Lymphoid Organs and Lymphocytes
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
thymus, salivary glands, bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, urogenital system, intestine, mammary glands, respiratory tract
List 3 of the 9 major lymphoid tissues
pluripotent stem cells
Lymphocytes develop from _____________________-
yolk sac/liver
where do lymphocytes origionate in the embryo/fetus?
bone marrow
where do lymphocytes origionate in the neonate and adult?
Bone marrow - bursa - B cell
Thymus - T cell
There are two divergent pathways for lymphocytes. What are they?
blood to secondary lymphoid organs
Naive lymphocytes constantly move from _______ to _______ and back again
thymus, bursa of fabricius, peyer's patch, bone marrow
What are the primary lymphoid organs?
tonsils, spleen, lymph nodes, peyer's patch, bone marrow
what are the secondary lymphoid organs?
primary lymphoid organs
____________________: sites of lymphocyte development
secondary lymphoid organs
________________: sites where lymphocytes respond to antigens
mature naive lymhocytes
What is the goal of primary lymphocytes?
To produce ______ _______ __________
dont react to self
during the initial selection in the primary lymphoid organs; immature lymphocytes are selected for those that dont what?
VDJ recombination, V, D, J
a process that generates diversity in antigen receptors, it involves the rearrangement of gene segments ____ ____ and ______ to create unique receptor genes
thymus
where do T lymphocytes mature?
t cells;
antigen presenting cells
Functionally, the cortex of the thymus produces _________ and the corticomedullary region and medulla produce _______________
cortex, medulla, antigen presenting cells
Immunocompetent naïve T cells circulate from the_______ to the _______ of the thymus. This maximizes lymphocytic exposure to the _______________ in the medulla.
does this react strongly with self antigens?
What question is asked when weeding out T cells via NEGATIVE selection
Does this react with self MHC?
What question is asked when weeding out T cells via POSITIVE selection
if it reacts to self,
if it doesnt or only weakly reacts to self MHC
What cells are weeded out during the the thymic selection process?
bone marrow, bursa, peyer's patches
where is the site of B lymphocyte maturation in adults and neonates
antigen presenting cells
Lymphocytes recirculate through secondary lymphoid organs. This maximizes encounters between _____________________ and lymphocytes
antigen, proliferate, differentiate
Lymphocytes recognize ________, interact with other cells, ________, and _________ to "effector" or memory lymphocytes
efferent lymph, venous blood
Differentiated lymphocytes leave via ________________ or ____________________
afferent lymphatics, efferent tubules, B cells, T cells
Antigens enter through _________________, and lymphatic fluid exits through the _______________________. The yellow follicles here are rich in ______ while the purple bands are rich in _____________
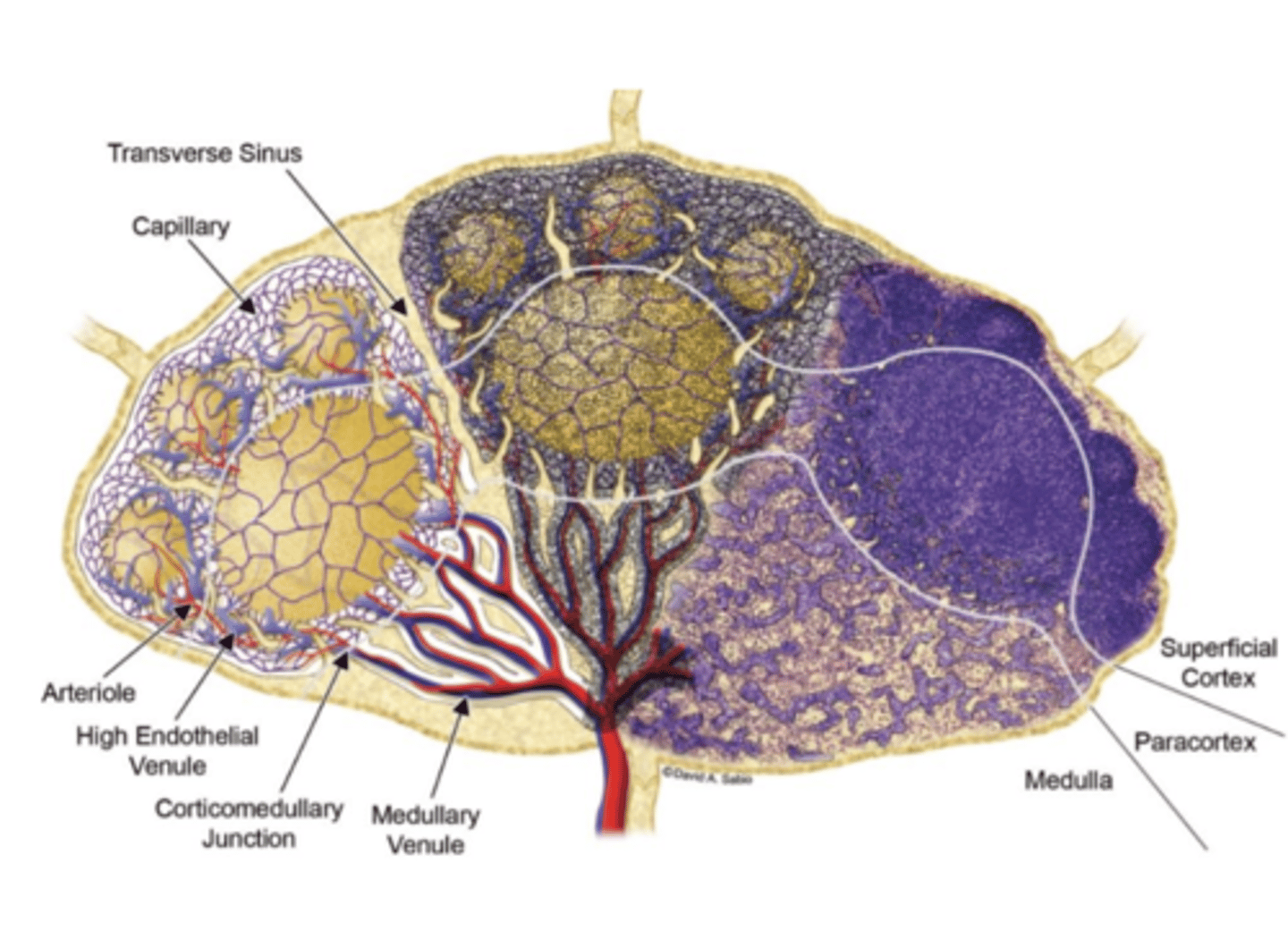
Spleen
________________: site of immune response to antigens specifically in the BLOOD
T cells
the spleen is rich in what kind of lymphocyte?
mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
_________________: Site of immune response to antigens along mucous membranes
M cells, peyers patch, naive T and B cells
___________ cells shuttle the bacteria to waiting dendrites that deliver it to the _____________.
The antigen is then brought to _______________.
They form receptors to this type of antigen.
false: they enter circulation, but ultimately return home to the site of exposure if not sued elsewhere
True/false: after exposure, lymphocytes form receptors and then leave this site of exposure to enter circulation for the rest of their days
cutaneous immune system
_________________: Process through which immune system responds to antigens penetrating stratified squamous epithelium
adhesion molecules and chemokines
Lymphocyte recirculation and rehoming is governed by ________ and _________
so sick
Read this super simple lymph timeline:
Mature naive Lymphocytes are circulating in lymph, they enter a lymph node and look for antigens, IF they find nothing, thye move on the next lymph node, If they find an antigen, they form receptors and continue circulating OR leave lymph via the thoracic duct into the bloodstream
true
true/false: most T cells are Helper T cells
40%, 2%
__________% of lymphocytes are found in the lymph nodes, but only about _______% of lymphocytes are seen in the blood
B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, NK cells, Regulatory lymphocytes
What are the types of lymphocytes? (4)
B and T lymphocytes
______ and ______________ are the only cells that recognize and respond specifically to antigens
true
true/false: Only a small number of naïve lymphocytes are dedicated to any single antigen epitope
Immunophenotype
process that identifies cells based on the types of antigens or markers on the surface of the cell
true
true/false: cell receptors are the defining criteria for any specific type of cell and define the isotype of antibody that a lymphocyte is capable of producing
regulatory receptors
T cells have a very large number of what kind of receptors?
native antigens, secrete antibodies
B cells typically recognize __________; ("big ol parasites with multiple epitopes") and their main function is to ___________
surface immunoglobulin
B cells' antigen receptors are ______________-
TCR + CD4
Helper T cells antigen receptors are _______________---
processed peptide, secrete cytokines
Helper T cells main antigen that they recognize is _________--and their main function is to _______________
TCR + CD8
cytotoxic t cells antigen receptors are:
processed peptide, kill abnormal cells
Cytotoxic Tcells main antigen that they recognize is _________--and their main function is to _______________
MHC class I
CD8 T cells, also known as cytotoxic or killer T cells, complex with antigen presented in association with a ___________molecule.
MHC Class II
CD4 T cells or helper cells bind to antigens presented in association with a _________________ molecule
up regulate cell mediated immunity,
up regulate antibody production
There are two types of helper T cells
T helper 1 cells do what?
And T helper 2 cells?
true
true/false: Receptor/ligand phenotypes can vary with lymphocyte maturation and activation status
cytokine receptors, antibody receptors, complement receptors, integrins, selectins
what molecules can regulate lymphocyte function?
tyrosine kinase phosphorylation
what is the key mechanism for cell activation? (a vital bridge between antigen recognition and subsequent immune response)
right, right...
read:....
Receptors with tyrosine kinase activity are present within the cell membrane. When bound to a signal molecule such as an antigen, the intrinsic tyrosine kinase domains of the receptor become closer in proximity, allowing for phosphorylation. Other intracytoplasmic signaling proteins join the phosphorylated complex, effectively transducing the signal through the cell
clonal expansion
Once activated, the naïve lymphocyte becomes an effector cell, and there is rapid proliferation and differentiation of that specific lymphocyte to form a clone designed to eliminate that specific antigen.