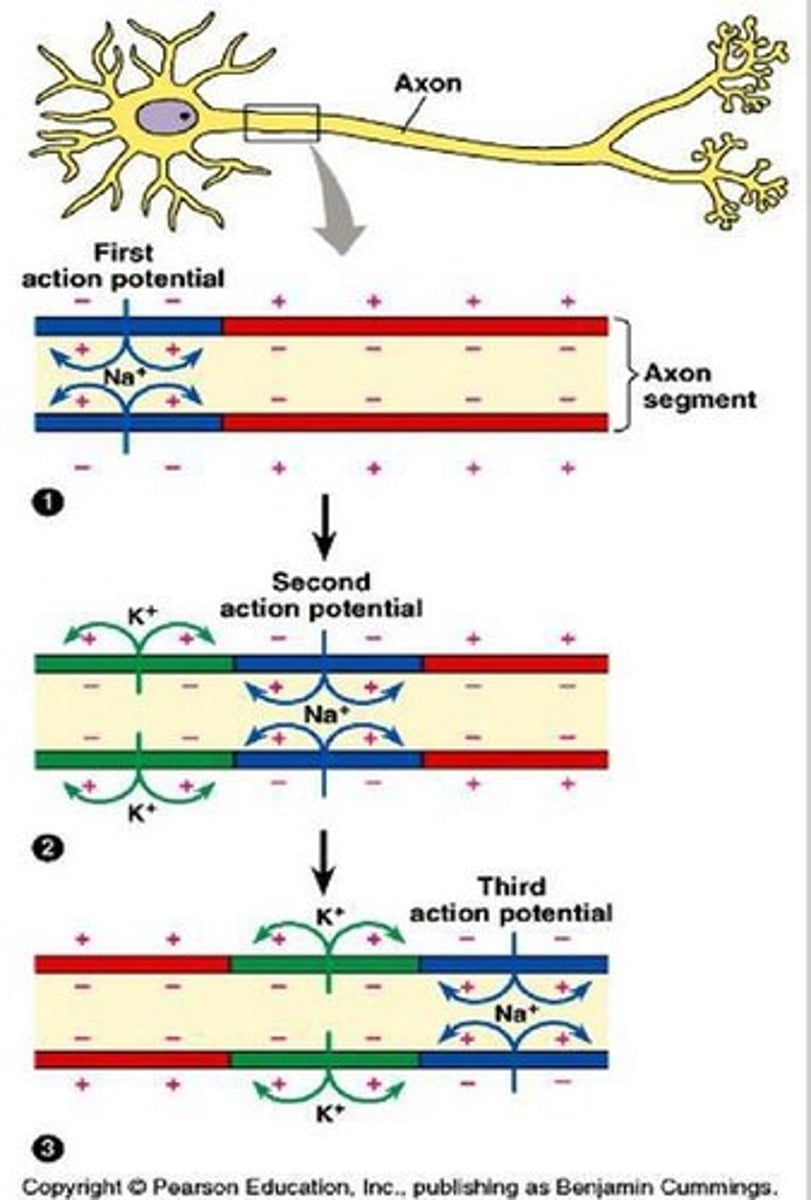
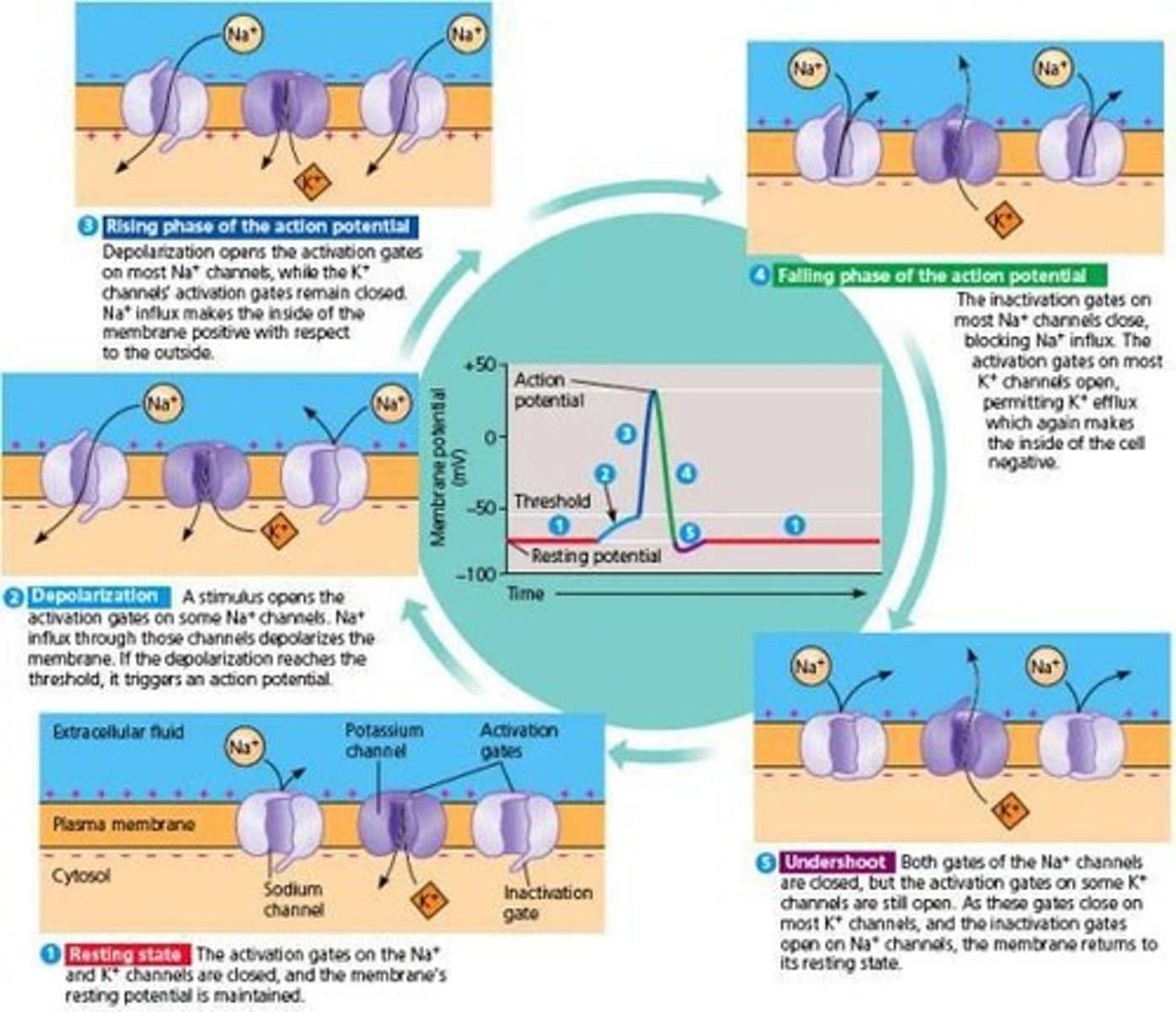
What is the action potential's duration and nature?
It lasts 1-5 ms and is an 'all-or-nothing' response.
What initiates an action potential?
A sufficiently strong stimulus that achieves the threshold of depolarization.
What happens during the depolarization phase of an action potential?
Voltage-gated Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to rush into the cell.
What is the absolute refractory period?
The time during which another action potential cannot be generated due to closed Na+ inactivation gates.
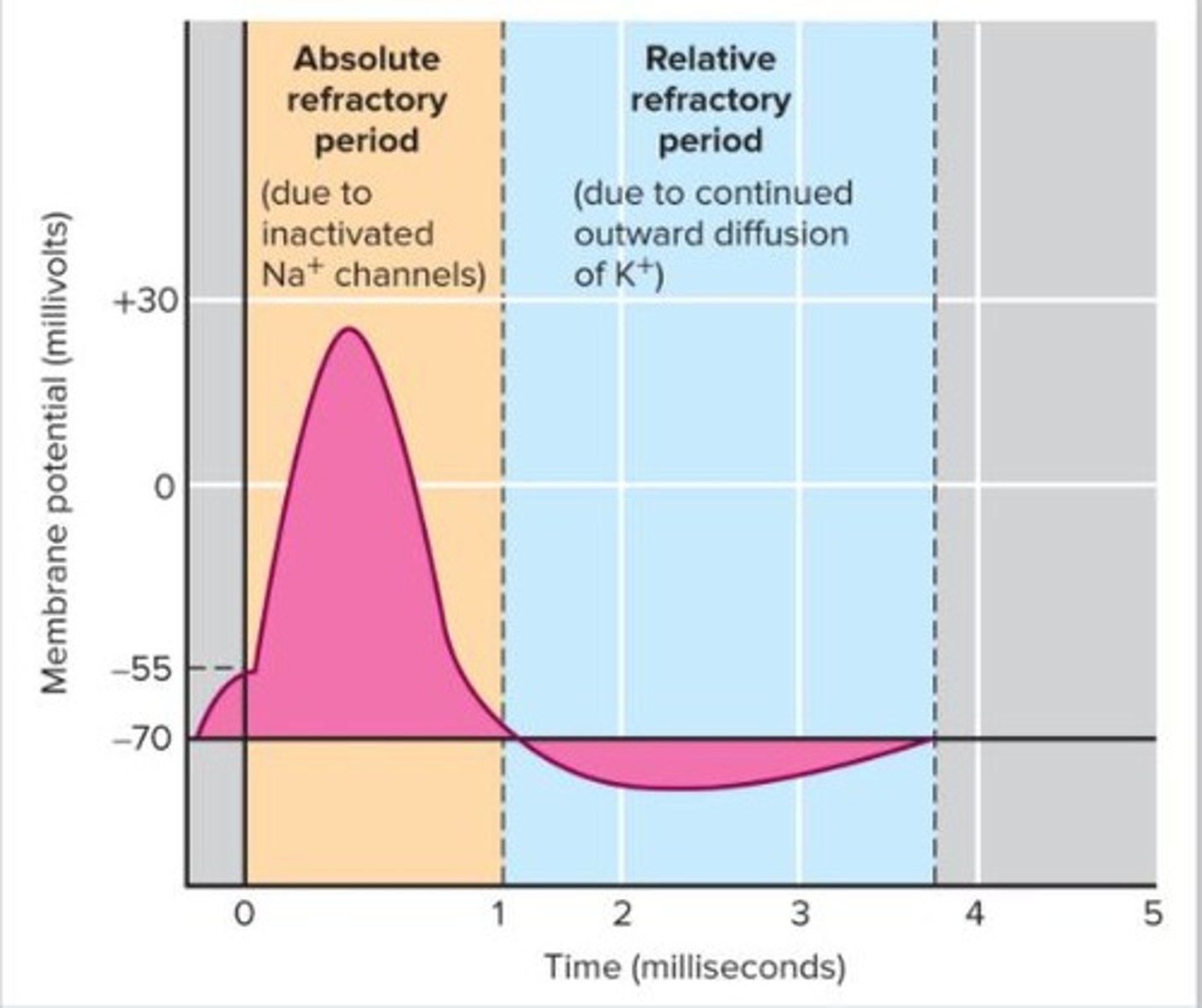
What is the role of voltage-gated K+ channels during an action potential?
They open and close more slowly than Na+ channels, contributing to repolarization.
What is a local potential?
A graded change in membrane potential that is not an action potential.
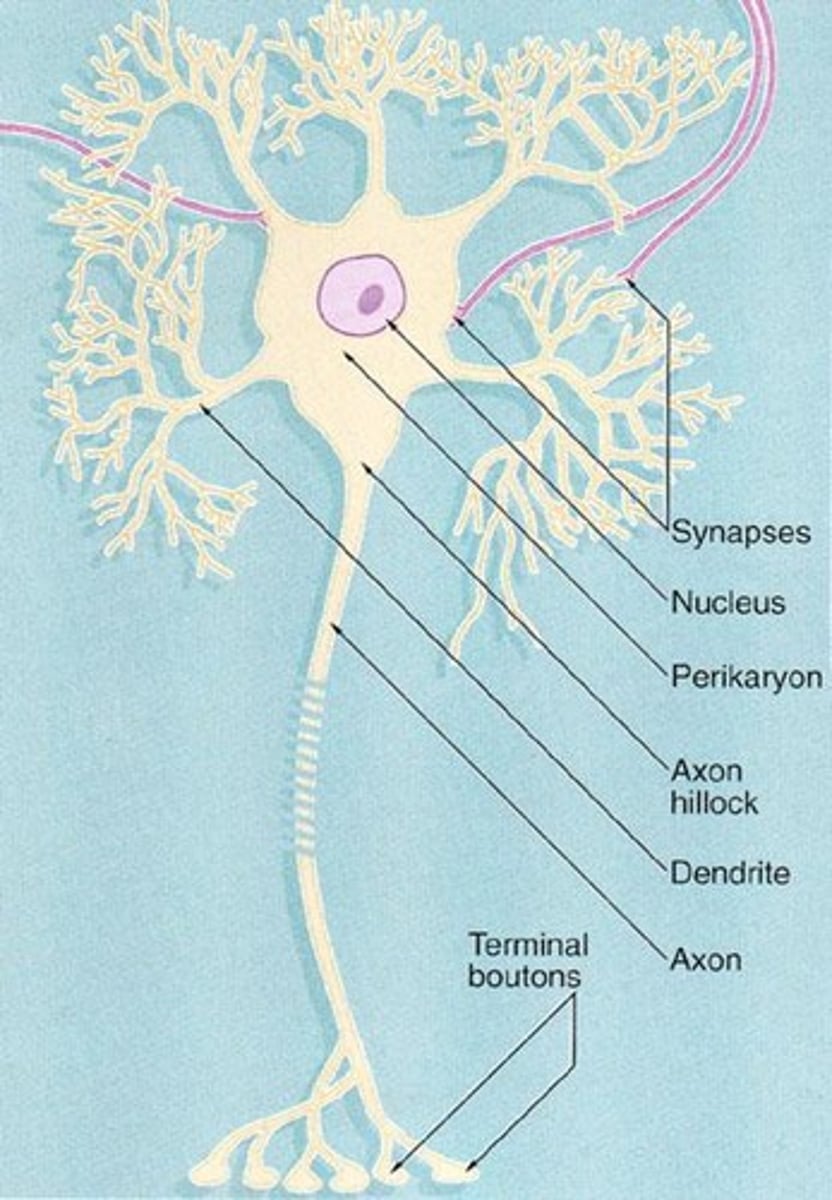
What is the significance of the axon hillock in action potentials?
It is where summation of local potentials occurs, determining if an action potential will be generated.
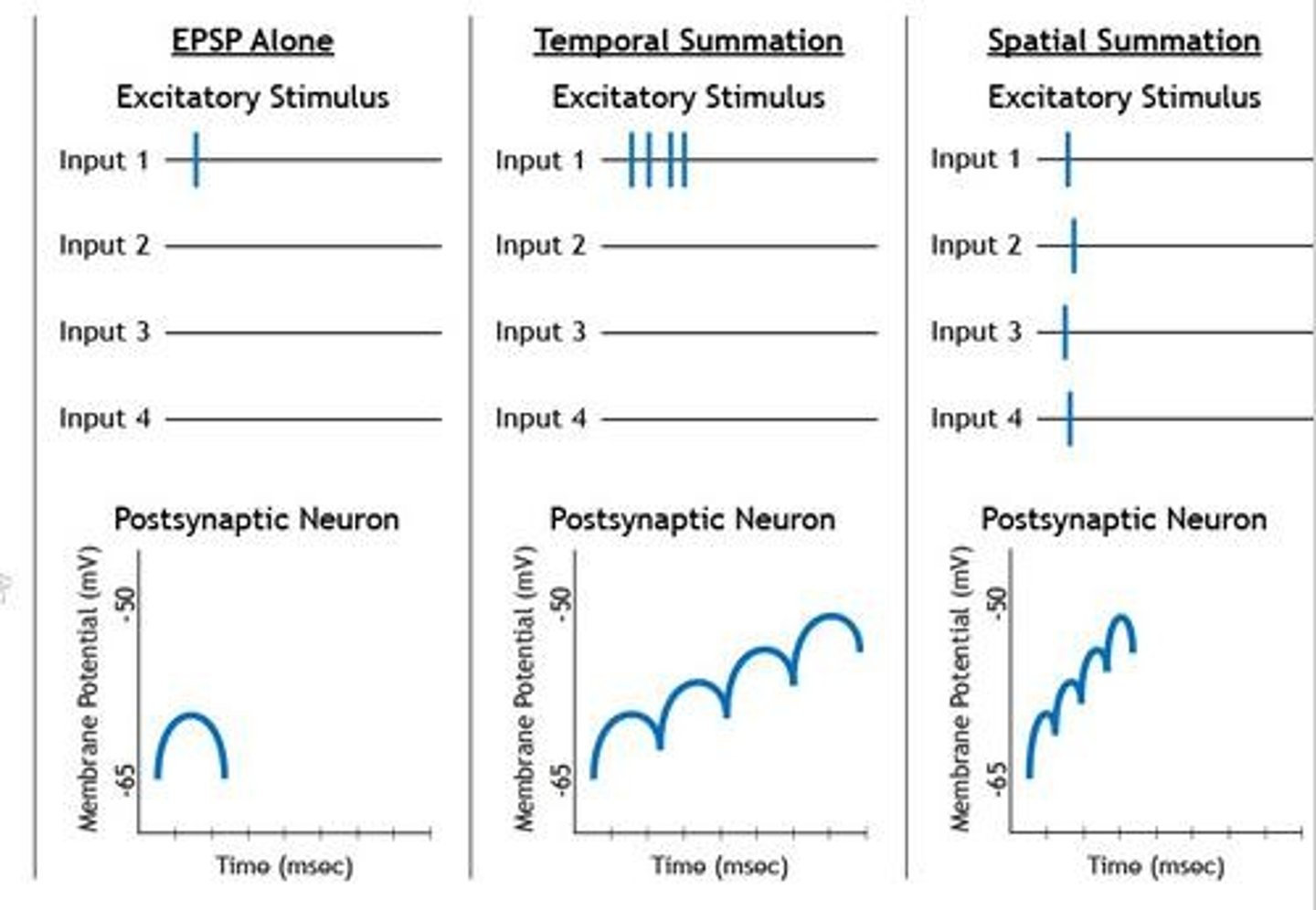
What is the difference between temporal and spatial summation?
Temporal summation involves multiple stimuli over time, while spatial summation involves stimuli from different locations.
What is a receptor potential?
A local potential produced by the opening of ion channels in response to a stimulus.
What is the relationship between stimulus magnitude and receptor potential?
The magnitude of the receptor potential is proportional to the magnitude of the stimulus.
What happens during the afterpotential phase of an action potential?
Hyperpolarization occurs due to K+ continuing to leave the cell.
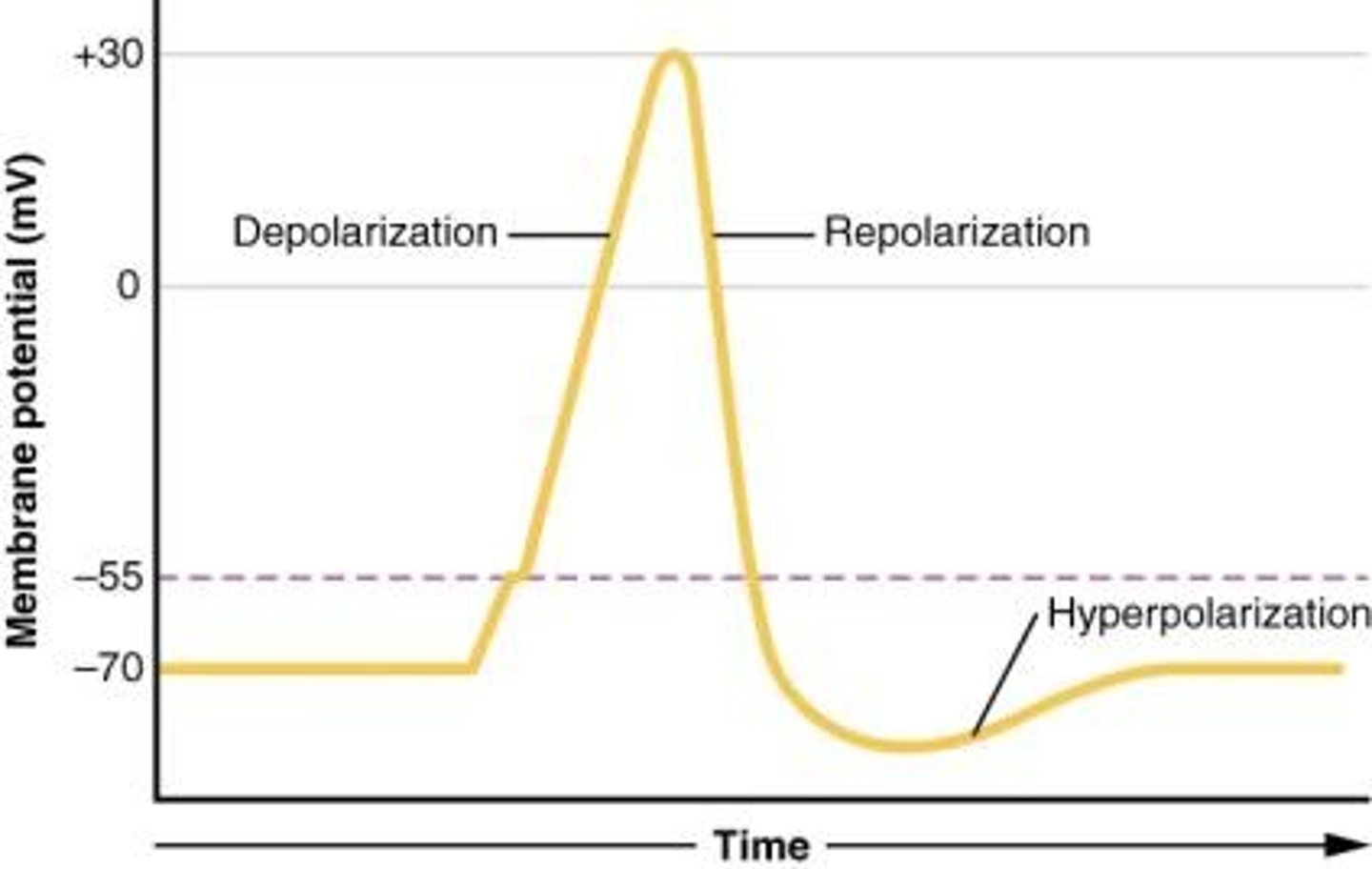
What does the term 'polarization' refer to in the context of membrane potential?
It refers to the state of the membrane potential being different from zero, indicating a charge difference.
What is the role of ATPase in maintaining membrane potentials?
It increases activity to restore gradients after action potentials.
How does the membrane potential change during an action potential?
It rapidly depolarizes to around +35 mV before repolarizing.
What is the binary code in the context of action potentials?
It refers to the way action potentials convey information as '0s' and '1s'.
What is the significance of the relative permeabilities of PK:PNa:PCl in resting membrane potential?
They determine how closely the resting potential fits the equilibrium potential for K+.
What is the primary function of action potentials?
To serve as a unit of information for signal propagation to other neurons, muscles, or glands.