cards 1 HTN HLD CAD
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
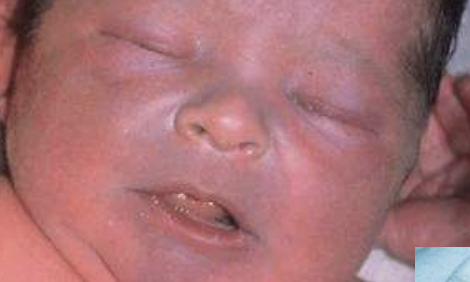
cyanosis
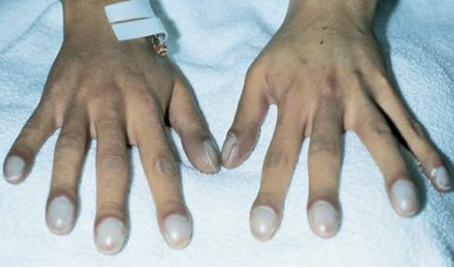
clubbing
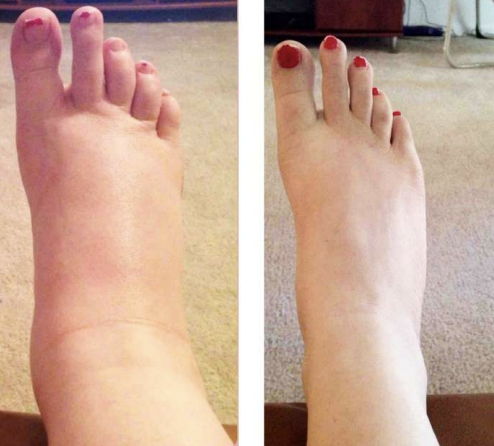
edema
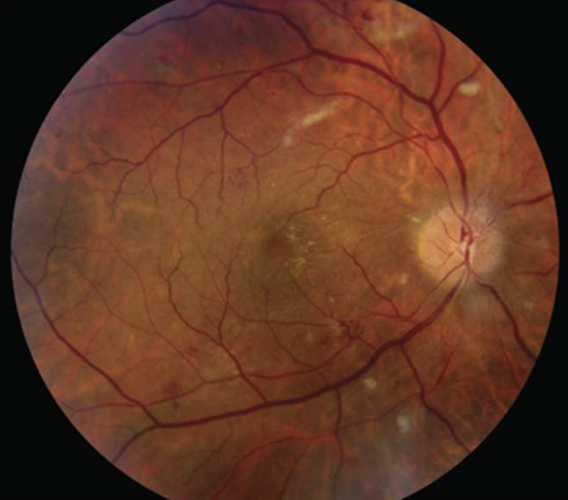
papilledema
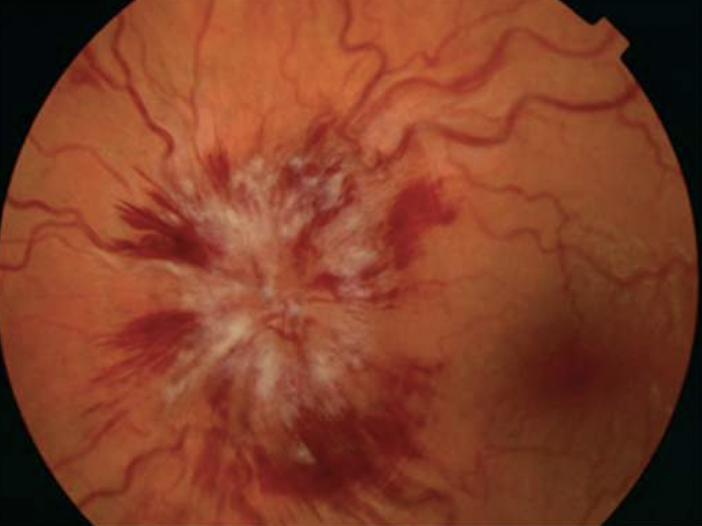
cotton wool spots
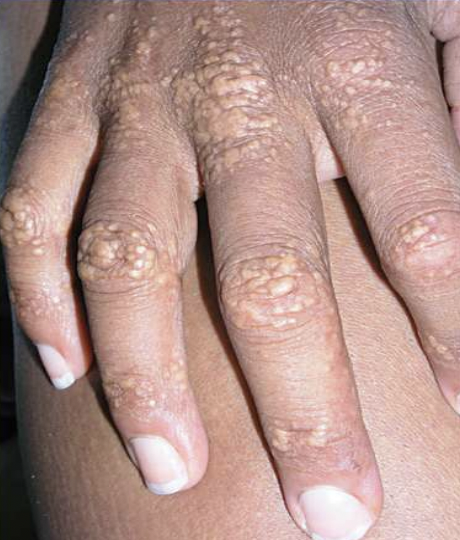
xanthomas
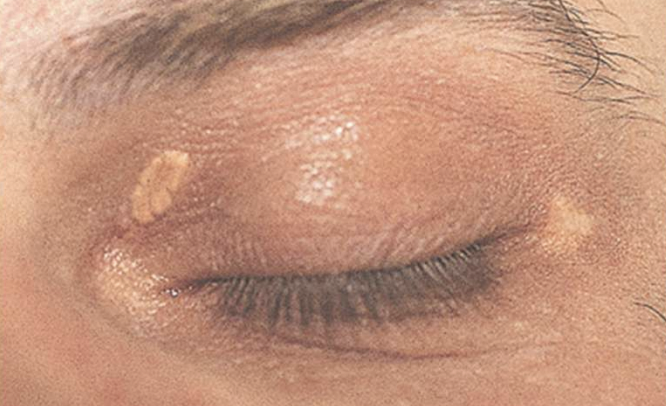
xanthelasma
S1 sound
lub
S1 actions
mitral and tricuspid valves close
aortic and pulmonic valves open
S2 sound
dub
S3 sound meaning
CHF, ventricular gallop
S2 actions
aortic and pulmonic valves close
mitral and tricuspid valves open
S4 action
aortic valve closes
S4 pathology
acute MI, LV stiff, severe HTN
aortic valve auscultation
2nd R ICS
pulmonic valve auscultation
2nd L ICS and 3rd R ICS
tricuspid valve auscultation
4-5th L ICS sternal border
mitral valve auscultation
5th L ICS at apex at MCL
narrow pulse pressure pathologies
shock and hypotension
widened pulse pressure pathologies
hypertension, severe aortic regurg, arteriovenous shunting, elderly
primary HTN
HTN d/t unidentified cause
primary HTN RF
fhx, smoking, EtOH, obesity
secondary HTN
HTN d/t identifiable cause
secondary HTN causes
medications, endocrine, neuro, kidneys, cardiac
HTN sx
HA, blurred vision, “heartbeat in my ear,” fatigue, flushing
HTN PE
papilledema, cotton wool spots, retinopathy, displacement of PMI, renal artery bruit
HTN EKG
possible LVH
hypertensive urgency
no end organ damage
hypertensive emergency
acute end organ damage
hypertensive emergency management
decrease MAP by no more than 25% w/in first hour and titrate meds to 160/110 w/in 2-6h
hypertensive emergency sx
CP, HA, blurred vision, palpitations, dizziness
hypertensive emergency PE
papilledema, AV nicking, cotton wool spots, S4, displaced PMI, heaves
hypertensive emergency RF
smoking, CAD
orthostatic hypotension
decrease in SBP of 20 or DBP of 10 w/in 1-2 min of moving supine to standing
meds causing orthostatic hypotension
thiazides, loop diuretics, alpha blockers, CCB, hydralazine
orthostatic hypotension non med causes
dehydration, GI blood loss, neurological illness
orthostatic hypotension sx
dizziness, weakness, fatigue, near syncope, syncope
hyperlipidemia hx/RF
fhx, smoking, diabetes, EtOH, thyroid
hyperlipidemia PE
xanthoma, xanthelasma, abdominal obesity
CP skin do not miss dx
herpes zoster
CP MSK do not miss dx
costochondritis, pectoral strain, rib fracture, cervical/thoracic spondylosis
CP esophageal do not miss dx
spasm, rupture, GERD, esophagitis
CP GI do not miss dx
PUD, GB disease, pancreatitis
CP pulmonary do not miss dx
pleural effusion, pneumonia, neoplasm, viral infection, PE
CP cards do not miss dx
ACS, MI, pericarditis, myocarditis, stable angina, arrhythmias
CP vascular do not miss dx
aortic dissection
angina
clinical syndrome with chest discomfort caused by transient ischemia
coronary artery disease
atherosclerotic plaque buildup in coronary arteries leading to narrowing or blockage that reduces blood flow to heart muscle
stable angina
chest discomfort or pressure that occurs predictably with exertion or emotional distress and is relieved with rest or nitro
acute coronary syndrome
medical emergency that refers to a spectrum of conditions caused by sudden, reduced blood flow to the heart muscle due to partial or complete blockage of a coronary artery
stable angina diagnostic
plain treadmill stress test
unstable angina
ischemia without cardiac muscle death (no elevated trop)
NSTEMI
partial blockage with myocardial necrosis
NSTEMI diagnostics
elevated trop, no ST elevation on EKG
STEMI
complete blockage with myocardial necrosis
STEMI diagnostics
elevated trop, ST elevation on EKG in 2-3 leads
stable angina HPI
gradual, dull aching/pressure/tightness/squeezing, intermittent, subsides in 5-20 min, lasts <20 min,
stable angina location
substernal, left precordium, radiation to throat, arm, or jaw
stable angina exacerbation cause
activity, cold, anxiety
stable angina alleviating factors
nitro, rest
stable angina associated sx
nausea, SOB
unstable angina HPI
sudden and severe onset, dull aching/pressure/tightness/squeezing, constant and severe, lasts >20 min
unstable angina location
substernal, left precordium, radiates to throat, arm, or jaw
unstable angina exacerbating factors
anything, occurs at rest, with minimal exertion, or progressively worsens
unstable angina alleviating factors
none - not relieved with rest or nitro
unstable angina associated sx
nausea, vomiting, SOB, diaphoresis
angina relevant pmhx/fhx/RF
DM, HTN, HLD, fhx CAD, smoking, EtOH, diet, exercise
CAD PE
S4, murmur, xanthomas or xanthelasma (HLD), irregular HR/arrhythmia, HTN, diabetic retinopathy, levine’s sign
levine’s sign
patient clenches their fist over their chest to describe the sensation of chest pain
acute coronary syndrome
unstable angina and NSTEMI
ACS HPI
unstable angina sx
ACS management
inpatient/ER, trop, EKG monitoring
STEMI HPI
unstable angina sx
STEMI management
cath lab within 90 min (“time is tissue”)
STEMI meds tx
plavix, heparin, beta blocker, statin
anterior STEMI artery
LAD
anterior STEMI EKG ST elevation
V1-V4
anterior STEMI EKG ST depression
inferior leads II, III, aVF
anteroseptal STEMI artery
proximal LAD
anteroseptal STEMI EKG ST elevation
V1-V3 maybe V4
anteroseptal STEMI EKG ST depression
inferior leads II, III, aVF
anterolateral STEMI artery
LAD or left circumflex
anterolateral STEMI EKG ST elevation
V3-V6, I, aVL
anterolateral STEMI EKG ST depression
inferior leads II, III, aVF
lateral STEMI artery
left circumflex
lateral STEMI EKG ST elevation
I, aVL, V5-V6
lateral STEMI EKG ST depression
inferior leads II, III, aVF
inferior STEMI artery
right coronary artery (80%) or left circumflex (20%)
inferior STEMI EKG ST elevation
II, III, aVF
inferior STEMI EKG ST depression
lateral leads I, aVL
sometimes anterior leads V1-V3
posterior STEMI artery
right coronary artery posterior descending or left circumflex artery
posterior STEMI EKG ST elevation
posterior leads V7-V9
posterior STEMI EKG ST depression
V1-V3
unstable angina tx
antiplatelet/anticoagulation
NSTEMI tx
antiplatelet/anticoagulation, cardiac cath