Beta Lactams MedChem
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
What is the characteristic beta lactam ring?
Cyclic amide - 4 membered ring with a N
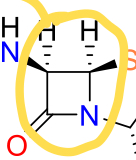
What are Beta lactams a substrate analogue?
D-Ala-D-Ala
What do B-lactam antibiotics inhibit?
Inhibit crosslinking step of peptidoglycan synthesis
What are the different type of B-lactam antibiotics?
Penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems
What is a diagram showing the timeline of penicillin discovery?
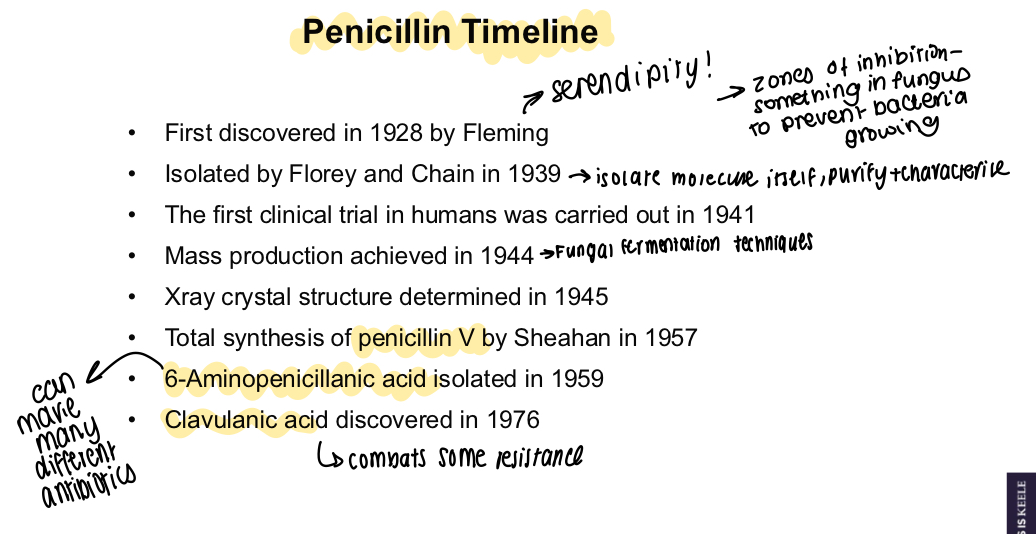
What is the SAR of penicillin?
Amide bond is essential, stereochemistry essential, bicyclic structure, free acid and B-lactam ring all essential to function
What does the SAR mean?
Structure activity relationship - use be retained for activity
What is a thiazolidine ring?
Saturated ring containing sulphur and nitrogen
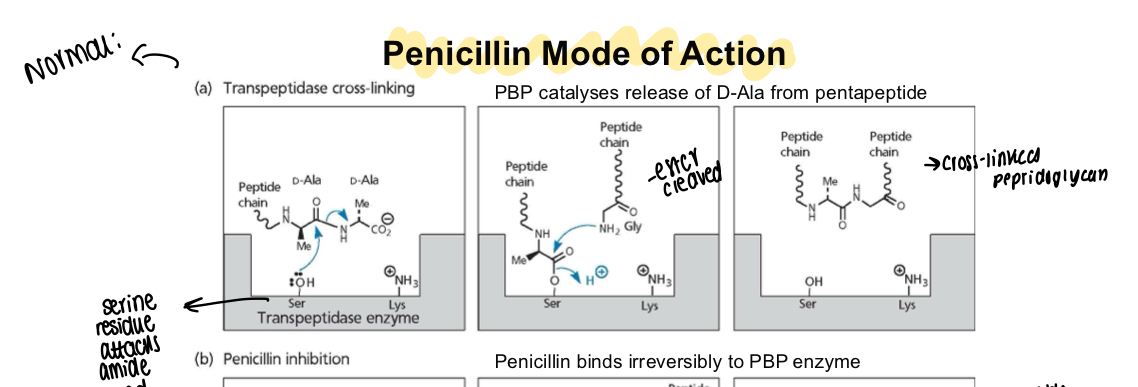
What is the mode of action of penicillin?
Binds to penicillin binding proteins - the beta lactam ring opens and forms a covalent bond irreversibly by acylating a serine residue within the active site of a PBP
What step does penicillin and analogues of this inhibit in peptidoglycan synthesis?
Transpeptidation
What are PBPs?
Transpeptidase enzymes that catalyse the crosslinking step in peptidoglycan synthesis
What do better antibiotics bind to in terms of PBPs?
More PBPs binding = better antibiotic
What is the structure of the B-lactam ring?
Not planar - amide bond forces the chain to be bent
What structure does the fused thiazolidine ring cause the lactam nitrogen to be in for penicillin?
Tetrahedral
Why is the lactam amide bond in a B-lactam antibiotic more labile than amide bond in a peptide?
More susceptible to attack as the bond is weak - the lone pair of electrons held in nitrogen sp3 hybrid orbital cannot overlap with the carbonyls p orbital
What is the normal action of PBP catalysing release of D-alanine?
Serine residue attacks the amide bond, ester is cleaved off and forms a peptide chain and makes cross-linked peptidoglycan
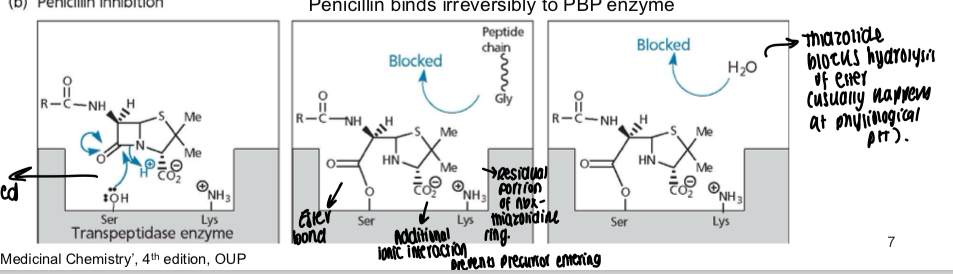
What is the action of PBP when penicillin inhibits it?
Amide bond in penicillin is cleaved and OH and NH3 groups interact with serine and lysine in the transpeptidase enzyme, ester bond is then made and an additional ionic interaction is made, the residual portion left of the Abx is the thiazolidine ring, thiazolidine ring blocks hydrolysis of ester
What was the first isolated penicillin?
Penicillin G
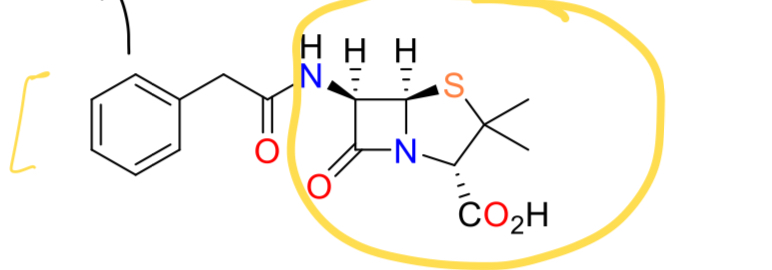
What are the properties of penicillin G?
Non-toxic, active against gram positive cocci and gram negative bacteria, narrow spectrum
What are the issues with penicillin G?
NOT orally active, acid sensitive and destroyed by B-lactamases
Why is penicillin G acid sensitive?
Has a 4 membered ring which is unstable and labile B-lactam ring is extremely reactive - acid catalysis opens the ring and relieves the strain
How does acid hydrolysis occur in all penicillins?
The pi electrons from the carbonyl group in side chain attack the carbonyl group of the lactam amide bond, oxygen kicks out hydrogen, proton transfer means B-lactam ring opens and won’t reform, 4 membered ring becomes strained and converts to penicilloic acid
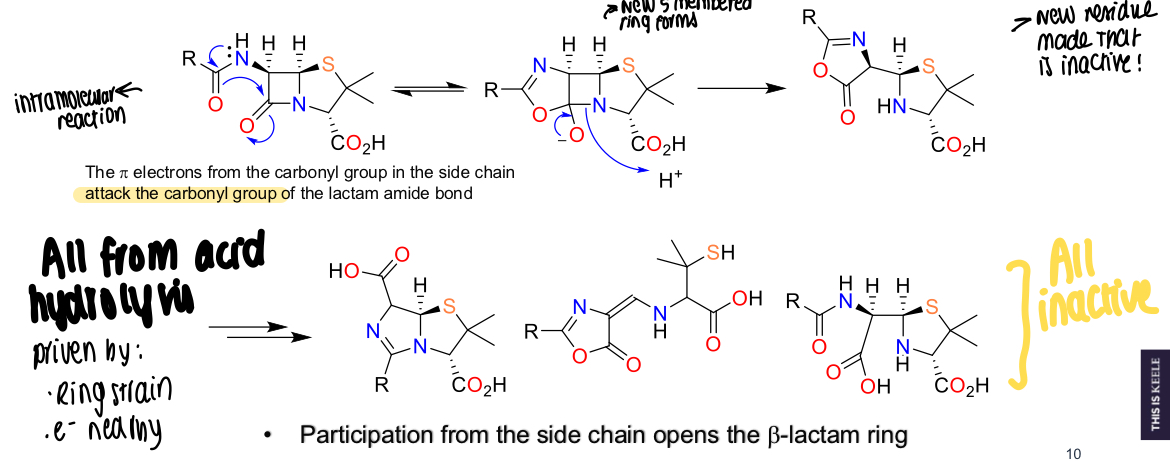
What type of reaction is acid hydrolysis classified as?
Intramolecular reaction
What is acid hydrolysis driven by in penicillins?
Ring strain and nearby electrons
Why is acid hydrolysis bad for penicilllins?
Makes inactive molecules
What is the main difference between penicillin G and V?
Oxygen added in side chain between beta lactam SAR and benzene ring
What effect does the added oxygen in penicillin V have for activity?
Electronegative oxygen draws electrons towards itself via inductive effect so decreases the ability of electrons in carbonyls to attack the b-lactam
What is a beneficial property of penicillin V?
Acid stable so can be taken orally
What are the drawbacks of penicillin V?
Less potent than penicillin G and also sensitive to B-lactamases
What property must penicillin structures side chain have to have an effect?
Electron withdrawing effects
What are some examples of semi-synthetic penicillins?
Penicillin G, 6-Aminopenicillanic acid
What are the issues with semi-synthetic penicillins?
Unstable so need to access something to give a core structure

What do gram negative bacteria have in their cell that allows resistance to penicillins?
B-Lactamase in periplasmic space surrounding the cell
How are lactamase-resistant derivatives designed?
Attaching bulky groups to the penicillin that prevent access to the enzyme active site but must prevent the drug from accessing target transpeptidase active site
What type of bacteria do b-lactamase resistant penicillins have little/no activity against?
Gram negative due to steric bulk
What is a positive to methicillin?
Resistant to B-lactamases due to methoxy group that donates into electron ring
What is the key issue with methicillin?
Sensitive to acid hydrolysis so not orally active
What is the activity of methicillin against bacteria?
Weak activity against gram positive, not active against gram negative
What is the term to describe methicillin resistance?
MRSA
What are some examples of penicillins that are stable to acid and B-lactamases?
Oxacillin, flucloxacillin, temocillin
What is flucloxacillin good for for bacteria?
Gram positive bacteria that produces beta lactamases
What is a positive of flucloxacillin?
Higher bioavailability than other analogues
What are the benefits of temocillin?
Good for gram negative bacteria and reserved for resistance to 3rd generation cephalosporins
What are some examples of broad spectrum penicillins?
Ampicillin, amoxicillin
What are the disadvantages of broad spectrum penicillins?
Unstable to penicillinases, widespread resistance
What is co-amoxiclav comprised of?
Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid
What is co-amoxiclav used to treat?
Gram positive and negative bacteria that has resistance strains
What are examples of suicide inhibitors?
Clavulanic acid and tazobactam
How do suicide inhibitors work?
Bond covalently and degrade within the active site of the lactamase enzyme, inactivating it
Is tazobactam active in the body?
No - destroyed by B-lactamases
How many covalent bonds does clavulanic acid form?
2 covalent bonds within the active site
What are examples of antipseudomonal penicillins?
Piperacilin, ticarcillin
What is piperacillin available as?
Only available in combination with tazobactam
What is ticarcillin available as?
Combination with clavulanic acid
What are the properties of antipseudomonal penicillins?
Broad spectrum, available in combination with B-lactamase inhibitor
What are antipseudomonal penicillins active against in terms of bacteria?
Gram negative pseudomonas infections - reserved for treating septicaemia, HAP and complex infections
What is the SAR of cephalosporins?
Essential amide bond, B-lactam essential, stereochemistry essential, bicyclic structure and free acid
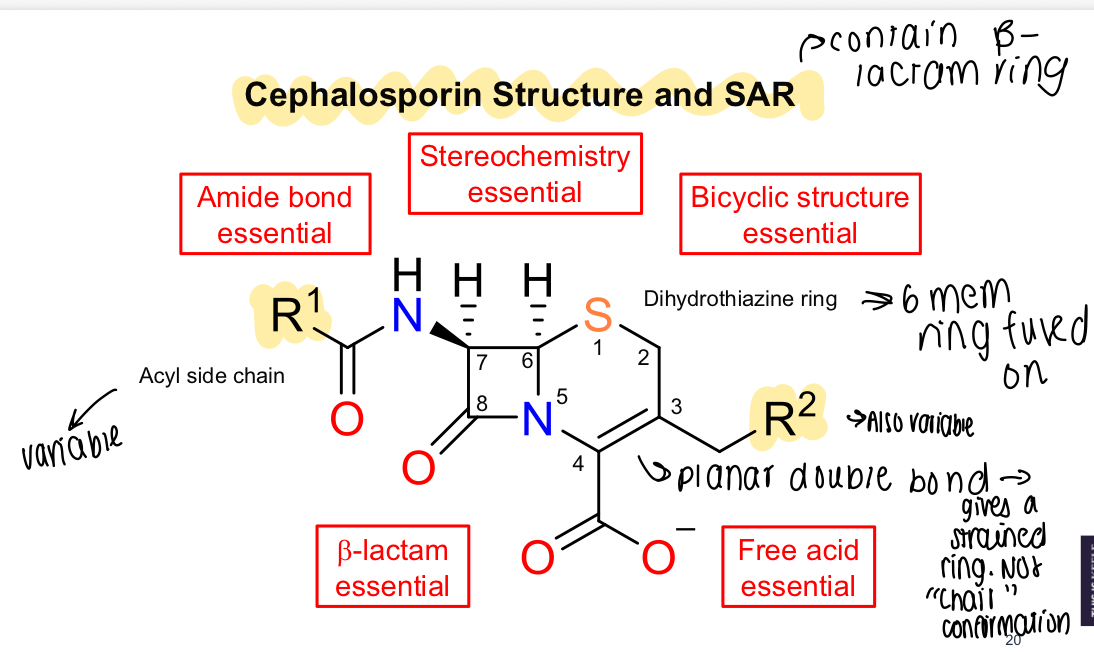
What does the planar double bond in the cephalosporin SAR mean for the ring?
Strained ring
What is cephalosporin C active against?
Gram positive and negative bacteria
What are the advantages of cephalosporin C?
Stable to acid and B-lactamase
What are the disadvantages of cephalosporin C?
Low potency, not orally active, difficult to isolate and purify
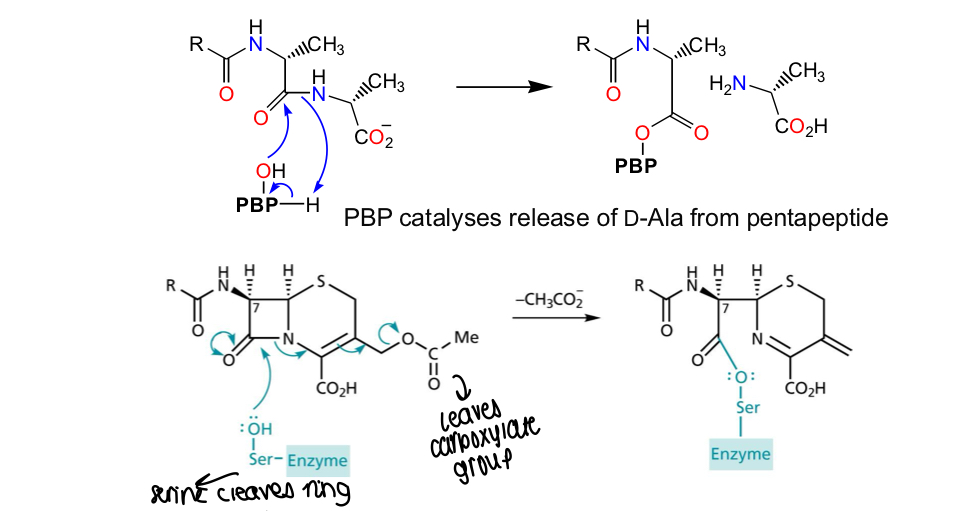
What is the MOA of cephalosporin C?
PBP catalyses release of D-alanine from the pentapeptide - in cephalosporin C, serine cleaves the ring structure and the carboxylate group leaves, bonding the serine to the cephalosporin
What are some properties of cephalosporins as a group?
Broader spectrum of activity than the penicillins and effective against many resistant strains of bacteria
What cephalosporin is an analogue of 6-APA?
7-aminocephalosporanic acid
What are the drawbacks of 7-aminocephalosporanic acid?
Not readily available, much more expensive to produce and investigate
How are most cephalosporins administered?
IV as typically poorly absorbed across gut wall
What is an example of a 1st generation cephalosporin?
Cefalexin
What are the positives of Cefalexin?
Orally active, broad spectrum, greater activity against gram positive
What group in Cefalexin compensates for the loss of the ester substituent?
Hydrophilic amino group
What cephalosporin has the same side chain as ampicillin?
Cefalexin
What is an example of a 2nd generation cephalosporin?
Cefuroxime
What is a benefit of Cefuroxime in comparison to 1st generation cephalosporins?
Greater resistance to B-lactamases
What functional group is Cefuroxime is stable to metabolism?
Urethane functional group
What is an example of a 3rd generation cephalosporin?
Ceftriaxone
What are the positives to ceftriaxone?
Broad spectrum, long half life, more active against gram negative bacteria than 2nd generation
What infections if ceftriaxone reserved for?
Serious infections e.g., pneumonia, septicaemia
What is the absorption like of cephalosporins in CNS?
Poorly absorbed unless membranes are inflamed
What is a use of ceftriaxone in relation to the CNS?
Can treat meningitis
What are the advantages of carbapenems?
Broad spectrum, bind to a range of PBPs, resistant to B-lactamases
What are examples of carbapenems?
Imipenem, ertapenem
What are carbapenems reserved for?
HAP and complex infections - resistance is increasing!